
- •1. Topographic Surface Anatomy
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •3. Superficial Face
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •4. Neck
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •5. Nasal Region
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •6. Oral Region
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •7. Pharynx
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •13. Cerebral Vasculature
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •14. Topographic Anatomy
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •16. Spinal Cord
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Thorax
- •18. Topographic Anatomy
- •Guides
- •Facts & Hints
- •19. Mammary Gland
- •Guides
- •Facts & Hints
- •20. Body Wall
- •Guides
- •Facts & Hints
- •21. Lungs
- •Guides
- •Facts & Hints
- •22. Heart
- •Guides
- •Facts & Hints
- •23. Mediastinum
- •Guides
- •Facts & Hints
- •Abdomen
- •24. Topographic Anatomy
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •25. Body Wall
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •26. Peritoneal Cavity
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •27. Viscera (Gut)
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •28. Viscera (Accessory Organs)
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •29. Visceral Vasculature
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •30. Innervation
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •32. Topographic Anatomy
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •35. Urinary Bladder
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •39. Testis, Epididymis & Ductus Deferens
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •40. Rectum
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •41. Vasculature
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •42. Innervation
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Upper Limb
- •43. Topographic Anatomy
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •48. Neurovasculature
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Lower Limb
- •49. Topographic Anatomy
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •51. Knee
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •54. Neurovasculature
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints

FACTS & HINTS
High-Yield Facts
Clinical Points
page 184 page 185
The thickness of the endometrium (vascular mucosal lining) changes throughout the menstrual cycle, undergoing thickening and shedding. Following menopause the uterus and vagina undergo atrophy
Because the upper two thirds of the vagina lie within the pelvic cavity, weakness of the pelvic floor muscles can lead to vaginal prolapse. The lumen of fallopian tubes communicates with the peritoneal cavityat its distal (ovarian) end.
The ovaryis covered onlybya thin layer of mesothelium, an extension of the mesovarium, to permit ovulation of the mature ovum into the peritoneal cavity.
Ectopic pregnancies are therefore possible within the peritoneum.
Fertilization of an ovum usuallyoccurs within the fallopian tubes at the ampulla (the widest part)
Ectopic pregnancies-implantation of a blastocyst other than in the uterine wall-can occur in the uterine tube (tubal pregnancy-most common ectopic pregnancy), into the ovary(ovarian pregnancy-rare) or into the abdominal wall (peritoneal pregnancy-veryrare)
Blockage of the uterine tubes as the result of disease is a common cause of infertility
Clinical Points
Cervical Cancer
Common between age 40 and 60 years
Was the leading cause of death of women in the United States until 1940, when detection of malignancies and premalignant conditions was made possible bythe development of Pap (Papanicolaou) smears.
Risk factors include: earlysexual activity, multiple sexual partners, human papillomavirus infection, and smoking Eighty-five percent to 90% are squamous cell carcinomas; 10% to 15% are adenocarcinomas
Fibroids
Benign tumors of smooth muscle cells of uterine myometrium
Occur in 30% all women
Can occur in anylocation within the uterus
Growth stimulated byestrogen and oral contraceptive pill
Symptoms usuallya result of compression effects
290 / 425

37 Perineum and External Genitalia: Female
STUDYAIMS
At the end of your study, you should be able to:
Outline the general organization of the perineum
Describe the contents of the urogenital and anal triangles
Describe the central perineal tendon and perineal membrane
Outline the fascial layers and spaces of the perineum
Describe the anatomyof the clitoris, labia, and vestibule
Outline the blood supplyof the external genitalia
Outline the innervation of the female external genitalia
291 / 425
GUIDE
Pelvis and Perineum: Perineum and External Genitalia: Female
[Plate 356, Female Perineum and External Genitalia (Pudendum or Vulva)]
292 / 425
[Plate 358, Female Perineum and Deep Perineum]
293 / 425
[Plate 359, Female Perineal Spaces]
Perineum
General organization (Same as male)
Narrow region between superior medial aspects of thigh
With lower limbs abducted in lithotomyposition, becomes a diamond-shaped area
Bounded bypelvic diaphragm superiorlyand superficial fascia and skin inferiorly
Anal canal, urethra, and vagina pass through the perineum
Boundaries:
Anteriorly: Pubic symphysis
Posteriorly: Inferior sacrum and coccyx
Anterolaterally: Ischiopubic rami
Laterally: Ischial tuberosities
Posterolaterally: Sacrotuberous ligaments
Divided into two triangles byimaginaryline between ischial tuberosities
Posteriorlyis anal triangle
Anteriorlyis urogenital triangle
Contents of the anal triangle (Same as male)
Anal canal and anus
External and internal anal sphincters
Ischiorectal fossa
Contents of urogenital triangle
Membranous and distal urethra
Vagina
Vulva (labia majora, labia minora, and clitoris)
Erectile bodies of vulva
page 186
294 / 425

page 187
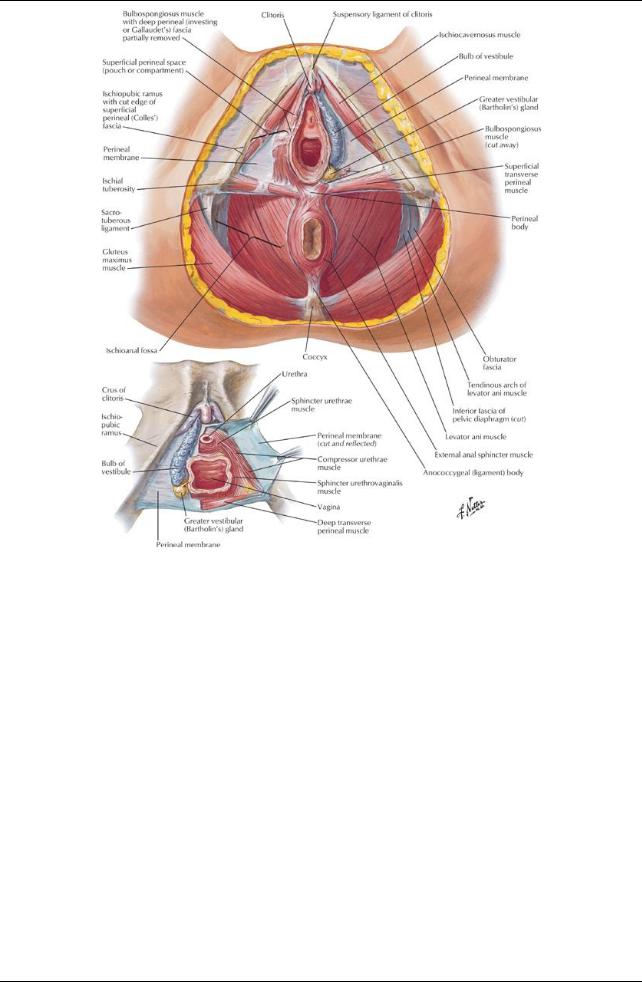
Central perineal tendon (perineal body) (Same as male)
Located at midpoint of the line dividing the urogenital from anal triangles
Mass of collagenous and elastic fibers
Deep to skin
Anterior to anal canal
Posterior to bulb of the penis (male) or vestibule (female)
Site of attachment for
Bulbospongiosus
Superficial transverse perineal muscles
Deep transverse perineal muscles
External anal sphincter
Fascicles of muscle from external sphincter urethrae and levator ani
Perineal membrane
Everything same as male, except
Sphincter urethrae (external urethral sphincter)
Mayexist in females
 Some fibers extending to the ischiopubic rami (compressor urethrae) and some encircling the vagina as well Pierced byvagina and urethra
Some fibers extending to the ischiopubic rami (compressor urethrae) and some encircling the vagina as well Pierced byvagina and urethra
Fascia and spaces of the urogenital triangle
Everything same as male, except
Superficial perineal space (pouch)
Between membranous layer of superficial fascia and perineal membrane
Contains:
Crura of clitoris and associated muscles
Bulbs of vestibule and associated muscles
Superficial transverse perineal muscles
Branches of internal pudendal vessels and pudendal nerves
Greater vestibular glands
Deep perineal space (pouch)
Lies between perineal membrane and pelvic diaphragm
Ischioanal fossae extend anteriorlyinto this space
Contains:
Proximal part of urethra
External sphincter urethrae muscle
Deep transverse perineal muscles
Vessels and nerves
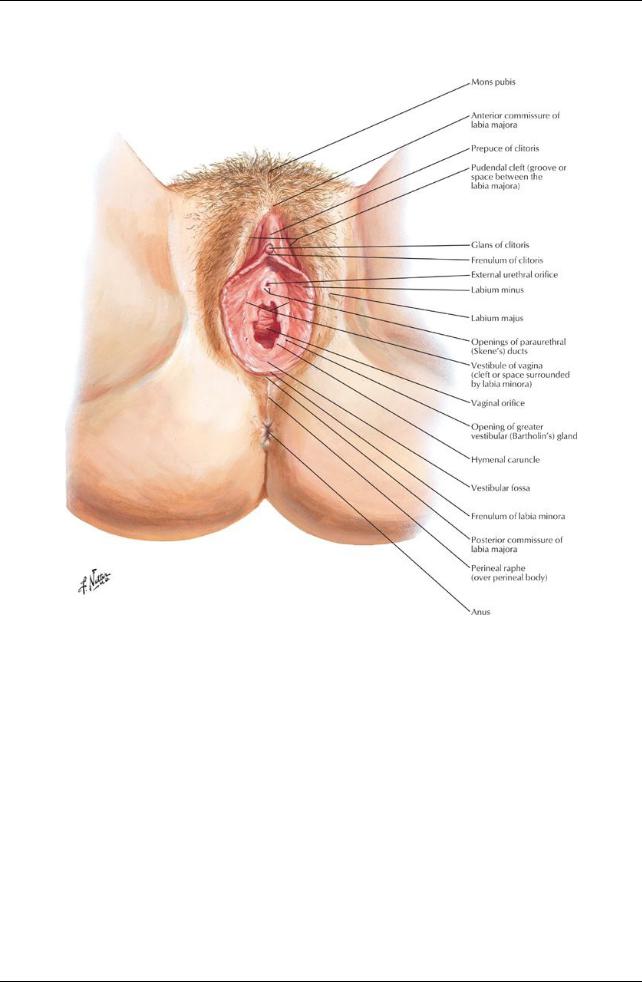
Female External Genitalia
Anatomical features
page 187 page 188
Female external genitalia collectivelycalled the vulva
Female external genitalia include
Mons pubis
Labia majora
Labia minora
Clitoris
Vestibule of vagina
Bulbs of vestibule
Greater vestibular glands
Mons pubis
Fattytissue lying anterior to pubic symphysis and superior pubic rami
Skin continuous with anterior abdominal wall
After pubertyis covered with pubic hair
Labia majora
Longitudinal folds of skin containing fat, smooth muscle, and termination of round ligament of uterus
Lie on either side of pudendal cleft
Externallycontain sebaceous glands and are covered bypubic hair
Internallyare smooth and hairless
Unite anteriorlyas the anterior commissure
Form a posterior commissure posteriorly, which disappears after childbirth
Labia minora
Longitudinal folds of hairless skin without fat enclosed bylabia majora
Surrounds vestibule of vagina
Extend from clitoris around urethra and vagina
Meet anteriorlyas a small fold = frenulum of the clitoris, which passes deep to the clitoris
Posteriorlyunite as frenulum (fourchette)
Vestibule
Region enclosed bylabia minora
295 / 425

Contains external urethral meatus, vaginal introitus (most inferior opening) and opening of ducts of paraurethral gland
Contains opening of ducts of greater vestibular (Bartholin's) glands One gland on either side of vestibule
Posterior to vaginal orifice
Ductal openings either side of vagina; secrete mucus during sexual arousal Contains bulbs of vestibule
Elongated masses of erectile tissue One on either side of vaginal introitus
Homologous to bulb of penis and corpus spongiosum
Clitoris
Resembles inverted 'V'
Composed of root and body, located where labia minora meet anteriorly
Lies 2 cm anterior to external urethral meatus
Bodycomposed of two crura, two corpora cavernosa, and glans clitoris
Highlyinnervated, becomes engorged during sexual arousal Prepuce of clitoris-anterior extension of labia minora
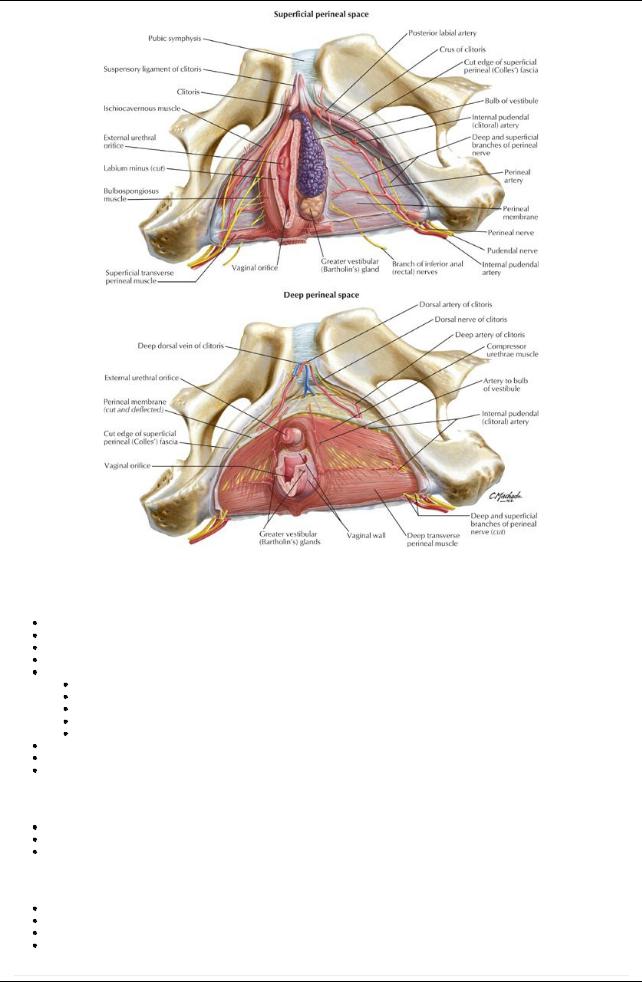
Vascular supply and innervation
[Plate 393, Nerves of Perineum and External Genitalia: Female]
Arterial supply
External pudendal arteries (branches of femoral artery)
Internal pudendal arteries
Labial and clitoral branches of internal pudendal artery
Venous drainage
Internal pudendal vein
Venae comitantes of internal pudendal artery
Lymphatic drainage
To superficial inguinal nodes
page 188
page 189
Innervation
296 / 425

Anterior labial nerves from ilioinguinal nerve
Perineal branch from posterior femoral cutaneous nerve
Posterior labial nerves from pudendal nerve
297 / 425
