
- •Contents
- •Preface
- •Contributors
- •1 Vessels
- •1.1 Aorta, Vena Cava, and Peripheral Vessels
- •Aorta, Arteries
- •Anomalies and Variant Positions
- •Dilatation
- •Stenosis
- •Wall Thickening
- •Intraluminal Mass
- •Perivascular Mass
- •Vena Cava, Veins
- •Anomalies
- •Dilatation
- •Intraluminal Mass
- •Compression, Infiltration
- •1.2 Portal Vein and Its Tributaries
- •Enlarged Lumen Diameter
- •Portal Hypertension
- •Intraluminal Mass
- •Thrombosis
- •Tumor
- •2 Liver
- •Enlarged Liver
- •Small Liver
- •Homogeneous Hypoechoic Texture
- •Homogeneous Hyperechoic Texture
- •Regionally Inhomogeneous Texture
- •Diffuse Inhomogeneous Texture
- •Anechoic Masses
- •Hypoechoic Masses
- •Isoechoic Masses
- •Hyperechoic Masses
- •Echogenic Masses
- •Irregular Masses
- •Differential Diagnosis of Focal Lesions
- •Diagnostic Methods
- •Suspected Diagnosis
- •3 Biliary Tree and Gallbladder
- •3.1 Biliary Tree
- •Thickening of the Bile Duct Wall
- •Localized and Diffuse
- •Bile Duct Rarefaction
- •Localized and Diffuse
- •Bile Duct Dilatation and Intraductal Pressure
- •Intrahepatic
- •Hilar and Prepancreatic
- •Intrapancreatic
- •Papillary
- •Abnormal Intraluminal Bile Duct Findings
- •Foreign Body
- •The Seven Most Important Questions
- •3.2 Gallbladder
- •Changes in Size
- •Large Gallbladder
- •Small/Missing Gallbladder
- •Wall Changes
- •General Hypoechogenicity
- •General Hyperechogenicity
- •General Tumor
- •Focal Tumor
- •Intraluminal Changes
- •Hyperechoic
- •Hypoechoic
- •Nonvisualized Gallbladder
- •Missing Gallbladder
- •Obscured Gallbladder
- •4 Pancreas
- •Diffuse Pancreatic Change
- •Large Pancreas
- •Small Pancreas
- •Hypoechoic Texture
- •Hyperechoic Texture
- •Focal Changes
- •Anechoic Lesion
- •Hypoechoic Lesion
- •Isoechoic Lesion
- •Hyperechoic Lesion
- •Irregular (Complex Structured) Lesion
- •Dilatation of the Pancreatic Duct
- •Marginal/Mild Dilatation
- •Marked Dilatation
- •5 Spleen
- •Nonfocal Changes of the Spleen
- •Diffuse Parenchymal Changes
- •Large Spleen
- •Small Spleen
- •Focal Changes of the Spleen
- •Anechoic Mass
- •Hypoechoic Mass
- •Hyperechoic Mass
- •Splenic Calcification
- •6 Lymph Nodes
- •Peripheral Lymph Nodes
- •Head/Neck
- •Extremities (Axilla, Groin)
- •Abdominal Lymph Nodes
- •Porta Hepatis
- •Splenic Hilum
- •Mesentery (Celiac, Upper and Lower Mesenteric Station)
- •Stomach
- •Focal Wall Changes
- •Extended Wall Changes
- •Dilated Lumen
- •Narrowed Lumen
- •Small/Large Intestine
- •Focal Wall Changes
- •Extended Wall Changes
- •Dilated Lumen
- •Narrowed Lumen
- •8 Peritoneal Cavity
- •Anechoic Structure
- •Hypoechoic Structure
- •Hyperechoic Structure
- •Anechoic Structure
- •Hypoechoic Structure
- •Hyperechoic Structure
- •Wall Structures
- •Smooth Margin
- •Irregular Margin
- •Intragastric Processes
- •Intraintestinal Processes
- •9 Kidneys
- •Anomalies, Malformations
- •Aplasia, Hypoplasia
- •Cystic Malformation
- •Anomalies of Number, Position, or Rotation
- •Fusion Anomaly
- •Anomalies of the Renal Calices
- •Vascular Anomaly
- •Diffuse Changes
- •Large Kidneys
- •Small Kidneys
- •Hypoechoic Structure
- •Hyperechoic Structure
- •Irregular Structure
- •Circumscribed Changes
- •Anechoic Structure
- •Hypoechoic or Isoechoic Structure
- •Complex Structure
- •Hyperechoic Structure
- •10 Adrenal Glands
- •Enlargement
- •Anechoic Structure
- •Hypoechoic Structure
- •Complex Echo Structure
- •Hyperechoic Structure
- •11 Urinary Tract
- •Malformations
- •Duplication Anomalies
- •Dilatations and Stenoses
- •Dilated Renal Pelvis and Ureter
- •Anechoic
- •Hypoechoic
- •Hypoechoic
- •Hyperechoic
- •Large Bladder
- •Small Bladder
- •Altered Bladder Shape
- •Intracavitary Mass
- •Hypoechoic
- •Hyperechoic
- •Echogenic
- •Wall Changes
- •Diffuse Wall Thickening
- •Circumscribed Wall Thickening
- •Concavities and Convexities
- •12.1 The Prostate
- •Enlarged Prostate
- •Regular
- •Irregular
- •Small Prostate
- •Regular
- •Echogenic
- •Circumscribed Lesion
- •Anechoic
- •Hypoechoic
- •Echogenic
- •12.2 Seminal Vesicles
- •Diffuse Change
- •Hypoechoic
- •Circumscribed Change
- •Anechoic
- •Echogenic
- •Irregular
- •12.3 Testis, Epididymis
- •Diffuse Change
- •Enlargement
- •Decreased Size
- •Circumscribed Lesion
- •Anechoic or Hypoechoic
- •Irregular/Echogenic
- •Epididymal Lesion
- •Anechoic
- •Hypoechoic
- •Intrascrotal Mass
- •Anechoic or Hypoechoic
- •Echogenic
- •13 Female Genital Tract
- •Masses
- •Abnormalities of Size or Shape
- •Uterus
- •Abnormalities of Size or Shape
- •Myometrial Changes
- •Intracavitary Changes
- •Endometrial Changes
- •Fallopian Tubes
- •Hypoechoic Mass
- •Anechoic Cystic Mass
- •Solid Echogenic or Nonhomogeneous Mass
- •14 Thyroid Gland
- •Diffuse Changes
- •Enlarged Thyroid Gland
- •Small Thyroid Gland
- •Hypoechoic Structure
- •Hyperechoic Structure
- •Circumscribed Changes
- •Anechoic
- •Hypoechoic
- •Isoechoic
- •Hyperechoic
- •Irregular
- •Differential Diagnosis of Hyperthyroidism
- •Types of Autonomy
- •15 Pleura and Chest Wall
- •Chest Wall
- •Masses
- •Parietal Pleura
- •Nodular Masses
- •Diffuse Pleural Thickening
- •Pleural Effusion
- •Anechoic Effusion
- •Echogenic Effusion
- •Complex Effusion
- •16 Lung
- •Masses
- •Anechoic Masses
- •Hypoechoic Masses
- •Complex Masses
- •Index
12
Prostate, Seminal Vesicles, Testis, Epididymis
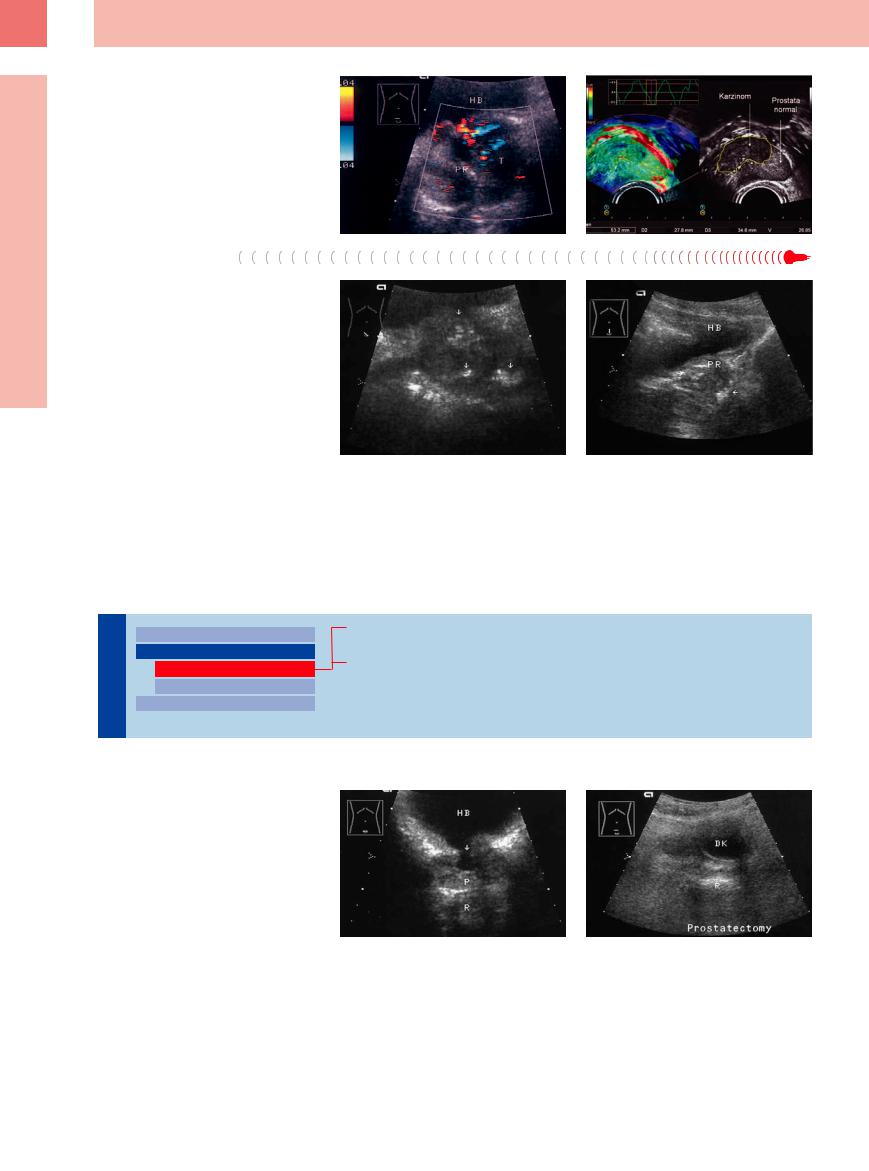
Fig. 12.10
a Prostatic carcinoma (T), color duplex: hypoechoic tumor foci in both lobes (surgery: T3 tumor). HB = bladder; PR = prostate.
b Elastosonography: hard carcinomatous parts are demarcated and color-coded dark green-blue in elastography (image courtesy of Dr. A. Auge, Gera, Germany).
Chronic Prostatitis
The complaints that are associated with acute and chronic prostatitis are fairly nonspecific, and so the diagnosis can be established only by identifying the causative organism and/or detecting signs of urethral inflammation at ureterocystoscopy.
The sonographic diagnosis is also uncertain. Circumscribed hypoechoic or anechoic areas are found in acute prostatitis, while chronic prostatitis shows zones of increased density or calcification that are responsible for the irregular structural transformation (Fig.12.11;
see also Fig.12.20).
Fig. 12.11 Findings consistent with chronic prostatitis. HB = bladder; PR = prostate.
a Irregular echo structure with numerous hyperechoic spots (corpora amylacea?, arrows); known prostatitis.
b Small prostate with microcalcifications and an irregular structure (45-year-old man).
■ Small Prostate
Regular
Prostate |
|
|
Enlarged Prostate |
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
Small Prostate |
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
Regular |
|
|
|
|
|
The |
|
|
|
Echogenic |
|
|
Circumscribed Lesion |
||
|
|
|
||
Operated Prostate
Radiation Therapy
Operated Prostate
Prostate


















































A small prostate found at ultrasound is usually a result of surgery. In patients who have had a transurethral resection (TUR), the size reduction results from a complete resection of the previously enlarged median lobe. Ultrasound demonstrates a small prostatic remnant and often shows a funnel-shaped, anechoic urethral orifice formed by the resection defect at the level of the bladder neck (Fig.12.12a).
A transabdominal total prostatectomy involves removing the enlarged median lobe in the plane of the surgical capsule, while a transabdominal tumor resection consists of a radical prostatovesiculectomy, in which case the prostate and seminal vesicles are completely absent (Fig.12.12b).
Fig. 12.12
a Small prostate (PR) following transurethral resection (TUR). The urethral orifice and prostatic urethra appear widened and anechoic after TUR. The expanded urethral orifice is funnel-shaped and fluid-filled (arrow). HB = bladder. R = rectum.
b Prostatectomy for carcinoma: nonvisualization of the prostate in a transabdominal low transverse scan. Urinary catheter (DK) is in place. Normally the seminal vesicle or prostate would be visualized between the bladder floor and rectum (R).
422
