
- •COMPUTATIONAL CHEMISTRY
- •CONTENTS
- •PREFACE
- •1.1 WHAT YOU CAN DO WITH COMPUTATIONAL CHEMISTRY
- •1.2 THE TOOLS OF COMPUTATIONAL CHEMISTRY
- •1.3 PUTTING IT ALL TOGETHER
- •1.4 THE PHILOSOPHY OF COMPUTATIONAL CHEMISTRY
- •1.5 SUMMARY OF CHAPTER 1
- •REFERENCES
- •EASIER QUESTIONS
- •HARDER QUESTIONS
- •2.1 PERSPECTIVE
- •2.2 STATIONARY POINTS
- •2.3 THE BORN–OPPENHEIMER APPROXIMATION
- •2.4 GEOMETRY OPTIMIZATION
- •2.6 SYMMETRY
- •2.7 SUMMARY OF CHAPTER 2
- •REFERENCES
- •EASIER QUESTIONS
- •HARDER QUESTIONS
- •3.1 PERSPECTIVE
- •3.2 THE BASIC PRINCIPLES OF MM
- •3.2.1 Developing a forcefield
- •3.2.2 Parameterizing a forcefield
- •3.2.3 A calculation using our forcefield
- •3.3 EXAMPLES OF THE USE OF MM
- •3.3.2 Geometries and energies of polymers
- •3.3.3 Geometries and energies of transition states
- •3.3.4 MM in organic synthesis
- •3.3.5 Molecular dynamics and Monte Carlo simulations
- •3.4 GEOMETRIES CALCULATED BY MM
- •3.5 FREQUENCIES CALCULATED BY MM
- •3.6 STRENGTHS AND WEAKNESSES OF MM
- •3.6.1 Strengths
- •3.6.2 Weaknesses
- •3.7 SUMMARY OF CHAPTER 3
- •REFERENCES
- •EASIER QUESTIONS
- •HARDER QUESTIONS
- •4.1 PERSPECTIVE
- •4.2.1 The origins of quantum theory: blackbody radiation and the photoelectric effect
- •4.2.2 Radioactivity
- •4.2.3 Relativity
- •4.2.4 The nuclear atom
- •4.2.5 The Bohr atom
- •4.2.6 The wave mechanical atom and the Schrödinger equation
- •4.3.1 Introduction
- •4.3.2 Hybridization
- •4.3.3 Matrices and determinants
- •4.3.4 The simple Hückel method – theory
- •4.3.5 The simple Hückel method – applications
- •4.3.6 Strengths and weaknesses of the SHM
- •4.4.1 Theory
- •4.4.2 An illustration of the EHM: the protonated helium molecule
- •4.4.3 The extended Hückel method – applications
- •4.4.4 Strengths and weaknesses of the EHM
- •4.5 SUMMARY OF CHAPTER 4
- •REFERENCES
- •EASIER QUESTIONS
- •5.1 PERSPECTIVE
- •5.2.1 Preliminaries
- •5.2.2 The Hartree SCF method
- •5.2.3 The HF equations
- •5.2.3.1 Slater determinants
- •5.2.3.2 Calculating the atomic or molecular energy
- •5.2.3.3 The variation theorem (variation principle)
- •5.2.3.4 Minimizing the energy; the HF equations
- •5.2.3.5 The meaning of the HF equations
- •5.2.3.6a Deriving the Roothaan–Hall equations
- •5.3 BASIS SETS
- •5.3.1 Introduction
- •5.3.2 Gaussian functions; basis set preliminaries; direct SCF
- •5.3.3 Types of basis sets and their uses
- •5.4 POST-HF CALCULATIONS: ELECTRON CORRELATION
- •5.4.1 Electron correlation
- •5.4.3 The configuration interaction approach to electron correlation
- •5.5.1 Geometries
- •5.5.2 Energies
- •5.5.2.1 Energies: Preliminaries
- •5.5.2.2 Energies: calculating quantities relevant to thermodynamics and to kinetics
- •5.5.2.2a Thermodynamics; “direct” methods, isodesmic reactions
- •5.5.2.2b Thermodynamics; high-accuracy calculations
- •5.5.2.3 Thermodynamics; calculating heats of formation
- •5.5.2.3a Kinetics; calculating reaction rates
- •5.5.2.3b Energies: concluding remarks
- •5.5.3 Frequencies
- •Dipole moments
- •Charges and bond orders
- •Electrostatic potential
- •Atoms-in-molecules
- •5.5.5 Miscellaneous properties – UV and NMR spectra, ionization energies, and electron affinities
- •5.5.6 Visualization
- •5.6 STRENGTHS AND WEAKNESSES OF AB INITIO CALCULATIONS
- •5.7 SUMMARY OF CHAPTER 5
- •REFERENCES
- •EASIER QUESTIONS
- •HARDER QUESTIONS
- •6.1 PERSPECTIVE
- •6.2 THE BASIC PRINCIPLES OF SCF SE METHODS
- •6.2.1 Preliminaries
- •6.2.2 The Pariser-Parr-Pople (PPP) method
- •6.2.3 The complete neglect of differential overlap (CNDO) method
- •6.2.4 The intermediate neglect of differential overlap (INDO) method
- •6.2.5 The neglect of diatomic differential overlap (NDDO) method
- •6.2.5.2 Heats of formation from SE electronic energies
- •6.2.5.3 MNDO
- •6.2.5.7 Inclusion of d orbitals: MNDO/d and PM3t; explicit electron correlation: MNDOC
- •6.3 APPLICATIONS OF SE METHODS
- •6.3.1 Geometries
- •6.3.2 Energies
- •6.3.2.1 Energies: preliminaries
- •6.3.2.2 Energies: calculating quantities relevant to thermodynamics and kinetics
- •6.3.3 Frequencies
- •6.3.4 Properties arising from electron distribution: dipole moments, charges, bond orders
- •6.3.5 Miscellaneous properties – UV spectra, ionization energies, and electron affinities
- •6.3.6 Visualization
- •6.3.7 Some general remarks
- •6.4 STRENGTHS AND WEAKNESSES OF SE METHODS
- •6.5 SUMMARY OF CHAPTER 6
- •REFERENCES
- •EASIER QUESTIONS
- •HARDER QUESTIONS
- •7.1 PERSPECTIVE
- •7.2 THE BASIC PRINCIPLES OF DENSITY FUNCTIONAL THEORY
- •7.2.1 Preliminaries
- •7.2.2 Forerunners to current DFT methods
- •7.2.3.1 Functionals: The Hohenberg–Kohn theorems
- •7.2.3.2 The Kohn–Sham energy and the KS equations
- •7.2.3.3 Solving the KS equations
- •7.2.3.4a The local density approximation (LDA)
- •7.2.3.4b The local spin density approximation (LSDA)
- •7.2.3.4c Gradient-corrected functionals and hybrid functionals
- •7.3 APPLICATIONS OF DENSITY FUNCTIONAL THEORY
- •7.3.1 Geometries
- •7.3.2 Energies
- •7.3.2.1 Energies: preliminaries
- •7.3.2.2 Energies: calculating quantities relevant to thermodynamics and kinetics
- •7.3.2.2a Thermodynamics
- •7.3.2.2b Kinetics
- •7.3.3 Frequencies
- •7.3.6 Visualization
- •7.4 STRENGTHS AND WEAKNESSES OF DFT
- •7.5 SUMMARY OF CHAPTER 7
- •REFERENCES
- •EASIER QUESTIONS
- •HARDER QUESTIONS
- •8.1 FROM THE LITERATURE
- •8.1.1.1 Oxirene
- •8.1.1.2 Nitrogen pentafluoride
- •8.1.1.3 Pyramidane
- •8.1.1.4 Beyond dinitrogen
- •8.1.2 Mechanisms
- •8.1.2.1 The Diels–Alder reaction
- •8.1.2.2 Abstraction of H from amino acids by the OH radical
- •8.1.3 Concepts
- •8.1.3.1 Resonance vs. inductive effects
- •8.1.3.2 Homoaromaticity
- •8.2 TO THE LITERATURE
- •8.2.1 Books
- •8.2.2 The Worldwide Web
- •8.3 SOFTWARE AND HARDWARE
- •8.3.1 Software
- •8.3.2 Hardware
- •8.3.3 Postscript
- •REFERENCES
- •INDEX
Chapter 8
Literature, Software, Books and Websites
The yeoman work in any science…is done by the experimentalist, who must
keep the theoretician honest.
Michio Kaku, Professor of Theoretical Physics, City University of New York.
8.1FROM THE LITERATURE
A small smorgasbord of published papers will be discussed here, to show how some of the things that we have seen in previous chapters have appeared in the literature.
8.1.1 To be or not to be
8.1.1.1Oxirene
Let us start with what looks like a simple problem: what can computational chemistry tell us about oxirene (oxacyclopropene, Fig. 8.1; the oxirene literature till 1983 has been reviewed [1]). Labeling one of the carbons of a diazo ketone  can lead to a ketene with scrambled labeling. After excluding the possibility of scrambling in the diazo compound, this indicates that an oxirene species is formed. However, this does not tell us whether this species is an intermediate or merely a transition state (Fig. 8.2). A straightforward way to try to answer this question would seem to be to calculate the frequencies, at the level used to optimize the structure, and see if there are any imaginary frequencies – a relative minimum has none, while a transition state has one (section 2.5). In a preliminary investigation [2] Schaefer and coworkers found that oxirene was a minimum with the Hartree-Fock (HF) (SCF) method, and also when electron correlation was taken into account (section 5.4) with the CISD and CCSD methods, using double-zeta basis sets (section 5.3). However, in going from HF to CISD to CCSD, the ring-opening frequency fell from 445 to 338 to
can lead to a ketene with scrambled labeling. After excluding the possibility of scrambling in the diazo compound, this indicates that an oxirene species is formed. However, this does not tell us whether this species is an intermediate or merely a transition state (Fig. 8.2). A straightforward way to try to answer this question would seem to be to calculate the frequencies, at the level used to optimize the structure, and see if there are any imaginary frequencies – a relative minimum has none, while a transition state has one (section 2.5). In a preliminary investigation [2] Schaefer and coworkers found that oxirene was a minimum with the Hartree-Fock (HF) (SCF) method, and also when electron correlation was taken into account (section 5.4) with the CISD and CCSD methods, using double-zeta basis sets (section 5.3). However, in going from HF to CISD to CCSD, the ring-opening frequency fell from 445 to 338 to  which was said to be a much steeper drop than would be expected. A very comprehensive investigation with the above (“To be …”) title [3], in which the frequencies of oxirene were examined at 46 (!) different levels failed to definitively settle the matter: even using CCSD(T) calculations with large basis sets the results were somewhat quirky, and in fact of the six highest levels used, three gave an imaginary frequency and three
which was said to be a much steeper drop than would be expected. A very comprehensive investigation with the above (“To be …”) title [3], in which the frequencies of oxirene were examined at 46 (!) different levels failed to definitively settle the matter: even using CCSD(T) calculations with large basis sets the results were somewhat quirky, and in fact of the six highest levels used, three gave an imaginary frequency and three

448 Computational Chemistry
Literature, Software, Books and Websites 449
all real frequencies. At the two highest levels the ring-opening frequency was real, but uncomfortably low (139 and 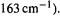 Oxirene is the most notorious case of an unsolved computational “existence theorem”.
Oxirene is the most notorious case of an unsolved computational “existence theorem”.
8.1.1.2Nitrogen pentafluoride
Nitrogen pentafluoride represents an interesting contrast to oxirene. Oxirene is, on paper, a reasonable molecule; there is no obvious reason why, however unstable it might be because of antiaromaticity [4] or strain, it should not be able to exist. On the other hand,  defies the hallowed octet rule; why should it be more reasonable than, say,
defies the hallowed octet rule; why should it be more reasonable than, say,  Yet a comprehensive computational study of this molecule left “little doubt” that it is a (relative) minimum on its potential energy surface [5]. The full armamentarium of post-HF methods, CASSDF, MRCI, CCSDT, CCSD(T), MP2 (section 5.4) and DFT (chapter 7) was employed here, and all agreed that
Yet a comprehensive computational study of this molecule left “little doubt” that it is a (relative) minimum on its potential energy surface [5]. The full armamentarium of post-HF methods, CASSDF, MRCI, CCSDT, CCSD(T), MP2 (section 5.4) and DFT (chapter 7) was employed here, and all agreed that  (section 2.6)
(section 2.6) 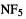 is a minimum.
is a minimum.
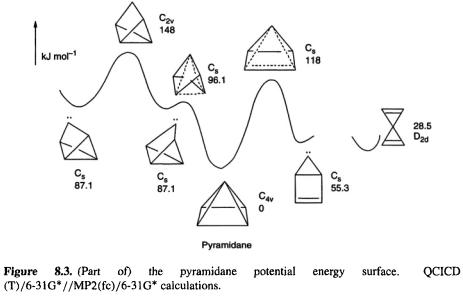
8.1.1.3 Pyramidane
If oxirene “should” exist and  “should” not, what are we to make of pyramidane (Fig. 8.3)? This molecule contradicts the traditional paradigm [6] of tetracoordinate carbon having its bonds tetrahedrally directed: the four bonds of the apical carbon point toward the base of a pyramid. Part of the calculated [7] potential energy surface of pyramidane is shown in Fig. 8.3. To improve the accuracy of the relative energies, the MP2 geometries were subjected to single-point calculations (section 5.5.2) using the QCI method (section 5.4.3), with the results shown (Fig. 8.3). At the QCISD(T)/6-31G*//MP(fc)/6-31G* level pyramidane is predicted to be a relative
“should” not, what are we to make of pyramidane (Fig. 8.3)? This molecule contradicts the traditional paradigm [6] of tetracoordinate carbon having its bonds tetrahedrally directed: the four bonds of the apical carbon point toward the base of a pyramid. Part of the calculated [7] potential energy surface of pyramidane is shown in Fig. 8.3. To improve the accuracy of the relative energies, the MP2 geometries were subjected to single-point calculations (section 5.5.2) using the QCI method (section 5.4.3), with the results shown (Fig. 8.3). At the QCISD(T)/6-31G*//MP(fc)/6-31G* level pyramidane is predicted to be a relative
