
- •1. Topographic Surface Anatomy
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •3. Superficial Face
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •4. Neck
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •5. Nasal Region
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •6. Oral Region
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •7. Pharynx
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •13. Cerebral Vasculature
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •14. Topographic Anatomy
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •16. Spinal Cord
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Thorax
- •18. Topographic Anatomy
- •Guides
- •Facts & Hints
- •19. Mammary Gland
- •Guides
- •Facts & Hints
- •20. Body Wall
- •Guides
- •Facts & Hints
- •21. Lungs
- •Guides
- •Facts & Hints
- •22. Heart
- •Guides
- •Facts & Hints
- •23. Mediastinum
- •Guides
- •Facts & Hints
- •Abdomen
- •24. Topographic Anatomy
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •25. Body Wall
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •26. Peritoneal Cavity
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •27. Viscera (Gut)
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •28. Viscera (Accessory Organs)
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •29. Visceral Vasculature
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •30. Innervation
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •32. Topographic Anatomy
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •35. Urinary Bladder
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •39. Testis, Epididymis & Ductus Deferens
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •40. Rectum
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •41. Vasculature
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •42. Innervation
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Upper Limb
- •43. Topographic Anatomy
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •48. Neurovasculature
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Lower Limb
- •49. Topographic Anatomy
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •51. Knee
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •54. Neurovasculature
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints

FACTS & HINTS
High-Yield Facts
Anatomic Points
The piriform fossa is a common site for fish bones to lodge. It is also a site where pharyngeal tumors can grow undetected for a period of time.
Aggregations of lymphoid tissue in the nasopharynxare called adenoids. Theycan become enlarged in children, causing obstruction of the nasopharynxand forcing the child to breathe through the mouth.
page 41
page 42
Clinical Points
Pharyngitis
Also called a sore throat
Usuallycaused byviral infection
In children, common cause of bacterial pharyngitis is beta hemolytic streptococcus
If infection is severe, auditorytubes can become blocked, predisposing to otitis media
Patient maycomplain of pain on swallowing and pain referred to the ear
On examination, the throat maybe reddened and cervical lymph nodes maybe enlarged
Clinical Points
Tonsillectomy
Surgical removal of the palatine and lingual tonsils
Tonsillectomyis advised if the patient has experienced recurrent attacks of tonsillitis, particularlyif theyresulted in airwayobstruction and hearing difficulties
Amajor and common surgical procedure performed in children in the USA
Recoveryusuallywithin 2 weeks, although for adults this maytake longer and can have a higher complication rate
50 / 425

8 Thyroid Gland and Larynx
STUDYAIMS
At the end of your study, you should be able to:
Know the general anatomyof the larynx
Describe the cartilaginous skeleton of the larynx
Describe the membranes of the larynx
Know the internal anatomyof the larynx
List the intrinsic and extrinsic muscles of the larynxand their function
Describe the arterial supply, venous and lymphatic drainage, and innervation of the larynx
Describe the structure of the thyroid gland
Describe the structure of the parathyroid glands
51 / 425

GUIDE
Head and Neck: Thyroid Gland and Larynx
Larynx: General Anatomy
Organ of phonation and sphincter guarding lower respiratorytract
Approximately8 cm long
Connects oropharynxwith trachea
Lies anterior to prevertebral muscles, fascia, and the bodies of C3-C6 vertebrae
Laryngeal skeleton
page 43
page 44
Comprised of three paired and three nonpaired cartilages Epiglottic cartilage (epiglottis)
Leaf-shaped elastic cartilage
Posterior to root of tongue and hyoid bone, anterior to laryngeal inlet
Broad superior end is free
Inferior end attached in midline to angle of thyroid laminae bythyroepiglottic ligament
Quadrangular membranes run between lateral sides of epiglottic cartilage and arytenoid cartilages on either side
Upper free margin of quadrangular membrane + covering mucosa = aryepiglottic fold
 During swallowing overlies laryngeal inlet Thyroid cartilage
During swallowing overlies laryngeal inlet Thyroid cartilage
Composed of two flat laminae
Lower two thirds of laminae fuse in midline to form laryngeal prominence (Adam's apple)
Upper one third of laminae diverge to form superior thyroid notch
Posterior superior border of each plate projects superiorlyas superior horns
Posterior inferior border of each plate projects inferiorlyas inferior horns
 Superior horns and superior borders of laminae attach to hyoid bone bythyrohyoid membrane Cricoid cartilage
Superior horns and superior borders of laminae attach to hyoid bone bythyrohyoid membrane Cricoid cartilage
Signet ring shaped, signet (lamina) facing posteriorly
Strong, thick, complete circle of cartilage
Attached to inferior thyroid bymedian cricothyroid ligament
 Attached to first tracheal ring bycricotracheal ligament Arytenoid cartilages (paired)
Attached to first tracheal ring bycricotracheal ligament Arytenoid cartilages (paired)
Pyramid shaped with three sides
Articulate with lateral superior parts of cricoid lamina Has three processes:
a.Apexat superior end
b.Vocal process projects anteriorly
c.Muscular process projects laterally
Apex: Corniculate cartilage sits atop; attaches to aryepiglottic fold
Vocal process: posterior attachment for vocal ligament
Muscular process: attachment for posterior and lateral cricoarytenoid muscles
Corniculate and cuneiform cartilages
Nodules in posterior aryepiglottic folds
Cuneiforms do not attach to other cartilages
Corniculates attach to apices of arytenoids
Membranes of the laryngeal skeleton
Cricothyroid ligaments
Median cricothyroid ligament
Lateral cricothyroid ligaments (conus elasticus)
Both attach to cricoid cartilage to inferior border of thyroid cartilage
Medial free edge of lateral cricothyroid ligaments = vocal ligaments, basis of true vocal cords
Quadrangular membrane
Inelastic connective tissue
Attaches lateral aspects of arytenoids and epiglottis
Lower free border = vestibular ligament (false vocal cord)
Covered byvestibular fold
Above vocal fold
Extends from thyroid cartilage to arytenoid cartilage
Upper free border forms aryepiglottic ligament
Covered with mucosa
Called aryepiglottic fold
Thyrohyoid membrane
Bridges gap between superior border and superior horns of thyroid cartilage and
Pierced bysuperior laryngeal vessels and internal laryngeal nerve
Mucous membrane
Respiratoryepithelium except over true and aryepiglottic folds
This is composed of stratified squamous epithelium
Internal anatomy of the larynx
52 / 425

page 44 page 45
Laryngeal cavity
From laryngeal inlet to tracheal cavity
Can be divided into three parts
Vestibule-above vestibular folds
Ventricle-sinus between vestibular folds above and vocal folds below
Infraglottic cavity-from below vocal folds to inferior border of cricoid cartilage
Vocal folds
Paired, project into laryngeal cavityon either side
Consist of
Vocal ligament-medial free edge of lateral cricothyroid ligament (conus elasticus)
Vocalis muscle-medial fibers of thyroid arytenoids muscle
Overlying mucosa
Source of sound
Produce audible vibrations when free edges of folds closelyapproximate each other
Are sphincter of larynxwhen folds are tightlyapproximated
Rima glottidis
Space between vocal folds
Varies in size with activity
During normal breathing: narrow wedge
During forced respiration: wide apart
During phonation: slit-like
Vestibular folds (false vocal cords)
Folds of mucous membrane over vestibular ligaments superior to vocal folds
Extend between thyroid and arytenoids cartilages
Protective in function
Ventricle of larynx: lateral outpocketings between vocal and vestibular folds on either side
Muscles of the larynx
Extrinsic muscles
Are muscles attached to hyoid bone and thus move thyroid
Infrahyoid muscles: lower larynxand hyoid bone
Sternohyoid
Omohyoid
Sternothyroid
Thyrohyoid
Suprahyoid muscles: Fixhyoid or elevate hyoid bone and larynx
Stylohyoid
Digastric
Mylohyoid
Stylopharyngeus-elevates hyoid bone and larynx
Intrinsic muscles
Alter length and tension of vocal cords
Alter rima glottides
Adductors
Lateral cricoarytenoid muscles
Transverse arytenoids
Abductors: posterior cricoarytenoid muscles
Sphincters
Transverse arytenoids muscles
Oblique arytenoids muscles
Aryepiglottic muscles
Tensors: cricothyroid muscles
Relaxers
Thyroarytenoid muscles
Vocalis muscles
All except cricothyroid supplied byrecurrent laryngeal nerve
page 45 page 46
|
Muscle |
Proximal |
Distal Attachment |
Innervation |
Blood Supply |
Action |
|
|
|
Attachment (Origin) |
(Insertion) |
|
|
|
|
|
Cricothyroid |
Anterior cricoid |
Inferior border of thyroid |
External branch of |
Superior and |
Lengthens and tenses vocal |
|
|
|
cartilage |
cartilage and its inferior |
superior laryngeal |
inferior thyroid |
ligaments |
|
|
|
|
horn |
nerve |
arteries |
|
|
|
Posterior |
Posterior surface of |
Muscular process of |
Recurrent |
Superior and |
Abducts vocal folds |
|
|
cricoarytenoid |
lamina of cricoid |
arytenoid cartilage |
laryngeal nerve |
inferior thyroid |
|
|
|
|
cartilage |
|
|
arteries |
|
|
|
Lateral |
Arch of cricoid |
Muscular process of |
Recurrent |
Superior and |
Adducts vocal folds |
|
|
cricoarytenoid |
cartilage |
arytenoid cartilage |
laryngeal nerve |
inferior thyroid |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
arteries |
|
|
|
Thyroarytenoid |
Posterior aspect of |
Muscular process of |
Recurrent |
Superior and |
Shortens and relaxes vocal |
|
|
|
thyroid cartilage |
arytenoid cartilage |
laryngeal nerve |
inferior thyroid |
cords |
|
|
|
|
|
|
arteries |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
53 / 425
Vocalis |
Vocal process of |
Vocal ligament |
Recurrent |
Superior and |
Tenses anterior vocal ligament |
|
arytenoids cartilage |
|
laryngeal nerve |
inferior thyroid |
and relaxes posterior vocal |
|
|
|
|
arteries |
ligament |
Transverse |
Arytenoid cartilage |
Opposite arytenoid |
Recurrent |
Superior and |
Closes intercartilaginous |
and oblique |
|
cartilage |
laryngeal nerve |
inferior thyroid |
portion of rima glottides |
arytenoids |
|
|
|
arteries |
|
Joints of the larynxand movements at the joints
Cricothyroid joints
Thyroid cartilage glides and rotates here
Changes length of vocal folds
Cricoarytenoid joints: movement of the arytenoids cartilage on the lamina of the cricoid
Slide towards each other and awayfrom each other
Rotate
Tilt forward and back
Arterial supply to larynx
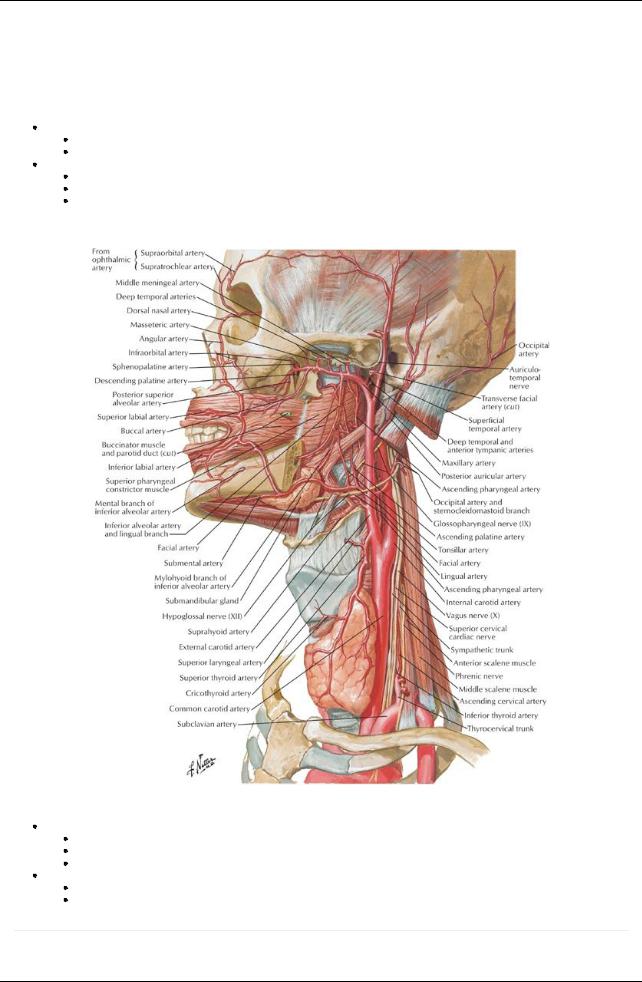
[Plate 69, Arteries of Oral and Pharyngeal Regions]
Superior laryngeal artery
Through gap in thyrohyoid membrane
Supplies internal larynx
Accompanies bysuperior laryngeal nerve
Inferior laryngeal artery
Supplies inferior internal larynx
Accompanied byrecurrent laryngeal nerve
page 46 page 47
Venous drainage of larynx
54 / 425
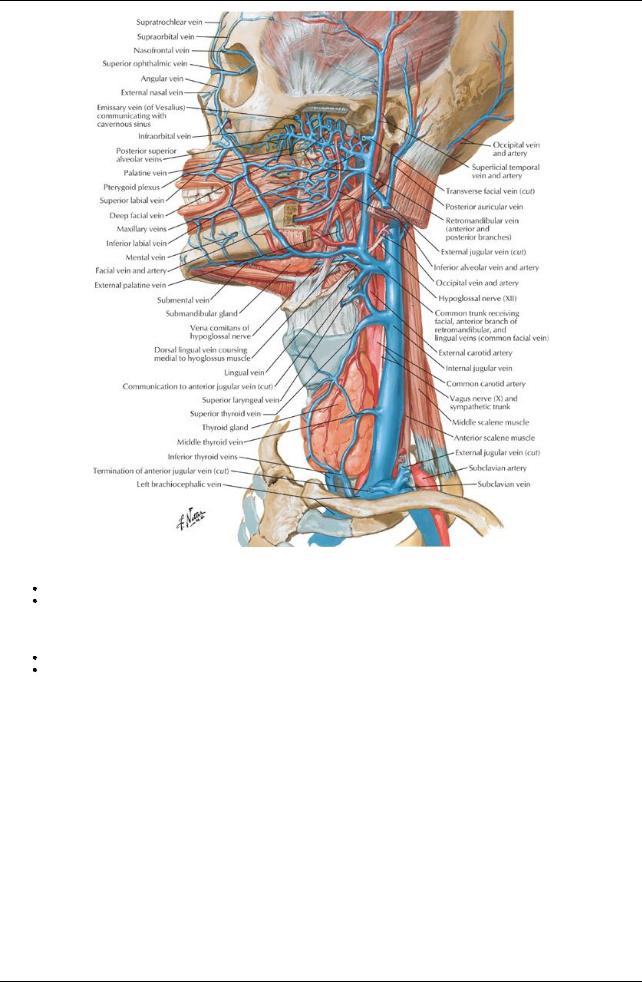
[Plate 70, Veins of Oral and Pharyngeal Regions]
Superior laryngeal vein to internal jugular vein
Inferior laryngeal vein → inferior thyroid vein or thyroid venous plexus (left brachiocephalic)
Lymphatic drainage of larynx
Above folds: to deep cervical nodes
Below folds: to paratracheal nodes to deep cervical nodes
Innervation of larynx
55 / 425
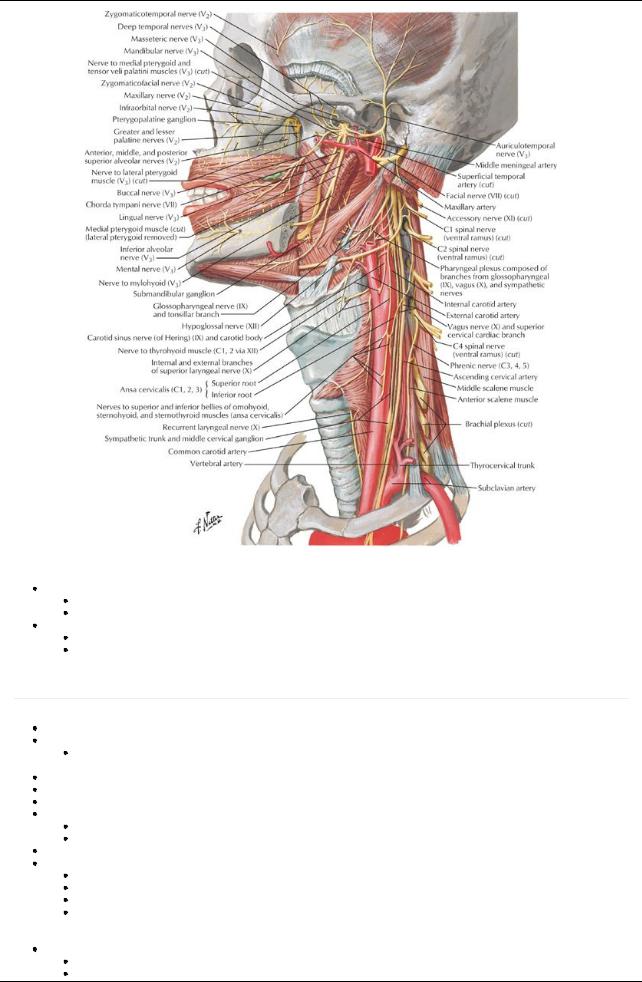
[Plate 71, Nerves of Oral and Pharyngeal Regions]
Sensory
Above vocal folds: internal laryngeal nerve (branch of superior laryngeal)
Below vocal folds: inferior laryngeal nerve (branch of recurrent laryngeal nerve)
Motor:
Recurrent laryngeal nerve to all intrinsic muscles except cricothyroid
External laryngeal nerve to cricothyroid
Thyroid Gland
page 47
page 48
H-shaped endocrine gland Produces two hormones
Thyroid hormone-controls metabolic rate
 Calcitonin-controls calcium metabolism Overlies anterior and lateral surface trachea Enclosed in thin fibrous capsule with septa into gland
Calcitonin-controls calcium metabolism Overlies anterior and lateral surface trachea Enclosed in thin fibrous capsule with septa into gland
Surrounded bypretracheal fascia (therefore moves on swallowing) Two lateral lobes linked byisthmus
Lobes extend from second to fifth tracheal ring
Isthmus lies at third tracheal ring
Occasionallya pyramidal lobe extends superiorlyfrom isthmus on left side Anatomic relationships
Anteriorly: sternohyoid and sternothyroid muscles jugular vein
Anterolaterally: infra-hyoid muscles sternocleidomastoid
Posterolaterally: carotid sheath
Posteromedially: trachea larynx
esophagus Innervation
Parasympathetic: external branch superior laryngeal nerve (branch vagus n.) Sympathetic
56 / 425

From: superior, middle, and inferior cervical ganglia
Vasomotor, not secretomotor
Arterial supply
Superior thyroid artery
Branch of external carotid artery
Divides into anterior and posterior branches
Anterior branch
Supplies anterior thyroid
Anastomoses with opposite anterior branch
Posterior branch
Supplies posterior thyroid
Anastomoses with inferior thyroid artery
Inferior thyroid artery
Branch thyrocervical trunk from subclavian artery
Supplies inferior pole of thyroid
Thyroid ima artery
Branch of aorta
Occurs in 10% of all people
Unpaired, on left of midline
Supplies isthmus
Venous drainage
Three pairs of thyroid veins
Superior thyroid vein
Drains superior region of thyroid
Tributaryof internal jugular
Middle thyroid veins
Drain middle of gland
Tributaries of internal jugular
Inferior thyroid veins
Drain inferior region of thyroid
Tributaries of brachiocephalic vein
Lymphatic drainage
Lymphatic vessels run with arteries
Drain to capsular network of lymphatics
→ prelaryngeal, pretracheal, or paratracheal nodes
→ deep cervical nodes
Innervation: sympathetic from cervical sympathetic ganglia
Parathyroid Gland
Small, oval endocrine glands
On medial half of posterior surface of lateral lobes of thyroid, external to capsule
Two pairs of glands
Superior glands slightlyabove entrance of inferior thyroid arteries
Inferior glands slightlybelow entrance of inferior thyroid arteries
Arterial supply
Superior thyroid artery
Inferior thyroid artery
Thyroid ima artery
Venous drainage
Parathyroid veins
→ thyroid plexus of veins
Lymph drainage: paratracheal and deep cervical lymph nodes
57 / 425
