
- •QoS Overview
- •“Do I Know This Already?” Quiz
- •QoS: Tuning Bandwidth, Delay, Jitter, and Loss Questions
- •Foundation Topics
- •QoS: Tuning Bandwidth, Delay, Jitter, and Loss
- •Bandwidth
- •The clock rate Command Versus the bandwidth Command
- •QoS Tools That Affect Bandwidth
- •Delay
- •Serialization Delay
- •Propagation Delay
- •Queuing Delay
- •Forwarding Delay
- •Shaping Delay
- •Network Delay
- •Delay Summary
- •QoS Tools That Affect Delay
- •Jitter
- •QoS Tools That Affect Jitter
- •Loss
- •QoS Tools That Affect Loss
- •Summary: QoS Characteristics: Bandwidth, Delay, Jitter, and Loss
- •Voice Basics
- •Voice Bandwidth Considerations
- •Voice Delay Considerations
- •Voice Jitter Considerations
- •Voice Loss Considerations
- •Video Basics
- •Video Bandwidth Considerations
- •Video Delay Considerations
- •Video Jitter Considerations
- •Video Loss Considerations
- •Comparing Voice and Video: Summary
- •IP Data Basics
- •Data Bandwidth Considerations
- •Data Delay Considerations
- •Data Jitter Considerations
- •Data Loss Considerations
- •Comparing Voice, Video, and Data: Summary
- •Foundation Summary
- •QoS Tools and Architectures
- •“Do I Know This Already?” Quiz
- •QoS Tools Questions
- •Differentiated Services Questions
- •Integrated Services Questions
- •Foundation Topics
- •Introduction to IOS QoS Tools
- •Queuing
- •Queuing Tools
- •Shaping and Policing
- •Shaping and Policing Tools
- •Congestion Avoidance
- •Congestion-Avoidance Tools
- •Call Admission Control and RSVP
- •CAC Tools
- •Management Tools
- •Summary
- •The Good-Old Common Sense QoS Model
- •GOCS Flow-Based QoS
- •GOCS Class-Based QoS
- •The Differentiated Services QoS Model
- •DiffServ Per-Hop Behaviors
- •The Class Selector PHB and DSCP Values
- •The Assured Forwarding PHB and DSCP Values
- •The Expedited Forwarding PHB and DSCP Values
- •The Integrated Services QoS Model
- •Foundation Summary
- •“Do I Know This Already?” Quiz Questions
- •CAR, PBR, and CB Marking Questions
- •Foundation Topics
- •Marking
- •IP Header QoS Fields: Precedence and DSCP
- •LAN Class of Service (CoS)
- •Other Marking Fields
- •Summary of Marking Fields
- •Class-Based Marking (CB Marking)
- •Network-Based Application Recognition (NBAR)
- •CB Marking show Commands
- •CB Marking Summary
- •Committed Access Rate (CAR)
- •CAR Marking Summary
- •Policy-Based Routing (PBR)
- •PBR Marking Summary
- •VoIP Dial Peer
- •VoIP Dial-Peer Summary
- •Foundation Summary
- •Congestion Management
- •“Do I Know This Already?” Quiz
- •Queuing Concepts Questions
- •WFQ and IP RTP Priority Questions
- •CBWFQ and LLQ Questions
- •Comparing Queuing Options Questions
- •Foundation Topics
- •Queuing Concepts
- •Output Queues, TX Rings, and TX Queues
- •Queuing on Interfaces Versus Subinterfaces and Virtual Circuits (VCs)
- •Summary of Queuing Concepts
- •Queuing Tools
- •FIFO Queuing
- •Priority Queuing
- •Custom Queuing
- •Weighted Fair Queuing (WFQ)
- •WFQ Scheduler: The Net Effect
- •WFQ Scheduling: The Process
- •WFQ Drop Policy, Number of Queues, and Queue Lengths
- •WFQ Summary
- •Class-Based WFQ (CBWFQ)
- •CBWFQ Summary
- •Low Latency Queuing (LLQ)
- •LLQ with More Than One Priority Queue
- •IP RTP Priority
- •Summary of Queuing Tool Features
- •Foundation Summary
- •Conceptual Questions
- •Priority Queuing and Custom Queuing
- •CBWFQ, LLQ, IP RTP Priority
- •Comparing Queuing Tool Options
- •“Do I Know This Already?” Quiz
- •Shaping and Policing Concepts Questions
- •Policing with CAR and CB Policer Questions
- •Shaping with FRTS, GTS, DTS, and CB Shaping
- •Foundation Topics
- •When and Where to Use Shaping and Policing
- •How Shaping Works
- •Where to Shape: Interfaces, Subinterfaces, and VCs
- •How Policing Works
- •CAR Internals
- •CB Policing Internals
- •Policing, but Not Discarding
- •Foundation Summary
- •Shaping and Policing Concepts
- •“Do I Know This Already?” Quiz
- •Congestion-Avoidance Concepts and RED Questions
- •WRED Questions
- •FRED Questions
- •Foundation Topics
- •TCP and UDP Reactions to Packet Loss
- •Tail Drop, Global Synchronization, and TCP Starvation
- •Random Early Detection (RED)
- •Weighted RED (WRED)
- •How WRED Weights Packets
- •WRED and Queuing
- •WRED Summary
- •Flow-Based WRED (FRED)
- •Foundation Summary
- •Congestion-Avoidance Concepts and Random Early Detection (RED)
- •Weighted RED (WRED)
- •Flow-Based WRED (FRED)
- •“Do I Know This Already?” Quiz
- •Compression Questions
- •Link Fragmentation and Interleave Questions
- •Foundation Topics
- •Payload and Header Compression
- •Payload Compression
- •Header Compression
- •Link Fragmentation and Interleaving
- •Multilink PPP LFI
- •Maximum Serialization Delay and Optimum Fragment Sizes
- •Frame Relay LFI Using FRF.12
- •Choosing Fragment Sizes for Frame Relay
- •Fragmentation with More Than One VC on a Single Access Link
- •FRF.11-C and FRF.12 Comparison
- •Foundation Summary
- •Compression Tools
- •LFI Tools
- •“Do I Know This Already?” Quiz
- •Foundation Topics
- •Call Admission Control Overview
- •Call Rerouting Alternatives
- •Bandwidth Engineering
- •CAC Mechanisms
- •CAC Mechanism Evaluation Criteria
- •Local Voice CAC
- •Physical DS0 Limitation
- •Max-Connections
- •Voice over Frame Relay—Voice Bandwidth
- •Trunk Conditioning
- •Local Voice Busyout
- •Measurement-Based Voice CAC
- •Service Assurance Agents
- •SAA Probes Versus Pings
- •SAA Service
- •Calculated Planning Impairment Factor
- •Advanced Voice Busyout
- •PSTN Fallback
- •SAA Probes Used for PSTN Fallback
- •IP Destination Caching
- •SAA Probe Format
- •PSTN Fallback Scalability
- •PSTN Fallback Summary
- •Resource-Based CAC
- •Resource Availability Indication
- •Gateway Calculation of Resources
- •RAI in Service Provider Networks
- •RAI in Enterprise Networks
- •RAI Operation
- •RAI Platform Support
- •Cisco CallManager Resource-Based CAC
- •Location-Based CAC Operation
- •Locations and Regions
- •Calculation of Resources
- •Automatic Alternate Routing
- •Location-Based CAC Summary
- •Gatekeeper Zone Bandwidth
- •Gatekeeper Zone Bandwidth Operation
- •Single-Zone Topology
- •Multizone Topology
- •Zone-per-Gateway Design
- •Gatekeeper in CallManager Networks
- •Zone Bandwidth Calculation
- •Gatekeeper Zone Bandwidth Summary
- •Integrated Services / Resource Reservation Protocol
- •RSVP Levels of Service
- •RSVP Operation
- •RSVP/H.323 Synchronization
- •Bandwidth per Codec
- •Subnet Bandwidth Management
- •Monitoring and Troubleshooting RSVP
- •RSVP CAC Summary
- •Foundation Summary
- •Call Admission Control Concepts
- •Local-Based CAC
- •Measurement-Based CAC
- •Resources-Based CAC
- •“Do I Know This Already?” Quiz
- •QoS Management Tools Questions
- •QoS Design Questions
- •Foundation Topics
- •QoS Management Tools
- •QoS Device Manager
- •QoS Policy Manager
- •Service Assurance Agent
- •Internetwork Performance Monitor
- •Service Management Solution
- •QoS Management Tool Summary
- •QoS Design for the Cisco QoS Exams
- •Four-Step QoS Design Process
- •Step 1: Determine Customer Priorities/QoS Policy
- •Step 2: Characterize the Network
- •Step 3: Implement the Policy
- •Step 4: Monitor the Network
- •QoS Design Guidelines for Voice and Video
- •Voice and Video: Bandwidth, Delay, Jitter, and Loss Requirements
- •Voice and Video QoS Design Recommendations
- •Foundation Summary
- •QoS Management
- •QoS Design
- •“Do I Know This Already?” Quiz
- •Foundation Topics
- •The Need for QoS on the LAN
- •Layer 2 Queues
- •Drop Thresholds
- •Trust Boundries
- •Cisco Catalyst Switch QoS Features
- •Catalyst 6500 QoS Features
- •Supervisor and Switching Engine
- •Policy Feature Card
- •Ethernet Interfaces
- •QoS Flow on the Catalyst 6500
- •Ingress Queue Scheduling
- •Layer 2 Switching Engine QoS Frame Flow
- •Layer 3 Switching Engine QoS Packet Flow
- •Egress Queue Scheduling
- •Catalyst 6500 QoS Summary
- •Cisco Catalyst 4500/4000 QoS Features
- •Supervisor Engine I and II
- •Supervisor Engine III and IV
- •Cisco Catalyst 3550 QoS Features
- •Cisco Catalyst 3524 QoS Features
- •CoS-to-Egress Queue Mapping for the Catalyst OS Switch
- •Layer-2-to-Layer 3 Mapping
- •Connecting a Catalyst OS Switch to WAN Segments
- •Displaying QoS Settings for the Catalyst OS Switch
- •Enabling QoS for the Catalyst IOS Switch
- •Enabling Priority Queuing for the Catalyst IOS Switch
- •CoS-to-Egress Queue Mapping for the Catalyst IOS Switch
- •Layer 2-to-Layer 3 Mapping
- •Connecting a Catalyst IOS Switch to Distribution Switches or WAN Segments
- •Displaying QoS Settings for the Catalyst IOS Switch
- •Foundation Summary
- •LAN QoS Concepts
- •Catalyst 6500 Series of Switches
- •Catalyst 4500/4000 Series of Switches
- •Catalyst 3550/3524 Series of Switches
- •QoS: Tuning Bandwidth, Delay, Jitter, and Loss
- •QoS Tools
- •Differentiated Services
- •Integrated Services
- •CAR, PBR, and CB Marking
- •Queuing Concepts
- •WFQ and IP RTP Priority
- •CBWFQ and LLQ
- •Comparing Queuing Options
- •Conceptual Questions
- •Priority Queuing and Custom Queuing
- •CBWFQ, LLQ, IP RTP Priority
- •Comparing Queuing Tool Options
- •Shaping and Policing Concepts
- •Policing with CAR and CB Policer
- •Shaping with FRTS, GTS, DTS, and CB Shaping
- •Shaping and Policing Concepts
- •Congestion-Avoidance Concepts and RED
- •WRED
- •FRED
- •Congestion-Avoidance Concepts and Random Early Detection (RED)
- •Weighted RED (WRED)
- •Flow-Based WRED (FRED)
- •Compression
- •Link Fragmentation and Interleave
- •Compression Tools
- •LFI Tools
- •Call Admission Control Concepts
- •Local-Based CAC
- •Measurement-Based CAC
- •Resources-Based CAC
- •QoS Management Tools
- •QoS Design
- •QoS Management
- •QoS Design
- •LAN QoS Concepts
- •Catalyst 6500 Series of Switches
- •Catalyst 4500/4000 Series of Switches
- •Catalyst 3550/3524 Series of Switches
- •Foundation Topics
- •QPPB Route Marking: Step 1
- •QPPB Per-Packet Marking: Step 2
- •QPPB: The Hidden Details
- •QPPB Summary
- •Flow-Based dWFQ
- •ToS-Based dWFQ
- •Distributed QoS Group–Based WFQ
- •Summary: dWFQ Options
Link Fragmentation and Interleaving 497
Multilink PPP LFI
The core concept behind LFI, and its benefits, is very straightforward. The details, however, can be a little confusing, mainly because IOS LFI tools interact directly with IOS queuing tools. In addition, the two LFI tools covered on the Cisco QoS exams happen to behave differently as to how they interact with queuing tools. So to understand where LFI functions take place, you need to examine each tool specifically. This section covers multilink PPP LFI (MLP LFI), with Frame Relay fragmentation (FRF) covered in the next section of this chapter.
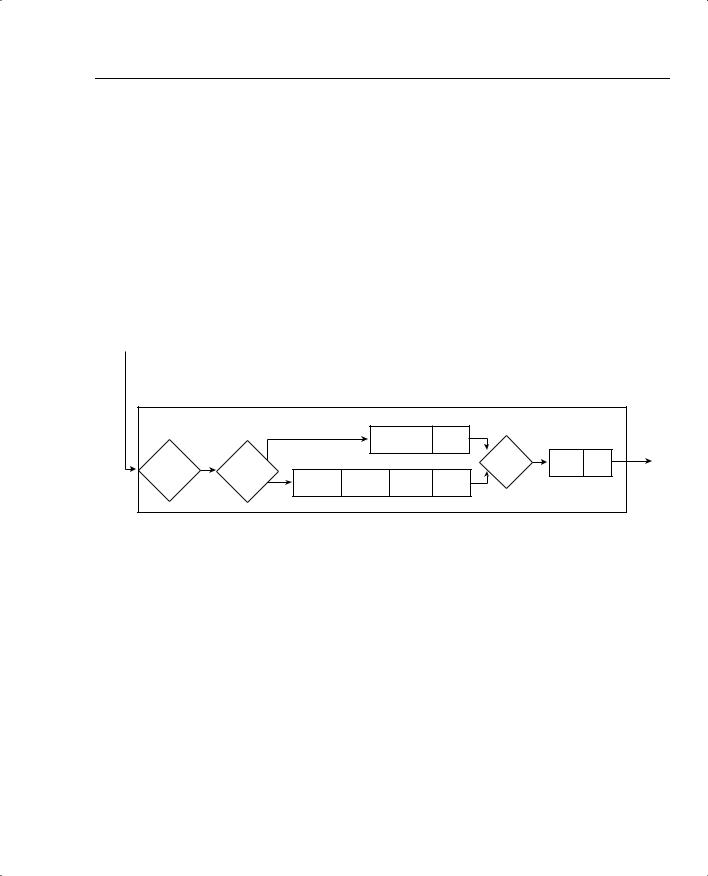
Figure 7-7 depicts how MLP LFI works with a queuing tool on an interface.
Figure 7-7 MLP LFI Interaction with Queuing
1500 Byte Packet Arrives, Followed by One 60 Byte Packet
R1 – Serial Interface 0 |
Actual Behavior with TX Queue |
|
|
|
|
Queue 1 |
|
|
|
|
|
Small |
TX Queue, Length 2 |
|
|
|
|
Packet |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Fragment |
Classify into |
|
|
Schedule |
Frag 2 Frag1 |
|
|
|
|
||
if > 300 |
|
|
|
|
|
Queues |
Frag 5 |
Frag 4 |
Frag 3 |
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
Queue 2 |
|
The figure outlines a lot of the detailed concepts behind LFI. In this example, a 1500-byte packet first arrives at R1, followed by a 60-byte packet. The fragmentation logic has been configured to fragment the frames down to a little more than 300 bytes, to make room for 300 bytes from the packet, and a little more for the data-link headers and trailers. After fragmentation, the queuing tool on the interface classifies the frames into their respective queues, which in this example happens to be two different queues. (The queuing tool’s classification step works exactly as described in chapter 4, “Congestion Management.”)
Now look to the far right side of the figure. The TX Queue is shown, with a queue length of 2. In this example, an assumption has been made that the small packet arrived after IOS had placed the first two fragments of the large packet into the two available slots in the TX Queue, with the last three fragments being placed into Queue 2. The TX Queue is always absolutely a single FIFO queue, as described in Chapter 4. In other words, the small packet does not interrupt the router while it is in the middle of sending fragment 1, nor does the small packet have a chance to be sent before fragment 2, because fragment 2 is already in the TX Queue. The best behavior the small packet can hope for is to be the next packet placed onto the end of the TX Queue. Therefore, for now, the small packet has been placed into Queue 1.
498 Chapter 7: Link-Efficiency Tools
Now look just to the left of the TX Queue, between the two interface output queues and the TX Queue. The term “schedule” reminds us that the queuing scheduler chooses the next packet to be moved from the output queues to the TX Queue (as described in Chapter 4). The queuing tool’s scheduler may decide to take the next packet from Queue 1 or Queue 2—a decision totally based on the logic of the queuing tool.
Interleaving occurs when the queuing scheduler decides to service the queue that holds the small packet next, rather than the queue holding the next fragment of the large packet. If Low Latency Queuing (LLQ) has been configured, and Queue 1 is the low-latency queue, the scheduler takes the small packet next, meaning that the small packet would be interleaved between fragments of the larger packet. If the queuing tool was Custom Queuing (CQ), and the queuing scheduler were able to send more bytes from Queue 2 in this cycle, fragment 3 would be sent next.
Maximum Serialization Delay and Optimum Fragment Sizes
How large should the fragments be to reduce serialization delay to an acceptable level? Well, the real answer lies in an analysis of the delay budgets for your network. From that analysis, you determine the maximum serialization delay you can have on each link.
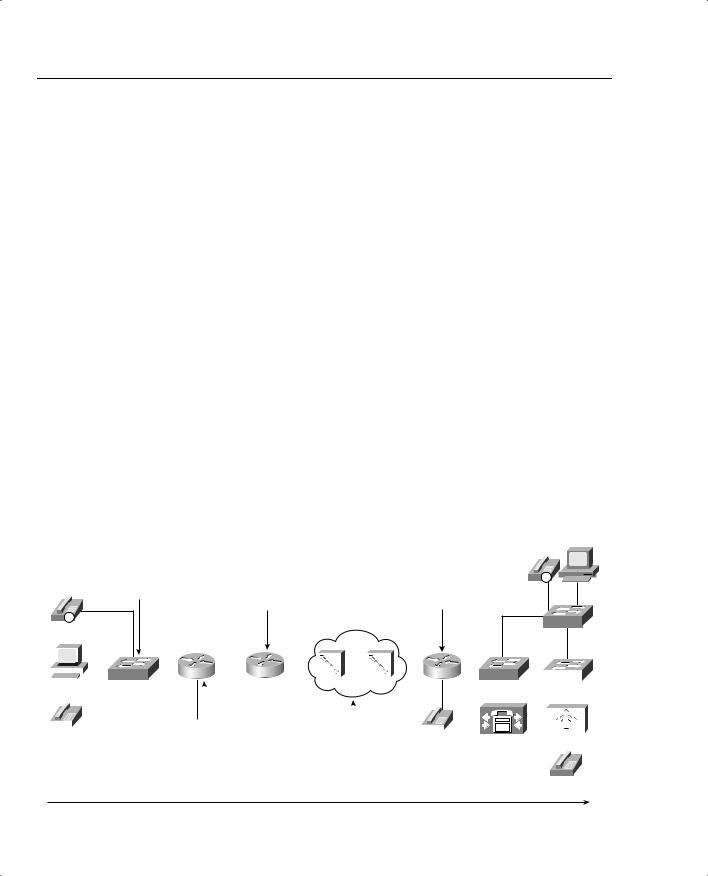
The delay budget includes many delay components, such as queuing delay, propagation delay, shaping delay, network delay, and serialization delay. Based on that delay budget, you determine how much serialization delay you can afford on a particular link. Figure 7-8 depicts example delay values for various delay components.
Figure 7-8 Review of Delay Components, Including Serialization Delay
|
|
|
|
Server 1 |
|
|
|
|
311 |
|
Forwarding: 0 |
Forwarding: 0 |
Forwarding: 0 |
IP |
211 |
Queuing: 0 |
Queuing: 15 |
Queuing: 0 |
|
Serialization: 0 |
Serialization: 4 |
Serialization: 0 |
|
|
|
|
Propagation: .5 |
Propagation: 0 |
|
IP |
|
|
|
SW3 |
|
|
|
|
Hannah
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
100 km |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
R1 |
56 kbps |
R2 |
128 |
|
|
|
|
T1 |
R3 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
SW1 |
|
kbps |
|
|
|
|
|
SW2 |
|
SW4 |
|
||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
201 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
301 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
|
|
|
Forwarding: 0 |
|
|
Network: 50 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Queuing: 15 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Serialization: 10 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Propagation: .5 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
351
Delays for Packets Flowing Left-to-Right: Total Delay: 95 ms
