
- •Contents
- •Preface
- •Contributors
- •1 Vessels
- •1.1 Aorta, Vena Cava, and Peripheral Vessels
- •Aorta, Arteries
- •Anomalies and Variant Positions
- •Dilatation
- •Stenosis
- •Wall Thickening
- •Intraluminal Mass
- •Perivascular Mass
- •Vena Cava, Veins
- •Anomalies
- •Dilatation
- •Intraluminal Mass
- •Compression, Infiltration
- •1.2 Portal Vein and Its Tributaries
- •Enlarged Lumen Diameter
- •Portal Hypertension
- •Intraluminal Mass
- •Thrombosis
- •Tumor
- •2 Liver
- •Enlarged Liver
- •Small Liver
- •Homogeneous Hypoechoic Texture
- •Homogeneous Hyperechoic Texture
- •Regionally Inhomogeneous Texture
- •Diffuse Inhomogeneous Texture
- •Anechoic Masses
- •Hypoechoic Masses
- •Isoechoic Masses
- •Hyperechoic Masses
- •Echogenic Masses
- •Irregular Masses
- •Differential Diagnosis of Focal Lesions
- •Diagnostic Methods
- •Suspected Diagnosis
- •3 Biliary Tree and Gallbladder
- •3.1 Biliary Tree
- •Thickening of the Bile Duct Wall
- •Localized and Diffuse
- •Bile Duct Rarefaction
- •Localized and Diffuse
- •Bile Duct Dilatation and Intraductal Pressure
- •Intrahepatic
- •Hilar and Prepancreatic
- •Intrapancreatic
- •Papillary
- •Abnormal Intraluminal Bile Duct Findings
- •Foreign Body
- •The Seven Most Important Questions
- •3.2 Gallbladder
- •Changes in Size
- •Large Gallbladder
- •Small/Missing Gallbladder
- •Wall Changes
- •General Hypoechogenicity
- •General Hyperechogenicity
- •General Tumor
- •Focal Tumor
- •Intraluminal Changes
- •Hyperechoic
- •Hypoechoic
- •Nonvisualized Gallbladder
- •Missing Gallbladder
- •Obscured Gallbladder
- •4 Pancreas
- •Diffuse Pancreatic Change
- •Large Pancreas
- •Small Pancreas
- •Hypoechoic Texture
- •Hyperechoic Texture
- •Focal Changes
- •Anechoic Lesion
- •Hypoechoic Lesion
- •Isoechoic Lesion
- •Hyperechoic Lesion
- •Irregular (Complex Structured) Lesion
- •Dilatation of the Pancreatic Duct
- •Marginal/Mild Dilatation
- •Marked Dilatation
- •5 Spleen
- •Nonfocal Changes of the Spleen
- •Diffuse Parenchymal Changes
- •Large Spleen
- •Small Spleen
- •Focal Changes of the Spleen
- •Anechoic Mass
- •Hypoechoic Mass
- •Hyperechoic Mass
- •Splenic Calcification
- •6 Lymph Nodes
- •Peripheral Lymph Nodes
- •Head/Neck
- •Extremities (Axilla, Groin)
- •Abdominal Lymph Nodes
- •Porta Hepatis
- •Splenic Hilum
- •Mesentery (Celiac, Upper and Lower Mesenteric Station)
- •Stomach
- •Focal Wall Changes
- •Extended Wall Changes
- •Dilated Lumen
- •Narrowed Lumen
- •Small/Large Intestine
- •Focal Wall Changes
- •Extended Wall Changes
- •Dilated Lumen
- •Narrowed Lumen
- •8 Peritoneal Cavity
- •Anechoic Structure
- •Hypoechoic Structure
- •Hyperechoic Structure
- •Anechoic Structure
- •Hypoechoic Structure
- •Hyperechoic Structure
- •Wall Structures
- •Smooth Margin
- •Irregular Margin
- •Intragastric Processes
- •Intraintestinal Processes
- •9 Kidneys
- •Anomalies, Malformations
- •Aplasia, Hypoplasia
- •Cystic Malformation
- •Anomalies of Number, Position, or Rotation
- •Fusion Anomaly
- •Anomalies of the Renal Calices
- •Vascular Anomaly
- •Diffuse Changes
- •Large Kidneys
- •Small Kidneys
- •Hypoechoic Structure
- •Hyperechoic Structure
- •Irregular Structure
- •Circumscribed Changes
- •Anechoic Structure
- •Hypoechoic or Isoechoic Structure
- •Complex Structure
- •Hyperechoic Structure
- •10 Adrenal Glands
- •Enlargement
- •Anechoic Structure
- •Hypoechoic Structure
- •Complex Echo Structure
- •Hyperechoic Structure
- •11 Urinary Tract
- •Malformations
- •Duplication Anomalies
- •Dilatations and Stenoses
- •Dilated Renal Pelvis and Ureter
- •Anechoic
- •Hypoechoic
- •Hypoechoic
- •Hyperechoic
- •Large Bladder
- •Small Bladder
- •Altered Bladder Shape
- •Intracavitary Mass
- •Hypoechoic
- •Hyperechoic
- •Echogenic
- •Wall Changes
- •Diffuse Wall Thickening
- •Circumscribed Wall Thickening
- •Concavities and Convexities
- •12.1 The Prostate
- •Enlarged Prostate
- •Regular
- •Irregular
- •Small Prostate
- •Regular
- •Echogenic
- •Circumscribed Lesion
- •Anechoic
- •Hypoechoic
- •Echogenic
- •12.2 Seminal Vesicles
- •Diffuse Change
- •Hypoechoic
- •Circumscribed Change
- •Anechoic
- •Echogenic
- •Irregular
- •12.3 Testis, Epididymis
- •Diffuse Change
- •Enlargement
- •Decreased Size
- •Circumscribed Lesion
- •Anechoic or Hypoechoic
- •Irregular/Echogenic
- •Epididymal Lesion
- •Anechoic
- •Hypoechoic
- •Intrascrotal Mass
- •Anechoic or Hypoechoic
- •Echogenic
- •13 Female Genital Tract
- •Masses
- •Abnormalities of Size or Shape
- •Uterus
- •Abnormalities of Size or Shape
- •Myometrial Changes
- •Intracavitary Changes
- •Endometrial Changes
- •Fallopian Tubes
- •Hypoechoic Mass
- •Anechoic Cystic Mass
- •Solid Echogenic or Nonhomogeneous Mass
- •14 Thyroid Gland
- •Diffuse Changes
- •Enlarged Thyroid Gland
- •Small Thyroid Gland
- •Hypoechoic Structure
- •Hyperechoic Structure
- •Circumscribed Changes
- •Anechoic
- •Hypoechoic
- •Isoechoic
- •Hyperechoic
- •Irregular
- •Differential Diagnosis of Hyperthyroidism
- •Types of Autonomy
- •15 Pleura and Chest Wall
- •Chest Wall
- •Masses
- •Parietal Pleura
- •Nodular Masses
- •Diffuse Pleural Thickening
- •Pleural Effusion
- •Anechoic Effusion
- •Echogenic Effusion
- •Complex Effusion
- •16 Lung
- •Masses
- •Anechoic Masses
- •Hypoechoic Masses
- •Complex Masses
- •Index
9 Kidneys
Kidneys 321
|
|
|
Anomalies, Malformations |
322 |
|||||
|
|
|
|||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
Aplasia, Hypoplasia |
322 |
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Renal Agenesis |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Hypoplasia |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Dysplasia |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Cystic Malformation |
324 |
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Autosomal Dominant Polycystic |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Kidney Disease (ADPKD) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Anomalies of Number, Position, |
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
or Rotation |
325 |
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Duplex Kidney |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Ectopic Kidney |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Malrotation |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Fusion Anomaly |
327 |
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Horseshoe Kidney |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Fetal Lobulation |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Anomalies of the Renal Calices |
328 |
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Caliceal Diverticulum |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Megacalicosis |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Vascular Anomaly |
328 |
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Aberrant Vessels |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Renovascular Malformations |
|
|
|
Diffuse Changes |
329 |
||||||
|
|
||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
Large Kidneys |
329 |
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
Constitutional/Acromegaly
Duplex Kidney, Single Kidney
Diabetic Nephropathy
Polycystic Kidney Disease
Acute Renal Failure,
Shock Kidney
Septic–Toxic Kidneys
Acute Urinary Retention,
Acute Outflow Obstruction
Renal Congestion Due to Heart Failure
Renal Vein Thrombosis
Acute Glomerulonephritis
Acute Pyelonephritis
AIDSand Heroin-induced
Nephropathy
Amyloidosis/Paraprotein Kidney
Pyonephrosis
Renal Tumor
Renal Allograft,
Allograft Rejection
Small Kidneys |
334 |
Hypoplasia
Renal Artery Stenosis, Embolism
Arteriosclerosis, Arteriolosclerosis
(Ischemic Nephropathy)
Chronic Pyelonephritis
Analgesic Nephropathy
Chronic Glomerulonephritis
Diabetic Nephropathy
Hypoechoic Structure |
337 |
||
|
|
Acute Renal Failure |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Acute Nephritis |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Right Ventricular Failure |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Renal Vein Thrombosis |
|
Hyperechoic Structure |
338 |
||
|
|
Hypoxemic Renal Shock |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Diabetic Nephropathy |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Acute and Chronic |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Glomerulonephritis |
|
|
|
Chronic Pyelonephritis |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Analgesic Nephropathy |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Septic–Toxic Kidneys |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Severe Metabolic Disorders |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Hyperechoic Structure (Continued) |
338 |
||
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
Light-chain Deposition Disease, |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Waldenström Macroglobulinemia |
|
|
|
|
|
Amyloidosis |
|
|
|
|
|
Infiltration by Lymphoma |
|
|
|
|
|
Atrophic Kidneys |
|
|
|
Irregular Structure |
343 |
||
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
Analgesic Nephropathy |
|
|
|
|
|
Diffuse Tumor Infiltration |
|
|
|
|
|
Purulent Pyelonephritis, |
|
|
|
|
|
Pyonephrosis |
|
Circumscribed Changes |
344 |
||||
|
|
Anechoic Structure |
344 |
||
|
|
||||
Renal Cysts, Polycystic Kidney/
Cystic Nephroma
Perirenal Cystic Masses
Lymph Cysts
Cystic Renal Cell Carcinoma,
Intracystic Carcinoma
Papillary Necrosis, Cystic Degeneration
of the Medullary Pyramids
Cavities
Abscess
Organized Hematoma
Urinoma, Seroma
Vascular Dilatations
Hydrocalices, Pyelectasis,
Hydronephrosis
Cyst-like Metastases
Hypoechoic or |
|
Isoechoic Structure |
350 |
Dromedary Hump,
Fetal Lobulation
Abscess
Hemorrhagic Cyst
Fresh Renal Infarct
Hematoma
Renal Cell Carcinoma
Urothelial Carcinoma
Malignant Lymphoma
Metastasis
Papillary Adenoma, Oncocytoma,
Inflammatory Tumor
Complex Structure |
356 |
Abscess, Pyonephrosis
Xanthomatous Pyelonephritis
Hematoma, Intracystic Hemorrhage
Renal Cell Carcinoma,
Cystic Renal Carcinoma,
Malignant Lymphoma
Renal Trauma
Hyperechoic Structure |
358 |
||
|
|
Renal Abscess, Carbuncles |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Hemorrhagic Cyst |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Renal Cell Carcinoma |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Angiomyolipoma |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Scars |
|
|
Echogenic Structure |
361 |
|
|
|
|
|
Papillary Calcification
Interlobar and Arcuate Arteries
Bacterial Gas Bubbles
Parenchymal Calcification
Nephrocalcinosis,
Medullary Sponge Kidney
Renal Tuberculosis,
Putty Kidney
Pyelocaliceal Stone,
Staghorn Calculus
9
Kidneys
Cortex. The renal cortex is a strip 6–10 mm wide located just beneath the fibrous renal capsule. Its boundary is formed by an imaginary line along the bases of the medullary pyramids. Extensions of the renal cortex, called the renal columns, extend between the 7–9 pyramids that make up the renal medulla. The renal
calices. Because of the high fluid content of the collecting ducts, the medullary pyramids appear markedly less echogenic in ultrasound than the renal cortex (Fig. 9.1).
Vessels. The vessels of the kidney, the renal artery and vein, divide into an anterior and a posterior branch at the renal hilum while still
the interlobular arteries, which pass radially into the renal cortex. The individual vessels are displayed particularly well by color Doppler sonography (CDS). The veins run parallel to the named arteries. The entire vascular system is also clearly visible in 3 D imaging.
Anatomical structures
●Renal hilum
●Renal cortex and medulla
●Medullary pyramids and papillae
●Renal vessels
Size
●Length 10–11.5 cm
●Width 5–7 cm
●Thickness 3–4 cm
Volume
●Normal: 90–170 mL
●Small: < 80 mL
●Large: > 180 mL
●Parenchymal thickness: 13–18 mm, thin < 12 mm
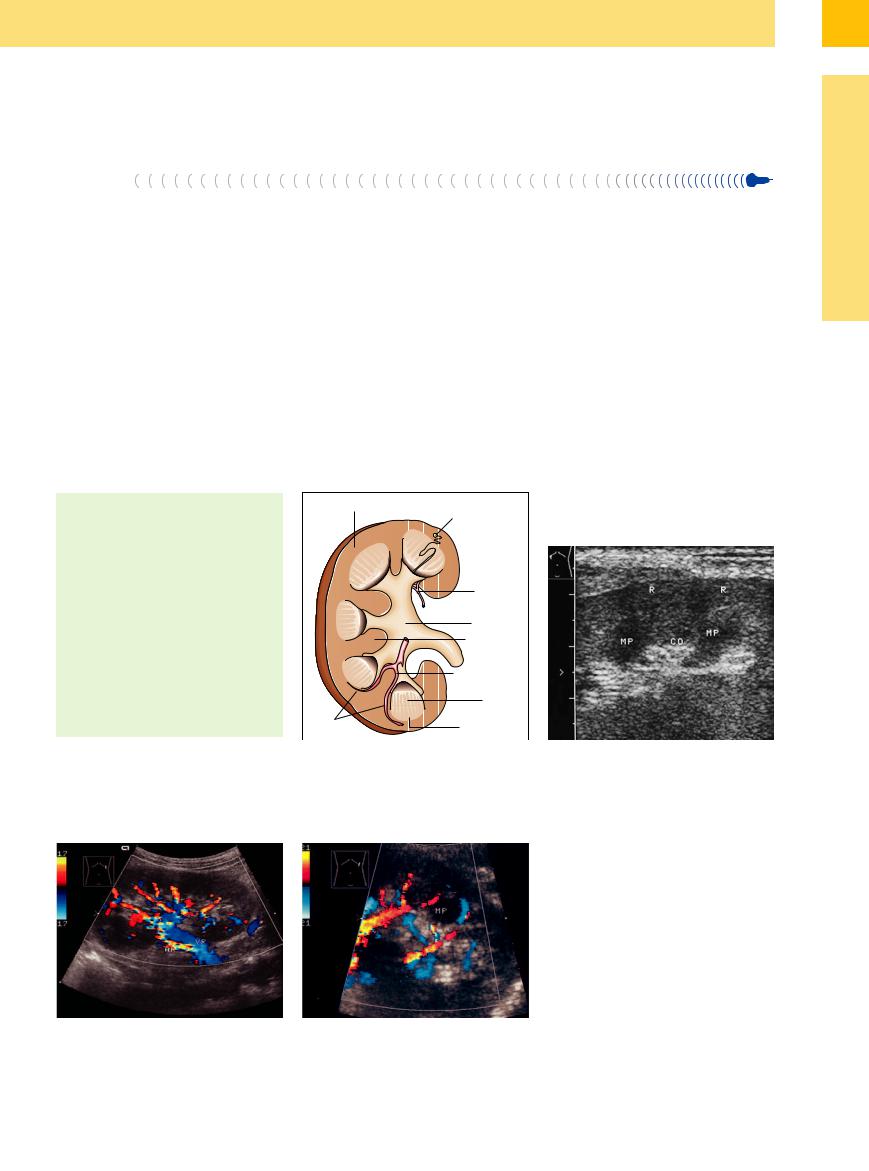
Fig. 9.1 Renal cortex and medulla.
aDiagram showing the medullary pyramids, vessels, and
amalpighian corpuscle.
b Close-up view of the right kidney, showing the relatively hypoechoic medullary pyramids (MP) and the cortex (R), bounded by an imaginary line connecting the bases of the pyramids. Between the medullary pyramids are the renal columns (CO).
Fig. 9.2 Radial branching of the segmental arteries into the interlobar vessels. Left kidney (enlarged following a right nephrectomy). AR = renal artery; VR = renal vein.
f Fig. 9.3 Detail view of a medullary pyramid (MP) with the surrounding interlobar vessels, which turn horizontally at the bases of the pyramids to form the arcuate vessels.
321
