
- •1. Topographic Surface Anatomy
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •3. Superficial Face
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •4. Neck
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •5. Nasal Region
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •6. Oral Region
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •7. Pharynx
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •13. Cerebral Vasculature
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •14. Topographic Anatomy
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •16. Spinal Cord
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Thorax
- •18. Topographic Anatomy
- •Guides
- •Facts & Hints
- •19. Mammary Gland
- •Guides
- •Facts & Hints
- •20. Body Wall
- •Guides
- •Facts & Hints
- •21. Lungs
- •Guides
- •Facts & Hints
- •22. Heart
- •Guides
- •Facts & Hints
- •23. Mediastinum
- •Guides
- •Facts & Hints
- •Abdomen
- •24. Topographic Anatomy
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •25. Body Wall
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •26. Peritoneal Cavity
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •27. Viscera (Gut)
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •28. Viscera (Accessory Organs)
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •29. Visceral Vasculature
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •30. Innervation
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •32. Topographic Anatomy
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •35. Urinary Bladder
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •39. Testis, Epididymis & Ductus Deferens
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •40. Rectum
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •41. Vasculature
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •42. Innervation
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Upper Limb
- •43. Topographic Anatomy
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •48. Neurovasculature
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Lower Limb
- •49. Topographic Anatomy
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •51. Knee
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •54. Neurovasculature
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints

FACTS & HINTS
High-Yield Facts
Clinical Points
Bartholin cyst
Cystic swelling of greater vestibular (Bartholin's) glands
Occurs when gland is infected or duct is blocked
Can enlarge to 4 to 5 cm
Carcinoma of the vulva
Mimics chronic ulcer
Patient presents with pain, a discharging ulcer and occasionallya lump
Metastasis is to inguinal lymph nodes
Greater vestibular gland is origin of most vulvular adenocarcinomas
Childbirth and the perineal body
Overt or occult tearing of perineal bodyresults in permanent weakness of pelvic floor
Can involve tearing of posterior vaginal wall and overlying skin
Slow to heal because of lack of vascular supply
Episiotomydone if tearing of perineum is predicted
Incision usuallymade from posterior vaginal wall through midline to just anterior to anus
298 / 425

38 Perineum and External Genitalia: Male
STUDYAIMS
At the end of your study, you should be able to:
Outline the general organization of the perineum
Describe the contents of the urogenital and anal triangles
Describe the central perineal tendon and perineal membrane
Outline the fascial layers and spaces of the perineum
Describe the anatomyof the scrotum
Describe the anatomyof the penis
299 / 425

GUIDE
Pelvis and Perineum: Perineum and External Genitalia: Male
[Plate 361, Male Perineum and External Genitalia (Deeper Dissection)]
Perineum
General organization (Same as female)
Narrow region between superior medial aspects of thigh
With lower limbs abducted in lithotomyposition, becomes a diamond-shaped area
Bounded bypelvic diaphragm superiorlyand superficial fascia and skin inferiorly
Anal canal, urethra, and vagina (females) pass through the perineum
Boundaries:
Anteriorly: Pubic symphysis
Posteriorly: Inferior sacrum and coccyx
Anterolaterally: Ischiopubic rami
Laterally: Ischial tuberosities
Posterolaterally: Sacrotuberous ligaments
Divided into two triangles byimaginaryline between ischial tuberosities
Posteriorlyis anal triangle
Anteriorlyis urogenital triangle
Contents of anal triangle (Same as female)
Anal canal and anus
External and internal anal sphincters
Ischiorectal fossa
Contents of urogenital triangle
Membranous and spongyurethra (males); distal urethra (females)
300 / 425

Vagina (females)
Proximal erectile bodies of the penis (males) and vulva (females)
Attachment of the scrotum
page 190 page 191
Central perineal tendon (perineal body) (Same as female)
Located at midpoint of the line dividing the urogenital from anal triangles
Mass of collagenous and elastic fibers
Deep to skin
Anterior to anal canal
Posterior to bulb of the penis (male) or vestibule (female)
Site of attachment for
Bulbospongiosus
Superficial transverse perineal muscles
Deep transverse perineal muscles
External anal sphincter
Fascicles of muscle from external sphincter urethrae and levator ani
Perineal membrane
Thin sheet of deep fascia
Runs between the two ischiopubic rami Spans anterior pelvic outlet
Pierced byurethra and ducts of bulbourethral glands
Is attached to perineal bodyat midpoint of posterior margin Thickened anterior margin = transverse perineal ligament Superficial transverse perineal muscles
Lie superficial to (external to) perineal membrane
 Extend from ischiopubic ramus on either side along posterior aspect of perineal membrane to attach to the perineal body Deep transverse perineal muscles
Extend from ischiopubic ramus on either side along posterior aspect of perineal membrane to attach to the perineal body Deep transverse perineal muscles
Lie deep to (internal to) perineal membrane
 Extend from ischiopubic ramus on either side along posterior aspect of perineal membrane to attach to the perineal body Sphincter urethrae (external urethral sphincter)
Extend from ischiopubic ramus on either side along posterior aspect of perineal membrane to attach to the perineal body Sphincter urethrae (external urethral sphincter)
Lies deep to (internal or superior to) perineal membrane
Circular fibers around membranous part of urethra in males
Anterior to deep transverse perineal muscles
Deep transverse perineal muscles and sphincter urethrae traditionallytermed urogenital diaphragm
Fascia and spaces of the urogenital triangle
page 191 page 192
Superficial fascia of the urogenital triangle has two layers, similar to the abdomen
Superficial fattylayer
Deep membranous layer (Colles' fascia)
 Superficial layer replaced in penis and scrotum bydartos layer (smooth or dartos muscle) Membranous layer of superficial fascia
Superficial layer replaced in penis and scrotum bydartos layer (smooth or dartos muscle) Membranous layer of superficial fascia
Posteriorlyattached to posterior margin of perineal membrane and perineal body
Laterallyattached to deep fascia (fascia lata) of superior medial thigh
 Anteriorlyis continuous with membranous layer of superficial fascia of abdomen (Scarpa's fascia) Deep perineal fascia (Gallaudet's fascia)
Anteriorlyis continuous with membranous layer of superficial fascia of abdomen (Scarpa's fascia) Deep perineal fascia (Gallaudet's fascia)
Invests ischiocavernosus, bulbospongiosus, and superficial transverse perineal muscles
 Fused to suspensoryligament of penis or clitoris Superficial perineal space (pouch)
Fused to suspensoryligament of penis or clitoris Superficial perineal space (pouch)
Between membranous layer of superficial fascia and perineal membrane
Contains in males:
Bulb and crura of penis and associated muscles Proximal spongyurethra
Superficial transverse perineal muscles
Branches of internal pudendal vessels and pudendal nerves Contains in females:
Crura of clitoris and associated muscles Bulbs of vestibule and associated muscles Superficial transverse perineal muscles
Branches of internal pudendal vessels and pudendal nerves Greater vestibular glands
Deep perineal space (pouch)
Lies between perineal membrane and pelvic diaphragm
Ischioanal fossae extend anteriorlyinto this space
Contains: Membranous urethra
External sphincter urethrae
Bulbourethral glands: secrete clear mucous during sexual excitation, ducts descend through perineal membrane and terminate in spongyurethra
Deep transverse perineal muscles
301 / 425
Vessels and nerves
Male External Genitalia
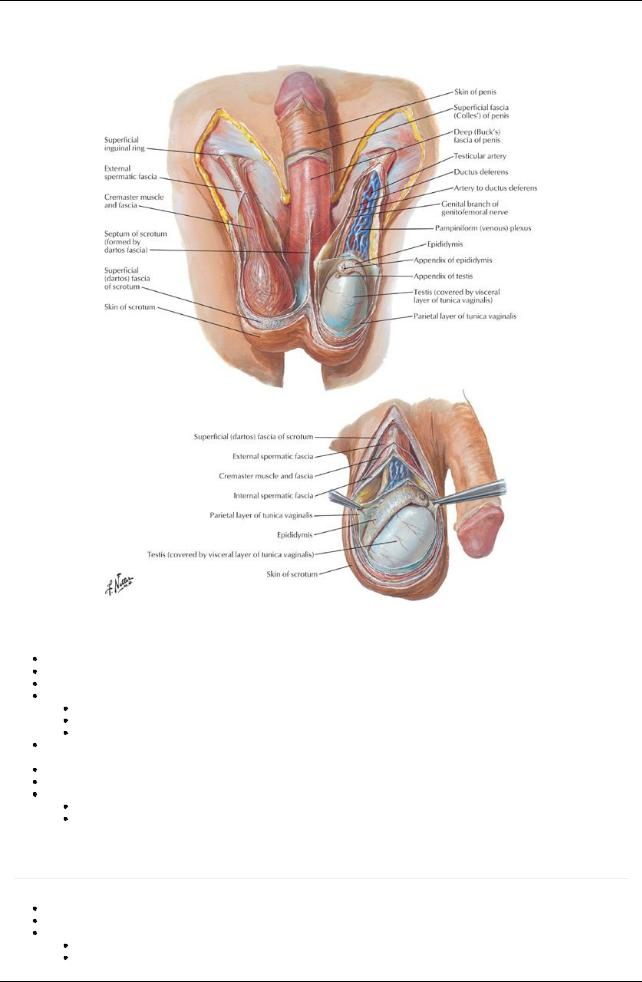
[Plate 367, Scrotum and Contents]
Scrotum
Sac derived from skin and superficial fascia of abdominal wall Contains testes, epididymis and distal portion spermatic cord
Skin shows midline scrotal raphe = fusion of bilateral labioscrotal swellings in embryo Dartos fascia
Continuation of deep membranous layer of superficial fascia of abdomen
Contains significant smooth muscle = dartos muscle
Extends inward, forming scrotal septum, separating right and left halves
Deep to dartos, tunics of spermatic cord (external spermatic, cremasteric and internal spermatic fascia form a fused layer around and external to tunica vaginalis
Supplied byexternal pudendal arteries and veins Lymphatics drain to superficial inguinal lymph nodes Innervated by
Anteriorly, ilioinguinal nerve and genital branch of genitofemoral
Posteriorly, posterior scrotal nerves (terminal branches of the pudendal) and perineal branches of the posterior femoral cutaneous nerves
Penis
page 192 page 193
Male organ of copulation
Composed of a body (shaft), root and glans Body is
Anchored in superficial perineal space (pouch) and attached to perineal membrane
Contains three cylindrical masses of erectile tissue
a. paired corpora cavernosa in parallel on dorsal surface
302 / 425

b. corpus spongiosum in midline of urethral surface (facing scrotum) Each erectile bodycovered bya fibrous tunic albuginea
Corpora cavernosa
Diverge posteriorlyto form the crura of the penis
 Each crus attaches to the inferior surface of corresponding ischiopubic ramus, anterior to ischial tuberosity Glans of the penis is the distal expansion of the corpus spongiosum: proximallyit forms bulb
Each crus attaches to the inferior surface of corresponding ischiopubic ramus, anterior to ischial tuberosity Glans of the penis is the distal expansion of the corpus spongiosum: proximallyit forms bulb
Membranous urethra pierces the perineal membrane and enters the bulb from above (so now is called spongyurethra) and terminates at external urethral meatus (at apexglans)
Root of penis is formed bybulb and crura
Two muscles are associated with erectile bodies
Bulbospongiosus muscle
Ischiocavernosus muscle
Bodyis surrounded bydeep fascia (Buck's fascia), external to tunic albuginea Skin of penis is connected to deep fascia byloose areolar connective tissue
At neck of the glans, the skin and connective tissue of the penis extends and a double-layered fold, the prepuce or foreskin Vessels and nerves run on dorsum of penis
Between skin and deep fascia
 Between deep fascia and tunica albuginea Innervation
Between deep fascia and tunica albuginea Innervation
Dorsal nerve of the penis from the pudendal nerve
Passes the length of the penis lateral to the dorsal arteryon that side Lies beneath deep fascia
Supplies skin and glans
Ilioinguinal nerve supplies skin of proximal shaft of penis
Erection controlled byparasympathetic nerves (pelvic splanchnic nerves), which relaxes smooth muscle in coiled arteries of penis supplying erectile bodies
Arterial supply
Dorsal arteries of penis from internal pudendal arteries run on either side of deep dorsal vein beneath deep fascia
Deep arteries from internal pudendal arteries Run distallywithin center of corpora cavernosa
Highlycoiled branches (helicine arteries) supplyerectile tissue
Arteryof bulb of penis from internal pudendal arterysupplies posterior corpus spongiosum
 External pudendal arteries supplyskin of penis (branch of femoral artery). Venous drainage
External pudendal arteries supplyskin of penis (branch of femoral artery). Venous drainage
Deep dorsal vein of penis receives blood from venous plexus
Drains to prostatic venous plexus and then to internal iliac/internal pudendal veins. Superficial dorsal vein of penis drains to superficial external pudendal vein
Lymphatic drainage mainlyto superficial inguinal nodes
Muscles of the penis
Muscle |
Proximal attachment |
Distal |
Innervation |
Action |
|
|
attachment |
|
|
Bulbospongiosus |
Ventral surface of bulb of penis |
Corpus |
Deep branch of perineal |
Compresses bulb of penis |
|
Perineal body |
spongiosus |
nerve from pudendal nerve |
Forces blood into bodyof |
|
|
|
|
penis during erection |
|
|
|
|
Compresses outflow veins |
Ischiocavernosus |
Inferior internal surface of ischiopubic |
Crus of |
Deep branch of perineal |
Forces blood into bodyof |
|
ramus and ischial tuberosity |
penis |
nerve from pudendal nerve |
penis during erection |
|
|
|
|
Compresses outflow veins |
303 / 425
