
- •BUSINESSES IN THE BOOK
- •Preface
- •Brief Contents
- •CONTENTS
- •Why Study Strategy?
- •Why Economics?
- •The Need for Principles
- •So What’s the Problem?
- •Firms or Markets?
- •A Framework for Strategy
- •Boundaries of the Firm
- •Market and Competitive Analysis
- •Positioning and Dynamics
- •Internal Organization
- •The Book
- •Endnotes
- •Costs
- •Cost Functions
- •Total Cost Functions
- •Fixed and Variable Costs
- •Average and Marginal Cost Functions
- •The Importance of the Time Period: Long-Run versus Short-Run Cost Functions
- •Sunk versus Avoidable Costs
- •Economic Costs and Profitability
- •Economic versus Accounting Costs
- •Economic Profit versus Accounting Profit
- •Demand and Revenues
- •Demand Curve
- •The Price Elasticity of Demand
- •Brand-Level versus Industry-Level Elasticities
- •Total Revenue and Marginal Revenue Functions
- •Theory of the Firm: Pricing and Output Decisions
- •Perfect Competition
- •Game Theory
- •Games in Matrix Form and the Concept of Nash Equilibrium
- •Game Trees and Subgame Perfection
- •Chapter Summary
- •Questions
- •Endnotes
- •Doing Business in 1840
- •Transportation
- •Communications
- •Finance
- •Production Technology
- •Government
- •Doing Business in 1910
- •Business Conditions in 1910: A “Modern” Infrastructure
- •Production Technology
- •Transportation
- •Communications
- •Finance
- •Government
- •Doing Business Today
- •Modern Infrastructure
- •Transportation
- •Communications
- •Finance
- •Production Technology
- •Government
- •Infrastructure in Emerging Markets
- •Three Different Worlds: Consistent Principles, Changing Conditions, and Adaptive Strategies
- •Chapter Summary
- •Questions
- •Endnotes
- •Definitions
- •Definition of Economies of Scale
- •Definition of Economies of Scope
- •Economies of Scale Due to Spreading of Product-Specific Fixed Costs
- •Economies of Scale Due to Trade-offs among Alternative Technologies
- •“The Division of Labor Is Limited by the Extent of the Market”
- •Special Sources of Economies of Scale and Scope
- •Density
- •Purchasing
- •Advertising
- •Costs of Sending Messages per Potential Consumer
- •Advertising Reach and Umbrella Branding
- •Research and Development
- •Physical Properties of Production
- •Inventories
- •Complementarities and Strategic Fit
- •Sources of Diseconomies of Scale
- •Labor Costs and Firm Size
- •Spreading Specialized Resources Too Thin
- •Bureaucracy
- •Economies of Scale: A Summary
- •The Learning Curve
- •The Concept of the Learning Curve
- •Expanding Output to Obtain a Cost Advantage
- •Learning and Organization
- •The Learning Curve versus Economies of Scale
- •Diversification
- •Why Do Firms Diversify?
- •Efficiency-Based Reasons for Diversification
- •Scope Economies
- •Internal Capital Markets
- •Problematic Justifications for Diversification
- •Diversifying Shareholders’ Portfolios
- •Identifying Undervalued Firms
- •Reasons Not to Diversify
- •Managerial Reasons for Diversification
- •Benefits to Managers from Acquisitions
- •Problems of Corporate Governance
- •The Market for Corporate Control and Recent Changes in Corporate Governance
- •Performance of Diversified Firms
- •Chapter Summary
- •Questions
- •Endnotes
- •Make versus Buy
- •Upstream, Downstream
- •Defining Boundaries
- •Some Make-or-Buy Fallacies
- •Avoiding Peak Prices
- •Tying Up Channels: Vertical Foreclosure
- •Reasons to “Buy”
- •Exploiting Scale and Learning Economies
- •Bureaucracy Effects: Avoiding Agency and Influence Costs
- •Agency Costs
- •Influence Costs
- •Organizational Design
- •Reasons to “Make”
- •The Economic Foundations of Contracts
- •Complete versus Incomplete Contracting
- •Bounded Rationality
- •Difficulties Specifying or Measuring Performance
- •Asymmetric Information
- •The Role of Contract Law
- •Coordination of Production Flows through the Vertical Chain
- •Leakage of Private Information
- •Transactions Costs
- •Relationship-Specific Assets
- •Forms of Asset Specificity
- •The Fundamental Transformation
- •Rents and Quasi-Rents
- •The Holdup Problem
- •Holdup and Ex Post Cooperation
- •The Holdup Problem and Transactions Costs
- •Contract Negotiation and Renegotiation
- •Investments to Improve Ex Post Bargaining Positions
- •Distrust
- •Reduced Investment
- •Recap: From Relationship-Specific Assets to Transactions Costs
- •Chapter Summary
- •Questions
- •Endnotes
- •What Does It Mean to Be “Integrated?”
- •The Property Rights Theory of the Firm
- •Alternative Forms of Organizing Transactions
- •Governance
- •Delegation
- •Recapping PRT
- •Path Dependence
- •Making the Integration Decision
- •Technical Efficiency versus Agency Efficiency
- •The Technical Efficiency/Agency Efficiency Trade-off
- •Real-World Evidence
- •Double Marginalization: A Final Integration Consideration
- •Alternatives to Vertical Integration
- •Tapered Integration: Make and Buy
- •Franchising
- •Strategic Alliances and Joint Ventures
- •Implicit Contracts and Long-Term Relationships
- •Business Groups
- •Keiretsu
- •Chaebol
- •Business Groups in Emerging Markets
- •Chapter Summary
- •Questions
- •Endnotes
- •Competitor Identification and Market Definition
- •The Basics of Competitor Identification
- •Example 5.1 The SSNIP in Action: Defining Hospital Markets
- •Putting Competitor Identification into Practice
- •Empirical Approaches to Competitor Identification
- •Geographic Competitor Identification
- •Measuring Market Structure
- •Market Structure and Competition
- •Perfect Competition
- •Many Sellers
- •Homogeneous Products
- •Excess Capacity
- •Monopoly
- •Monopolistic Competition
- •Demand for Differentiated Goods
- •Entry into Monopolistically Competitive Markets
- •Oligopoly
- •Cournot Quantity Competition
- •The Revenue Destruction Effect
- •Cournot’s Model in Practice
- •Bertrand Price Competition
- •Why Are Cournot and Bertrand Different?
- •Evidence on Market Structure and Performance
- •Price and Concentration
- •Chapter Summary
- •Questions
- •Endnotes
- •6: Entry and Exit
- •Some Facts about Entry and Exit
- •Entry and Exit Decisions: Basic Concepts
- •Barriers to Entry
- •Bain’s Typology of Entry Conditions
- •Analyzing Entry Conditions: The Asymmetry Requirement
- •Structural Entry Barriers
- •Control of Essential Resources
- •Economies of Scale and Scope
- •Marketing Advantages of Incumbency
- •Barriers to Exit
- •Entry-Deterring Strategies
- •Limit Pricing
- •Is Strategic Limit Pricing Rational?
- •Predatory Pricing
- •The Chain-Store Paradox
- •Rescuing Limit Pricing and Predation: The Importance of Uncertainty and Reputation
- •Wars of Attrition
- •Predation and Capacity Expansion
- •Strategic Bundling
- •“Judo Economics”
- •Evidence on Entry-Deterring Behavior
- •Contestable Markets
- •An Entry Deterrence Checklist
- •Entering a New Market
- •Preemptive Entry and Rent Seeking Behavior
- •Chapter Summary
- •Questions
- •Endnotes
- •Microdynamics
- •Strategic Commitment
- •Strategic Substitutes and Strategic Complements
- •The Strategic Effect of Commitments
- •Tough and Soft Commitments
- •A Taxonomy of Commitment Strategies
- •The Informational Benefits of Flexibility
- •Real Options
- •Competitive Discipline
- •Dynamic Pricing Rivalry and Tit-for-Tat Pricing
- •Why Is Tit-for-Tat So Compelling?
- •Coordinating on the Right Price
- •Impediments to Coordination
- •The Misread Problem
- •Lumpiness of Orders
- •Information about the Sales Transaction
- •Volatility of Demand Conditions
- •Facilitating Practices
- •Price Leadership
- •Advance Announcement of Price Changes
- •Most Favored Customer Clauses
- •Uniform Delivered Prices
- •Where Does Market Structure Come From?
- •Sutton’s Endogenous Sunk Costs
- •Innovation and Market Evolution
- •Learning and Industry Dynamics
- •Chapter Summary
- •Questions
- •Endnotes
- •8: Industry Analysis
- •Performing a Five-Forces Analysis
- •Internal Rivalry
- •Entry
- •Substitutes and Complements
- •Supplier Power and Buyer Power
- •Strategies for Coping with the Five Forces
- •Coopetition and the Value Net
- •Applying the Five Forces: Some Industry Analyses
- •Chicago Hospital Markets Then and Now
- •Market Definition
- •Internal Rivalry
- •Entry
- •Substitutes and Complements
- •Supplier Power
- •Buyer Power
- •Commercial Airframe Manufacturing
- •Market Definition
- •Internal Rivalry
- •Barriers to Entry
- •Substitutes and Complements
- •Supplier Power
- •Buyer Power
- •Professional Sports
- •Market Definition
- •Internal Rivalry
- •Entry
- •Substitutes and Complements
- •Supplier Power
- •Buyer Power
- •Conclusion
- •Professional Search Firms
- •Market Definition
- •Internal Rivalry
- •Entry
- •Substitutes and Complements
- •Supplier Power
- •Buyer Power
- •Conclusion
- •Chapter Summary
- •Questions
- •Endnotes
- •Competitive Advantage Defined
- •Maximum Willingness-to-Pay and Consumer Surplus
- •From Maximum Willingness-to-Pay to Consumer Surplus
- •Value-Created
- •Value Creation and “Win–Win” Business Opportunities
- •Value Creation and Competitive Advantage
- •Analyzing Value Creation
- •Value Creation and the Value Chain
- •Value Creation, Resources, and Capabilities
- •Generic Strategies
- •The Strategic Logic of Cost Leadership
- •The Strategic Logic of Benefit Leadership
- •Extracting Profits from Cost and Benefit Advantage
- •Comparing Cost and Benefit Advantages
- •“Stuck in the Middle”
- •Diagnosing Cost and Benefit Drivers
- •Cost Drivers
- •Cost Drivers Related to Firm Size, Scope, and Cumulative Experience
- •Cost Drivers Independent of Firm Size, Scope, or Cumulative Experience
- •Cost Drivers Related to Organization of the Transactions
- •Benefit Drivers
- •Methods for Estimating and Characterizing Costs and Perceived Benefits
- •Estimating Costs
- •Estimating Benefits
- •Strategic Positioning: Broad Coverage versus Focus Strategies
- •Segmenting an Industry
- •Broad Coverage Strategies
- •Focus Strategies
- •Chapter Summary
- •Questions
- •Endnotes
- •The “Shopping Problem”
- •Unraveling
- •Alternatives to Disclosure
- •Nonprofit Firms
- •Report Cards
- •Multitasking: Teaching to the Test
- •What to Measure
- •Risk Adjustment
- •Presenting Report Card Results
- •Gaming Report Cards
- •The Certifier Market
- •Certification Bias
- •Matchmaking
- •When Sellers Search for Buyers
- •Chapter Summary
- •Questions
- •Endnotes
- •Market Structure and Threats to Sustainability
- •Threats to Sustainability in Competitive and Monopolistically Competitive Markets
- •Threats to Sustainability under All Market Structures
- •Evidence: The Persistence of Profitability
- •The Resource-Based Theory of the Firm
- •Imperfect Mobility and Cospecialization
- •Isolating Mechanisms
- •Impediments to Imitation
- •Legal Restrictions
- •Superior Access to Inputs or Customers
- •The Winner’s Curse
- •Market Size and Scale Economies
- •Intangible Barriers to Imitation
- •Causal Ambiguity
- •Dependence on Historical Circumstances
- •Social Complexity
- •Early-Mover Advantages
- •Learning Curve
- •Reputation and Buyer Uncertainty
- •Buyer Switching Costs
- •Network Effects
- •Networks and Standards
- •Competing “For the Market” versus “In the Market”
- •Knocking off a Dominant Standard
- •Early-Mover Disadvantages
- •Imperfect Imitability and Industry Equilibrium
- •Creating Advantage and Creative Destruction
- •Disruptive Technologies
- •The Productivity Effect
- •The Sunk Cost Effect
- •The Replacement Effect
- •The Efficiency Effect
- •Disruption versus the Resource-Based Theory of the Firm
- •Innovation and the Market for Ideas
- •The Environment
- •Factor Conditions
- •Demand Conditions
- •Related Supplier or Support Industries
- •Strategy, Structure, and Rivalry
- •Chapter Summary
- •Questions
- •Endnotes
- •The Principal–Agent Relationship
- •Combating Agency Problems
- •Performance-Based Incentives
- •Problems with Performance-Based Incentives
- •Preferences over Risky Outcomes
- •Risk Sharing
- •Risk and Incentives
- •Selecting Performance Measures: Managing Trade-offs between Costs
- •Do Pay-for-Performance Incentives Work?
- •Implicit Incentive Contracts
- •Subjective Performance Evaluation
- •Promotion Tournaments
- •Efficiency Wages and the Threat of Termination
- •Incentives in Teams
- •Chapter Summary
- •Questions
- •Endnotes
- •13: Strategy and Structure
- •An Introduction to Structure
- •Individuals, Teams, and Hierarchies
- •Complex Hierarchy
- •Departmentalization
- •Coordination and Control
- •Approaches to Coordination
- •Types of Organizational Structures
- •Functional Structure (U-form)
- •Multidivisional Structure (M-form)
- •Matrix Structure
- •Matrix or Division? A Model of Optimal Structure
- •Network Structure
- •Why Are There So Few Structural Types?
- •Structure—Environment Coherence
- •Technology and Task Interdependence
- •Efficient Information Processing
- •Structure Follows Strategy
- •Strategy, Structure, and the Multinational Firm
- •Chapter Summary
- •Questions
- •Endnotes
- •The Social Context of Firm Behavior
- •Internal Context
- •Power
- •The Sources of Power
- •Structural Views of Power
- •Do Successful Organizations Need Powerful Managers?
- •The Decision to Allocate Formal Power to Individuals
- •Culture
- •Culture Complements Formal Controls
- •Culture Facilitates Cooperation and Reduces Bargaining Costs
- •Culture, Inertia, and Performance
- •A Word of Caution about Culture
- •External Context, Institutions, and Strategies
- •Institutions and Regulation
- •Interfirm Resource Dependence Relationships
- •Industry Logics: Beliefs, Values, and Behavioral Norms
- •Chapter Summary
- •Questions
- •Endnotes
- •Glossary
- •Name Index
- •Subject Index

284 • Chapter 8 • Industry Analysis
CHAPTER SUMMARY
An industry analysis provides an overview of the potential profitability of the average firm in an industry.
A comprehensive analysis examines the five forces: internal rivalry, entry, substitutes, buyer power, and supplier power. The latter four operate independently and may also intensify internal rivalry.
Internal rivalry is fierce if competition drives prices toward costs. This is more likely when there are many firms, products are perceived to be homogeneous, consumers are motivated and able to shop around, prices may be set secretly, sales orders are large and received infrequently, and the industry has excess capacity.
The threat of entry is high if firms can easily enter an industry and capture market share from profitable incumbents while intensifying price competition.
Substitutes also capture sales and intensify price rivalry.
Buyers and suppliers exert power directly by renegotiating the terms of contracts to extract profits from profitable industries, and indirectly by shopping around for the best prices.
The government can affect profitability and should be considered either as part of the five forces or as a separate force.
Profits may be threatened by any or all of the five forces. Although it is useful to construct a “five-forces scorecard” on which the forces can be rated, the exercise of assessing the five forces is more important than the actual scores. Through this exercise, the analyst develops deep knowledge of key strategic issues affecting the industry in question.
A sound five-forces analysis should be based on economic principles. The tools for analyzing internal rivalry, entry, and substitutes are derived from industrial organization and game theory, which are discussed in Chapters 5, 6, and 7. The tools for analyzing buyer and supplier power are derived from the economics of vertical relationships, which were discussed in Chapters 3 and 4.
QUESTIONS
1.It has been said that Porter’s five-forces analysis turns antitrust law on its head. What do you think this means?
2.Comment on the following: All of wisdom contained in the five-forces framework is reflected in the economic identity:
Profit 5 (Price 2 Average Cost) 3 Quantity
3.How does the magnitude of scale economies affect the intensity of each of the five forces?
4.How does capacity utilization affect the intensity of internal rivalry? The extent of entry barriers?
5.How does the magnitude of consumer switching costs affect the intensity of internal rivalry? Of entry?
Appendix: Template for Doing a Five-Forces Analysis • 285
6.How do exit barriers affect internal rivalry? Entry?
7.Rivalry among firms in an industry is typically stronger when which of the following is true about the underlying industry economics? (Note: It is possible that more than one—or none—of the answers to this question are correct. You must choose all correct answers to get full credit.)
(a)Fixed costs of production are high.
(b)There are two competitors in the industry.
(c)Products are differentiated.
(d)Production capacity in the industry is low relative to current demand.
8.Consider an industry whose demand fluctuates over time. Suppose that this industry faces high supplier power. Briefly state how this high supplier power will affect the variability of profits over time.
9.What does the concept of coopetition add to the five-forces approach to industry analysis?
10. Coopetition often requires firms to communicate openly. How is this different from collusion? How can antitrust enforcers distinguish between coopetition and collusion?
11. In the United States, the incomes of specialists such as heart surgeons can easily triple the incomes of primary care practitioners. Use the five forces to offer explanations for this disparity. Can you think of any other possible explanations?
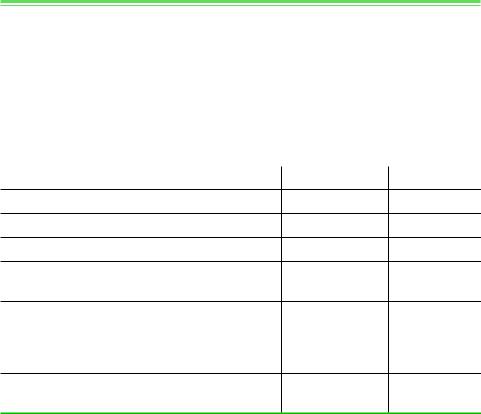
APPENDIX: TEMPLATE FOR DOING A FIVE-FORCES ANALYSIS
Factors Affecting Rivalry among Existing Competitors
To what extent does pricing rivalry or nonprice competition (e.g., advertising) erode the profitability of a typical firm in this industry?
|
Characterization |
Future Trend |
|
(Current) |
|
Degree of seller concentration?
Rate of industry growth?
Significant cost differences among firms?
Excess capacity?
Cost structure of firms: sensitivity of costs to capacity utilization?
Degree of product differentiation among sellers? Brand loyalty to existing sellers? Cross-price elasticities of demand among competitors in industry?
Buyers’ costs of switching from one competitor to another?
286 • Chapter 8 • Industry Analysis
|
Characterization |
Future Trend |
|
(Current) |
|
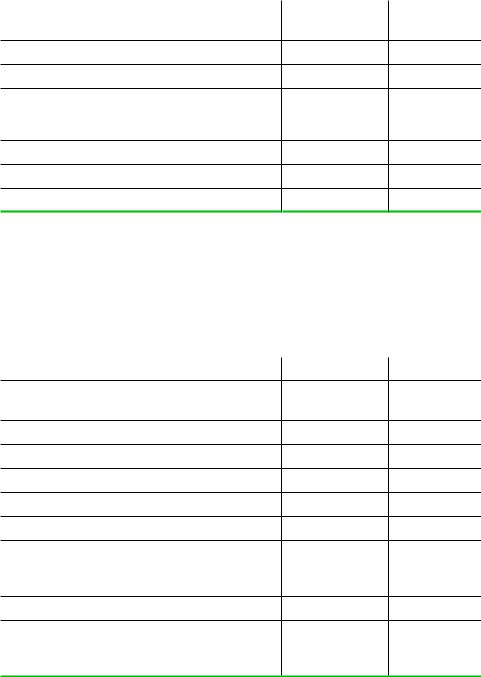
Are prices and terms of sales transactions observable?
Can firms adjust prices quickly?
Large and/or infrequent sales orders?
Use of “facilitating practices” (price leadership, advance announcement of price changes)?
History of “cooperative” pricing?
Strength of exit barriers?
High industry price elasticity of demand?
Factors Affecting the Threat of Entry
To what extent does the threat or incidence of entry work to erode the profitability of a typical firm in this industry?
|
Characterization |
Future Trend |
|
(Current) |
|
|
|
|
Significant economies of scale?
Importance of reputation or established brand loyalties in purchase decision?
Entrants’ access to distribution channels?
Entrants’ access to raw materials?
Entrants’ access to technology/know-how?
Entrants’ access to favorable locations?
Experience-based advantages of incumbents?
Network externalities: demand-side advantages to incumbents from large installed base?
Government protection of incumbents?
Perceptions of entrants about expected retaliation of incumbents/reputations of incumbents for “toughness”?
Appendix: Template for Doing a Five-Forces Analysis • 287
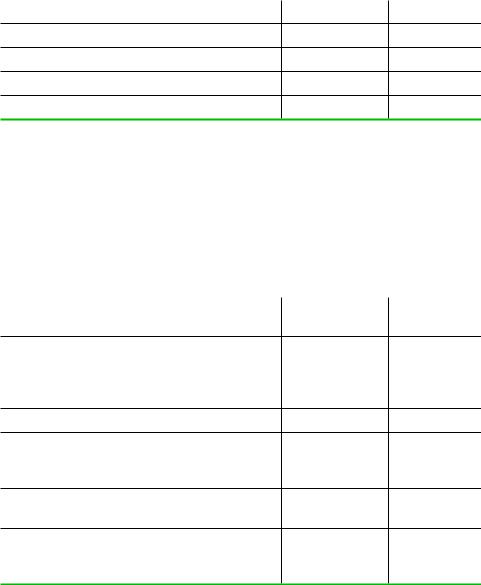
Factors Affecting or Reflecting Pressure from Substitute Products and Support from Complements
To what extent does competition from substitute products outside the industry erode the profitability of a typical firm in the industry?
|
Characterization |
Future Trend |
|
(Current) |
|
Availability of close substitutes?
Price-value characteristics of substitutes?
Price elasticity of industry demand?
Availability of close complements?
Price-value characteristics of complements?
Factors Affecting or Reflecting Power of Input Suppliers
To what extent do individual suppliers have the ability to negotiate high input prices with typical firms in this industry? To what extent do input prices deviate from those that would prevail in a perfectly competitive input market in which input suppliers act as price takers?
|
Characterization |
Future Trend |
|
(Current) |
|
Is the supplier industry more concentrated than the industry it sells to?
Do firms in industry purchase relatively small volumes relative to other customers of supplier? Is typical firm’s purchase volume small relative to sales of typical supplier?
Few substitutes for suppliers’ input?
Do firms in industry make relationship-specific investments to support transactions with specific suppliers?
Do suppliers pose credible threat of forward integration into the product market?
Are suppliers able to price-discriminate among prospective customers according to ability/ willingness to pay for input?
