
- •1. Topographic Surface Anatomy
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •3. Superficial Face
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •4. Neck
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •5. Nasal Region
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •6. Oral Region
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •7. Pharynx
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •13. Cerebral Vasculature
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •14. Topographic Anatomy
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •16. Spinal Cord
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Thorax
- •18. Topographic Anatomy
- •Guides
- •Facts & Hints
- •19. Mammary Gland
- •Guides
- •Facts & Hints
- •20. Body Wall
- •Guides
- •Facts & Hints
- •21. Lungs
- •Guides
- •Facts & Hints
- •22. Heart
- •Guides
- •Facts & Hints
- •23. Mediastinum
- •Guides
- •Facts & Hints
- •Abdomen
- •24. Topographic Anatomy
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •25. Body Wall
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •26. Peritoneal Cavity
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •27. Viscera (Gut)
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •28. Viscera (Accessory Organs)
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •29. Visceral Vasculature
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •30. Innervation
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •32. Topographic Anatomy
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •35. Urinary Bladder
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •39. Testis, Epididymis & Ductus Deferens
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •40. Rectum
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •41. Vasculature
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •42. Innervation
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Upper Limb
- •43. Topographic Anatomy
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •48. Neurovasculature
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Lower Limb
- •49. Topographic Anatomy
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •51. Knee
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •54. Neurovasculature
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints

40 Rectum
STUDYAIMS
At the end of your study, you should be able to:
Describe the gross structure of the rectum, including its musculature
List the relations of the rectum
Outline the blood and vascular supplyof the rectum
Describe structures that maybe palpated on digital rectal examination
Describe the anatomyof the anus
Describe the blood and vasculature supplyto the different regions of the anus
310 / 425
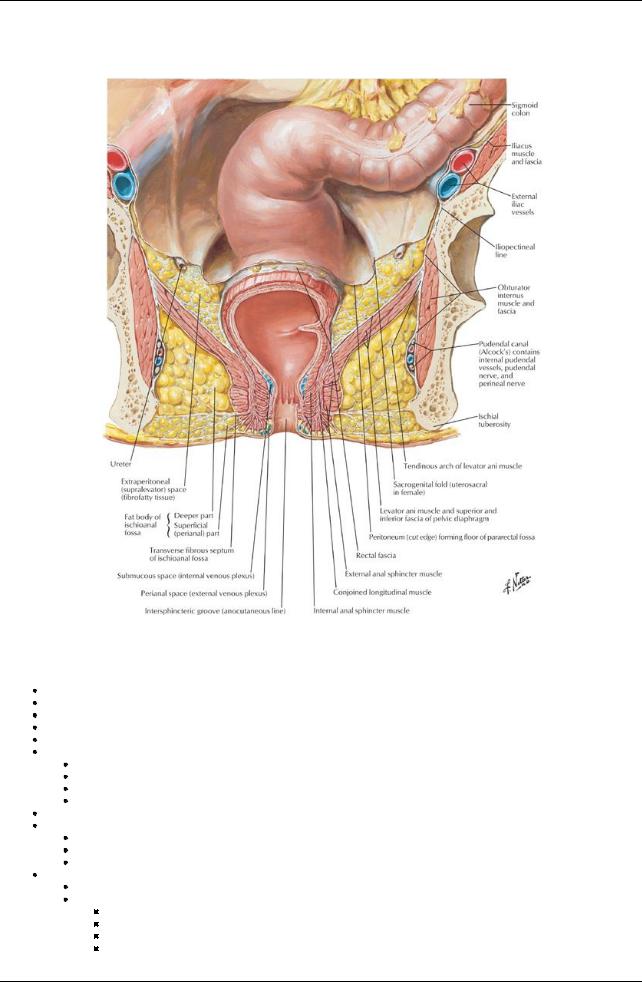
GUIDE
Pelvis and Perineum: Rectum and Anal Canal
[Plate 372, Ischioanal Fossae]
Rectum
Gross structure
Approximately12 cm in length
Is a part of the large bowel
Commences at level S3 vertebral bodyand follows the curve of the sacrum and coccyx
Is a continuation of the sigmoid colon at rectosigmoid junction
Extends from rectosigmoid junction to anal canal (anorectal junction)
Anorectal junction
Lies at level of pelvic floor
Puborectalis muscle forms a U-shaped sling at this point
Perineal flexure annulates anorectal junction
Is palpated as anorectal ring on digital rectal examination
Three lateral curves/flexures in the rectum (upper and lower curves deviate to the right; the middle to the left)
Rectal ampulla
In region of middle and lower curves
Somewhat dilated
Verydistensible
Internal structure
Smooth mucosa, changes from rugose mucosa of sigmoid colon
Transverse rectal folds
Three infoldings of mucosa and submucosa project into lumen
Superior, middle, and inferior
Called rectal valves of Houston
Result from three lateral flexures
311 / 425

Relations
page 199 page 200
Peritoneum
Upper third of rectum covered byperitoneum on anterior aspect and sides
Middle third of rectum covered byperitoneum on anterior surface only
Lower third of rectum below peritoneal reflection
Pararectal fossae on lateral sides of rectum in peritoneal cavity
Rectovesical septum of pelvic fascia separates rectum from prostate
Rectovaginal septum of pelvic fascia separates rectum from vagina
Lateral ligaments of rectum-condensations of pelvic fascia around middle rectal vessels
Relations of Rectum
|
|
Relations |
|
Posterior |
Sacrum |
|
|
Coccyx |
|
|
Piriformis muscle |
|
|
Superior rectal vessels |
|
|
Hypogastric plexus (ANS) |
|
|
Sympathetic trunk nerves |
|
|
Sacral plexus |
|
Inferior |
Levator ani muscles |
|
Lateral |
Pelvic plexus nerves (ANS) |
|
|
Ureters |
|
Anterior |
Sigmoid colon |
|
|
Ileum |
|
Anterior structures palpable on rectal examination |
Prostate (males) |
|
|
Base bladder |
|
|
Seminal vesicles (males) |
|
|
Ampullae of ductus deferens (males) |
|
|
Cervix(females) |
Blood supply |
|
|
Arterial
Mainlybysuperior rectal artery(continuation of inferior mesenteric artery)
Also supplied bythe middle rectal arteries (from internal iliac arteries) to the middle and inferior parts
Inferior rectal arteries supplythe anorectal junctions and anal canal
Superior, middle, and inferior rectal arteries anastomose with each other
Venous
Chief drainage via a rectal venous plexus to the superior rectal vein
Middle and inferior rectal veins also drain the rectum
Superior rectal vein drains to the portal system
Middle and inferior rectal veins drain to the inferior vena cava via the internal iliac vein
Anastomoses between these veins link the portal and system systems
Lymphatic drainage
Lymphatic vessels from superior half of rectum drain to pararectal nodes and from there to inferior mesenteric and lumbar nodes
Lymphatic vessels from the inferior half of the rectum travel with the middle rectal vessels to the internal iliac nodes and anastomose with the lymphatics of the anal canal
Nerve supply
Sympathetic innervation
From lumbar sympathetic fibers via the inferior mesenteric arteries and the superior rectal arteries to the superior rectal plexus to blood vessels of rectum
Parasympathetic innervation
Are the main motor fibers to muscles of the rectal wall
From the pelvic splanchnic nerves (S2-S4) via the inferior hypogastric (pelvic) plexus to middle rectal plexus Visceral afferent (sensory) fibers travel via the inferior hypogastric (pelvic)
plexus and pelvic splanchnics back to spinal cord
page 200 page 201
Anal Canal
Gross structure
Terminal part of gastrointestinal tract Is approximately3 cm long
Commences at anorectal junction and ends at anus Encircled byinternal and external sphincter muscles Descends between perineal bodyand anococcygeal ligament
Mucosal lining of superior has longitudinal ridges-anal columns
Inferior ends of columns joined byanal valves
Behind valves are small sinuses: anal sinuses
Anal glands (mucus) emptyinto anal sinuses
Inferior end of anal valves forms an irregular line: pectinate (or dentate) line
Pectinate line divides the superior portion of the anal canal, derived from embryonic endoderm (hindgut), from the inferior portion derived
312 / 425

from ectoderm (proctodeum)
Inferior half lined bynonkeratinized squamous epithelium (skin)
Vascular, nerve and lymphatic supplyof these two regions different as a result of different embryologic origin
Vascular, Lymphatic, and Nerve Supply to the Anal Canal
Supply |
Above Pectinate Line |
Below Pectinate Line |
Arterial |
Superior rectal artery |
Inferior rectal arteries |
Venous |
Internal plexus drains to superior rectal vein and portal |
Internal venous plexus drains to inferior rectal veins and |
|
system |
caval system |
Lymphatic |
To internal iliac and common iliac and lumbar nodes |
To superficial inguinal nodes |
Nerve |
From inferior hypogastric (pelvic) plexus (both sympathetic |
From inferior rectal nerves, branches of the pudendal |
|
and parasympathetic; sensitive to stretching only) |
nerves (sensitive to pain, temperature and touch) |
Has two sphincters: external (voluntary) and internal (involuntary)
External sphincter
Described as having superficial, subcutaneous, and deep parts Parts are not readilydistinguishable
Fibers attach to the central perineal tendon (body) anteriorlyand anococcygeal ligament posteriorly
Internal sphincter: internal circular muscular layer continuous from rectum around upper two thirds of anal canal
Anorectal Musculature
Ischiorectal (Ischioanal) fossae
page 201
page 202
Fat filled, wedge-shaped recesses either side of anal canal Communicate with each other posteriorlyover the anococcygeal ligament Bounded by
Laterally: ischium and obturator internus muscle and fascia
Medially: anal canal surrounded byexternal anal sphincter
Anteriorlybyexternal sphincter urethrae and deep transverse perineal muscles
Superiorlybypelvic diaphragm
Inferiorlybysuperficial perineal fascia and skin
Filled with fat spanned byfibrous bands to support anal canal but compressible during defecation
On lateral walls are found internal pudendal vessels and pudendal nerve within pudendal (Alcock's) canal in the fascia of the internal surfaces of obturator muscles
Extends anteriorlysuperior to perineal membrane as anterior recesses of ischiorectal (ischioanal) fossae Important site abscess formation
313 / 425
