
- •Analysis and Application of Analog Electronic Circuits to Biomedical Instrumentation
- •Dedication
- •Preface
- •Reader Background
- •Rationale
- •Description of the Chapters
- •Features
- •The Author
- •Table of Contents
- •1.1 Introduction
- •1.2 Sources of Endogenous Bioelectric Signals
- •1.3 Nerve Action Potentials
- •1.4 Muscle Action Potentials
- •1.4.1 Introduction
- •1.4.2 The Origin of EMGs
- •1.5 The Electrocardiogram
- •1.5.1 Introduction
- •1.6 Other Biopotentials
- •1.6.1 Introduction
- •1.6.2 EEGs
- •1.6.3 Other Body Surface Potentials
- •1.7 Discussion
- •1.8 Electrical Properties of Bioelectrodes
- •1.9 Exogenous Bioelectric Signals
- •1.10 Chapter Summary
- •2.1 Introduction
- •2.2.1 Introduction
- •2.2.4 Schottky Diodes
- •2.3.1 Introduction
- •2.4.1 Introduction
- •2.5.1 Introduction
- •2.5.5 Broadbanding Strategies
- •2.6 Photons, Photodiodes, Photoconductors, LEDs, and Laser Diodes
- •2.6.1 Introduction
- •2.6.2 PIN Photodiodes
- •2.6.3 Avalanche Photodiodes
- •2.6.4 Signal Conditioning Circuits for Photodiodes
- •2.6.5 Photoconductors
- •2.6.6 LEDs
- •2.6.7 Laser Diodes
- •2.7 Chapter Summary
- •Home Problems
- •3.1 Introduction
- •3.2 DA Circuit Architecture
- •3.4 CM and DM Gain of Simple DA Stages at High Frequencies
- •3.4.1 Introduction
- •3.5 Input Resistance of Simple Transistor DAs
- •3.7 How Op Amps Can Be Used To Make DAs for Medical Applications
- •3.7.1 Introduction
- •3.8 Chapter Summary
- •Home Problems
- •4.1 Introduction
- •4.3 Some Effects of Negative Voltage Feedback
- •4.3.1 Reduction of Output Resistance
- •4.3.2 Reduction of Total Harmonic Distortion
- •4.3.4 Decrease in Gain Sensitivity
- •4.4 Effects of Negative Current Feedback
- •4.5 Positive Voltage Feedback
- •4.5.1 Introduction
- •4.6 Chapter Summary
- •Home Problems
- •5.1 Introduction
- •5.2.1 Introduction
- •5.2.2 Bode Plots
- •5.5.1 Introduction
- •5.5.3 The Wien Bridge Oscillator
- •5.6 Chapter Summary
- •Home Problems
- •6.1 Ideal Op Amps
- •6.1.1 Introduction
- •6.1.2 Properties of Ideal OP Amps
- •6.1.3 Some Examples of OP Amp Circuits Analyzed Using IOAs
- •6.2 Practical Op Amps
- •6.2.1 Introduction
- •6.2.2 Functional Categories of Real Op Amps
- •6.3.1 The GBWP of an Inverting Summer
- •6.4.3 Limitations of CFOAs
- •6.5 Voltage Comparators
- •6.5.1 Introduction
- •6.5.2. Applications of Voltage Comparators
- •6.5.3 Discussion
- •6.6 Some Applications of Op Amps in Biomedicine
- •6.6.1 Introduction
- •6.6.2 Analog Integrators and Differentiators
- •6.7 Chapter Summary
- •Home Problems
- •7.1 Introduction
- •7.2 Types of Analog Active Filters
- •7.2.1 Introduction
- •7.2.3 Biquad Active Filters
- •7.2.4 Generalized Impedance Converter AFs
- •7.3 Electronically Tunable AFs
- •7.3.1 Introduction
- •7.3.3 Use of Digitally Controlled Potentiometers To Tune a Sallen and Key LPF
- •7.5 Chapter Summary
- •7.5.1 Active Filters
- •7.5.2 Choice of AF Components
- •Home Problems
- •8.1 Introduction
- •8.2 Instrumentation Amps
- •8.3 Medical Isolation Amps
- •8.3.1 Introduction
- •8.3.3 A Prototype Magnetic IsoA
- •8.4.1 Introduction
- •8.6 Chapter Summary
- •9.1 Introduction
- •9.2 Descriptors of Random Noise in Biomedical Measurement Systems
- •9.2.1 Introduction
- •9.2.2 The Probability Density Function
- •9.2.3 The Power Density Spectrum
- •9.2.4 Sources of Random Noise in Signal Conditioning Systems
- •9.2.4.1 Noise from Resistors
- •9.2.4.3 Noise in JFETs
- •9.2.4.4 Noise in BJTs
- •9.3 Propagation of Noise through LTI Filters
- •9.4.2 Spot Noise Factor and Figure
- •9.5.1 Introduction
- •9.6.1 Introduction
- •9.7 Effect of Feedback on Noise
- •9.7.1 Introduction
- •9.8.1 Introduction
- •9.8.2 Calculation of the Minimum Resolvable AC Input Voltage to a Noisy Op Amp
- •9.8.5.1 Introduction
- •9.8.5.2 Bridge Sensitivity Calculations
- •9.8.7.1 Introduction
- •9.8.7.2 Analysis of SNR Improvement by Averaging
- •9.8.7.3 Discussion
- •9.10.1 Introduction
- •9.11 Chapter Summary
- •Home Problems
- •10.1 Introduction
- •10.2 Aliasing and the Sampling Theorem
- •10.2.1 Introduction
- •10.2.2 The Sampling Theorem
- •10.3 Digital-to-Analog Converters (DACs)
- •10.3.1 Introduction
- •10.3.2 DAC Designs
- •10.3.3 Static and Dynamic Characteristics of DACs
- •10.4 Hold Circuits
- •10.5 Analog-to-Digital Converters (ADCs)
- •10.5.1 Introduction
- •10.5.2 The Tracking (Servo) ADC
- •10.5.3 The Successive Approximation ADC
- •10.5.4 Integrating Converters
- •10.5.5 Flash Converters
- •10.6 Quantization Noise
- •10.7 Chapter Summary
- •Home Problems
- •11.1 Introduction
- •11.2 Modulation of a Sinusoidal Carrier Viewed in the Frequency Domain
- •11.3 Implementation of AM
- •11.3.1 Introduction
- •11.3.2 Some Amplitude Modulation Circuits
- •11.4 Generation of Phase and Frequency Modulation
- •11.4.1 Introduction
- •11.4.3 Integral Pulse Frequency Modulation as a Means of Frequency Modulation
- •11.5 Demodulation of Modulated Sinusoidal Carriers
- •11.5.1 Introduction
- •11.5.2 Detection of AM
- •11.5.3 Detection of FM Signals
- •11.5.4 Demodulation of DSBSCM Signals
- •11.6 Modulation and Demodulation of Digital Carriers
- •11.6.1 Introduction
- •11.6.2 Delta Modulation
- •11.7 Chapter Summary
- •Home Problems
- •12.1 Introduction
- •12.2.1 Introduction
- •12.2.2 The Analog Multiplier/LPF PSR
- •12.2.3 The Switched Op Amp PSR
- •12.2.4 The Chopper PSR
- •12.2.5 The Balanced Diode Bridge PSR
- •12.3 Phase Detectors
- •12.3.1 Introduction
- •12.3.2 The Analog Multiplier Phase Detector
- •12.3.3 Digital Phase Detectors
- •12.4 Voltage and Current-Controlled Oscillators
- •12.4.1 Introduction
- •12.4.2 An Analog VCO
- •12.4.3 Switched Integrating Capacitor VCOs
- •12.4.6 Summary
- •12.5 Phase-Locked Loops
- •12.5.1 Introduction
- •12.5.2 PLL Components
- •12.5.3 PLL Applications in Biomedicine
- •12.5.4 Discussion
- •12.6 True RMS Converters
- •12.6.1 Introduction
- •12.6.2 True RMS Circuits
- •12.7 IC Thermometers
- •12.7.1 Introduction
- •12.7.2 IC Temperature Transducers
- •12.8 Instrumentation Systems
- •12.8.1 Introduction
- •12.8.5 Respiratory Acoustic Impedance Measurement System
- •12.9 Chapter Summary
- •References
Operational Amplifiers |
261 |
VφHI
|
|
|
|
|
_ |
|
|
RSFF |
VC-2 |
CH |
|
|
OS-3 |
Q |
P3 |
R |
_ |
(N LO) |
|
|
(N HI) |
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
Q |
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Vs
Q |
Vo |
|
(N HI) |
||
|
S
VC-1 |
(N LO) |
CL |
|
|
OS-2 |
Q |
P2 |
|
|
|
|
|
(N LO) |
||||
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
VφLO |
|
|
|
|
|
|
_ |
P1 |
|
|
|
|
|
OS-1 |
Q |
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
(N HI) |
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
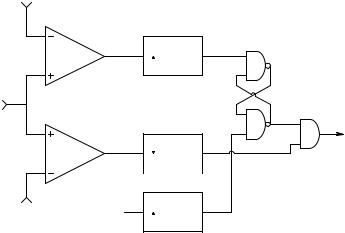
FIGURE 6.14
A nerve spike pulse-height window that produces an output pulse only if an input spike rises to its peak inside the window and then falls below the lower “sill.” No output pulse is produced if an input spike rises through the window and exceeds the upper level, then falls below the sill.
impulses recorded with extra-cellular microelectrodes that fall within a narrow range of amplitudes (the window). This processing enables other simultaneously recorded, very large (or small) action potentials to be ignored while the desired pulses can be counted, processed, and their instantaneous frequency calculated, etc.
Figure 6.14 illustrates the organization of this window circuit. Note that this circuit involves sequential as well as combinational logic. Critical waveforms of this window circuit are shown in Figure 6.15. Note that three oneshot multivibrators are used to generate narrow (e.g., 500 ns) output pulses given input logic state transitions. The NAND gate RS flip-flop serves as a “memory” that a rising Vs has exceeded VφLO. Note that, if Vs exceeds VφLO, the output of VC-2, CH, goes HI. This event triggers OS-3 to reset the RSFF Q output to LO, disabling the output AND gate.
Now when the large input again falls below VφLO, the P2 pulse does not produce an output. Only the falling edge of VC-1’s output, CL, can produce an output. The second Vs pulse in Figure 6.15 lies in the window. The rising edge of CL sets the RSFF Q output high, enabling the AND gate. When Vs falls below VφLO, OS-2 produces a positive pulse that appears at Vo, signaling a pulse that occurred inside the window. (A functionally similar nerve spike pulse-height window was described by Northrop and Grossman, 1974.)
6.5.3Discussion
The preceding sections described the basic behavior of VCs. Note that comparators are intended to signal analog voltage inequalities to appropriate
© 2004 by CRC Press LLC

262 |
Analysis and Application of Analog Electronic Circuits |
Vs |
VφHI |
VφLO |
t |
0 |
CL |
P2
CH |
P3
 FF Q (AND enable)
FF Q (AND enable)
P1
Vo
FIGURE 6.15
Critical waveforms for the pulse-height window of Figure 6.14. See text for description.
logic circuits or transistor switches; op amps are for conditioning analog signals, giving an analog output. An important point is that an open-loop op amp (one without feedback) makes a poor comparator. Yes, op amps generally have very high gain differential input gains and high CMRRs, but
rapid changes in Vo are limited by the op amps’ slew rate, η. η is typically on the order of 20 V/μs, which means it takes Vo roughly 250 ns to slew 5 V.
Op amp outputs are generally not logic-level compatible; they swing to ±(VCC − Vδ), where Vδ is a fixed voltage by which a saturated Vo fails to reach the supply voltage. Vδ is different for different designs of op amps. It is not good design practice to use op amps for comparator applications.
© 2004 by CRC Press LLC
