
- •1. Topographic Surface Anatomy
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •3. Superficial Face
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •4. Neck
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •5. Nasal Region
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •6. Oral Region
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •7. Pharynx
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •13. Cerebral Vasculature
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •14. Topographic Anatomy
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •16. Spinal Cord
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Thorax
- •18. Topographic Anatomy
- •Guides
- •Facts & Hints
- •19. Mammary Gland
- •Guides
- •Facts & Hints
- •20. Body Wall
- •Guides
- •Facts & Hints
- •21. Lungs
- •Guides
- •Facts & Hints
- •22. Heart
- •Guides
- •Facts & Hints
- •23. Mediastinum
- •Guides
- •Facts & Hints
- •Abdomen
- •24. Topographic Anatomy
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •25. Body Wall
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •26. Peritoneal Cavity
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •27. Viscera (Gut)
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •28. Viscera (Accessory Organs)
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •29. Visceral Vasculature
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •30. Innervation
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •32. Topographic Anatomy
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •35. Urinary Bladder
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •39. Testis, Epididymis & Ductus Deferens
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •40. Rectum
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •41. Vasculature
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •42. Innervation
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Upper Limb
- •43. Topographic Anatomy
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •48. Neurovasculature
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Lower Limb
- •49. Topographic Anatomy
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •51. Knee
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •54. Neurovasculature
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
GUIDE
Upper Limb: Shoulder and Axilla
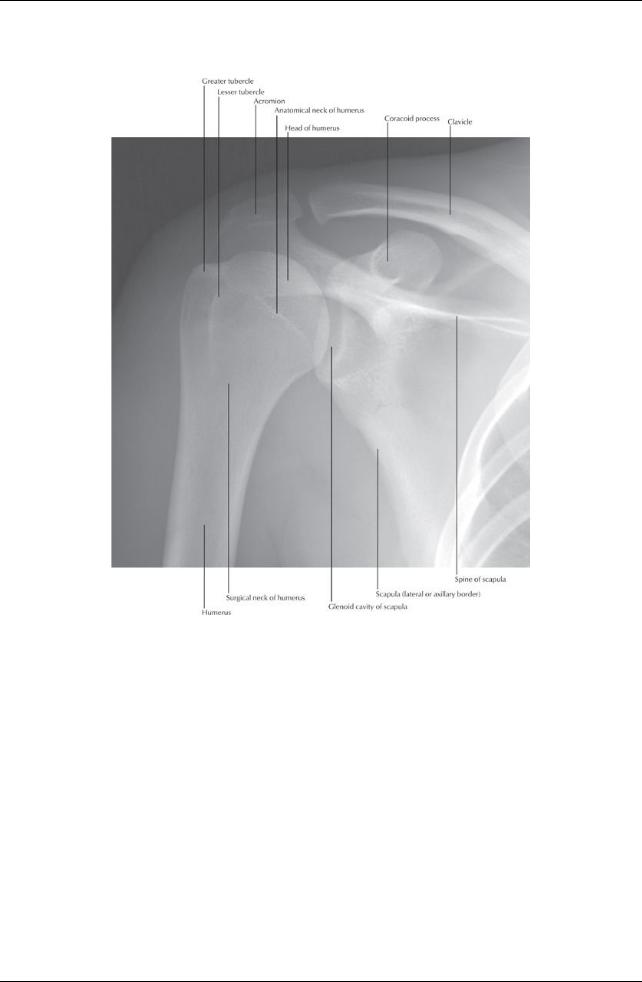
[Plate 409, Shoulder: Anteroposterior Radiograph]
330 / 425
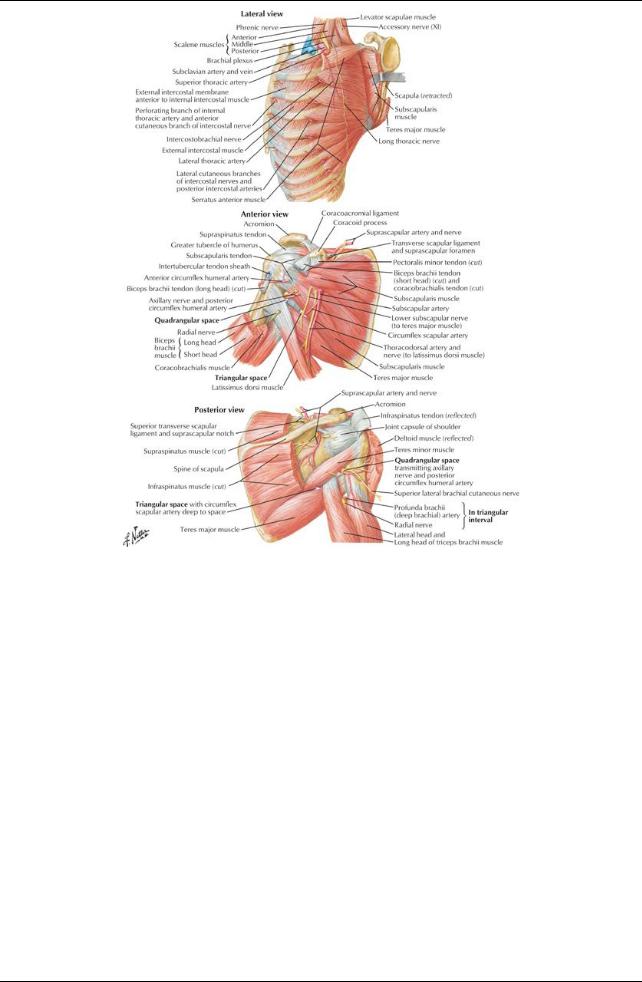
[Plate 414, Scapulothoracic and Scapulohumeral Dissection]
331 / 425

[Plate 416, Pectoral, Clavipectoral, and Axillary Fasciase]
332 / 425
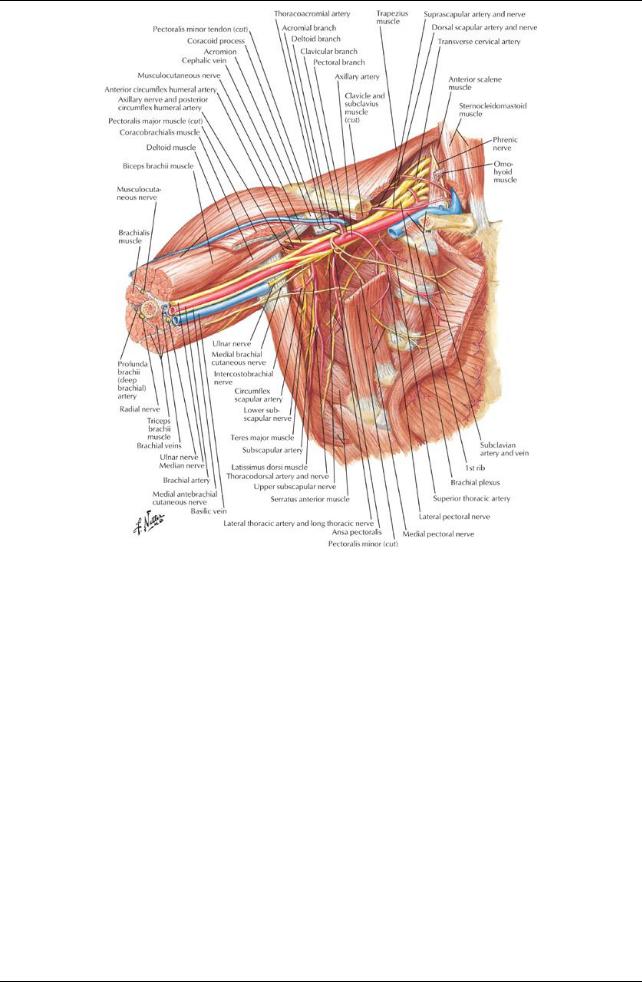
[Plate 417, Axilla (Dissection): Anterior View]
333 / 425
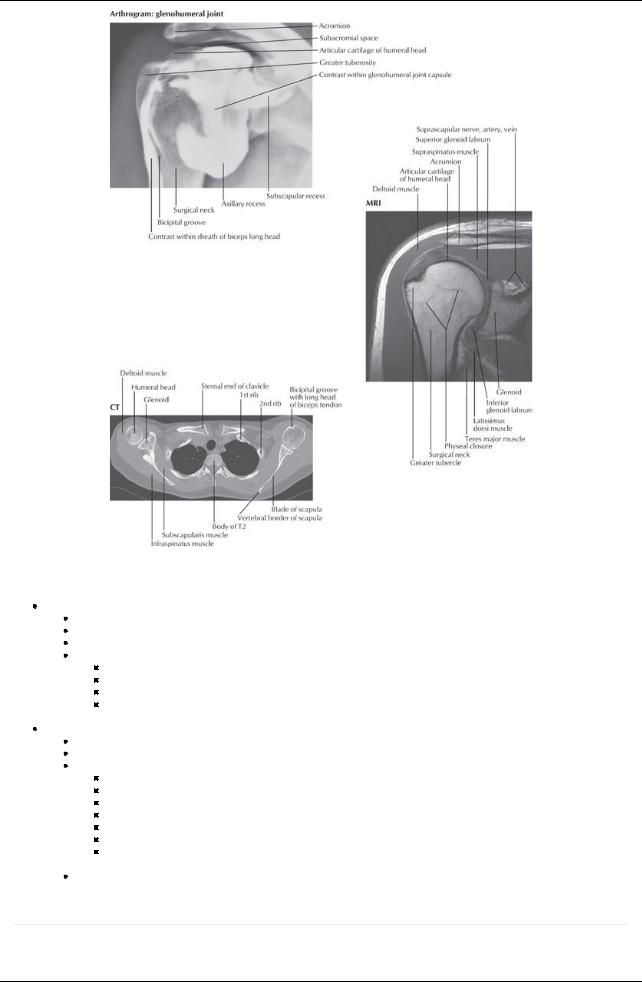
[Plate 468, Shoulder Arthrogram, MRI, and CT]
Bones
Clavicle: with sternal and acromial ends
Double-curved long bone
Sternal end articulates with manubrium of sternum
Acromial end articulates with acromion
Osteological features
Deltoid tubercle for attachment of the deltoid muscle
Conoid tubercle for attachment of conoid ligament
Subclavian groove for attachment of subclavius muscle
Trapezoid line where trapezoid ligament attaches
 Serves as a strut suspending the scapula and limb with maximum freedom Scapula: lying against posterolateral thorax
Serves as a strut suspending the scapula and limb with maximum freedom Scapula: lying against posterolateral thorax
Triangular flat bone
Lies posterolateral on second through seventh ribs
Osteological features
Concave costal surface = subscapular fossa
Posterior surface divided byspine = transverse ridge of bone
Supraspinous fossa
Infraspinous fossa
Acromion = flattened lateral end of spine
Coracoid process = anterior projection above glenoid cavity
Glenoid cavity= socket for head of humerus
 Suprascapular notch (scapular notch) = notch found on superior border, two thirds of the wayalong laterally Capable of considerable movement over thoracic wall
Suprascapular notch (scapular notch) = notch found on superior border, two thirds of the wayalong laterally Capable of considerable movement over thoracic wall
Joints
page 213
page 214
334 / 425

[Plate 410, Shoulder (Glenohumeral Joint)]
Sternoclavicular Joint
Saddle-type, synovial joint
Divided into two compartments byan articular disc
Movements
Elevation with posterior rotation
Protraction
Depression
Articulation between concave facet of manubrium and concave facet of clavicle
Strengthened byanterior and posterior sternoclavicular, costoclavicular, and interclavicular ligaments
Blood supply: Branches of suprascapular and internal thoracic arteries
 Nerve supply: Branches of the supraclavicular nerve, and nerve to subclavius Acromioclavicular Joint
Nerve supply: Branches of the supraclavicular nerve, and nerve to subclavius Acromioclavicular Joint
Plane-type, synovial joint
No demonstrable movement; muscles moving the scapula cause the acromion to move on the clavicle
Articulation between concave facet of acromion and convexfacet of clavicle
Strengthened byacromioclavicular and coracoclavicular (conoid and trapezoid) ligaments
Coracoclavicular
Unites coracoid process and clavicle
Has two component ligaments
Conoid: vertical, in shape of inverted pyramid
Trapezoid: horizontal, extends laterallyto inferior surface of clavicle
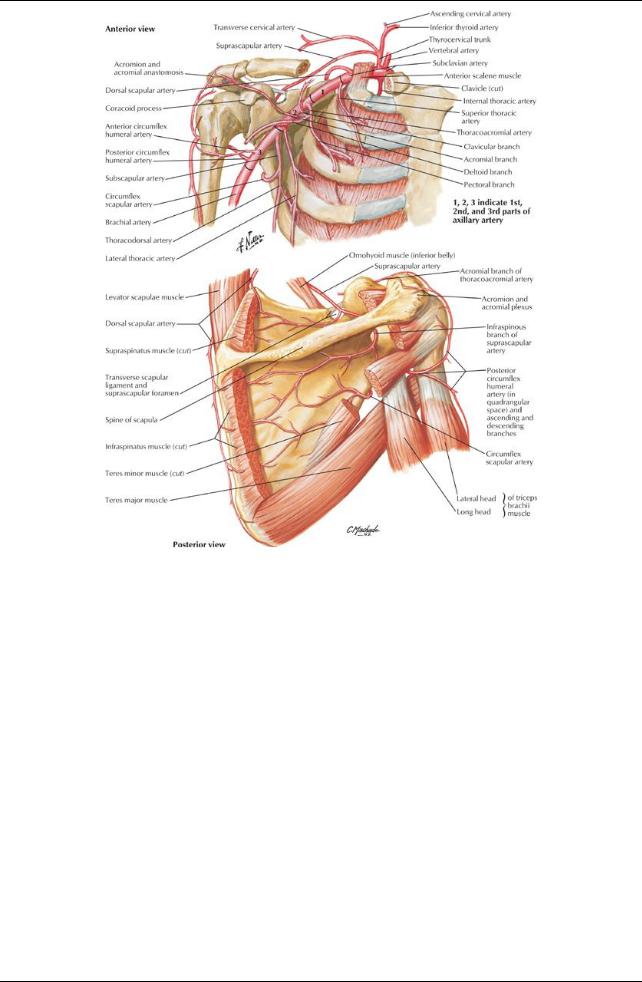
Blood supply: Branches of suprascapular and thoracoacromial arteries
 Nerve supply: Branches of the supraclavicular, lateral pectoral and axillarynerves Shoulder (Glenohumeral) Joint
Nerve supply: Branches of the supraclavicular, lateral pectoral and axillarynerves Shoulder (Glenohumeral) Joint
Multiaxial, synovial ball-and-socket joint
Movements
Flexion/extension
Abduction/adduction
Internal/external (medial/lateral) rotation
Circumduction
Articulation of head of humerus with the shallow glenoid cavityof the scapula
Joint socket deepened byglenoid labrum (fibrocartilaginous ring) and supported bythe rotator cuff muscles (see below)
335 / 425

Loose fibrous capsule encloses and contains two apertures
Between the tubercles of the humerus for passage of long head of biceps brachii, which attaches to supraglenoid tubercle within the joint
 Anterior opening, inferior to coracoid process, for communication between subscapular bursa and synovial cavityof joint Blood supply: Branches of anterior and posterior circumflexhumeral arteries from the axillaryand suprascapular arteryfrom the subclavian
Anterior opening, inferior to coracoid process, for communication between subscapular bursa and synovial cavityof joint Blood supply: Branches of anterior and posterior circumflexhumeral arteries from the axillaryand suprascapular arteryfrom the subclavian
Nerve supply: Branches of suprascapular, axillary, and lateral pectoral nerves Ligaments of glenohumeral joint
Glenohumeral ligaments-strengthen capsule anteriorly
Coracohumeral ligament-strengthens joint superiorly
Transverse humeral ligament-bridges gap between greater and lesser tubercle and holds tendon of biceps brachii in place Coracoacromial ligament-from acromion to coracoid process, prevents displacement of humeral head superiorly
LIGAMENT |
ATTACHMENTS |
COMMENT |
Joint capsule |
Margin of glenoid cavity→ anatomical neck of humerus |
Loose fibrous capsule |
|
|
Weakest inferiorly |
Glenohumeral |
Supraglenoid tubercle → blend with fibrous capsule (superior, |
Reinforce anterior capsule |
|
middle and inferior bands) |
|
Coracohumeral |
Coracoid process → greater tubercle of humerus |
Strong |
Transverse |
Bridges intertubercular groove between greater and lesser tubercles |
Holds tendon of biceps brachii in |
humeral |
|
intertubercular groove |
Coracoacromial |
Coracoid process → acromion |
Completes coracoacromial arch protecting |
|
|
humeral head |
Bursae (Important ones)
Contain thin layer of synovial fluid
Located where tendons rub against bone, ligaments, or tendons and when skin moves over bone directlybeneath Subscapular bursa
Between tendon of subscapularis muscle and neck of scapula
 Communicates with cavityof the shoulder joint Subacromial (subdeltoid) bursa
Communicates with cavityof the shoulder joint Subacromial (subdeltoid) bursa
Between deltoid, supraspinatus tendon and glenohumeral capsule
Does not communicate with cavityof shoulder
Facilitates movement of deltoid over joint capsule and supraspinatus tendon under coracoacromial arch
Muscles of the Scapula
336 / 425

[Plate 411, Muscles of Shoulder]
Muscle |
Origin |
Insertion |
Innervation |
Blood Supply |
Action |
Trapezius |
Medial third of superior |
Lateral third of |
Spinal root of |
Transverse |
Elevates scapula (descending part), |
|
nuchal line, external |
posterior clavicle, |
accessory |
cervical artery, |
retracts scapula (transverse part), |
|
occipital protuberance, |
medial acromion, |
nerve (CN XI) |
dorsal |
depresses scapula (ascending |
|
ligamentum nuchae, |
superior edge of |
and C3 and |
scapular |
part); rotates scapula (descending |
|
spinous processes of C7- |
spine of scapula |
C4 |
artery |
and ascending parts acting |
|
T12 |
|
|
|
together) |
Latissimus |
Spinous processes of T7- |
Floor of |
Thoracodorsal |
Thoracodorsal |
Extends, adducts and medially |
dorsi |
T12, thoracolumbar fascia, |
intertubercular |
nerve (C6-C7) |
artery |
rotates arm, draws shoulder |
|
iliac crest, lower three to |
sulcus of humerus |
|
|
downwards and backward |
|
four ribs |
|
|
|
|
page 215 page 216
Muscle |
Origin |
Insertion |
Innervation |
Blood Supply |
Action |
Levator |
Posterior tubercles of |
Medial border of scapula |
Dorsal scapular |
Dorsal scapular |
Elevates scapula |
scapulae |
transverse processes |
above base of spine of |
and cervical (C3- |
artery, transverse |
medially, inferiorlyrotates |
|
C1-C4 |
scapula |
C4) nerves |
cervical artery |
glenoid cavity |
Rhomboid |
Ligamentum nuchae, |
Medial border of scapula |
Dorsal scapular |
Dorsal scapular |
Retracts and stabilizes |
minor |
spinous processes of |
above base of spine of |
nerve (C4-C5) |
artery |
the scapula |
|
C7 and TI |
scapula |
|
|
|
Rhomboid |
Spinous processes of |
Medial border of scapula |
Dorsal scapular |
Dorsal scapular |
Retracts and rotates |
major |
T2-T5 |
below base of spine of |
nerve (C4-C5) |
artery |
scapula to depress the |
|
|
scapula |
|
|
glenoid cavity |
|
Muscle |
Origin |
Insertion |
Innervation |
Blood Supply |
Action |
|
|
Deltoid |
Lateral third of anterior |
Deltoid |
Anterior and |
Posterior circumflex |
Clavicular part-flexes and medially |
|
|
|
clavicle, lateral |
tuberosityof |
posterior |
humeral artery, |
rotates arm; acromial part-abducts |
|
|
|
acromion, inferior edge |
humerus |
branches of |
deltoid branch of |
arm; spinal part-extends and |
|
|
|
of spine of scapula |
|
axillarynerve |
thoracoacromial |
laterallyrotates arm |
|
|
|
|
|
(C5,C6) |
artery |
|
|
|
Supraspinatus |
Supraspinous fossa of |
Superior facet |
Suprascapular |
Suprascapular artery |
Initiates arm abduction, acts with |
|
|
|
scapula |
of greater |
nerve (C5,C6) |
|
rotator cuff muscles |
|
337 / 425

|
|
tubercle of |
|
|
|
|
|
humerus |
|
|
|
Infraspinatus |
Intraspinous fossa of |
Middle facet of |
Suprascapular |
Suprascapular artery |
Lateral rotation of arm (with teres |
|
scapula |
greater |
nerve (C5,C6) |
|
minor) |
|
|
tubercle of |
|
|
|
|
|
humerus |
|
|
|
Teres minor |
Upper two thirds of |
Inferior facet |
Posterior |
Circumflexscapular |
Lateral rotation of arm, adduction |
|
posterior surface of |
of greater |
branch of |
artery |
|
|
lateral border of |
tubercle of |
axillarynerve |
|
|
|
scapula |
humerus |
(C5,C6) |
|
|
Teres major |
Posterior surface of |
Medial lip of |
Inferior |
Circumflexscapular |
Adducts and mediallyrotates arm |
|
inferior angle of |
intertubercular |
subscapular |
artery |
|
|
scapula |
sulcus |
nerve (C5,C6) |
|
|
Subscapularis |
Subscapular fossa |
Lesser |
Superior and |
Subscapular artery, |
Mediallyrotates arm and adducts |
|
|
tubercle of |
inferior |
lateral thoracic artery |
it; helps hold humeral head in |
|
|
humerus |
subscapular |
|
glenoid cavity |
|
|
|
nerves (C5-C6) |
|
|
Superficial extrinsic (Join axial skeleton to the appendicular skeleton)
Trapezius
Latissimus dorsi
Deep extrinsic
Levator scapulae
Rhomboid major and minor
Intrinsic
Deltoid: Gives shoulder its rounded appearance, abducts arm past 15 degrees
Teres major:Adducts and mediallyrotates arm
Teres minor: Hidden bydeltoid, assists lateral rotation of arm and adduction
Supraspinatus: Initiates arm abduction
Infraspinatus: Laterallyrotates arm
Subscapularis: Primarymedial rotator of the arm, also adducts
Rotator cuff
Four of scapulohumeral muscles
Supraspinatus
Infraspinatus
Teres minor
Teres major
Form musculotendinous cuff around glenohumeral joint
Blend with articular capsule to reinforce it
Hold head of humerus in glenoid cavity
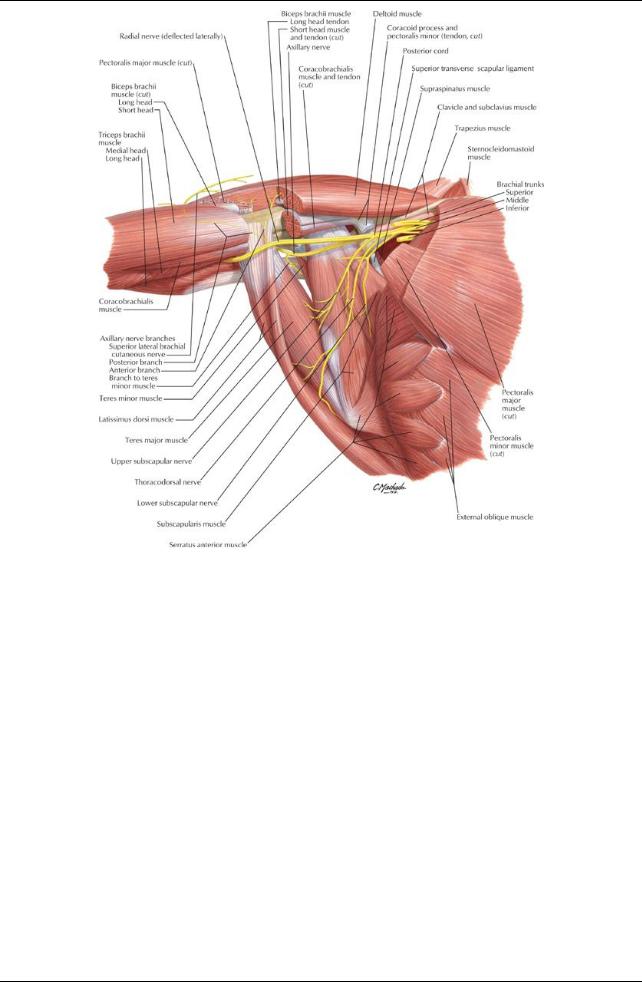
Axilla
338 / 425
[Plate 412, Axilla: Posterior Wall and Cord]
339 / 425
[Plate 415, Axillary Artery and Anastomoses around Scapula]
340 / 425
[Plate 418, Brachial Plexus: Schema]
page 217 page 218
Pyramid-shaped area inferior to glenohumeral joint containing important neurovascular structures to the upper limb Boundaries
Base: skin of armpit and axillaryfascia from arm to thoracic wall
Apex: bounded bythe first rib, clavicle, and superior border of the scapula
Anterior wall (anterior axillaryfold): pectoralis major and minor
Posterior wall (posterior fold): subscapularis, teres major, latissimus dorsi
Medial wall: ribs 1 through 4, serratus anterior, and intercostal muscles
Lateral wall: intertubercular groove of humerus
Contents (see Section 6-6: Upper Limb: Neurovasculature for details)
Axillaryarteryand branches
Axillaryvein and tributaries
Axillarylymph nodes (five major collections)
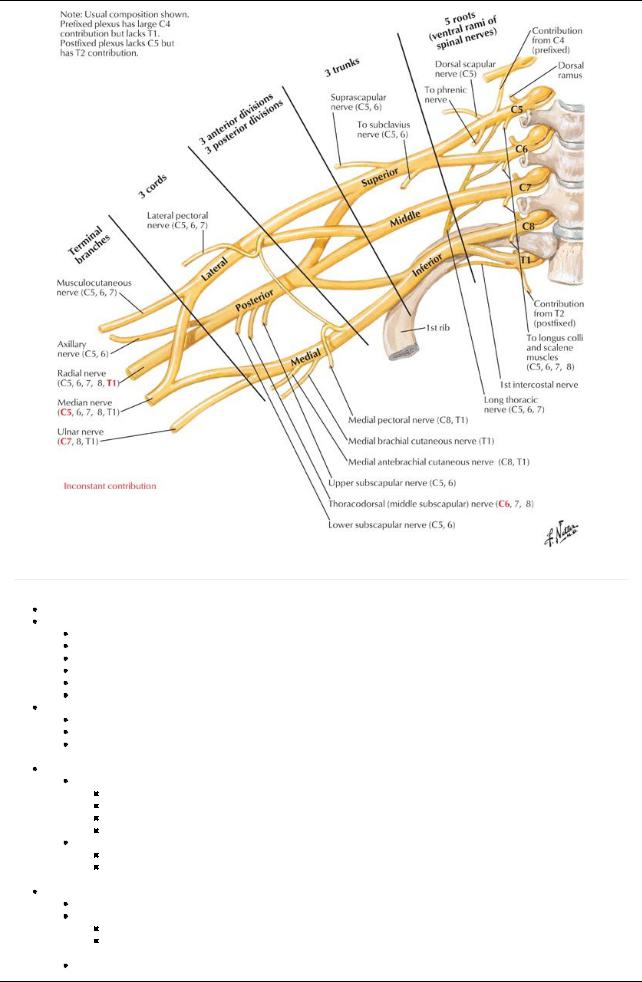
 Brachial plexus Fascia
Brachial plexus Fascia
Pectoral fascia
Attaches to clavicle and sternum
Invests the pectoralis major
Extends laterallyas the axillaryfascia
Continues inferiorlywith fascia of abdominal wall
Clavipectoral fascia
Invests subclavius and pectoralis minor
Continues superiorlyas the costocoracoid membrane (pierced bythe lateral pectoral nerve)
 Axillarysheath: invests axillaryarteryand brachial plexus AxillaryLymph Nodes
Axillarysheath: invests axillaryarteryand brachial plexus AxillaryLymph Nodes
Arranged in five main groups
Apical group
Along medial side of axillaryvein and first part of axillaryartery
Receives lymph from all other groups
 Efferent lymphatic vessels from these nodes form subclavian lymphatic trunk Pectoral (anterior) group
Efferent lymphatic vessels from these nodes form subclavian lymphatic trunk Pectoral (anterior) group
341 / 425

Medial wall of axilla
Receives lymph from breast, anterior thoracic wall
Subscapular group
Along posterior axillaryfold
Receives lymph from posterior thoracic wall and scapula
Humeral (lateral) group
Along lateral wall of axilla
Receives lymph from upper limb
Central group
Deep to pectoralis minor
Receives lymph from pectoral, subscapular, and humeral groups
342 / 425
