
- •1. Topographic Surface Anatomy
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •3. Superficial Face
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •4. Neck
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •5. Nasal Region
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •6. Oral Region
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •7. Pharynx
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •13. Cerebral Vasculature
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •14. Topographic Anatomy
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •16. Spinal Cord
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Thorax
- •18. Topographic Anatomy
- •Guides
- •Facts & Hints
- •19. Mammary Gland
- •Guides
- •Facts & Hints
- •20. Body Wall
- •Guides
- •Facts & Hints
- •21. Lungs
- •Guides
- •Facts & Hints
- •22. Heart
- •Guides
- •Facts & Hints
- •23. Mediastinum
- •Guides
- •Facts & Hints
- •Abdomen
- •24. Topographic Anatomy
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •25. Body Wall
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •26. Peritoneal Cavity
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •27. Viscera (Gut)
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •28. Viscera (Accessory Organs)
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •29. Visceral Vasculature
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •30. Innervation
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •32. Topographic Anatomy
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •35. Urinary Bladder
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •39. Testis, Epididymis & Ductus Deferens
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •40. Rectum
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •41. Vasculature
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •42. Innervation
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Upper Limb
- •43. Topographic Anatomy
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •48. Neurovasculature
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Lower Limb
- •49. Topographic Anatomy
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •51. Knee
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •54. Neurovasculature
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints

FACTS & HINTS
High-Yield Facts
Clinical Points
Pregnancy:In pregnancythe placenta can be palpated above the pubic symphysis at 12 weeks, at the umbilicus at 12 weeks, and at the xiphisternum at 40 weeks.
Acute UrinaryRetention:The bladder, if distended, maybe palpated and percussed up to the umbilicus. On examination, the bladder is dull to percussion and in acute urinaryretention, the patient mayalso complain of tenderness on palpation in the suprapubic region. Supracristal Line:Auseful landmark when performing a lumbar puncture since it corresponds to the 4th lumbar vertebral body. Lumbar puncture in adults is performed in the lateral decubitus position in the L4-L5 interspace.
Pilonidal Sinus:Ablind ending hair-filled tract most commonlyfound in the midline of the natal cleft overlying the lower sacrum and coccyx and occurs in 26/1000 persons in the United States. The sinus can become infected, creating a so-called pilonidal abscess that usually requires drainage and/or excision of the sinus.
257 / 425

33 Bones and Ligaments
STUDYAIMS
At the end of your study, you should be able to:
Identifythe components of the bonypelvis
Define the boundaries of the pelvic cavity
Describe the joints of the pelvis
Describe the ligaments that strengthen the pelvis
Outline the keydifferences between the male and female pelvis
List the structures that pass through the greater and lesser sciatic foramina
258 / 425

GUIDE
Pelvis and Perineum: Bones and Ligaments
[Plate 333, Radiographs of Male and Female Pelvis]
259 / 425
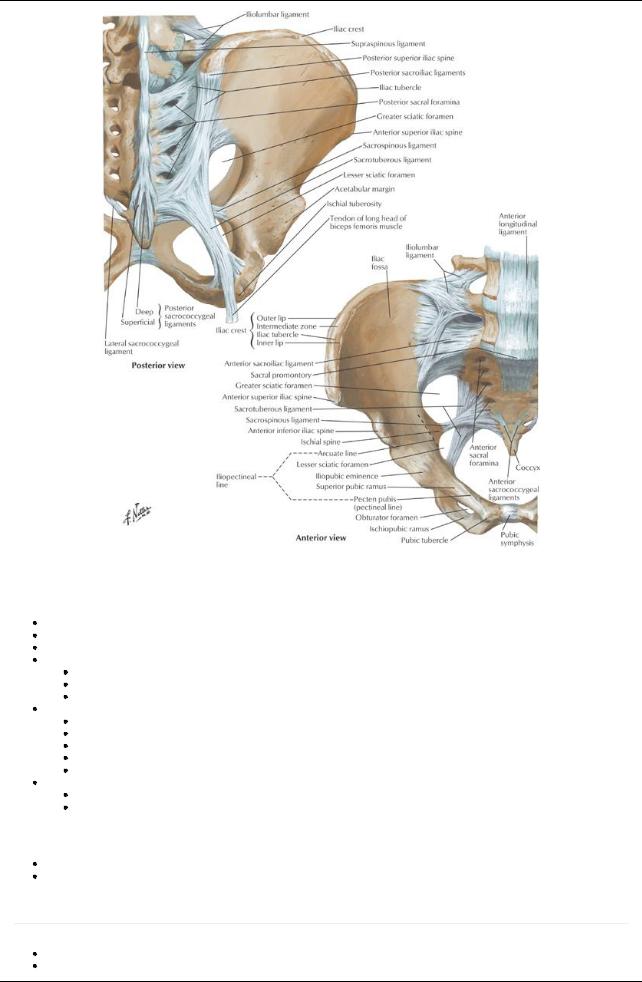
[Plate 335, Bones and Ligaments of Pelvis]
Bones and Boundaries of the Pelvis
Bony pelvis
Is a strong ring
Supports the weight of the body
Provides attachment for powerful muscles that move the lower limb
Composed of four bones
Two hip bones or innominate bones
Sacrum-five fused sacral vertebrae
Coccyx-four (+ 1) fused coccygeal vertebrae
Hip or innominate bones each formed from
Ilium
Ischium
Pubis
Fuse at puberty
Are united bycartilage at the acetabulum
Pelvic girdle
Is formed of hip bones and sacrum
Transmits weight from upper bodyto lower limbs
Pelvic walls
Formed bybones of bonypelvis, ligaments, muscle, and fascia
Surround pelvic cavity
Pelvic cavity
page 168
page 169
Basin shaped
Surrounded bybonypelvis
260 / 425

Boundaries:
Superiorly-pelvic inlet and inferior abdominal cavity
Inferiorly-pelvic diaphragm
Anterior wall-bodies and rami of pubic bone and pubic symphysis
Posterior wall-sacrum and coccyx, adjacent ilia and overlying piriformis muscle
Lateral walls-hip bones, obturator foramen and membrane, and overlying obturator internus muscle
Pelvic inlet, outlet, and brim
Inlet defined byan oblique plane
Extends from promontoryto the superior aspect of the pubic symphysis
Lies at an angle approximately55 degrees from horizontal
Rim of pelvic inlet = pelvic brim, composed of a bonyline running through
Sacral promontory
Arcuate line of the ilium
Pectineal line of the pubis (pecten pubis)
Pubic crest
Superior edge of pubic symphysis
Pelvic outlet is bounded by
Tip of coccyx
Sacrotuberous ligaments
Inferior ischiopubic rami and ischial tuberosities
Inferior edge of pubic symphysis
Pelvic inlet divides pelvis into two parts
True pelvis or lesser pelvis or pelvis minor, which
lies between pelvic inlet and outlet
contains the pelvic viscera
False pelvis or greater pelvis or pelvis major, which
lies above pelvic brim
between the iliac fossae
contains part of the ileum and sigmoid colon
The birth canal includes the pelvic inlet, true pelvis, cervix, vagina, and pelvic outlet
Joints of the Pelvis
Lumbosacral joints
Composed of
Intervertebral joint via intervertebral disc between L4 and S1
Two posterior zygapophysial joints
Reinforced byiliolumbar ligaments
Sacroiliac joint
Articulation between ear-shaped surfaces of the sacrum and ilium
Atypical synovial joint formed with fibrocartilage rather than hyaline cartilage
Movement is verylimited
Stabilized byinterosseous and anterior and posterior sacroiliac ligaments
Pubic symphysis
page 169
page 170
Union of bodies of right and left pubic bones Secondarycartilaginous joint Fibrocartilaginous interpubic disc in the joint
Stabilized bysuperior and inferior pubic ligaments
Affected bythe hormone relaxin during pregnancyto permit freer movement between vertebral column and to increase pelvic diameter during childbirth
Sacrococcygeal joint
Articulation between sacrum and coccyx
Secondarycartilaginous joint
Stabilized byanterior and posterior sacrococcygeal ligaments
Ligaments of the Pelvis
The weight of the bodyacting through the spine will tend to rotate the sacrum, tipping the lower part backwards. This movement is prevented bythe sacrospinous and sacrotuberous ligaments.
Sacrospinous ligament: extends from lateral border sacrum to ischial spine
 Sacrotuberous ligament: larger and extends from dorsum and lateral border sacrum and posterior surface ilium to ischial tuberosity Attachments of sacrospinous and sacrotuberous ligaments enclose the lesser and greater sciatic notches, respectively, forming the greater and lesser foramina
Sacrotuberous ligament: larger and extends from dorsum and lateral border sacrum and posterior surface ilium to ischial tuberosity Attachments of sacrospinous and sacrotuberous ligaments enclose the lesser and greater sciatic notches, respectively, forming the greater and lesser foramina
261 / 425

Structures Passing Through the Greater and Lesser Sciatic Foramina
|
Greater Sciatic Foramen |
Lesser Sciatic Foramen |
|
Piriformis muscle |
Tendon of obturator internus |
|
Sciatic nerve |
Nerve to obturator internus |
|
Inferior gluteal nerve and artery |
Pudendal nerve |
|
Internal pudendal nerve, artery, and vein |
Internal pudendal artery |
|
Nerve to obturator internus muscle |
|
|
Nerve to quadratus femoris |
|
|
Posterior cutaneous nerve of the thigh |
|
Sex Differences of Pelvis |
|
|
Differences linked to function
Pregnancyand childbirth in females
Heavier build and larger muscles of men
Main differences
Pelvis is heavier and has more pronounced muscle attachment sites in men than in women
Pubic arch is narrower and the subpubic angle more acute in men than women
Ischial tuberosities are closer in men than in women, and the pelvis outlet is thus comparativelysmaller.
All of the ilia are less flared in men than in women, so the greater pelvis is deeper.
Pelvic inlet is heart-shaped in men and more transverselyoval in women
Obturator foramen is round in men and oval in women
Female pelvis is broader than in men, to allow the passage of the fetal head
262 / 425
