
- •1. Topographic Surface Anatomy
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •3. Superficial Face
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •4. Neck
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •5. Nasal Region
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •6. Oral Region
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •7. Pharynx
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •13. Cerebral Vasculature
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •14. Topographic Anatomy
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •16. Spinal Cord
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Thorax
- •18. Topographic Anatomy
- •Guides
- •Facts & Hints
- •19. Mammary Gland
- •Guides
- •Facts & Hints
- •20. Body Wall
- •Guides
- •Facts & Hints
- •21. Lungs
- •Guides
- •Facts & Hints
- •22. Heart
- •Guides
- •Facts & Hints
- •23. Mediastinum
- •Guides
- •Facts & Hints
- •Abdomen
- •24. Topographic Anatomy
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •25. Body Wall
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •26. Peritoneal Cavity
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •27. Viscera (Gut)
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •28. Viscera (Accessory Organs)
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •29. Visceral Vasculature
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •30. Innervation
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •32. Topographic Anatomy
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •35. Urinary Bladder
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •39. Testis, Epididymis & Ductus Deferens
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •40. Rectum
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •41. Vasculature
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •42. Innervation
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Upper Limb
- •43. Topographic Anatomy
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •48. Neurovasculature
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Lower Limb
- •49. Topographic Anatomy
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •51. Knee
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •54. Neurovasculature
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints

28 Viscera (Accessory Organs)
STUDYAIMS
At the end of your study, you should be able to:
Describe the structure of the liver, its relations, and neurovascular supply
Describe the structure of the gallbladder, its neurovascular supply, and understand the biliarysystem
Describe the structure of the pancreas, its relations, and neurovascular supply
Describe the structure of the spleen, its relations, and neurovascular supply
223 / 425
GUIDE
Abdomen: Viscera (Accessory Organs)
Liver
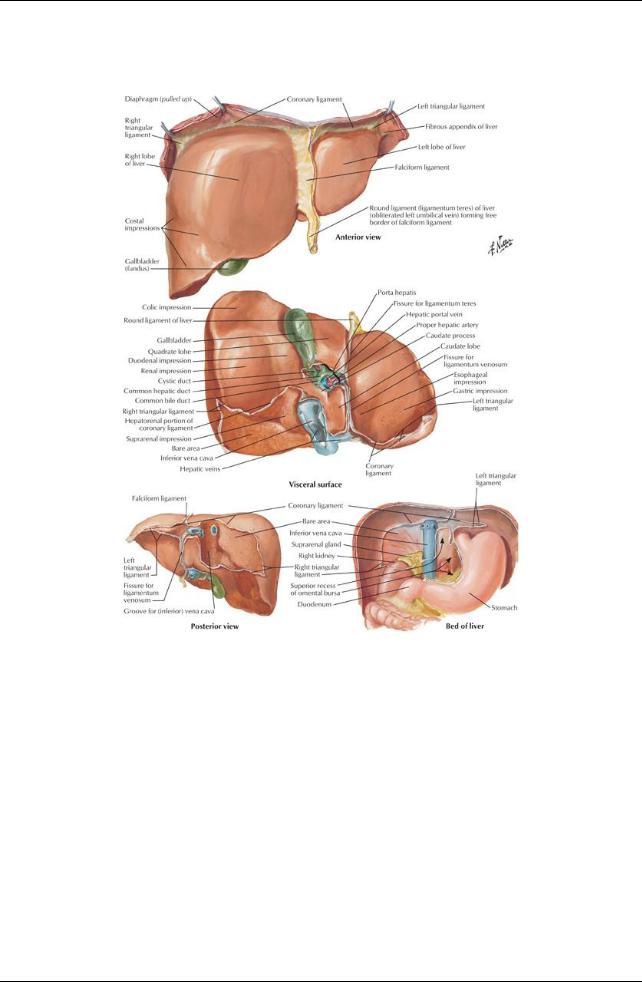
[Plate 277, Surfaces and Bed of Liver]
224 / 425
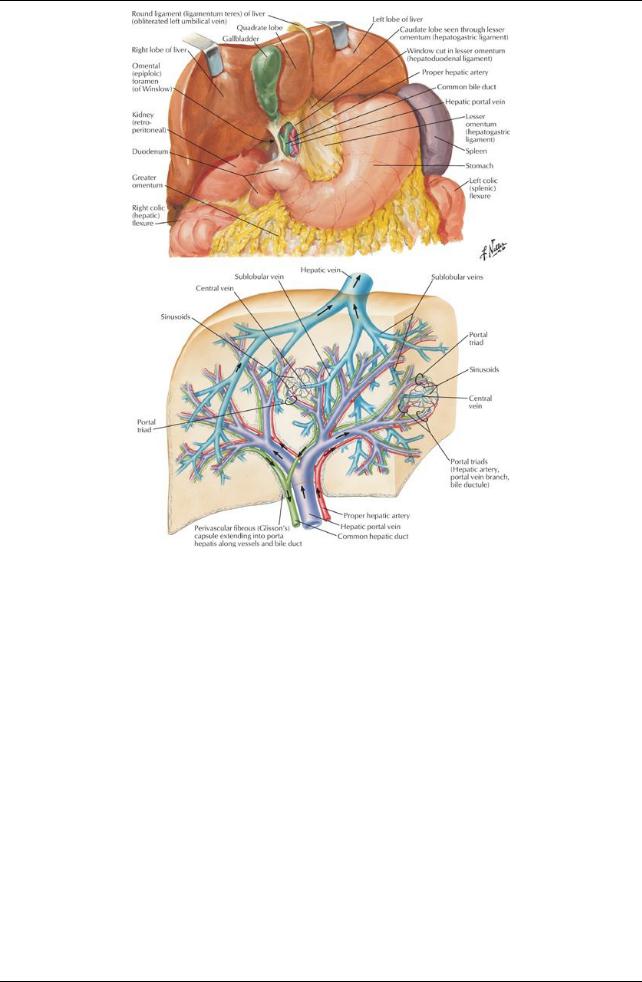
[Plate 278, Liver in Situ: Vascular and Duct Systems]
225 / 425

[Plate 279, Liver Structure: Schema]
page 148
page 149
Largest gland in the body(approximately1.5 kg)
Surfaces
Smooth diaphragmatic surface, covered byperitoneum except over bare area
Reflection of peritoneum from the diaphragm to liver forms the coronaryligament
Has anterior and posterior layers
Where layers meet on right = right triangular ligament
Posterior layer is continuous with lesser omentum
Left triangular ligament formed bythe falciform ligament and lesser omentum
Visceral surface
Separated anteriorlyfrom anterior and superior surfaces bysharp inferior border
Covered byperitoneum except at the porta hepatis and bed of the gall bladder
Related to: Right side of anterior stomach
First part of duodenum
Gall bladder
Right colic flexure and transverse colon
Right kidneyand suprarenal glands
Ligaments
Falciform ligament
Peritoneal reflection from upper anterior abdominal wall from umbilicus to liver
Has ligamentum teres hepatis (round ligament) in free edge
Ligamentum teres hepatis (round ligament of liver)
Fibrous remnant of umbilical vein
Extended from umbilicus to liver
Ligamentum venosum
Remnant of the ductus venosus
Extended in fetus between the umbilical vein and inferior vena cava (IVC)
Recesses:
Subphrenic recess separates liver from diaphragm (split byfalciform ligament)
Hepatorenal recess
On the right side
226 / 425
Separates liver anteriorlyfrom kidneyand suprarenal gland posteriorly
Lobes
Left, right, caudate, quadrate
Functional "left liver" includes left lobe, caudate and quadrate lobes
Porta hepatis
Transverse fissure on visceral surface between caudate and quadrate lobes
Provides entrance/exit for:
Portal vein
Hepatic artery
Hepatic nerve plexus
Hepatic ducts (left and right converge to form the common hepatic duct)
Lymphatic vessels
Vascular supply(Section 4-6: Abdomen-Visceral Vasculature)
Liver receives blood from
Portal vein (70%)
Hepatic artery(30%)
Hepatic veins (3)
Formed byunion of central veins
Drain directlyinto the IVC inferior to diaphragm
Lymphatics
Drain mainlyto the hepatic nodes at the porta hepatis
From hepatic nodes → celiac nodes → cisterna chyli
Nervous supply(Section 4-7: Abdomen-Innervation) is derived from the hepatic nerve plexus
Accompanies branches of hepatic arteryand portal vein
Sympathetic fibers from celiac plexus
Parasympathetic fibers from anterior and posterior vagal trunks
Role unknown except for vasoconstriction
Gallbladder
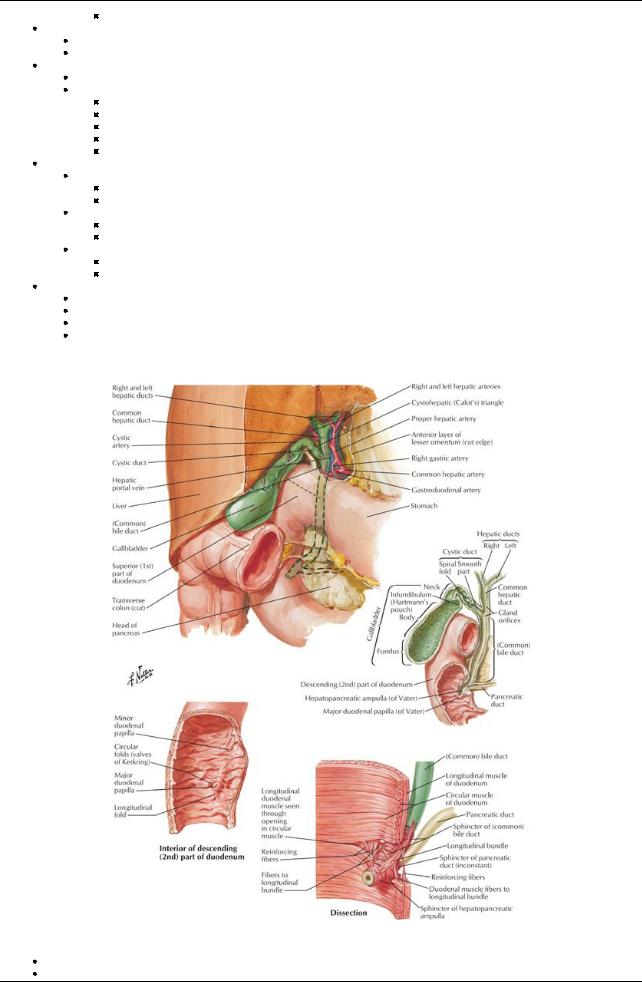
[Plate 280, Gallbladder, Extrahepatic Bile Ducts, and Pancreatic Duct]
Lies in fossa at junction of right and left lobes of liver
Connected to liver byfibrous capsule of liver
227 / 425
Stores bile produced bythe liver
Parts
Fundus-located at tip of ninth costal cartilage
Body-also in contact with transverse colon and first part of duodenum
Neck
Has S-shaped bend to joint cystic duct
Mucosa thrown into a spiral fold-the spiral valve-to keep cystic duct open
Cystic duct connects to common hepatic duct to form the common bile duct
Vascular supply(Section 4-6: Abdomen-Visceral Vasculature)
Artery: cystic arteryfrom right hepatic artery
Cystic veins
Veins draining neck and biliaryducts emptyinto portal vein
Veins draining the bodyand fundus drain directlyinto the liver
Lymph drains to the hepatic nodes
Nervous supply(Section 4-7: Abdomen-Innervation)
Sympathetic from celiac plexus
Parasympathetic from vagus
Sensoryfrom right phrenic
page 149
page 150
Pancreas
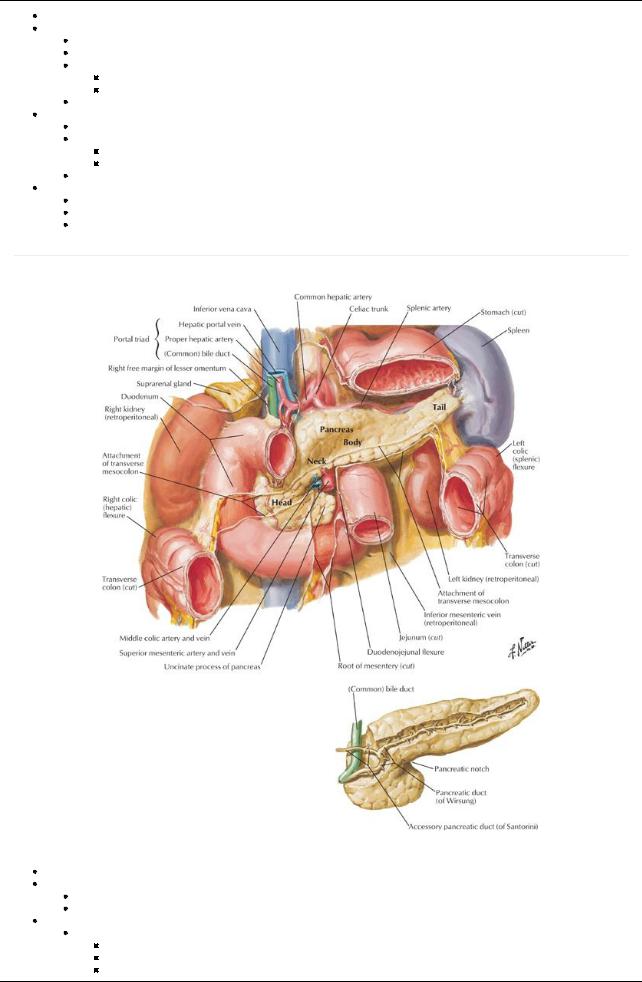
[Plate 281, Pancreas in Situ]
Lies retroperitoneallyand transverselyacross posterior abdominal wall
Digestive gland with exocrine and endocrine functions
Exocrine: secretion of digestive juices
Endocrine: secretion of insulin and glucagon
Parts:
Head
Encircled byC-shaped curve of duodenum
Overlies IVC, left and right renal veins and right renal artery.
Contains embedded bile duct
228 / 425

Has a projection from inferior part-the incanate process-that extends to the left
Neck:
Overlies superior mesenteric vessels
Is adjacent to pylorus of stomach
Superior mesenteric vein (SMV) joins splenic vein to form portal vein posterior to neck
Body
Crosses bodyof L2 and aorta
Lies in floor of omental bursa
Related anteriorlyto the stomach
Is in contact posteriorlywith aorta, superior mesenteric artery(SMA), left suprarenal gland, left kidney, and related vessels
Tail
Lies anterior to the left kidney
 Related to hilum of spleen and left colic flexure Main pancreatic duct
Related to hilum of spleen and left colic flexure Main pancreatic duct
Begins in the tail and runs towards the head
Turns inferiorlyto join common bile duct to form hepatopancreatic ampulla (of Vater)
Opens on major duodenal papilla in descending portion of duodenum
 Surrounded bythe sphincter of Oddi-smooth muscle Accessorypancreatic duct
Surrounded bythe sphincter of Oddi-smooth muscle Accessorypancreatic duct
Opens at summit of minor duodenal papilla
Can connect with main pancreatic duct (60% of time)
Can be main duct for pancreatic secretions
 Variation as a result of type of fusion or lack of fusion of dorsal and ventral pancreatic ducts during embryonic development Vascular supply(Section 4-6: Abdomen-Visceral Vasculature)
Variation as a result of type of fusion or lack of fusion of dorsal and ventral pancreatic ducts during embryonic development Vascular supply(Section 4-6: Abdomen-Visceral Vasculature)
Arteries
Mainlyfrom branches of splenic artery
Also from gastroduodenal, superior mesenteric, superior, and inferior pancreaticoduodenal arteries
Veins
Mainlydrain to splenic vein
Also drain to SMVand then portal vein
Lymph
Follow blood vessels
 Mainlydrain into the pancreaticosplenic nodes along splenic artery Nervous supply(Section 4-7: Abdomen-Innervation)
Mainlydrain into the pancreaticosplenic nodes along splenic artery Nervous supply(Section 4-7: Abdomen-Innervation)
From the vagus
From thoracic splanchnic nerves
Fibers from celiac and superior mesenteric plexuses pass along arteries
page 150
page 151
Spleen
Largest lymphatic organ, veryvascular Located in left upper quadrant (LUQ)
Related posteriorlywith ribs 9 to 11 (separated bydiaphragm) Covered byperitoneum except at the hilum
Surrounded bya thin capsule of fibroelastic connective tissue Relations:
Anterior: stomach (gastrosplenic ligament)
Posterior: diaphragm
Inferior: splenic flexure of colon
Medial: left kidney(splenorenal ligament)
 Tail of pancreas extends to hilum Ligamentous attachments
Tail of pancreas extends to hilum Ligamentous attachments
Gastrosplenic ligament to greater curvature of stomach
Splenorenal ligament to left kidney
Both ligaments attach to hilum
 Spleen sits on phrenicocolic ligament (sustentaculum lienis) Vascular supply(Section 4-6: Abdomen-Visceral Vasculature)
Spleen sits on phrenicocolic ligament (sustentaculum lienis) Vascular supply(Section 4-6: Abdomen-Visceral Vasculature)
Artery: splenic artery
Twisted course from origin at celiac trunk
Divides into five or more branches that enter at the hilum
Lack of anastomoses between branches results in two to three vascular segments with avascular planes in between.
Vein: splenic vein
Formed from several tributaries at the hilum
Runs to the right behind bodyand tail of pancreas
Joins the SMVto form the portal vein
 Lymph: drains to the pancreaticosplenic nodes Nervous supply(Section 4-7: Abdomen-Innervation)
Lymph: drains to the pancreaticosplenic nodes Nervous supply(Section 4-7: Abdomen-Innervation)
Derived from the celiac plexus
Travels along branches of splenic artery Vasomotor function
229 / 425
