
- •Contents
- •Preface
- •Contributors
- •1 Vessels
- •1.1 Aorta, Vena Cava, and Peripheral Vessels
- •Aorta, Arteries
- •Anomalies and Variant Positions
- •Dilatation
- •Stenosis
- •Wall Thickening
- •Intraluminal Mass
- •Perivascular Mass
- •Vena Cava, Veins
- •Anomalies
- •Dilatation
- •Intraluminal Mass
- •Compression, Infiltration
- •1.2 Portal Vein and Its Tributaries
- •Enlarged Lumen Diameter
- •Portal Hypertension
- •Intraluminal Mass
- •Thrombosis
- •Tumor
- •2 Liver
- •Enlarged Liver
- •Small Liver
- •Homogeneous Hypoechoic Texture
- •Homogeneous Hyperechoic Texture
- •Regionally Inhomogeneous Texture
- •Diffuse Inhomogeneous Texture
- •Anechoic Masses
- •Hypoechoic Masses
- •Isoechoic Masses
- •Hyperechoic Masses
- •Echogenic Masses
- •Irregular Masses
- •Differential Diagnosis of Focal Lesions
- •Diagnostic Methods
- •Suspected Diagnosis
- •3 Biliary Tree and Gallbladder
- •3.1 Biliary Tree
- •Thickening of the Bile Duct Wall
- •Localized and Diffuse
- •Bile Duct Rarefaction
- •Localized and Diffuse
- •Bile Duct Dilatation and Intraductal Pressure
- •Intrahepatic
- •Hilar and Prepancreatic
- •Intrapancreatic
- •Papillary
- •Abnormal Intraluminal Bile Duct Findings
- •Foreign Body
- •The Seven Most Important Questions
- •3.2 Gallbladder
- •Changes in Size
- •Large Gallbladder
- •Small/Missing Gallbladder
- •Wall Changes
- •General Hypoechogenicity
- •General Hyperechogenicity
- •General Tumor
- •Focal Tumor
- •Intraluminal Changes
- •Hyperechoic
- •Hypoechoic
- •Nonvisualized Gallbladder
- •Missing Gallbladder
- •Obscured Gallbladder
- •4 Pancreas
- •Diffuse Pancreatic Change
- •Large Pancreas
- •Small Pancreas
- •Hypoechoic Texture
- •Hyperechoic Texture
- •Focal Changes
- •Anechoic Lesion
- •Hypoechoic Lesion
- •Isoechoic Lesion
- •Hyperechoic Lesion
- •Irregular (Complex Structured) Lesion
- •Dilatation of the Pancreatic Duct
- •Marginal/Mild Dilatation
- •Marked Dilatation
- •5 Spleen
- •Nonfocal Changes of the Spleen
- •Diffuse Parenchymal Changes
- •Large Spleen
- •Small Spleen
- •Focal Changes of the Spleen
- •Anechoic Mass
- •Hypoechoic Mass
- •Hyperechoic Mass
- •Splenic Calcification
- •6 Lymph Nodes
- •Peripheral Lymph Nodes
- •Head/Neck
- •Extremities (Axilla, Groin)
- •Abdominal Lymph Nodes
- •Porta Hepatis
- •Splenic Hilum
- •Mesentery (Celiac, Upper and Lower Mesenteric Station)
- •Stomach
- •Focal Wall Changes
- •Extended Wall Changes
- •Dilated Lumen
- •Narrowed Lumen
- •Small/Large Intestine
- •Focal Wall Changes
- •Extended Wall Changes
- •Dilated Lumen
- •Narrowed Lumen
- •8 Peritoneal Cavity
- •Anechoic Structure
- •Hypoechoic Structure
- •Hyperechoic Structure
- •Anechoic Structure
- •Hypoechoic Structure
- •Hyperechoic Structure
- •Wall Structures
- •Smooth Margin
- •Irregular Margin
- •Intragastric Processes
- •Intraintestinal Processes
- •9 Kidneys
- •Anomalies, Malformations
- •Aplasia, Hypoplasia
- •Cystic Malformation
- •Anomalies of Number, Position, or Rotation
- •Fusion Anomaly
- •Anomalies of the Renal Calices
- •Vascular Anomaly
- •Diffuse Changes
- •Large Kidneys
- •Small Kidneys
- •Hypoechoic Structure
- •Hyperechoic Structure
- •Irregular Structure
- •Circumscribed Changes
- •Anechoic Structure
- •Hypoechoic or Isoechoic Structure
- •Complex Structure
- •Hyperechoic Structure
- •10 Adrenal Glands
- •Enlargement
- •Anechoic Structure
- •Hypoechoic Structure
- •Complex Echo Structure
- •Hyperechoic Structure
- •11 Urinary Tract
- •Malformations
- •Duplication Anomalies
- •Dilatations and Stenoses
- •Dilated Renal Pelvis and Ureter
- •Anechoic
- •Hypoechoic
- •Hypoechoic
- •Hyperechoic
- •Large Bladder
- •Small Bladder
- •Altered Bladder Shape
- •Intracavitary Mass
- •Hypoechoic
- •Hyperechoic
- •Echogenic
- •Wall Changes
- •Diffuse Wall Thickening
- •Circumscribed Wall Thickening
- •Concavities and Convexities
- •12.1 The Prostate
- •Enlarged Prostate
- •Regular
- •Irregular
- •Small Prostate
- •Regular
- •Echogenic
- •Circumscribed Lesion
- •Anechoic
- •Hypoechoic
- •Echogenic
- •12.2 Seminal Vesicles
- •Diffuse Change
- •Hypoechoic
- •Circumscribed Change
- •Anechoic
- •Echogenic
- •Irregular
- •12.3 Testis, Epididymis
- •Diffuse Change
- •Enlargement
- •Decreased Size
- •Circumscribed Lesion
- •Anechoic or Hypoechoic
- •Irregular/Echogenic
- •Epididymal Lesion
- •Anechoic
- •Hypoechoic
- •Intrascrotal Mass
- •Anechoic or Hypoechoic
- •Echogenic
- •13 Female Genital Tract
- •Masses
- •Abnormalities of Size or Shape
- •Uterus
- •Abnormalities of Size or Shape
- •Myometrial Changes
- •Intracavitary Changes
- •Endometrial Changes
- •Fallopian Tubes
- •Hypoechoic Mass
- •Anechoic Cystic Mass
- •Solid Echogenic or Nonhomogeneous Mass
- •14 Thyroid Gland
- •Diffuse Changes
- •Enlarged Thyroid Gland
- •Small Thyroid Gland
- •Hypoechoic Structure
- •Hyperechoic Structure
- •Circumscribed Changes
- •Anechoic
- •Hypoechoic
- •Isoechoic
- •Hyperechoic
- •Irregular
- •Differential Diagnosis of Hyperthyroidism
- •Types of Autonomy
- •15 Pleura and Chest Wall
- •Chest Wall
- •Masses
- •Parietal Pleura
- •Nodular Masses
- •Diffuse Pleural Thickening
- •Pleural Effusion
- •Anechoic Effusion
- •Echogenic Effusion
- •Complex Effusion
- •16 Lung
- •Masses
- •Anechoic Masses
- •Hypoechoic Masses
- •Complex Masses
- •Index
Extremities (Axilla, Groin)
Nodes |
Peripheral Lymph Nodes |
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
Head/Neck |
|
Lymph |
|
Extremities (Axilla, Groin) |
|||
|
|||||
Abdominal Lymph Nodes |
|||||
|
|
|
|||
Enlargement of locoregional lymph nodes is observed particularly in injuries of the extremities. If axillary lymph nodes are enlarged, the possibility of involvement of the breast has to be kept in mind.
Inflammatory Lymph Nodes
Metastases
Malignant Lymphoma
Other Structures
Inflammatory Lymph Nodes 












































Sometimes reactive lymph nodes can become |
echoic border. Vascularization may be rarefied |
rather large (Fig. 6.15, Fig. 6.16); in most cases |
or marked. Complete healing will leave con- |
the hilar sign is present and marked (Fig. 6.17). |
stant regressive hyperechoic lymph nodes. Re- |
In a few patients, the cortex of the lymph nodes |
active regressive lymph nodes in the groin are |
may be nothing more than a delicate hypo- |
almost mandatory. |
6
Peripheral Lymph Nodes
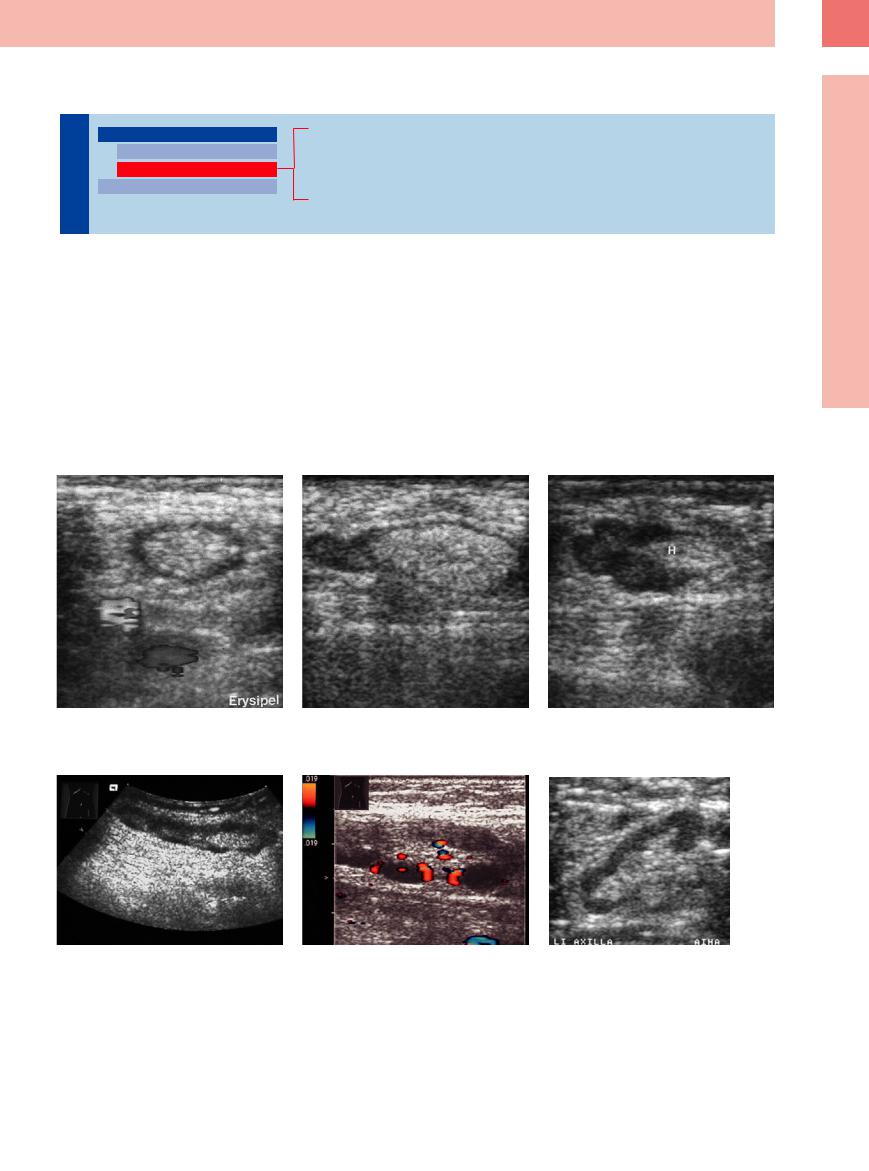
Fig. 6.15a–c Reactive inguinal lymph nodes in erysipelas displaying different levels of hypoechoic parenchyma. H = hilum.
Fig. 6.16a and b A 42-year-old patient with known Hodgkin disease, now presenting with lymphadenopathy in the left groin; elongated lymph node with hilar sign and markedly inhomogeneous texture of the parenchyma. Histology confirmed reactive lymphadenopathy.
Fig. 6.17 A 33-year-old patient with autoimmune hemolytic anemia and sarcoidosis. Large lymph node with hilar sign present in the left axilla. Follow-up indicated reactive lymphadenopathy.
245
6
Lymph Nodes
Metastases
Metastases are much more common in the axilla than in the groin (Figs. 6.18, 6.19, 6.20, 6.21, 6.22). In breast cancer they are mostly homo-
genous and hypoechoic (Fig. 6.18) and their sizes differ widely. Very small lymph node metastases are frequently found in malignant
melanoma (Fig. 6.22); in vascular invasion, compression syndrome is a not uncommon finding.
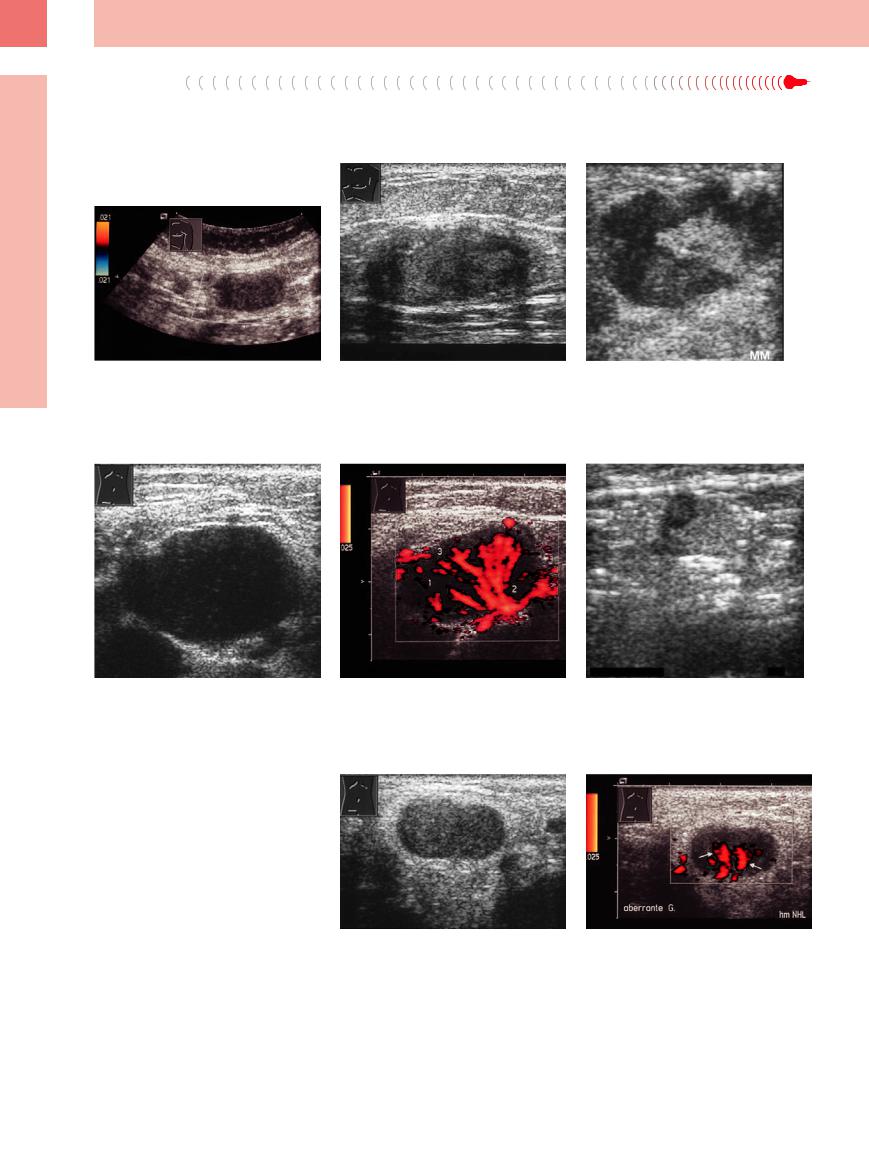
Fig. 6.18 Homogeneous hypoechoic lymph node in breast cancer. After two cycles of doxorubicin (Adriamycin) plus cyclophosphamide, no more flow signal was observed; this was interpreted as positive response to treatment. Histological work-up of the lymph node did not yield any remaining vital tumor tissue.
Fig. 6.21
a Large hypoechoic lymph node invaded by cancer of the rectum.
Fig. 6.19 Lymph node invaded by neuroendocrine cancer.
b Abnormal flow pattern on color-flow Doppler scanning. 1 = focal lack of vessels; 2 = aberrant vessels; 3 = subcapsular vessels.
Fig. 6.20 Lymph node in the left axilla invaded by malignant melanoma; the hilar sign is still present.
Fig. 6.22 Hyperechoic metastasis of malignant melanoma in an inguinal lymph node.
Malignant Lymphoma
















































The picture is similar to that of the head/neck region (Fig. 6.23). Here, too, impaired venous or lymphatic drainage due to lymphomas can often be expected (Fig. 6.24). Invasive growth into the soft tissue has been observed, particularly in T-cell lymphoma of the groin. In these cases, the lymphoma may be visualized as being ill-defined and hyperechoic to the adjacent soft tissues.
Fig. 6.23 Lymph node with pathological vascular pattern in malignant lymphoma.
246
