
- •1. Topographic Surface Anatomy
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •3. Superficial Face
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •4. Neck
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •5. Nasal Region
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •6. Oral Region
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •7. Pharynx
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •13. Cerebral Vasculature
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •14. Topographic Anatomy
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •16. Spinal Cord
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Thorax
- •18. Topographic Anatomy
- •Guides
- •Facts & Hints
- •19. Mammary Gland
- •Guides
- •Facts & Hints
- •20. Body Wall
- •Guides
- •Facts & Hints
- •21. Lungs
- •Guides
- •Facts & Hints
- •22. Heart
- •Guides
- •Facts & Hints
- •23. Mediastinum
- •Guides
- •Facts & Hints
- •Abdomen
- •24. Topographic Anatomy
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •25. Body Wall
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •26. Peritoneal Cavity
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •27. Viscera (Gut)
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •28. Viscera (Accessory Organs)
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •29. Visceral Vasculature
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •30. Innervation
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •32. Topographic Anatomy
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •35. Urinary Bladder
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •39. Testis, Epididymis & Ductus Deferens
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •40. Rectum
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •41. Vasculature
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •42. Innervation
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Upper Limb
- •43. Topographic Anatomy
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •48. Neurovasculature
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Lower Limb
- •49. Topographic Anatomy
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •51. Knee
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •54. Neurovasculature
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints

54 Neurovasculature
STUDYAIMS
At the end of your study, you should be able to:
Describe the arterial supplyof the lower limb, distinguishing the arteries supplying each of the compartments of the thigh and leg
Know the surface markings to locate the femoral arteryand palpate the pulses of the popliteal, posterior tibial, and dorsalis pedis arteries Describe the venous drainage of the lower limb
Describe the lymphatic drainage of the lower limb
Know the nervous innervation to the compartments of the thigh and leg and recognize the course of the major nerves of the lower limb Understand the dermatome and myotome maps of the lower limb
418 / 425

GUIDE
Lower Limb: Neurovasculature
Vascular Supply: Arteries
[Plate 490, Arteries and Nerves of Thigh: Posterior View]
419 / 425
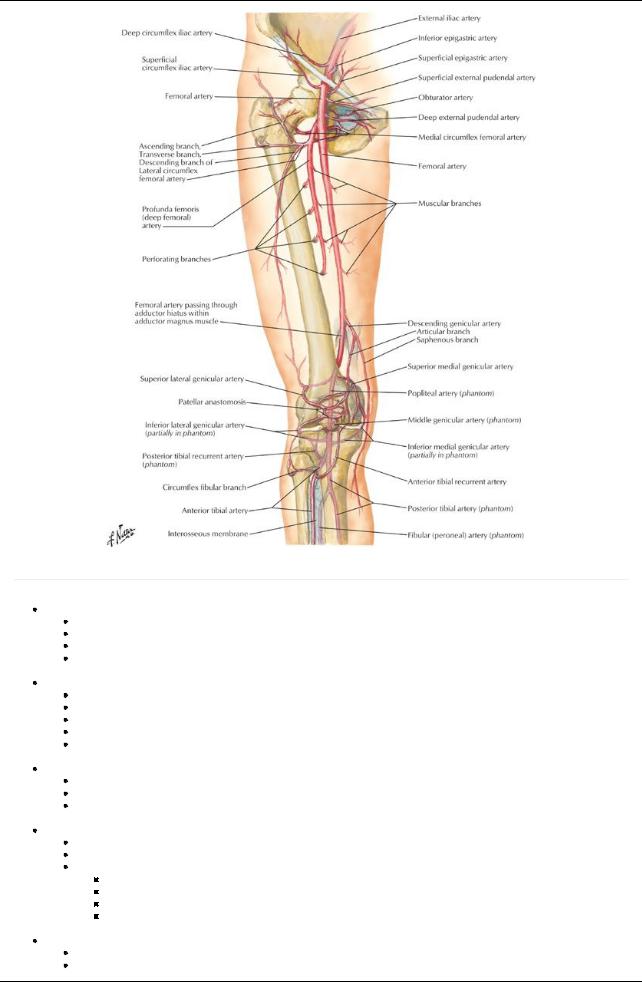
[Plate 500, Arteries of Thigh and Knee: Schema]
page 270 page 271
Femoral artery
Continuation of the external iliac artery
Main arteryof lower limb
Palpable inferior to the midinguinal point, not at the midpoint of the inguinal ligament
Descends in femoral triangle on iliopsoas and pectineus, lateral to femoral vein
 Enters adductor canal deep to sartorius and exits at adductor hiatus Profunda femoris (deep arteryof thigh)
Enters adductor canal deep to sartorius and exits at adductor hiatus Profunda femoris (deep arteryof thigh)
Main arteryto the thigh
Largest branch of femoral
Arises from lateral aspect of femoral in femoral triangle
Supplies anterior and medial (adductor) compartments of the thigh
Supplies posterior compartment byperforating arteries
 Gives off medial and lateral circumflexfemoral arteries that supplythe head of the femur and muscles of lateral thigh Obturator artery
Gives off medial and lateral circumflexfemoral arteries that supplythe head of the femur and muscles of lateral thigh Obturator artery
Branch of the internal iliac artery(or may arise from the inferior epigastric)
Enters thigh through obturator foramen
Divides into anterior and posterior branches
 Supplies adductor compartment of the thigh along with profunda femoris Popliteal artery
Supplies adductor compartment of the thigh along with profunda femoris Popliteal artery
Continuation of the femoral artery(at adductor hiatus)
Palpable in the popliteal fossa (best felt when knee is flexed)
Gives off five genicular branches supplying articular capsule and ligaments of knee joint
Medial and lateral superior genicular
Middle genicular
Medial and lateral inferior genicular
Form anastomosis around knee joint
 Bifurcates into anterior and posterior tibial arteries Anterior tibial artery
Bifurcates into anterior and posterior tibial arteries Anterior tibial artery
Smaller of two terminal branches of popliteal Passes through gap in interosseous membrane
420 / 425

Supplies muscles of anterior compartment of the leg
Descends on interosseous membrane and becomes dorsalis pedis artery
Posterior tibial artery
Larger of two terminal branches of popliteal
Supplies muscles of posterior compartment
Gives off fibular artery
Descends deep to soleus
Provides main blood supplyto foot, after passing inferior to medial malleolus
Palpable behind the medial malleolus
Gives off nutrient arteryto the tibia
Circumflexfibular artery
Arises from origin of anterior or posterior tibial
Passes over neck of fibula to anastomosis around knee
Fibular artery
Largest branch of posterior tibial
Supplies muscles of lateral compartment of the leg
Begins below tendinous arch of soleus
Gives off nutrient arteryto the fibula
Pierces interosseous membrane to reach dorsum of foot
Dorsalis pedis
Continuation of the anterior tibial artery
Palpable between the first and second metatarsal heads
Divides into plantar and arcuate arteries
Supplies muscles on dorsum of foot
Pierces first dorsal interosseous muscle as deep plantar arteryof foot (plantar arterial arch)
Medial plantar artery
Smaller of two terminal branches of posterior tibial artery
Supplies muscles of great toe, skin on medial side of sole
Gives off plantar digital arteries
Lateral plantar artery
Larger than medial
Accompanies lateral plantar nerve
Arches mediallyacross foot, beginning at base of fifth metatarsal as deep plantar arch
Gives off four plantar metatarsal arteries
Joins branches of medial plantar to form plantar digital arteries to toes
Vascular Supply: Veins
page 271
page 272
Lower limb has superficial and deep venous systems with perforating veins communicating between them
Veins have valves
Veins of foot
Superficial
Metatarsal veins merge to form dorsal venous arch
Communicates with plantar arch
Both drain mediallyto great saphenous vein and laterallyto small saphenous vein
Deep
Begin as dorsal digital and plantar digital veins
Merge to deep veins accompanying arteries in leg and thigh
Superficial veins of leg and thigh
Great saphenous vein
Courses along medial side of dorsum of the foot
Passes in front of medial malleolus (location for venous cut down for emergency IV access here)
Anastomoses freelywith small saphenous vein
Ascends medial side of leg, then posterior to the knee
Ascends along medial thigh to saphenous hiatus in fascia lata
Traverses hiatus to emptyinto femoral vein
Has manyvalves
Small saphenous vein
Runs behind the lateral malleolus
Ascends along lateral border of calcaneal tendon
Pierces the deep fascia
Ascends between heads of gastrocnemius
Empties into popliteal vein
Accompanied bythe sural nerve
Deep veins of leg and thigh
Accompanyall major arteries (venae comitantes)
Are usuallypaired
Are variable and anastomose freely
Unite to form the popliteal vein and ascend as femoral vein
Perforating veins
Penetrate deep fascia
Connect superficial and deep veins
Have valves
Lymphatics
421 / 425
Superficial lymphatics follow the superficial veins
Lymphatics following the great saphenous drain into superficial inguinal nodes
Lymphatics following the small saphenous vein drain into popliteal nodes
Deep lymphatics
Follow vasculature in the muscle compartments
Drain to deep inguinal nodes
Popliteal nodes drain into the deep inguinal nodes
Nerves
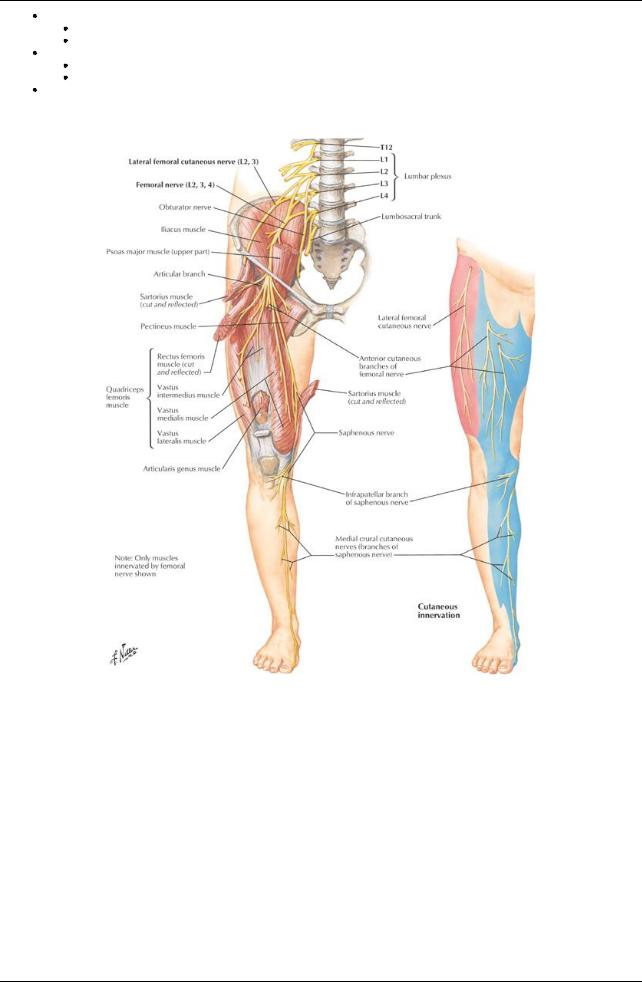
[Plate 526, Femoral Nerve and Lateral Cutaneous Nerve of Thigh]
422 / 425
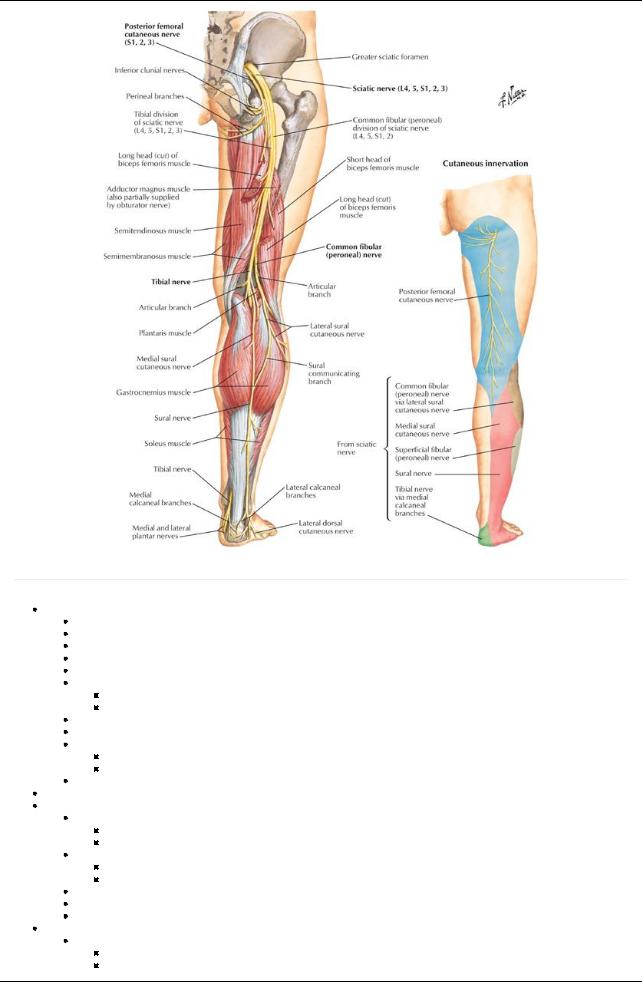
[Plate 528, Sciatic Nerve and Posterior Femoral Cutaneous Nerve]
page 272 page 273
Cutaneous nerves
Subcostal nerve (T12) to skin anterior to greater trochanter
Iliohypogastric nerve (L1) to superior lateral buttock
Ilioinguinal (L1) to proximal and medial thigh
Genitofemoral nerve (L2-L3) to immediatelyinferior to middle inguinal ligament
Lateral femoral cutaneous ((L2-L3) to lateral and anterior thigh
Femoral nerve (L2-L4)
Via anterior femoral cutaneous branches to anterior and medial thigh
Via saphenous nerve to medial side of leg and foot
Obturator nerve-branch to anterior, medial and posterior proximal thigh
Posterior femoral cutaneous nerve-to posterior thigh and popliteal region
Sciatic nerve
Supplies foot and most of leg
Via sural, common, superficial, and deep fibular nerves
Cluneal nerves (superior middle and inferior)-buttock
Nerves to muscles of lower limb from lumbosacral plexus
Nerves in the gluteal region
Superior gluteal nerve (L4-S1)
Emerges superior to piriformis
Supplies gluteus medius, gluteus minimus and tensor fasciae latae
Inferior gluteal nerve (L5-S2)
Inferior to piriformis
Supplies gluteus maximus
Nerve to quadratus femoris (L4-S1): also supplies inferior gemellus
Pudendal nerve (S2-S4): supplies the perineum (not structures in the gluteal region)
Nerve to obturator internus (L5-S2)
Nerves to anterior and lateral thigh
Femoral nerve (L2-L4)
Enters thigh lateral and deep to femoral artery
Supplies the anterior compartment of the thigh
423 / 425

Obturator nerve (L2-L4)
Enters thigh through obturator foramen and divides into anterior and posterior branches
Supplies medial (adductor) compartment of thigh
Nerves of posterior thigh
Sciatic nerve (L5-S2)
Enters gluteal region from pelvis through greater sciatic foramen
Emerges inferior to the piriformis muscle
Supplies no structures in the gluteal region
Supplies posterior thigh muscles
Bifurcates in lower third of thigh into tibial and common fibular nerves
Via tibial and common fibular nerves, supplies all leg and foot muscles
Nerves of leg
Tibial nerve
Supplies the posterior compartment of leg
Ends bydividing into medial and lateral planter nerves
Common fibular nerve
Wraps around fibular head
Divides into deep and superficial peroneal nerves
Deep fibular nerve supplies anterior compartment of leg
Superficial fibular nerve supplies lateral compartment of leg
Nerves of foot
Medial plantar to 3½ muscles of plantar foot
Lateral plantar to remaining muscle of plantar foot
Dermatomes
Myotomes
Agroup of muscles supplied byfibers from a single spinal nerve or a discrete group of spinal nerves is called a myotome
Myotomes of the Lower Limb
|
|
L2 |
L3 |
L4 |
L5 |
S1 |
S2 |
Hip |
Flexion |
X |
X |
|
|
|
|
|
Extension |
|
|
X |
X |
|
|
Knee |
Extension |
|
X |
X |
|
|
|
|
Flexion |
|
|
|
X |
X |
|
Ankle |
Dorsiflexion |
|
|
X |
X |
|
|
|
Plantarflexion |
|
|
|
|
X |
X |
Foot |
Inversion |
|
|
X |
X |
|
|
|
Eversion |
|
|
|
X |
X |
|
|
Intrinsic |
|
|
|
|
|
X |
424 / 425
