
- •Contents
- •Preface
- •Contributors
- •1 Vessels
- •1.1 Aorta, Vena Cava, and Peripheral Vessels
- •Aorta, Arteries
- •Anomalies and Variant Positions
- •Dilatation
- •Stenosis
- •Wall Thickening
- •Intraluminal Mass
- •Perivascular Mass
- •Vena Cava, Veins
- •Anomalies
- •Dilatation
- •Intraluminal Mass
- •Compression, Infiltration
- •1.2 Portal Vein and Its Tributaries
- •Enlarged Lumen Diameter
- •Portal Hypertension
- •Intraluminal Mass
- •Thrombosis
- •Tumor
- •2 Liver
- •Enlarged Liver
- •Small Liver
- •Homogeneous Hypoechoic Texture
- •Homogeneous Hyperechoic Texture
- •Regionally Inhomogeneous Texture
- •Diffuse Inhomogeneous Texture
- •Anechoic Masses
- •Hypoechoic Masses
- •Isoechoic Masses
- •Hyperechoic Masses
- •Echogenic Masses
- •Irregular Masses
- •Differential Diagnosis of Focal Lesions
- •Diagnostic Methods
- •Suspected Diagnosis
- •3 Biliary Tree and Gallbladder
- •3.1 Biliary Tree
- •Thickening of the Bile Duct Wall
- •Localized and Diffuse
- •Bile Duct Rarefaction
- •Localized and Diffuse
- •Bile Duct Dilatation and Intraductal Pressure
- •Intrahepatic
- •Hilar and Prepancreatic
- •Intrapancreatic
- •Papillary
- •Abnormal Intraluminal Bile Duct Findings
- •Foreign Body
- •The Seven Most Important Questions
- •3.2 Gallbladder
- •Changes in Size
- •Large Gallbladder
- •Small/Missing Gallbladder
- •Wall Changes
- •General Hypoechogenicity
- •General Hyperechogenicity
- •General Tumor
- •Focal Tumor
- •Intraluminal Changes
- •Hyperechoic
- •Hypoechoic
- •Nonvisualized Gallbladder
- •Missing Gallbladder
- •Obscured Gallbladder
- •4 Pancreas
- •Diffuse Pancreatic Change
- •Large Pancreas
- •Small Pancreas
- •Hypoechoic Texture
- •Hyperechoic Texture
- •Focal Changes
- •Anechoic Lesion
- •Hypoechoic Lesion
- •Isoechoic Lesion
- •Hyperechoic Lesion
- •Irregular (Complex Structured) Lesion
- •Dilatation of the Pancreatic Duct
- •Marginal/Mild Dilatation
- •Marked Dilatation
- •5 Spleen
- •Nonfocal Changes of the Spleen
- •Diffuse Parenchymal Changes
- •Large Spleen
- •Small Spleen
- •Focal Changes of the Spleen
- •Anechoic Mass
- •Hypoechoic Mass
- •Hyperechoic Mass
- •Splenic Calcification
- •6 Lymph Nodes
- •Peripheral Lymph Nodes
- •Head/Neck
- •Extremities (Axilla, Groin)
- •Abdominal Lymph Nodes
- •Porta Hepatis
- •Splenic Hilum
- •Mesentery (Celiac, Upper and Lower Mesenteric Station)
- •Stomach
- •Focal Wall Changes
- •Extended Wall Changes
- •Dilated Lumen
- •Narrowed Lumen
- •Small/Large Intestine
- •Focal Wall Changes
- •Extended Wall Changes
- •Dilated Lumen
- •Narrowed Lumen
- •8 Peritoneal Cavity
- •Anechoic Structure
- •Hypoechoic Structure
- •Hyperechoic Structure
- •Anechoic Structure
- •Hypoechoic Structure
- •Hyperechoic Structure
- •Wall Structures
- •Smooth Margin
- •Irregular Margin
- •Intragastric Processes
- •Intraintestinal Processes
- •9 Kidneys
- •Anomalies, Malformations
- •Aplasia, Hypoplasia
- •Cystic Malformation
- •Anomalies of Number, Position, or Rotation
- •Fusion Anomaly
- •Anomalies of the Renal Calices
- •Vascular Anomaly
- •Diffuse Changes
- •Large Kidneys
- •Small Kidneys
- •Hypoechoic Structure
- •Hyperechoic Structure
- •Irregular Structure
- •Circumscribed Changes
- •Anechoic Structure
- •Hypoechoic or Isoechoic Structure
- •Complex Structure
- •Hyperechoic Structure
- •10 Adrenal Glands
- •Enlargement
- •Anechoic Structure
- •Hypoechoic Structure
- •Complex Echo Structure
- •Hyperechoic Structure
- •11 Urinary Tract
- •Malformations
- •Duplication Anomalies
- •Dilatations and Stenoses
- •Dilated Renal Pelvis and Ureter
- •Anechoic
- •Hypoechoic
- •Hypoechoic
- •Hyperechoic
- •Large Bladder
- •Small Bladder
- •Altered Bladder Shape
- •Intracavitary Mass
- •Hypoechoic
- •Hyperechoic
- •Echogenic
- •Wall Changes
- •Diffuse Wall Thickening
- •Circumscribed Wall Thickening
- •Concavities and Convexities
- •12.1 The Prostate
- •Enlarged Prostate
- •Regular
- •Irregular
- •Small Prostate
- •Regular
- •Echogenic
- •Circumscribed Lesion
- •Anechoic
- •Hypoechoic
- •Echogenic
- •12.2 Seminal Vesicles
- •Diffuse Change
- •Hypoechoic
- •Circumscribed Change
- •Anechoic
- •Echogenic
- •Irregular
- •12.3 Testis, Epididymis
- •Diffuse Change
- •Enlargement
- •Decreased Size
- •Circumscribed Lesion
- •Anechoic or Hypoechoic
- •Irregular/Echogenic
- •Epididymal Lesion
- •Anechoic
- •Hypoechoic
- •Intrascrotal Mass
- •Anechoic or Hypoechoic
- •Echogenic
- •13 Female Genital Tract
- •Masses
- •Abnormalities of Size or Shape
- •Uterus
- •Abnormalities of Size or Shape
- •Myometrial Changes
- •Intracavitary Changes
- •Endometrial Changes
- •Fallopian Tubes
- •Hypoechoic Mass
- •Anechoic Cystic Mass
- •Solid Echogenic or Nonhomogeneous Mass
- •14 Thyroid Gland
- •Diffuse Changes
- •Enlarged Thyroid Gland
- •Small Thyroid Gland
- •Hypoechoic Structure
- •Hyperechoic Structure
- •Circumscribed Changes
- •Anechoic
- •Hypoechoic
- •Isoechoic
- •Hyperechoic
- •Irregular
- •Differential Diagnosis of Hyperthyroidism
- •Types of Autonomy
- •15 Pleura and Chest Wall
- •Chest Wall
- •Masses
- •Parietal Pleura
- •Nodular Masses
- •Diffuse Pleural Thickening
- •Pleural Effusion
- •Anechoic Effusion
- •Echogenic Effusion
- •Complex Effusion
- •16 Lung
- •Masses
- •Anechoic Masses
- •Hypoechoic Masses
- •Complex Masses
- •Index
1.2Portal Vein and Its Tributaries
C. Goerg
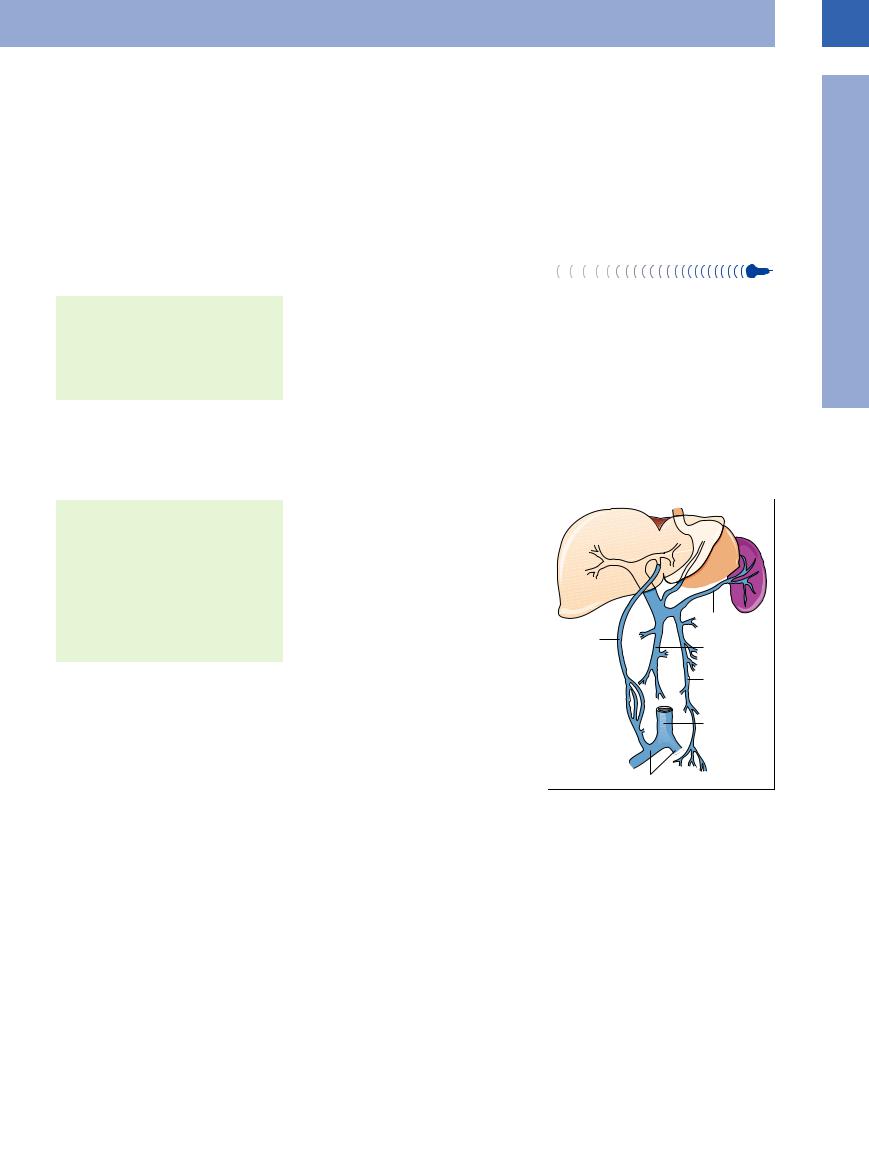
The portal venous system is comprised of four regions: intrahepatic branches of the portal vein; portal vein at the porta hepatis; splenic vein; and splanchnic veins. Blood from the splanchnic region (including the spleen) normally flows in hepatopetal fashion.
Anatomy
































Size |
Size and shape. |
The diameter of the portal |
|
vein displays a |
somewhat wider range be- |
||
● Portal vein at the hilum: 1.0–1.5 cm |
|||
tween individuals (see Fig.1.93). In fasting pa- |
|||
● Splenic vein at the hilum: 0.5–1.0 cm |
|||
tients, a diameter of up to 15 mm is considered |
|||
|
|||
Flow |
normal. Usually, the portal vein has an oval |
||
● Mean flow velocity of the portal vein: |
shape in the transverse plane. The mean portal |
||
15–20 cm/s
flow velocity has been reported as 15–20 cm/s, with a wide range of values here as well.
Under normal conditions the diameter of the splenic vein at the hilum should be less than 7 mm ( 1.6e,f). The mesenteric vein is compressible and exhibits respiratory caliber variations of more than 15%.
1.6e,f). The mesenteric vein is compressible and exhibits respiratory caliber variations of more than 15%.
Topography 





















































Position
●Splenic vein posterior to the pancreas
●Mesenteric vein parallel to the superior mesenteric artery
●Portal vein posterior to the bile duct and hepatic artery
●Intrahepatic bifurcation of the portal vein into left and right branch
Lead Structure
● Posterior to the pancreatic head
The main portal tract receives the blood flow of the left gastric vein cranially, in the region of the hilum ( 1.6a–c). The splenic vein is regarded as the leading structure for portrayal of
1.6a–c). The splenic vein is regarded as the leading structure for portrayal of
the pancreas and can be followed into the splenic hilum ( 1.6 d–f). The superior mesenteric vein parallels the superior mesenteric artery and can be detected, together with its branches, in the inferior parts of the mesentery (Fig.1.83).
1.6 d–f). The superior mesenteric vein parallels the superior mesenteric artery and can be detected, together with its branches, in the inferior parts of the mesentery (Fig.1.83).
Within the liver the portal trunk divides like a “staghorn” into the left and right portal branches ( 1.6 g). The main right portal branch gives off the anterior branch, which supplies segments V and VIII, while its posterior branch supplies segments VI and VII (
1.6 g). The main right portal branch gives off the anterior branch, which supplies segments V and VIII, while its posterior branch supplies segments VI and VII ( 1.6h,i). The left portal branch divides into the so-called horizontal and umbilical parts, supplying segments I, II, III, and IV (
1.6h,i). The left portal branch divides into the so-called horizontal and umbilical parts, supplying segments I, II, III, and IV ( 1.6j–o). Anomalies of the intrahepatic branches of the portal vein are rare.
1.6j–o). Anomalies of the intrahepatic branches of the portal vein are rare.
Fig. 1.83 Portocaval collaterals accessible to ultrasound in |
portal hypertension.
1
Portal Vein and Its Tributaries
39
1
Vessels
 1.6 Topographic Anatomy of the Portal Vein and Its Tributaries
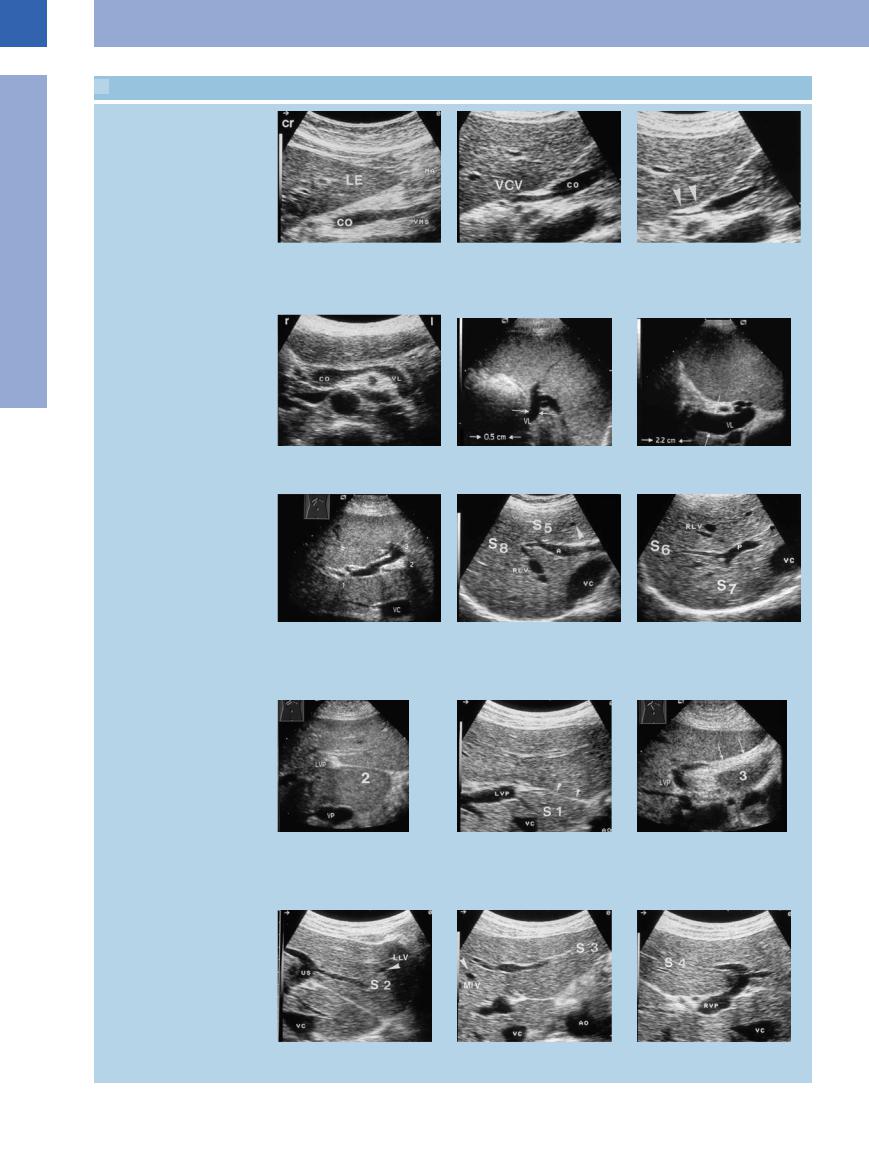
1.6 Topographic Anatomy of the Portal Vein and Its Tributaries
Portal vein and its tributaries
a Inflow of the superior mesenteric vein |
b and c Junction of the left gastric vein |
c Expiration (arrows). |
(VMS) into the venous confluence. LE = |
(VCV) with the confluence of the superior |
|
liver; CO = venous confluence; MA = |
mesenteric and splenic veins (co); respi- |
|
stomach. |
ratory variation in the lumen diameter. |
|
|
b Inspiration. |
|
d Transverse epigastric view with splenic |
e Splenic vein (VL, arrows) with normal |
f Splenic vein (VL) in portal hypertension. |
vein (VL). CO = venous confluence. |
lumen diameter. |
|
Intrahepatic right and left branches of the portal veins with liver segments
g Subcostal view of the liver with left and |
h Right anterior branch of the portal vein |
i Posterior branch of the main right |
right branches of the portal vein. VC = |
(A) with branches supplying the anterior |
portal vein trunk (P) supplying the |
vena cava; 1, 2, 3 = segments I–III. |
segments V (S 5) (inferior) and VIII (S 8) |
posterior segments VI (S 6) (inferior) and |
|
(superior). RLV = right hepatic vein. |
VII (S 7) (superior) of the right hepatic |
|
|
lobe. RLV = right hepatic vein; VC = vena |
|
|
cava. |
j–l The left portal vein (LVP) supplies |
k Segment I. Anterior venous ligament |
l The ligamentum teres stretches be- |
segments I–IV (S 1–S 3). |
(arrows). AO = aorta; VC = vena cava. |
tween the left branch of the portal vein |
j The venous ligament runs from the left |
|
(3) and the umbilicus. LVP = left portal |
branch of the portal vein (2) to the |
|
vein. |
posteroinferior aspect of the liver. LVP = |
|
|
left portal vein; VC = vena cava. |
|
|
m Segment II. US = umbilical segment, |
n Segment III. AO = aorta; VC = vena cava. o Segment IV. RVP = right branch of |
LLV = left hepatic vein. |
portal vein. |
40
