
- •Contents
- •Preface
- •Contributors
- •1 Vessels
- •1.1 Aorta, Vena Cava, and Peripheral Vessels
- •Aorta, Arteries
- •Anomalies and Variant Positions
- •Dilatation
- •Stenosis
- •Wall Thickening
- •Intraluminal Mass
- •Perivascular Mass
- •Vena Cava, Veins
- •Anomalies
- •Dilatation
- •Intraluminal Mass
- •Compression, Infiltration
- •1.2 Portal Vein and Its Tributaries
- •Enlarged Lumen Diameter
- •Portal Hypertension
- •Intraluminal Mass
- •Thrombosis
- •Tumor
- •2 Liver
- •Enlarged Liver
- •Small Liver
- •Homogeneous Hypoechoic Texture
- •Homogeneous Hyperechoic Texture
- •Regionally Inhomogeneous Texture
- •Diffuse Inhomogeneous Texture
- •Anechoic Masses
- •Hypoechoic Masses
- •Isoechoic Masses
- •Hyperechoic Masses
- •Echogenic Masses
- •Irregular Masses
- •Differential Diagnosis of Focal Lesions
- •Diagnostic Methods
- •Suspected Diagnosis
- •3 Biliary Tree and Gallbladder
- •3.1 Biliary Tree
- •Thickening of the Bile Duct Wall
- •Localized and Diffuse
- •Bile Duct Rarefaction
- •Localized and Diffuse
- •Bile Duct Dilatation and Intraductal Pressure
- •Intrahepatic
- •Hilar and Prepancreatic
- •Intrapancreatic
- •Papillary
- •Abnormal Intraluminal Bile Duct Findings
- •Foreign Body
- •The Seven Most Important Questions
- •3.2 Gallbladder
- •Changes in Size
- •Large Gallbladder
- •Small/Missing Gallbladder
- •Wall Changes
- •General Hypoechogenicity
- •General Hyperechogenicity
- •General Tumor
- •Focal Tumor
- •Intraluminal Changes
- •Hyperechoic
- •Hypoechoic
- •Nonvisualized Gallbladder
- •Missing Gallbladder
- •Obscured Gallbladder
- •4 Pancreas
- •Diffuse Pancreatic Change
- •Large Pancreas
- •Small Pancreas
- •Hypoechoic Texture
- •Hyperechoic Texture
- •Focal Changes
- •Anechoic Lesion
- •Hypoechoic Lesion
- •Isoechoic Lesion
- •Hyperechoic Lesion
- •Irregular (Complex Structured) Lesion
- •Dilatation of the Pancreatic Duct
- •Marginal/Mild Dilatation
- •Marked Dilatation
- •5 Spleen
- •Nonfocal Changes of the Spleen
- •Diffuse Parenchymal Changes
- •Large Spleen
- •Small Spleen
- •Focal Changes of the Spleen
- •Anechoic Mass
- •Hypoechoic Mass
- •Hyperechoic Mass
- •Splenic Calcification
- •6 Lymph Nodes
- •Peripheral Lymph Nodes
- •Head/Neck
- •Extremities (Axilla, Groin)
- •Abdominal Lymph Nodes
- •Porta Hepatis
- •Splenic Hilum
- •Mesentery (Celiac, Upper and Lower Mesenteric Station)
- •Stomach
- •Focal Wall Changes
- •Extended Wall Changes
- •Dilated Lumen
- •Narrowed Lumen
- •Small/Large Intestine
- •Focal Wall Changes
- •Extended Wall Changes
- •Dilated Lumen
- •Narrowed Lumen
- •8 Peritoneal Cavity
- •Anechoic Structure
- •Hypoechoic Structure
- •Hyperechoic Structure
- •Anechoic Structure
- •Hypoechoic Structure
- •Hyperechoic Structure
- •Wall Structures
- •Smooth Margin
- •Irregular Margin
- •Intragastric Processes
- •Intraintestinal Processes
- •9 Kidneys
- •Anomalies, Malformations
- •Aplasia, Hypoplasia
- •Cystic Malformation
- •Anomalies of Number, Position, or Rotation
- •Fusion Anomaly
- •Anomalies of the Renal Calices
- •Vascular Anomaly
- •Diffuse Changes
- •Large Kidneys
- •Small Kidneys
- •Hypoechoic Structure
- •Hyperechoic Structure
- •Irregular Structure
- •Circumscribed Changes
- •Anechoic Structure
- •Hypoechoic or Isoechoic Structure
- •Complex Structure
- •Hyperechoic Structure
- •10 Adrenal Glands
- •Enlargement
- •Anechoic Structure
- •Hypoechoic Structure
- •Complex Echo Structure
- •Hyperechoic Structure
- •11 Urinary Tract
- •Malformations
- •Duplication Anomalies
- •Dilatations and Stenoses
- •Dilated Renal Pelvis and Ureter
- •Anechoic
- •Hypoechoic
- •Hypoechoic
- •Hyperechoic
- •Large Bladder
- •Small Bladder
- •Altered Bladder Shape
- •Intracavitary Mass
- •Hypoechoic
- •Hyperechoic
- •Echogenic
- •Wall Changes
- •Diffuse Wall Thickening
- •Circumscribed Wall Thickening
- •Concavities and Convexities
- •12.1 The Prostate
- •Enlarged Prostate
- •Regular
- •Irregular
- •Small Prostate
- •Regular
- •Echogenic
- •Circumscribed Lesion
- •Anechoic
- •Hypoechoic
- •Echogenic
- •12.2 Seminal Vesicles
- •Diffuse Change
- •Hypoechoic
- •Circumscribed Change
- •Anechoic
- •Echogenic
- •Irregular
- •12.3 Testis, Epididymis
- •Diffuse Change
- •Enlargement
- •Decreased Size
- •Circumscribed Lesion
- •Anechoic or Hypoechoic
- •Irregular/Echogenic
- •Epididymal Lesion
- •Anechoic
- •Hypoechoic
- •Intrascrotal Mass
- •Anechoic or Hypoechoic
- •Echogenic
- •13 Female Genital Tract
- •Masses
- •Abnormalities of Size or Shape
- •Uterus
- •Abnormalities of Size or Shape
- •Myometrial Changes
- •Intracavitary Changes
- •Endometrial Changes
- •Fallopian Tubes
- •Hypoechoic Mass
- •Anechoic Cystic Mass
- •Solid Echogenic or Nonhomogeneous Mass
- •14 Thyroid Gland
- •Diffuse Changes
- •Enlarged Thyroid Gland
- •Small Thyroid Gland
- •Hypoechoic Structure
- •Hyperechoic Structure
- •Circumscribed Changes
- •Anechoic
- •Hypoechoic
- •Isoechoic
- •Hyperechoic
- •Irregular
- •Differential Diagnosis of Hyperthyroidism
- •Types of Autonomy
- •15 Pleura and Chest Wall
- •Chest Wall
- •Masses
- •Parietal Pleura
- •Nodular Masses
- •Diffuse Pleural Thickening
- •Pleural Effusion
- •Anechoic Effusion
- •Echogenic Effusion
- •Complex Effusion
- •16 Lung
- •Masses
- •Anechoic Masses
- •Hypoechoic Masses
- •Complex Masses
- •Index
Vesiculitis 






















































Acute and chronic vesiculitis may be suppurative (empyema) or may consist of diffuse inflammation. Bacteriology will often identify a causative organism.
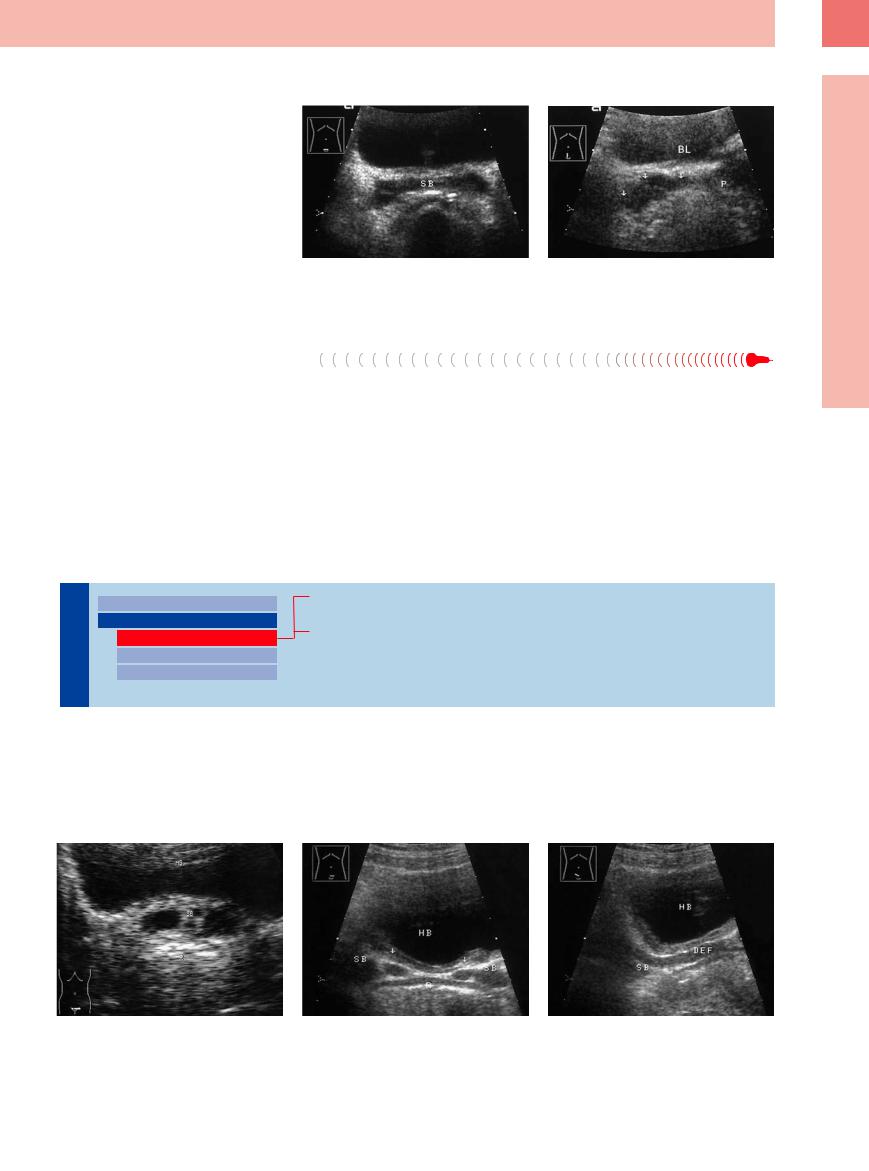
Sonographically, the seminal vesicles exhibit unilateral or bilateral hypoechoic swelling. Because of their dilatation, the vesicles may show a hypoechoic string-of-beads transformation or a plump, elliptical appearance (Fig.12.22).
Fig. 12.22 Purulent vesiculitis. |
b Longitudinal scan direction: intensively hypoechoic |
a Inferior abdominal transverse scan: swollen, intensely |
swelling (arrows). P= prostate; HB = bladder. |
hypoechoic seminal vesicles (SB), regression under anti- |
|
biotic therapy. |
|
Tumor Infiltration









Infiltration of the seminal vesicles by prostatic carcinoma is more frequently unilateral than bilateral. The tumor structure is hypoechoic, and the vesicles show irregular expansion. The tumor extensions may arise from the surroundings, from the prostate, or even from the rectum. Primary carcinomas are practically nonexistent (see Fig.12.18).
■ Circumscribed Change
Anechoic
Vesicles |
|
Anechoic |
||
|
|
|
Diffuse Change |
|
Seminal |
Circumscribed Change |
|||
|
Echogenic |
|||
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Irregular |
Dilatation, Cyst
Abscess
Dilatation, Cyst
Cyst 



















































A row of elliptical, anechoic lesions found in the |
similar, but round and smooth; they are |
seminal vesicle (usually incidentally) repre- |
thought to be associated with ipsilateral kidney |
sents foci of vesicular ectasia. They may be a |
agenesias (Fig.12.23). |
manifestation of vesiculitis. Primary cysts are |
|
12
Circumscribed Change
Fig. 12.23 Bilateral cystic masses in the seminal vesicles. HB = bladder; SB = seminal vesicle; R = rectum.
a Probable areas of ectasia.
b Medially situated cystic masses (arrows).
c When the vesicles (SB) are scanned at an oblique angle, each mass elongates into a vas deferens (DEF) (see also
Fig. 12.25).
427
12
Prostate, Seminal Vesicles, Testis, Epididymis
Abscess
Circumscribed anechoic to hypoechoic lesions in the seminal vesicles can also result from abscess formation. The diagnosis is established by the clinical features and by transabdominal or transrectal sonography, possibly combined with percutaneous drainage.
Echogenic
Vesicles |
|
Anechoic |
||
|
|
|
Diffuse Change |
|
Seminal |
Circumscribed Change |
|||
|
Echogenic |
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Irregular |
Stones, Calcifications
Stones, Calcifications 
















































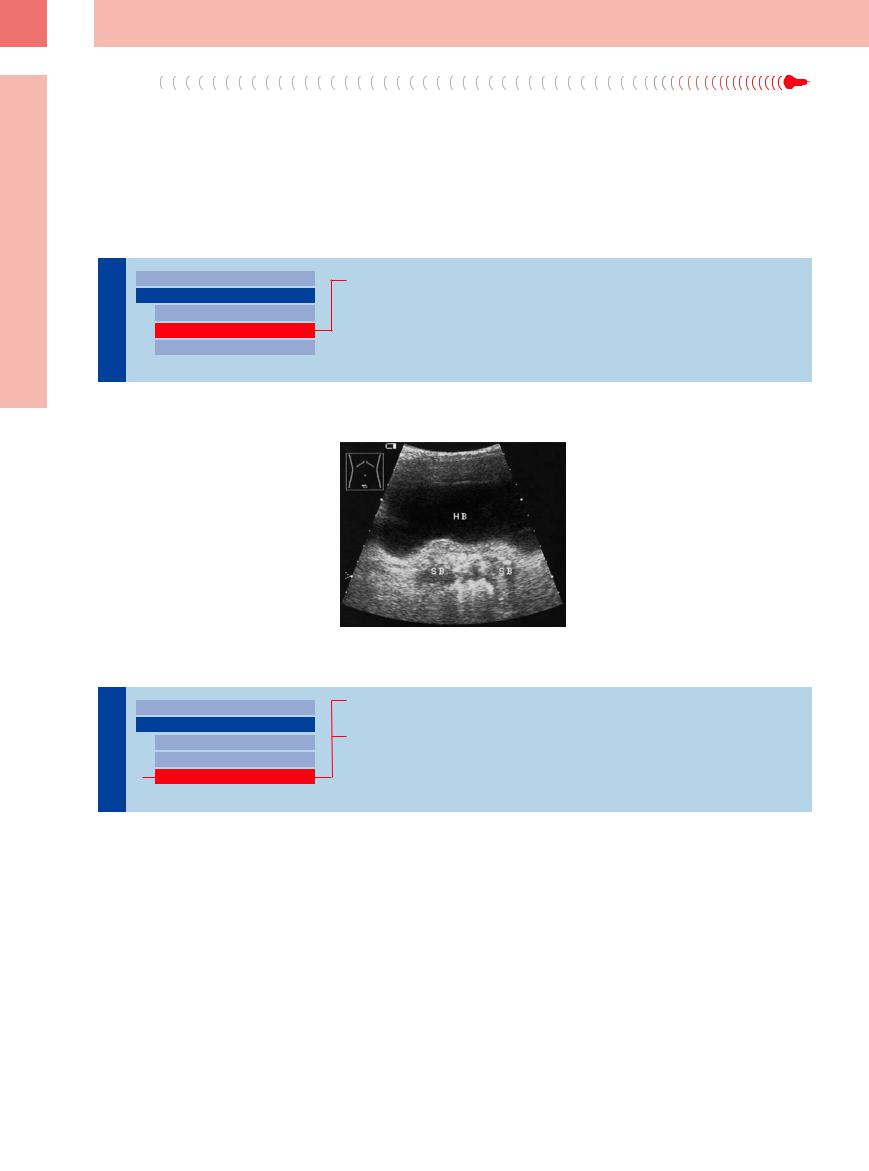
Echogenic areas in the seminal vesicles repre- |
Fig. 12.24 Irregularly hyperechoic seminal vesicles with |
sent stones or calcifications. Their ultrasound |
calcifications, acoustic shadows, and echogenic reverber- |
features are identical to those of prostatic |
ations. HB = bladder; SB = seminal vesicle. |
stones and calcifications, but transabdominal |
|
ultrasound can definitely localize them to the |
|
seminal vesicle (Fig.12.24). |
|
Irregular
Seminal Vesicles

Diffuse Change
Circumscribed Change
Anechoic
Echogenic
Irregular
Chronic Vesiculitis
Tumor Infiltration
Chronic Vesiculitis


















































Irregular structures with mixed hyperechoic/ hypoechoic or cystic areas are seen in chronic vesiculitis or may be detected incidentally with no apparent cause.
Tumor Infiltration


















































Cancer infiltrating the seminal vesicles displays structural irregularities similar to those commonly seen in prostatic carcinoma. Detection of the primary tumor confirms the diagnosis (Fig.12.18b).
428
