
- •1. Topographic Surface Anatomy
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •3. Superficial Face
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •4. Neck
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •5. Nasal Region
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •6. Oral Region
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •7. Pharynx
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •13. Cerebral Vasculature
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •14. Topographic Anatomy
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •16. Spinal Cord
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Thorax
- •18. Topographic Anatomy
- •Guides
- •Facts & Hints
- •19. Mammary Gland
- •Guides
- •Facts & Hints
- •20. Body Wall
- •Guides
- •Facts & Hints
- •21. Lungs
- •Guides
- •Facts & Hints
- •22. Heart
- •Guides
- •Facts & Hints
- •23. Mediastinum
- •Guides
- •Facts & Hints
- •Abdomen
- •24. Topographic Anatomy
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •25. Body Wall
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •26. Peritoneal Cavity
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •27. Viscera (Gut)
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •28. Viscera (Accessory Organs)
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •29. Visceral Vasculature
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •30. Innervation
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •32. Topographic Anatomy
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •35. Urinary Bladder
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •39. Testis, Epididymis & Ductus Deferens
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •40. Rectum
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •41. Vasculature
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •42. Innervation
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Upper Limb
- •43. Topographic Anatomy
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •48. Neurovasculature
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Lower Limb
- •49. Topographic Anatomy
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •51. Knee
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •54. Neurovasculature
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints

23 Mediastinum
STUDYAIMS
At the end of your study, you should be able to:
Identifythe mediastinum
Identifythe major arteries and veins of the mediastinum
Identifythe trachea
Identifythe esophagus
174 / 425
GUIDES
Thorax: Mediastinum
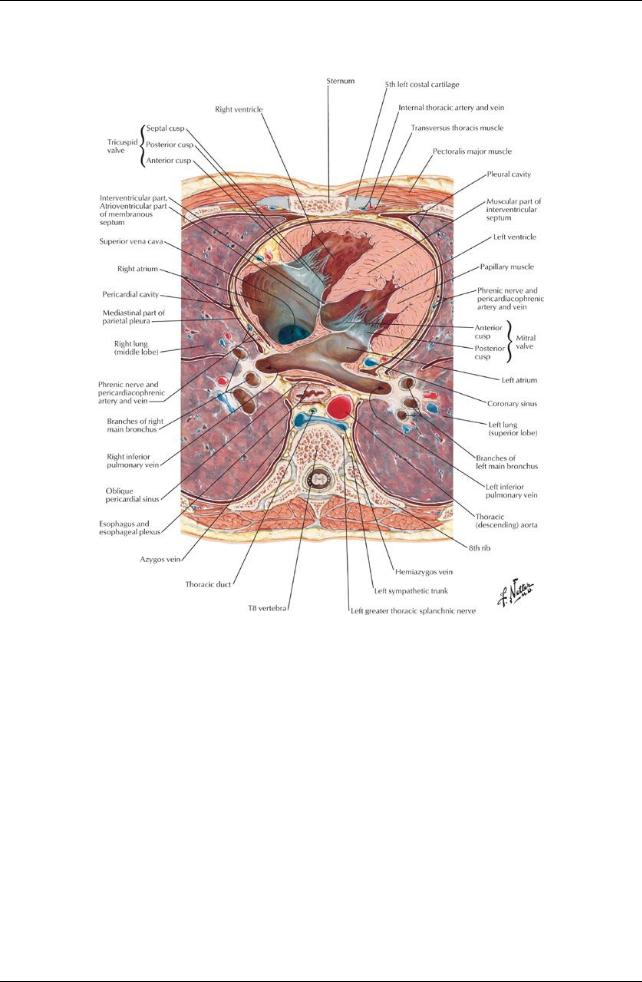
[Plate 210, Mediastinum: Cross Section]
175 / 425
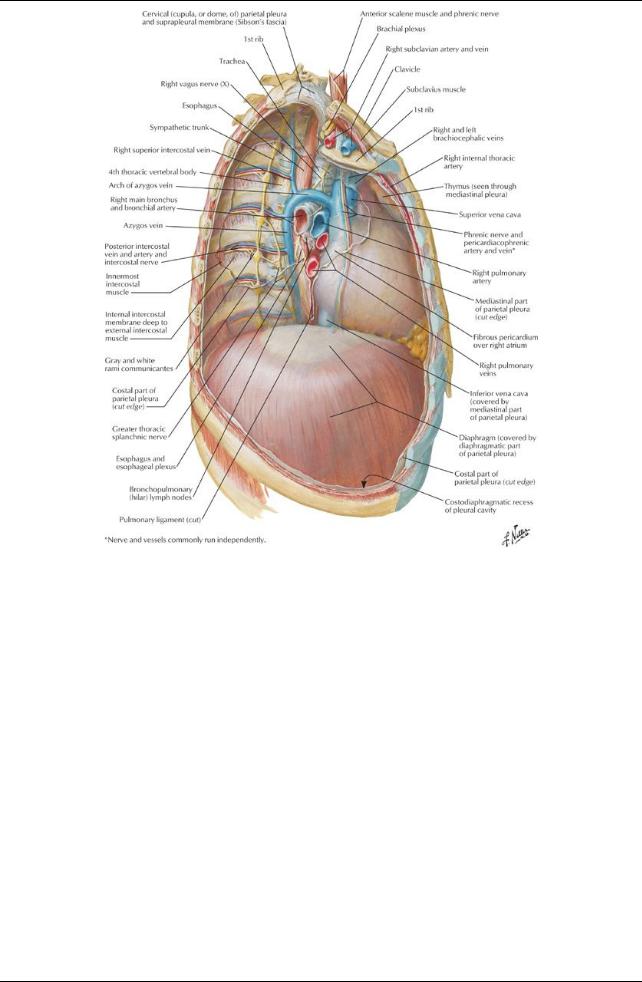
[Plate 224, Mediastinum: Right Lateral View]
176 / 425

[Plate 225, Mediastinum: Left Lateral View]
General Description
page 118
page 119 page 119
page 120 page 120
page 121
The mediastinum is the central compartment of the thoraxbetween the two pleural cavities.
Stretches from the thoracic inlet to the diaphragm and from the sternum to the bodies of the thoracic vertebrae posteriorly. Its contents include the heart, trachea, esophagus, great vessels of the heart, lymph nodes, nerves, and fat.
The mediastinum is divided into two parts:
The superior part extends from the thoracic inlet to a plane at the level of the sternal angle and the T4/5 intervertebral disc
 The inferior mediastinum extends from this plane to the diaphragm. Superior mediastinum contains the
The inferior mediastinum extends from this plane to the diaphragm. Superior mediastinum contains the
superior vena cava
arch of the aorta and its branches
trachea
phrenic nerves
thoracic duct
esophagus
vagus nerves
left recurrent laryngeal nerve
thymus
Inferior mediastinum is subdivided into
anterior mediastinum
middle mediastinum
posterior mediastinum
The anterior mediastinum contains fat and the remnants of the thymus gland
The middle mediastinum contains the heart surrounded bythe pericardium and the roots of the great vessels. The great vessels are:
ascending aorta
superior vena cava
pulmonarytrunk
The posterior mediastinum contains
177 / 425

esophagus and the esophageal plexus descending aorta
thoracic duct tracheobronchial lymph nodes azygos and hemiazygos veins thoracic sympathetic trunks thoracic splanchnic nerves
Structures in the Mediastinum a. Thymus gland
plays a central role in the development of the immune system
lies posterior to the manubrium
receives blood from the internal thoracic and anterior intercostal arteries is graduallyreplace byadipose tissue after puberty
b.Heart and pericardial sac (Section 3-5: Thorax-Heart)
c.Superior vena cava
Formed bythe union of two brachiocephalic veins
Returns blood to the heart from all structures above the diaphragm except the heart and lungs
Descends verticallyand terminates in the right atrium
Lies to the right of the ascending aorta and to the left of the right phrenic nerve
 Receives azygous veins before piercing fibrous pericardium d. Brachiocephalic veins
Receives azygous veins before piercing fibrous pericardium d. Brachiocephalic veins
Are formed in the root of the neck posterior to the sternoclavicular joints byunion of the internal jugular and subclavian veins.
Right brachiocephalic vein
receives lymph from the right lymph duct.
is accompanied byright phrenic vein.
Left brachiocephalic vein
is twice as long as the right
runs obliquelydown and behind the manubrium
crosses the roots of the three major branches of the aorta
receives lymph from the thoracic duct
e. Aorta
Ascending
begins at the aortic orifice
ascends to the 2nd right sternocostal joint
Arch
Begins at the 2nd right sternocostal joint and arches superiorlyand to the left
Anterior to the right pulmonaryarteryand bifurcation of the trachea
Passes over the root of the right lung
Ends at the bodyof the T4 vertebra
Descending (thoracic)
begins at the bodyof T4 vertebra
descends on the left side of the bodies of T5-12 vertebrae, posterior to the root of the left lung and the pericardium
enters the abdomen through the aortic hiatus at the T12 vertebral body
has a number of branches:
bronchial (1-2)
pericardial (twigs)
superior phrenic (1 pair)
esophageal (2)
posterior intercostal (9 pairs)
subcostal (1 pair)
f. Trachea
Continues from the larynx
Contains cartilaginous semicircular rings
Is completed bymuscle posteriorly
Descends anterior to the esophagus, slightlyto the right of the midsagittal plane
Bifurcates into right and left main bronchi at level of T4/T5 (angle of Louis)
 Right bronchi divides into upper and lower lobar bronchi before entering the right lung g. Esophagus
Right bronchi divides into upper and lower lobar bronchi before entering the right lung g. Esophagus
Is a fibromuscular tube from the pharynxto the stomach
Contains both circular and longitudinal muscles, both skeletal and smooth
upper 1/3-skeletal muscle
lower 2/3-smooth muscle
Passes through right crus of diaphragm at T10
Continues for 1-2 cm below diaphragm
Supplied byesophageal plexus of nerves derived from
right and left vagal nerves
sympathetic nerves
Surrounded bya number of lymph nodes:
inferior deep cervical nodes
posterior mediastinal nodes
intercostal nodes
paratracheal nodes
superior and inferior tracheobronchial nodes.
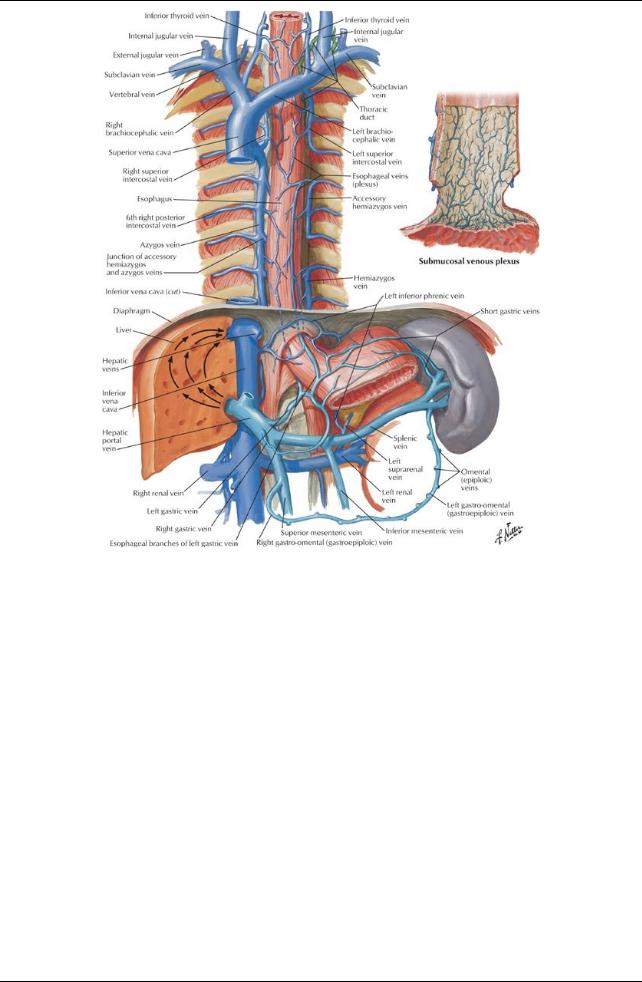
Vascular supply
 arterial: esophageal branches of the thoracic aorta venous: azygos, hemiazygos and accessoryazygos veins h. Thoracic duct
arterial: esophageal branches of the thoracic aorta venous: azygos, hemiazygos and accessoryazygos veins h. Thoracic duct
Originates from the cisterna chili in the abdomen Contains valves
178 / 425

Ascends through the aortic hiatus in the diaphragm
Lies anterior to the bodies of T6-12 vertebral bodies, between the thoracic aorta and the azygos vein
Conveys lymph from the limbs, pelvic and abdominal cavities, left side of the thorax, left upper limb and left side of the head and neck
 Empties into the venous system at the junction of the left internal jugular and left subclavian veins i. Azygos venous system
Empties into the venous system at the junction of the left internal jugular and left subclavian veins i. Azygos venous system
Drains blood from the back and thoracoabdominal walls
Is highlyvariable
Is composed of an unpaired azygos vein and its main tributary, the hemiazygos vein.
Offers an alternate route for blood to reach the heart if the inferior vena cava is blocked
Azygos vein
arises from ascending lumbar and/or renal veins and subcostal veins
ascends on the right side of the bodies of T5-T12 vertebrae
arches over the root of the right lung to join the superior vena cava
receives blood from
hemiazygos vein
posterior intercostals veins
esophageal veins
bronchial veins
communications with the vertebral venous plexus
Hemiazygos vein
arises from the left subcostal and ascending lumbar veins
ascends on the left side of the vertebral column from T12-T9
crosses the T9 vertebrae posterior to the aorta, esophagus and thoracic duct to emptyinto the azygos vein
receives blood from
inferior three posterior intercostals
inferior esophageal veins
accessoryhemiazygos (occasionally)
Accessoryhemiazygos vein
begins at the 4th or 5th intercostal space on the left
descends on the left side of vertebrae T5-T8
crosses over T7 or T8 vertebrae to join the azygos
sometimes joins the hemiazygos
receives blood from
posterior intercostal veins from the 4th through 8th intercostal spaces

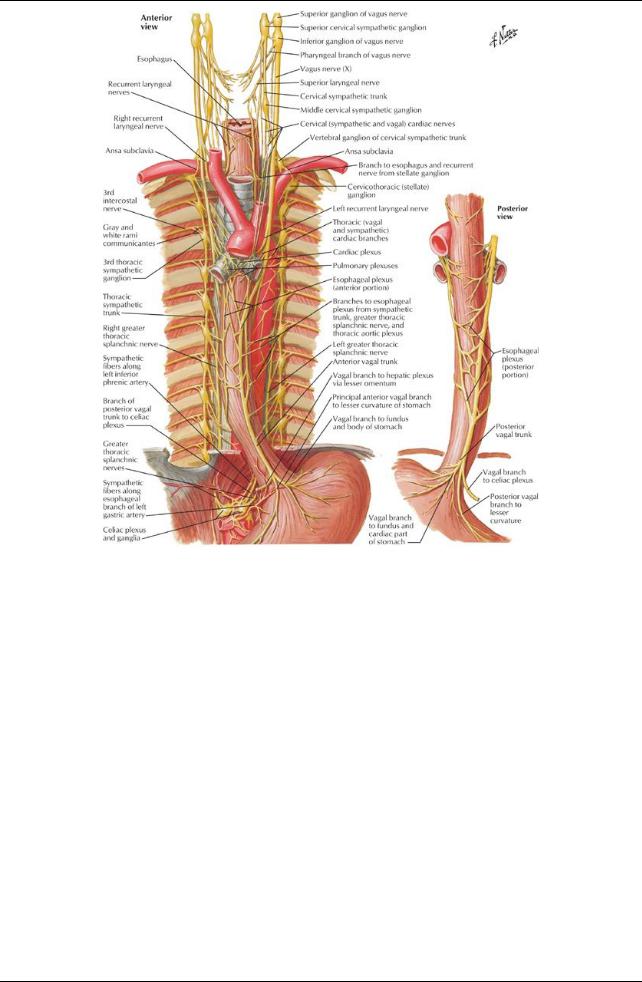
 left superior intercostal vein (occasionally) j. Vagus nerves and recurrent laryngeal nerves
left superior intercostal vein (occasionally) j. Vagus nerves and recurrent laryngeal nerves
The right vagus nerve
enters the thoraxanterior to the right subclavian arteryand immediatelygives rise to the right recurrent laryngeal nerve, which loops around the right subclavian arteryand ascends into the neck
descends on the right side of the trachea
passes posterior to the right brachiocephalic vein, superior vena cava and root of the right lung
gives rise to branches of the right pulmonaryplexus
continues to the esophagus, where it contributes to the esophageal nerve plexus and continues as the anterior vagal trunk into the abdomen
The left vagus nerve
enters the mediastinum between the left common carotid and left subclavian arteries
descends with the left phrenic nerve to the aortic arch
gives off the left recurrent laryngeal nerve just below the arch, which loops around the arch and ascends into the neck
passes posterior to the root of the left lung where it contributes to the left pulmonaryplexus
continues as a single nerve to the esophagus where it contributes to the esophageal nerve plexus and continues as the posterior vagal trunk into the abdomen
k. Phrenic nerves
Supplymotor and sensoryfibers to the diaphragm
Enter the superior mediastinum between the subclavian arteryand brachiocephalic vein on either side
Pass anterior to the roots of the lungs, unlike the vagus nerve
The right phrenic nerve descends on the right side of the inferior vena cava to the diaphragm
The left phrenic nerve
crosses the arch of the aorta
descends anterior to the root of the left lung and along the pericardium over the left atrium and ventricle pierces the diaphragm to the left of the pericardium
1. Thoracic sympathetic trunks
Are continuous with the cervical and lumbar sympathetic trunks
Shift mediallyas theydescend, crossing from the heads of the ribs to the costovertebral joints to the sides of the vertebral bodies
Give off the paired thoracic splanchnic nerves
greater splanchnic: from T5-T9 vertebral levels
lesser splanchnic: from T10-T11 vertebral levels least splanchnic: from T12 vertebral level
179 / 425
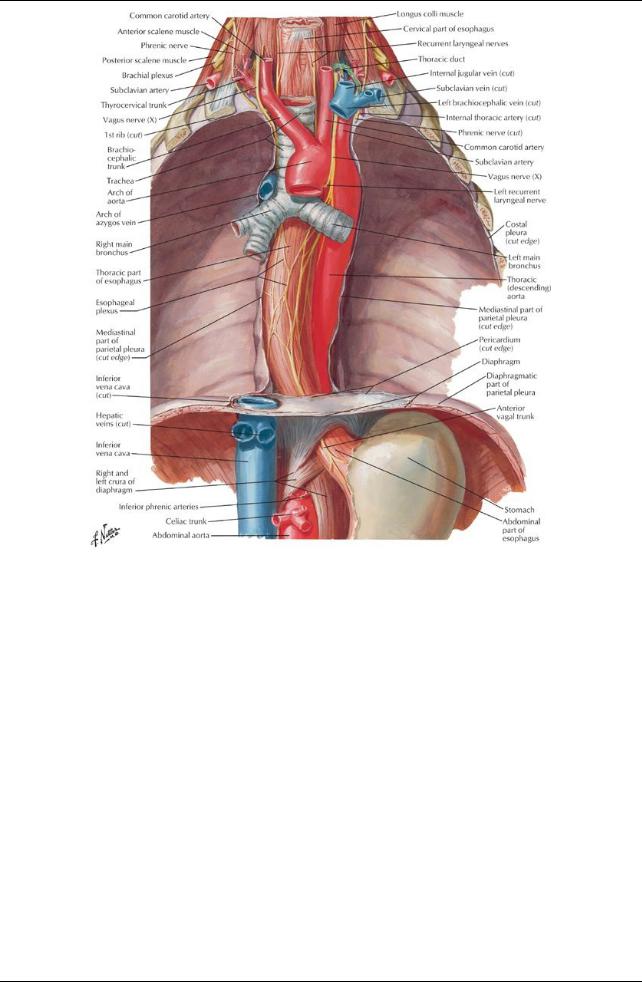
[Plate 226, Esophagus In Situ]
180 / 425
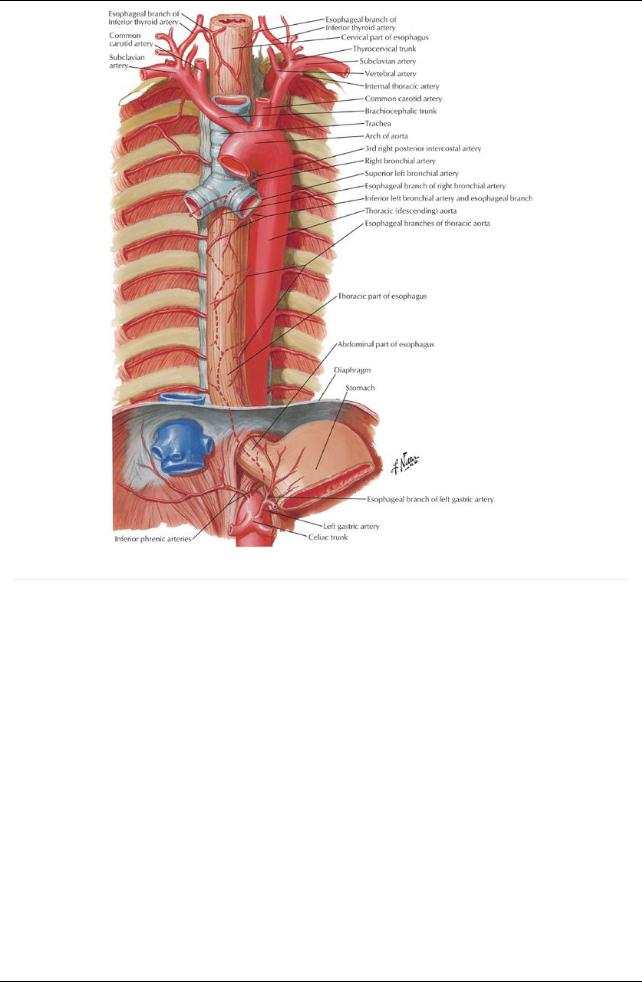
[Plate 231, Arteries of Esophagus]
page 121
page 122
181 / 425
[Plate 232, Veins of Esophagus]
182 / 425
[Plate 234, Nerves of Esophagus]
183 / 425
