
- •Contents
- •Preface
- •Contributors
- •1 Vessels
- •1.1 Aorta, Vena Cava, and Peripheral Vessels
- •Aorta, Arteries
- •Anomalies and Variant Positions
- •Dilatation
- •Stenosis
- •Wall Thickening
- •Intraluminal Mass
- •Perivascular Mass
- •Vena Cava, Veins
- •Anomalies
- •Dilatation
- •Intraluminal Mass
- •Compression, Infiltration
- •1.2 Portal Vein and Its Tributaries
- •Enlarged Lumen Diameter
- •Portal Hypertension
- •Intraluminal Mass
- •Thrombosis
- •Tumor
- •2 Liver
- •Enlarged Liver
- •Small Liver
- •Homogeneous Hypoechoic Texture
- •Homogeneous Hyperechoic Texture
- •Regionally Inhomogeneous Texture
- •Diffuse Inhomogeneous Texture
- •Anechoic Masses
- •Hypoechoic Masses
- •Isoechoic Masses
- •Hyperechoic Masses
- •Echogenic Masses
- •Irregular Masses
- •Differential Diagnosis of Focal Lesions
- •Diagnostic Methods
- •Suspected Diagnosis
- •3 Biliary Tree and Gallbladder
- •3.1 Biliary Tree
- •Thickening of the Bile Duct Wall
- •Localized and Diffuse
- •Bile Duct Rarefaction
- •Localized and Diffuse
- •Bile Duct Dilatation and Intraductal Pressure
- •Intrahepatic
- •Hilar and Prepancreatic
- •Intrapancreatic
- •Papillary
- •Abnormal Intraluminal Bile Duct Findings
- •Foreign Body
- •The Seven Most Important Questions
- •3.2 Gallbladder
- •Changes in Size
- •Large Gallbladder
- •Small/Missing Gallbladder
- •Wall Changes
- •General Hypoechogenicity
- •General Hyperechogenicity
- •General Tumor
- •Focal Tumor
- •Intraluminal Changes
- •Hyperechoic
- •Hypoechoic
- •Nonvisualized Gallbladder
- •Missing Gallbladder
- •Obscured Gallbladder
- •4 Pancreas
- •Diffuse Pancreatic Change
- •Large Pancreas
- •Small Pancreas
- •Hypoechoic Texture
- •Hyperechoic Texture
- •Focal Changes
- •Anechoic Lesion
- •Hypoechoic Lesion
- •Isoechoic Lesion
- •Hyperechoic Lesion
- •Irregular (Complex Structured) Lesion
- •Dilatation of the Pancreatic Duct
- •Marginal/Mild Dilatation
- •Marked Dilatation
- •5 Spleen
- •Nonfocal Changes of the Spleen
- •Diffuse Parenchymal Changes
- •Large Spleen
- •Small Spleen
- •Focal Changes of the Spleen
- •Anechoic Mass
- •Hypoechoic Mass
- •Hyperechoic Mass
- •Splenic Calcification
- •6 Lymph Nodes
- •Peripheral Lymph Nodes
- •Head/Neck
- •Extremities (Axilla, Groin)
- •Abdominal Lymph Nodes
- •Porta Hepatis
- •Splenic Hilum
- •Mesentery (Celiac, Upper and Lower Mesenteric Station)
- •Stomach
- •Focal Wall Changes
- •Extended Wall Changes
- •Dilated Lumen
- •Narrowed Lumen
- •Small/Large Intestine
- •Focal Wall Changes
- •Extended Wall Changes
- •Dilated Lumen
- •Narrowed Lumen
- •8 Peritoneal Cavity
- •Anechoic Structure
- •Hypoechoic Structure
- •Hyperechoic Structure
- •Anechoic Structure
- •Hypoechoic Structure
- •Hyperechoic Structure
- •Wall Structures
- •Smooth Margin
- •Irregular Margin
- •Intragastric Processes
- •Intraintestinal Processes
- •9 Kidneys
- •Anomalies, Malformations
- •Aplasia, Hypoplasia
- •Cystic Malformation
- •Anomalies of Number, Position, or Rotation
- •Fusion Anomaly
- •Anomalies of the Renal Calices
- •Vascular Anomaly
- •Diffuse Changes
- •Large Kidneys
- •Small Kidneys
- •Hypoechoic Structure
- •Hyperechoic Structure
- •Irregular Structure
- •Circumscribed Changes
- •Anechoic Structure
- •Hypoechoic or Isoechoic Structure
- •Complex Structure
- •Hyperechoic Structure
- •10 Adrenal Glands
- •Enlargement
- •Anechoic Structure
- •Hypoechoic Structure
- •Complex Echo Structure
- •Hyperechoic Structure
- •11 Urinary Tract
- •Malformations
- •Duplication Anomalies
- •Dilatations and Stenoses
- •Dilated Renal Pelvis and Ureter
- •Anechoic
- •Hypoechoic
- •Hypoechoic
- •Hyperechoic
- •Large Bladder
- •Small Bladder
- •Altered Bladder Shape
- •Intracavitary Mass
- •Hypoechoic
- •Hyperechoic
- •Echogenic
- •Wall Changes
- •Diffuse Wall Thickening
- •Circumscribed Wall Thickening
- •Concavities and Convexities
- •12.1 The Prostate
- •Enlarged Prostate
- •Regular
- •Irregular
- •Small Prostate
- •Regular
- •Echogenic
- •Circumscribed Lesion
- •Anechoic
- •Hypoechoic
- •Echogenic
- •12.2 Seminal Vesicles
- •Diffuse Change
- •Hypoechoic
- •Circumscribed Change
- •Anechoic
- •Echogenic
- •Irregular
- •12.3 Testis, Epididymis
- •Diffuse Change
- •Enlargement
- •Decreased Size
- •Circumscribed Lesion
- •Anechoic or Hypoechoic
- •Irregular/Echogenic
- •Epididymal Lesion
- •Anechoic
- •Hypoechoic
- •Intrascrotal Mass
- •Anechoic or Hypoechoic
- •Echogenic
- •13 Female Genital Tract
- •Masses
- •Abnormalities of Size or Shape
- •Uterus
- •Abnormalities of Size or Shape
- •Myometrial Changes
- •Intracavitary Changes
- •Endometrial Changes
- •Fallopian Tubes
- •Hypoechoic Mass
- •Anechoic Cystic Mass
- •Solid Echogenic or Nonhomogeneous Mass
- •14 Thyroid Gland
- •Diffuse Changes
- •Enlarged Thyroid Gland
- •Small Thyroid Gland
- •Hypoechoic Structure
- •Hyperechoic Structure
- •Circumscribed Changes
- •Anechoic
- •Hypoechoic
- •Isoechoic
- •Hyperechoic
- •Irregular
- •Differential Diagnosis of Hyperthyroidism
- •Types of Autonomy
- •15 Pleura and Chest Wall
- •Chest Wall
- •Masses
- •Parietal Pleura
- •Nodular Masses
- •Diffuse Pleural Thickening
- •Pleural Effusion
- •Anechoic Effusion
- •Echogenic Effusion
- •Complex Effusion
- •16 Lung
- •Masses
- •Anechoic Masses
- •Hypoechoic Masses
- •Complex Masses
- •Index
3
Biliary Tree and Gallbladder
Intrapancreatic
Tree |
|
|
|
|
Thickening of the Bile Duct Wall |
Benign Intrapancreatic Stenosis |
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
Bile Duct Rarefaction |
Cancer of the Pancreatic Head |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
Biliary |
|
|
|
|
Bile Duct Dilatation and Intraductal Pressure |
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
Intrahepatic |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Hilar and Prepancreatic |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Intrapancreatic |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Papillary |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Abnormal Intraluminal Bile Duct Findings |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Differential Diagnosis of Sonographic |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Cholestasis |
|
|
Benign Intrapancreatic Stenosis |
|
|
|||||
One of the most common causes of benign |
(compared with the more plump cut-off ap- |
are benign pancreatic masses along the line of |
|||||
intrapancreatic stenosis, apart from the acute |
pearance in malignancies) (Fig. 3.25), this pre- |
focal mesenchymal lesions, or nonpancreatic |
|||||
passage of gallstones, is marked chronic pan- |
liminary diagnosis is well founded. Biliary ob- |
causes such as completely stone-filled CBD or |
|||||
creatitis: in the presence of the typical sono- |
struction may also be caused by pseudocysts |
multiple papillomata (Fig. 3.24c,d). |
|||||
graphic signs (see Fig. 3.10a,b, Fig. 3.23) and |
and acute (segmental cephalic) pancreatitis. |
|
|||||
the |
pointed cone-shaped obstructed CBD |
Other rare causes described in the literature |
|
||||
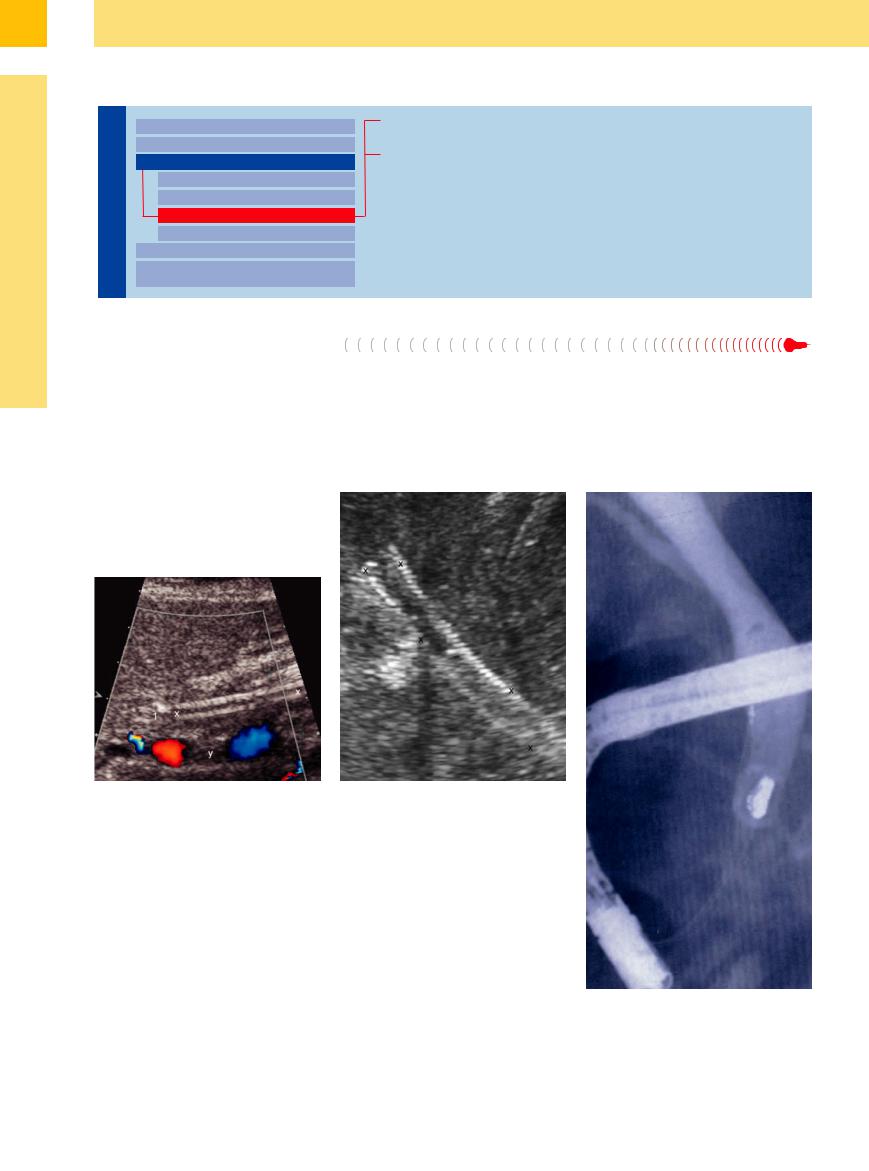
Fig. 3.23 |
b Bilioduodenal self-expanding stent (x), no further |
a Bilioduodenal stent (x) draining the CBD (1); lympha- |
stenosis, good function. |
denopathy (y), inferior caval vein (6). |
|
Fig. 3.24 Rare findings in ERC.
a Limits of biliary sonography: migrated shell not visible.
138
3
Bile Duct Dilatation and Intraductal Pressure
b Clip after cholecystectomy. |
c Choledocholithiasis with multiple calculi without sur- |
d Multiple (histologically adenomatous) polyps. |
|
rounding fluid. |
|
Cancer of the Pancreatic Head 











































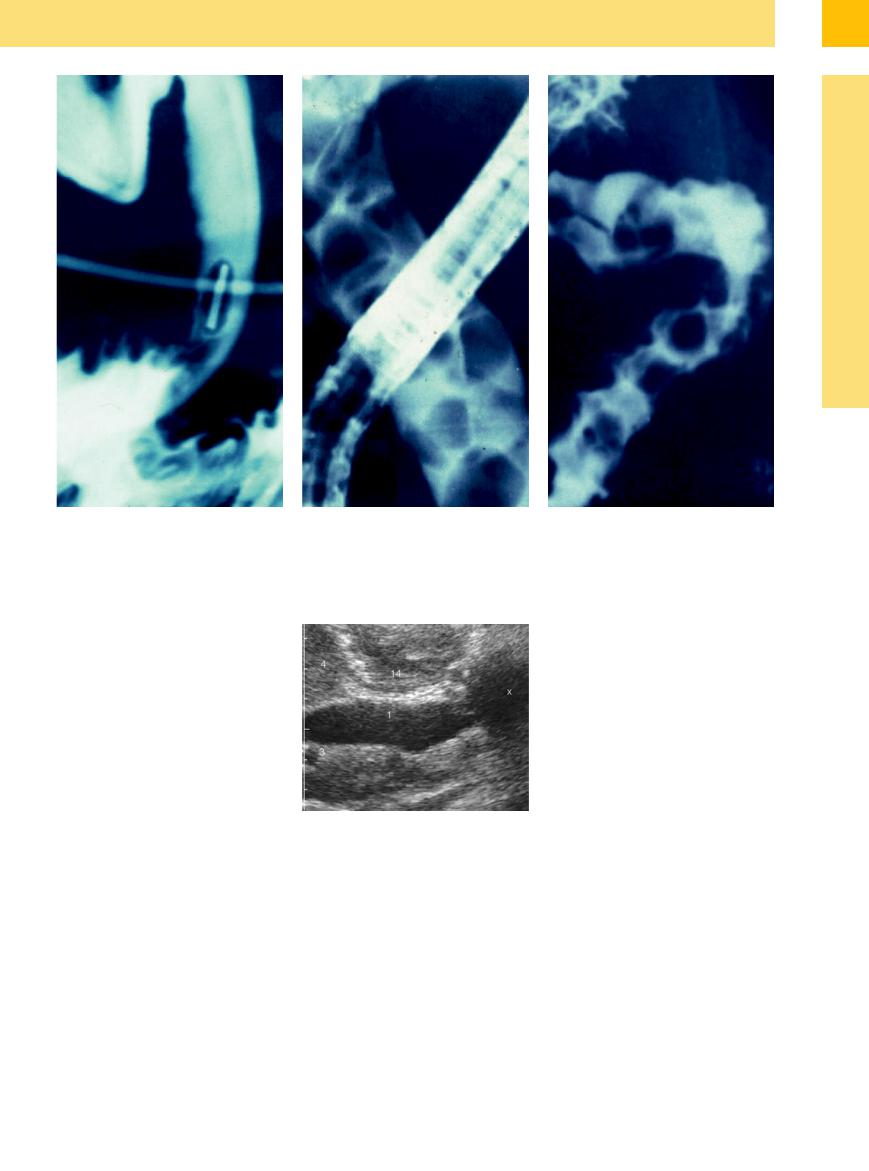
Most cases of malignant intrapancreatic obstruction (Fig. 3.25) are due to ductal carcinoma of the pancreatic head. But at times (undifferentiated carcinoma), even histology may not be able to differentiate between ductal pancreatic carcinoma and CCC of the intrapancreatic CBD. Pancreatic metastases are rare by themselves and will hardly result in obstruction of the biliary passage.
Fig. 3.25 Cancer of the pancreatic head (x), obstructing the CBD (1); hepatic artery (3); liver (4); posterior wall of the gastric antrum (14).
139
