
- •Электронное оглавление
- •ОТ РЕДАКТОРА
- •Aknowledgements
- •I. ОБЩЕТЕОРЕТИЧЕСКИЕ АСПЕКТЫ ИЗУЧЕНИЯ ДИСКУРСА В СОВРЕМЕННОЙ ЛИНГВИСТИКЕ
- •Библиографический список литературы
- •ЯЗЫКОВАЯ СПОСОБНОСТЬ КАК ОБЪЕКТ ИНТЕРПРЕТАЦИОННОГО ПОДХОДА В ПСИХОЛИНГВИСТИКЕ. И.А. Макарова
- •Библиографический список литературы
- •ОСНОВЫ КОНЦЕПТУАЛЬНОГО ИНТЕГРИРОВАНИЯ МЕНТАЛЬНЫХ ПРОСТРАНСТВ. Л.А. Манерно
- •Рис. 1. Представление роли прагматического коннектора, участвующего в реализации конкретного элемента дискурса
- •Рис. 2. Концептуальное интегрирование ментальных пространств анализируемой фразы
- •Рис. 3. Вводные и классифицирующее ментальные пространства основных лексических единиц текста рекламы
- •Рис. 4. Интегрированное пространство анализируемого отрывка рекламного дискурса
- •Библиографический список литературы
- •AN ANALYSIS OF FORCE DYNAMICS IN DISCOURSE. Mary Elaine Meagher
- •Introduction
- •1. Research protocol
- •1.1. Instrument
- •1.2. Subject
- •1.3. Method
- •1.3.1. Force Dynamics
- •13.2. Mental space construction
- •2. RB Scientist (IF-UNAM)
- •2.1. Corpus
- •2.2 Mental space construction
- •Figure 1. Mental space construction
- •2.3. Force dynamic analysis
- •Figure 2. Force dynamic analysis
- •2.4. Results
- •3. Conclusions
- •References
- •RELEVANCE THEORY IN TEXT AND DISCOURSE. Jutta Muschard
- •1. What is relevance theory?
- •1.1. Contextual effects
- •1.2. Processing effort
- •1.3. Optimal relevance
- •1.4. Concepts and entries
- •2. What's the good of relevance theory?
- •2.1. Translation studies and relevance theory
- •2.1.1. Legal text
- •2.1.2. Literary text
- •2.1.3. Result
- •2.2 Humour theories
- •REFERENCES
- •РЕЛЕВАНТНОСТЬ КАК КОГНИТИВНАЯ И ЛИНГВИСТИЧЕСКАЯ КАТЕГОРИЯ. Л.В. Правикова
- •1. Предпосылки теории релевантности
- •2. Концептуальное ядро языка теории релевантности
- •3. Интердисциплинарные связи теории релевантности
- •Библиографический список литературы
- •II . СЕТЕВЫЕ ИССЛЕДОВАНИЯ В ЛИНГВИСТИКЕ. ФРЕЙМОВАЯ СЕМАНТИКА
- •ОПЫТ ИССЛЕДОВАНИЯ МЕЖФРЕЙМОВЫХ СВЯЗЕЙ В НОМИНАТИВНОМ ПРОСТРАНСТВЕ, СВЯЗАННОМ С АМЕРИКАНСКИМИ ПРАЗДНИКАМИ. В. В. Визаулина
- •Рис. Тематические фреймы
- •Таблица. Составляющие нижних уровней фреймов
- •Библиографический список литературы
- •КРИТИКА «СЕТЕВОГО» ПОДХОДА К СЕМАНТИКЕ ПРЕДЛОГОВ (ПО РАБОТАМ С. РАЙС). E.E. Голубкова
- •Рис. 1. Два вида сетей концептуальной категории по С, Райс
- •Рис. 2. Сдвиг значения и его отражение в вертикальной сети
- •Рис. 3. Вертикальные сети Р. Лэнекера
- •Рис. 4. Доменное пространство предлогов
- •Библиографический список литературы
- •Библиографический список литературы
- •Рис. 1. Факторы быстрого распознавания рекламного текста
- •Рис. 2. Фрейм концепта «журнал»
- •Рис. 3. Тематический фрейм анализируемого рекламного сообщения
- •Рис. 4. Лексический фрейм анализируемого сообщения
- •Рис. 5. Фрейм словосочетания toothpaste
- •Рис. 6. Фрейм торговой марки
- •Библиографический список литературы
- •Рис. Связи между значениями слов в рамках лексико-семантического поля
- •Библиографический список литературы
- •Библиографический список литературы
- •III . КОРПУСНАЯ И КОМПЬЮТЕРНАЯ ЛИНГВИСТИКА. МЕДИАЛИНГВИСТИКА
- •КОГНИТИВНО-ПРАГМАТИЧЕСКИЕ ОСОБЕННОСТИ ПОСТРОЕНИЯ ДИСКУРСА В СРЕДСТВАХ МАССОВОЙ ИНФОРМАЦИИ. О. В. Александрова
- •Библиографический список литературы
- •REFERENCES
- •ВВЕДЕНИЕ ДИСКУРСИВНЫХ ДАННЫХ В СОВРЕМЕННЫЕ ГРАММАТИКИ. B.A. Гуреев
- •Библиографический список литературы
- •ЭЛЛИПТИЧЕСКИЕ СТРУКТУРЫ С РЕДУКЦИЕЙ ПРИГЛАГОЛЬНЫХ АКТАНТОВ В ЯЗЫКЕ ПРЕССЫ. Н.С. Колотилова
- •Библиографический список литературы
- •ЖАНРОВО-РЕЧЕВАЯ ОРГАНИЗАЦИЯ ТЕКСТА И ЕЁ ПРЕДСТАВЛЕНИЕ В ЯЗЫКЕ (НА МАТЕРИАЛЕ НЕМЕЦКИХ ЖУРНАЛЬНЫХ ТЕКСТОВ РУБРИКИ «ОПРОС МНЕНИЙ»). О.В. Крылова
- •Условные обозначения
- •Библиографический список литературы
- •ТРАНСФОРМАЦИИ В ГРАММАТИЧЕСКОМ ОФОРМЛЕНИИ ГРУППЫ СУЩЕСТВИТЕЛЬНЫХ В СОВРЕМЕННОМ НЕМЕЦКОМ ЯЗЫКЕ (НА МАТЕРИАЛЕ ТЕКСТОВ ПРЕССЫ). Н.В. Рябченко
- •Рис. Существительные смешанного склонения
- •Библиографический список литературы
- •КОНЦЕПТЫ И ИХ СВЯЗИ В ТЕКСТЕ . H.A. Сёмнина
- •Таблица 1. Концепты, раскрывающие признаки деятеля и их выражение в тексте
- •Таблица 2. Концепты, раскрывающие пространственно-временные характеристики деятельности и их выражение в тексте
- •Таблица 3. Концепты, обозначающие компоненты деятельности и их выражение в тексте
- •Рис. 1. Концептуальная система гипертекста о компании AMD
- •Рис. 2. Иерархическая организация концептов, представляющих продукт деятельности
- •Библиографический список литературы
- •ГИПЕРТЕКСТ И СЛОВООБРАЗОВАТЕЛЬНЫЙ СЛОВАРЬ. И.Н. Туласов
- •Рис. 1. Стартовая страница словообразовательного словаря
- •Рис. 2. Немецкий алфавит как система пинков
- •Рис. 3. Алфавитный перечень лемм
- •Рис. 4. Страница словообразовательных элементов
- •Рис. 5. Основная схема линков словаря
- •Библиографический список литературы
- •IV. НАУЧНЫЙ ДИСКУРС. ТЕРМИН И ЕГО ХАРАКТЕРИСТИКИ
- •НАУЧНЫЙ ДИСКУРС О ТЕКСТЕ. A.A. Абдулфанова
- •Библиографический список литературы
- •Библиографический список литературы
- •РОЛЬ ТЕРМИНА В НАУЧНОЙ КОММУНИКАЦИИ. П.Ф. Ельцова
- •Библиографический список литературы
- •ЛИНГВИСТИЧЕСКАЯ РЕПРЕЗЕНТАЦИЯ МЕНТАЛЬНОГО МОДУСА ЭМОЦИОНАЛЬНОЙ ОЦЕНКИ В КРИТИЧЕСКОМ ТЕКСТЕ. И.Ю. Кремер
- •Библиографический список литературы
- •Принятые сокращения
- •Библиографический список литературы
- •Библиографический список литературы
- •ЭКОЛОГИЧЕСКИЙ ДИСКУРС: К ПРОБЛЕМЕ ОПРЕДЕЛЕНИЯ ЛИНГВОКУЛЬТУРОЛОГИЧЕСКИХ ПАРАМЕТРОВ И ТИПОВ ТЕКСТОВ (НА МАТЕРИАЛЕ НЕМЕЦКОГО ЯЗЫКА). И.Н. Рогожникова
- •Библиографический список литературы
- •V. ОСОБЕННОСТИ ЯЗЫКОВОЙ КАРТИНЫ МИРА И ЕЁ ОТРАЖЁННОСТЬ В ЛИТЕРАТУРНЫХ ПРОИЗВЕДЕНИЯХ И СЛОВАРНЫХ ИСТОЧНИКАХ.
- •КОМПЛИМЕНТ КАК КОМПОНЕНТ МАНИПУЛЯТИВНОГО ДИСКУРСА (на материале американского варианта английского языка). A.B. Бобенко
- •Библиографический список литературы
- •Таблица. Представленность структурных типов слов в текстовых источниках
- •Библиографический список литературы
- •Библиографический список литературы
- •ЦВЕТООБОЗНАЧЕНИЕ И СТРАТЕГИИ ДИСКУРСА. И.С. Гаврилина
- •Библиографический список литературы
- •Цитируемая литература
- •ОСОБЕННОСТИ ФУНКЦИОНИРОВАНИЯ АНГЛИЙСКИХ ЛИЧНЫХ ИМЁН В ЭПИСТОЛЯРНОМ КОНТЕКСТЕ. С.И. Гарагуля
- •Рис. 1. Система имени Molly Tompkins
- •Рис. 2. Система имени актрисы Patrick Campbell
- •Библиографический список литературы
- •РОЛЬ КОНТЕКСТА В ОПРЕДЕЛЕНИИ СЕМАНТИЧЕСКОЙ СТРУКТУРЫ ГЛАГОЛА (НА ПРИМЕРЕ ГЛАГОЛА GLITTER). Е.В. Калинычева
- •Библиографический список литературы
- •РУССКАЯ И АМЕРИКАНСКАЯ МЕЧТА И ЕЁ ВОПЛОЩЕНИЕ В ЯЗЫКЕ И КУЛЬТУРЕ. T.A. Комова
- •Рис. «Поле» мечты в русском и английском языках
- •Библиографический список литературы
- •ЛИЧНОЕ ИМЯ КАК КУЛЬТУРНЫЙ СИМВОЛ: СТЕРЕОТИПЫ И МИФЫ. С. M. Пан
- •Библиографический список литературы
- •ДИСКУРСНАЯ ОБУСЛОВЛЕННОСТЬ СЕМАНТИЧЕСКОГО ВАРЬИРОВАНИЯ ПРЕДЛОГОВ. H.A. Пескова
- •Рис.1. Семантическая структура предлога "at"
- •Рис. 2. Внутрисистемная иерархия единиц семантического варьирования
- •Библиографический список литературы
- •РЕАЛИЗАЦИЯ ПРАГМАТИЧЕСКОЙ ФУНКЦИИ РЕЧЕВОГО АКТА НЕСОГЛАСИЯ/ ОТКАЗА. И.А. Постоенко
- •Библиографический список литературы
- •Список использованных художественных произведений и принятые сокращения
- •Библиографический список литературы
- •ОСОБЕННОСТИ МОРФОЛОГИИ ТЕКСТА ЛИМЕРИКА. Ю. П. Суханова
- •Библиографический список литературы
- •ДЕЙКСИС КАК СВОЙСТВО НОМИНАЦИИ. С.Б. Уланова
- •Рис. 1. Дейктическая деятельность 187
- •Рис 2. Дейксис в процессе номинации
- •Библиографический список литературы
- •Рис. Лексико-семантические варианты английского слова "room"
- •Библиографический список литературы
- •НЕСКОЛЬКО СЛОВ ОБ ОБРАЗЦОВОМ ЧИТАТЕЛЕ. И.А. Щирова
- •Библиографический список литературы
- •VI. СПЕЦИФИЧЕСКИЕ ХАРАКТЕРИСТИКИ РАЗНООБРАЗНЫХ ВИДОВ ТЕКСТА И ДИСКУРСА
- •ОСОБЕННОСТИ АКТУАЛЬНОГО ЧЛЕНЕНИЯ ПРЕДЛОЖЕНИЙ С НЕМЕЦКОЙ КОНСТРУКЦИЕЙ "SEIN + ZU + INFINITIV". Л.А. Алексанова
- •Таблица
- •Библиографический список литературы
- •Список источников примеров и их сокращений
- •АНТОНИМИЧЕСКАЯ КОГЕЗИЯ В СОВРЕМЕННОМ АНГЛИЙСКОМ ЯЗЫКЕ. H.Б. Боева
- •Библиографический список литературы
- •Библиографический список литературы
- •К ВОПРОСУ О ПРИСОЕДИНИТЕЛЬНЫХ ПРЕДЛОЖЕНИЯХ В НЕМЕЦКОМ ЯЗЫКЕ. Л.В. Колотилова
- •Библиографический список литературы
- •КОММУНИКАТИВНЫЙ АСПЕКТ ЭКОНОМИИ: ИМПЛИЦИТЕН ЛИ СИНТАКСИЧЕСКИЙ ЭЛЛИПСИС? M. M. Коровкин
- •Библиографический список литературы
- •НЕСТАНДАРТНЫЕ РЕЧЕВЫЕ ДЕЙСТВИЯ В ДИАЛОГИЧЕСКОМ ДИСКУРСЕ. Л.А. Нефёдова
- •Библиографический список литературы
- •СТИЛИСТИЧЕСКИЕ СТРАТЕГИИ В ЖАНРАХ ТЕМАТИЧЕСКОЙ СТАТЬИ (FEATURE) И БИОГРАФИЧЕСКОГО ОЧЕРКА (PROFILE). В.А. Тырыгина
- •Библиографический список литературы
- •ЯВЛЕНИЕ ПОВТОРА В ФУНКЦИОНАЛЬНО-СТИЛИСТИЧЕСКОМ АСПЕКТЕ. O.B. Червакова
- •Библиографический список литературы
- •ОТ АНАЛИЗА ТЕКСТА К АНАЛИЗУ ДИСКУРСА. B.E. Чернявская
- •Библиографический список литературы
- •СОДЕРЖАНИЕ
- •CONTENTS
Янко Слава (Библиотека Fort/Da) || slavaaa@yandex.ru || http://yanko.lib.ru || Icq# 75088656
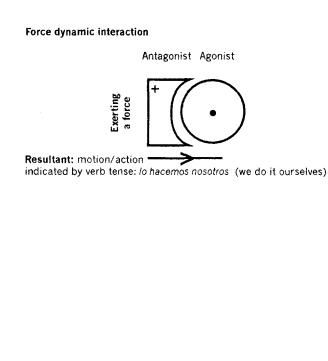
2.3. Force dynamic analysis
The agonist of the basic force dynamic relationship in this discourse fragment is cf nosotros los científicos (we the scientists). Their intrinsic tendency regarding doing the work of the engineers is rest/inaction. The antagonist is xr (~xc) = hr or the absence of a value for the ideal xc in reality space R. The intrinsic tendency of the antagonist is motion/action: exerting a force that opposes the intrinsic tendency of the agonist (rest/inaction). The antagonist is relatively stronger than the agonist and the resultant is motion/action indicated by the verb tense of lo hacemos nosotros (we do it ourselves) in frequency subspace F (See Figure 2).
Figure 2. Force dynamic analysis
There is a trans-spatial interaction between the absence of the ideal value for xr in R and the event occurring in subspace F. However since space R in its entirety expresses the absence of value for xr (both explicitly and metaphorically), we can affirm the existence of a force dynamic interaction between the antagonist - space R - and the agonist cf in F; the resultant being the event occupying subspace F.
Syntactic force dynamics come into play as the conjunctions como (since) and porque (because) mark the discourse expressing causal agency leading to the event in frequency subspace F: como eso no no no sucede (since that does not not not occur) and porque existe un hueco allí (because there is a gap there). There is tension between counterfactual space С that expresses an ideal and reality space R that describes its absence. Strong negatives mark the absence of the ideal in R as Spanish subjuntivo pretérito (past subjunctive) in С and present indicative in R further emphasize this contrast.
Lexical force dynamics are apparent in items like apoyo (support) and fuerte (strong). The basic meaning of apoyo (support) from the physical force domain is «anything that detains another entity, supports it or constitutes its base» [7. P. 122]. Here the force dynamic opposition is between the force of gravity and an opposing force that detains movement. The resultant is rest/inaction.
The meaning of support pertinent for this corpus is «help, collaboration, manifestation of solidarity or adhesion» [7]. This seems to be an example of a metaphorical mapping of the meaning of force dynamics from a physical domain to a different domain where mental and emotional attitudes are at the least partial components of meaning. According to Eve Sweetser [8. P. 18] it seems clear that more abstract domains of meaning tend to derive their vocabulary from more concrete domains (rather than vice versa) and, furthermore, there is a deep cognitive
33
Текст и дискурс: традиционный и когнитивно-функциональный аспекты исследования= Рязань, 2002. - 236 с.
