
- •1. Topographic Surface Anatomy
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •3. Superficial Face
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •4. Neck
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •5. Nasal Region
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •6. Oral Region
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •7. Pharynx
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •13. Cerebral Vasculature
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •14. Topographic Anatomy
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •16. Spinal Cord
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Thorax
- •18. Topographic Anatomy
- •Guides
- •Facts & Hints
- •19. Mammary Gland
- •Guides
- •Facts & Hints
- •20. Body Wall
- •Guides
- •Facts & Hints
- •21. Lungs
- •Guides
- •Facts & Hints
- •22. Heart
- •Guides
- •Facts & Hints
- •23. Mediastinum
- •Guides
- •Facts & Hints
- •Abdomen
- •24. Topographic Anatomy
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •25. Body Wall
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •26. Peritoneal Cavity
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •27. Viscera (Gut)
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •28. Viscera (Accessory Organs)
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •29. Visceral Vasculature
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •30. Innervation
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •32. Topographic Anatomy
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •35. Urinary Bladder
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •39. Testis, Epididymis & Ductus Deferens
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •40. Rectum
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •41. Vasculature
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •42. Innervation
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Upper Limb
- •43. Topographic Anatomy
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •48. Neurovasculature
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Lower Limb
- •49. Topographic Anatomy
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •51. Knee
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •54. Neurovasculature
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints

51 Knee
STUDYAIMS
At the end of your study, you should be able to:
Understand the movements of the knee joint
Describe the attachments and functions of the ligaments strengthening the joint
Identifythe major bursae surrounding the knee and understand their function
Identifythe margins of the popliteal fossa and describe its contents
396 / 425
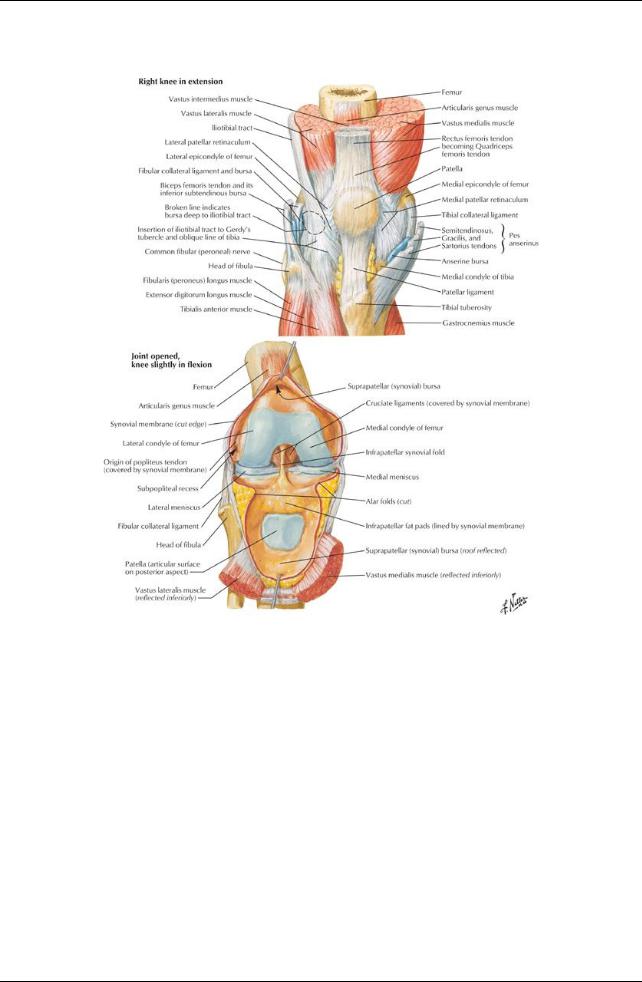
GUIDE
Lower Limb: Knee
[Plate 495, Knee: Anterior Views]
397 / 425

[Plate 496, Knee: Interior]
398 / 425
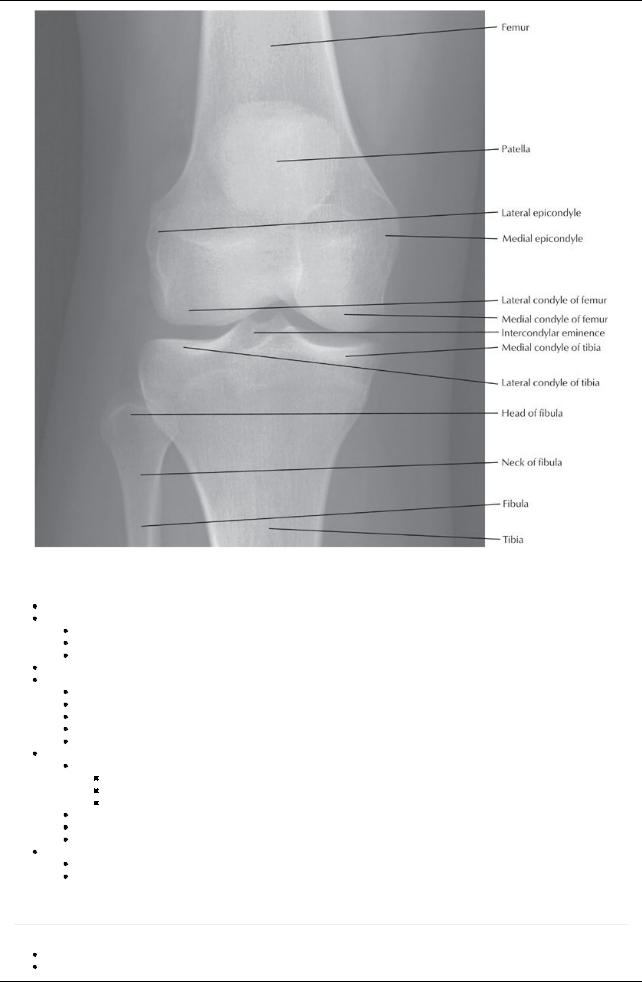
[Plate 498, Knee: Anteroposterior Radiograph]
Knee Joint
Biaxial, hinge-type synovial joint
Movements
Flexion and extension
Some gliding and rolling
Some medial and lateral rotation about vertical axis
Articular capsule-thin and weak, offers little support in itself
Fibrous capsule
Strong
Attaches to femur superior to condyles
Attaches to articular margin of tibia
Deficient superiorlyon lateral tibial condyle, to allow passage of popliteus tendon
Deficient inferiorlywhere tendon of popliteus crosses
Blood supply
Genicular branches of the femoral and popliteal arteries
Lateral and medial superior genicular
Middle genicular
Lateral and medial inferior genicular
Anterior tibial recurrent → anterior and posterior recurrent arteries
Circumflexfibular artery→ anterior and posterior recurrent arteries
Arteries form genicular anastomosis around the knee
Nerve supply(see Section 7-2: Lower Limb: Hip and Thigh)
Obturator
Articular branches of femoral, tibial, and common fibular nerves
Bones Articulating in the Knee Joint
page 254
page 255
Lateral and medial articulations between femoral condyles and tibial condyles
Smooth superior surface of tibia for articulation called tibial plateau
399 / 425

Intermediate articulation between patella and femur
Patella
Large sesamoid bone embedded in the quadriceps tendon
Articulation called patellofemoral joint
Ligaments Reinforcing Fibrous Capsule
[Plate 497, Knee: Cruciate and Collateral Ligaments]
Extracapsular
Medial (tibial) collateral ligament
Flat and band-like
Attached to medial meniscus on deep surface
Lateral (fibular) collateral ligament
Strong and cord-like
Separated bylateral meniscus bytendon of popliteus muscle
Splits tendon of biceps prior to its insertion
Patellar ligament
Oblique popliteal ligament
Arcuate popliteal ligament
Intracapsular ligaments
Anterior cruciate ligament
Extends from posterior medial side of lateral femoral condyle to anterior intercondylar area of tibia
Taut when knee is fullyextended
Prevents posterior displacement of femur on tibia and hyperextension of joint
Intracapsular but extrasynovial
Posterior cruciate ligament
Stronger of two cruciate ligaments
Extends from lateral surface of medial condyle of femur to posterior intercondylar region of tibia
Taut during flexion
Prevents anterior displacement of femur on tibia
Medial and lateral menisci
Crescentic plates of fibrocartilage
Wedge-shaped to deepen articulating surface of tibia
400 / 425
Function as "shock absorbers"
Transverse ligament of knee joins anterior surfaces of menisci
Medial meniscus
C-shaped
Adherent to tibial collateral ligament
Lateral meniscus
O-shaped
Joined to posterior cruciate ligament and medial femoral condyle byposterior meniscofemoral ligament
Ligaments of the Knee Joint
Ligament |
Attachments |
Function |
Extracapsular Ligaments |
|
|
Patellar |
Patella → tibial tuberosity |
Continuation of quadriceps tendon |
Tibial collateral |
Medial femoral epicondyle → medial tibial condyle |
Limits extension |
|
(and meniscus) |
Limits abduction |
Fibular collateral |
Lateral femoral epicondyle → fibular head |
Limits extension |
|
|
Limits adduction |
Arcuate popliteal |
Fibular head → capsule |
Limits medial rotation |
Oblique popliteal |
Lateral femur → posterior tibia |
Limits hyperextension |
Intracapsular Ligaments |
|
|
Anterior cruciate |
Lateral femoral condyle → anterior intercondylar |
Prevents posterior slipping of femur on tibia (Torn in |
(extrasynovial) |
tibia |
hyperextension) |
Posterior cruciate |
Medial femoral condyle → posterior intercondylar |
Prevents anterior slipping of femur on tibia |
(extrasynovial) |
tibia |
|
Transverse |
Anterior edges of menisci |
Stabilizes menisci |
Posterior |
Posterior of lateral meniscus → medial femoral |
Stabilizes lateral meniscus |
meniscofemoral |
condyle |
|
Bursae Around the Knee Joint
Many(12+) bursae surround the knee
Facilitate movement of the tendons and skin over the joint during flexion or extension
Needed because most tendons pull verticallyacross joint
Four bursae communicate with the synovial cavityof the knee
Suprapatellar
Popliteus
Anserine
Gastrocnemius bursae
Suprapatellar bursa
Particularlyvulnerable to infection following penetrating trauma
Allows spread of infection directlyinto the knee joint
Main Bursae of the Knee
Bursa |
Location |
Suprapatellar |
Between femur and quadriceps tendon |
Popliteus |
Between lateral tibial condyle and popliteus tendon |
Anserine |
Between tibial collateral ligament and tendons of sartorius, gracilis, and semitendinosus |
Gastrocnemius |
Deep to proximal attachment of medial gastrocnemius head |
Semimembranosus |
Deep to tendon of semimembranosus |
Semitendinosus |
Deep to heads of gastrocnemius muscles |
Prepatellar |
Between skin and anterior surface of patella |
Subcutaneous infrapatellar |
Between skin and tibial tuberosity |
Deep infrapatellar |
Between tibia and patellar ligament |
Popliteal Fossa
page 256 page 257
Boundaries
Superomedially: semitendinosus and semimembranosus
Superolaterally: biceps femoris
Inferomediallyand laterally: medial and lateral heads of the gastrocnemius
Floor: popliteal surface of femur, oblique popliteal ligament, fascia over popliteus muscle
Roof: skin and fascia
Contents
Small saphenous vein
Popliteal arteryand veins (deeper than the nerves)
Tibial nerve and common fibular nerve (from the sciatic)
Posterior cutaneous nerve of thigh
Lymphatic vessels and nodes
Order of structures (lateral to medial): tibial nerve, vein, artery
401 / 425

402 / 425
