
- •1. Topographic Surface Anatomy
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •3. Superficial Face
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •4. Neck
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •5. Nasal Region
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •6. Oral Region
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •7. Pharynx
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •13. Cerebral Vasculature
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •14. Topographic Anatomy
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •16. Spinal Cord
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Thorax
- •18. Topographic Anatomy
- •Guides
- •Facts & Hints
- •19. Mammary Gland
- •Guides
- •Facts & Hints
- •20. Body Wall
- •Guides
- •Facts & Hints
- •21. Lungs
- •Guides
- •Facts & Hints
- •22. Heart
- •Guides
- •Facts & Hints
- •23. Mediastinum
- •Guides
- •Facts & Hints
- •Abdomen
- •24. Topographic Anatomy
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •25. Body Wall
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •26. Peritoneal Cavity
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •27. Viscera (Gut)
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •28. Viscera (Accessory Organs)
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •29. Visceral Vasculature
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •30. Innervation
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •32. Topographic Anatomy
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •35. Urinary Bladder
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •39. Testis, Epididymis & Ductus Deferens
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •40. Rectum
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •41. Vasculature
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •42. Innervation
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Upper Limb
- •43. Topographic Anatomy
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •48. Neurovasculature
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Lower Limb
- •49. Topographic Anatomy
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •51. Knee
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •54. Neurovasculature
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints

FACTS & HINTS
HIGH-YIELD FACTS
Clinical Points
Subluxation of the Radial Head (Nursemaid Elbow)
Caused bysudden pulling on the upper limb with the forearm pronated
Distal attachment of the annular ligament is torn and radial head slips out, trapping the ligament between it and the capitulum Preschool children, especiallygirls, most vulnerable
Head of radius is repositioned bysupinating forearm fullyand then flexing elbow
Bursitis of the Elbow
Repeated pressure or friction on a bursa maycause it to become inflamed and tender
Subcutaneous olecranon bursitis ("student's elbow") most common, often occurring in students (from resting elbows on desk), darts players and from falls and abrasions to the elbow
Subtendinous olecranon bursitis less common, as is bicipitoradial bursitis
Epicondylitis
Activities involving repetitive movements of wrist maylead to localized elbow pain
Repeated extension of wrist causes lateral epicondylitis ("tennis elbow")-microtrauma of common extensor muscle origin, with pain felt over the lateral aspect of the elbow
Medial epicondylitis ("golfer's elbow") from repeated wrist flexion, with pain felt over the medial epicondyle, especiallyon resisted wrist flexion
Bursitis or synovitis maycoexist with epicondylitis
MNEMONICS
Memory Aids
Radial nerve innervates the BEST! |
Brachioradialis |
|
Extensors |
|
Supinator |
|
Triceps |
Muscles that flexthe elbow: |
Three B's Bend the elBow |
|
Brachialis Biceps |
|
Brachioradialis |
358 / 425

47 Wrist and Hand
STUDYAIMS
At the end of your study, you should be able to:
Describe the radiocarpal joint, its movements, and supporting ligaments
Know the bones of the hand and their organization
Describe the movements at the carpometacarpal, metacarpophalangeal, and interphalangeal joints
Describe the organization of the deep fascia of the hand
Understand the arrangement of the intrinsic muscles of the hand
359 / 425
GUIDE
Upper Limb: Wrist and Hand
[Plate 441, Movement of Wrist]
360 / 425

[Plate 442, Ligaments of Wrist]
361 / 425

[Plate 443, Ligaments of Wrist (Continued)]
362 / 425
[Plate 445, Wrist and Hand Radiographs]
363 / 425
[Plate 455, Wrist and Hand: Superficial Radial Dissection]
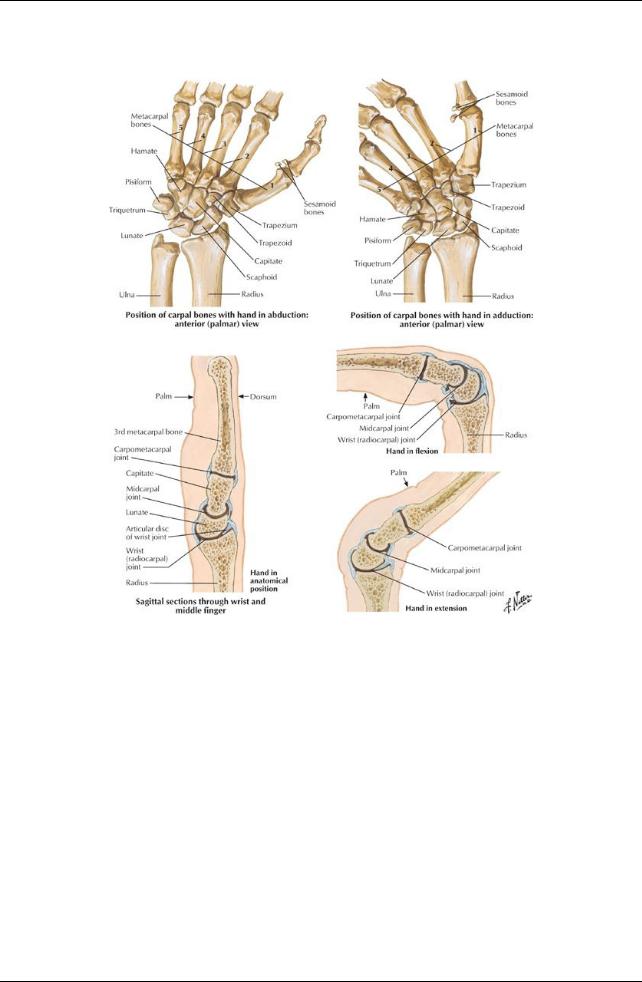
Wrist (Radiocarpal) Joint
Biaxial synovial joint
Located at a line joining the styloid processes of the radius and ulna
Articulation of distal end of radius and articular disc of radioulnar joint with the proximal row of carpal bones (except the pisiform)
Fibrous capsule surrounds the wrist
From distal ends of radius and ulna to proximal row of carpal bones
Lined bya synovial membrane with numerous folds
Movements
Flexion/extension
Abduction/adduction (radial/ulnar abduction)
Circumduction
Adduction greater than abduction
Ligaments
Dorsal and palmar radiocarpal ligaments from the radius to the two rows of carpals on the palmar and dorsal sides
Ulnar collateral ligament from the ulnar styloid process to the triquetrum
Radial styloid ligament from the radial styloid process to the scaphoid
Blood supply: Branches of the dorsal and palmar carpal arches
Nerve supply
Anterior interosseous branch of median nerve
Posterior interosseous branch of radial nerve Dorsal and deep branches of ulnar nerve
Hand
page 230
page 231
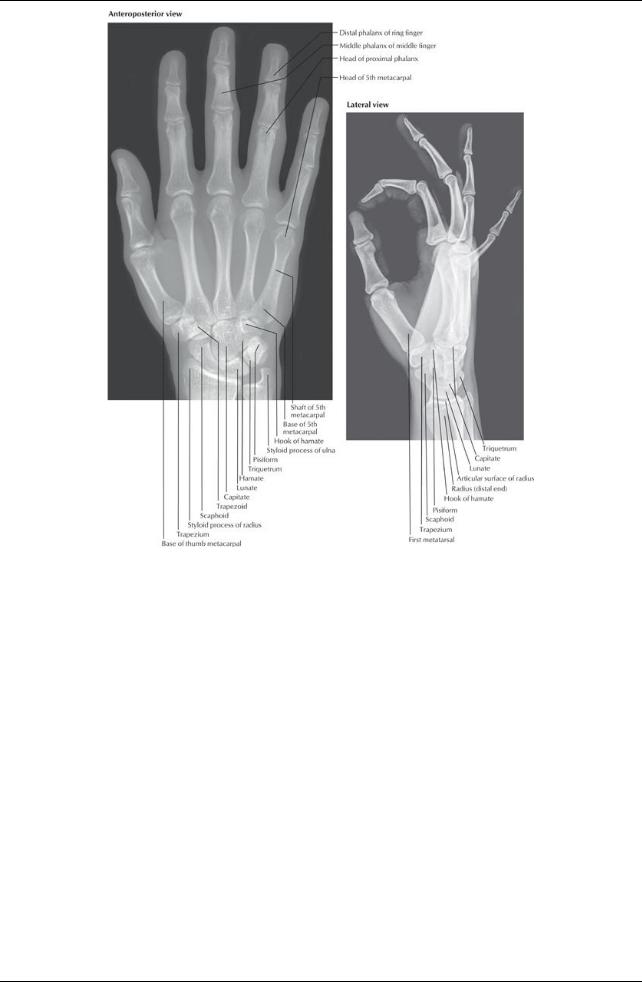
Bones (27)
Carpal bones (bones of the wrist or carpus)
Proximal row: Scaphoid, lunate, triquetrum, pisiform,
Distal row: Trapezium, trapezoid, capitate, hamate
Metacarpals (5) consist of
364 / 425

Base (proximal)-articulate with distal row of carpal bones
Body
Head (distal)-articulate with proximal phalanges and form knuckles
Phalanges (14)
Each digit has three phalanges: proximal, middle, and distal, except for
Thumb (has two)
Each phalanxhas a base (proximal), body, and head (distal)
Decrease in size from proximal to distal
Major Joints of the Hand
Carpometacarpal, metacarpophalangeal, and interphalangeal are all synovial joints supplied bybranches of adjacent vessels and nerves Intercarpal joints
Joints between carpal bones of first row and joints between carpal bones of second row
Midcarpal joint between first and second rows
Supported byanterior, posterior, and interosseous ligaments
Function as a single unit
 Small gliding movements between carpal bones Carpometacarpal joints
Small gliding movements between carpal bones Carpometacarpal joints
Plane type synovial joints, except for carpometacarpal of thumb (saddle type)
Medial four carpometacarpal joints in one fibrous joint capsule
Separate capsule for thumb
Joint for thumb between the trapezium and first metacarpal
Allows flexion, extension, abduction, adduction, circumduction, and opposition

 Loose joint capsule allows for free movement Metacarpophalangeal joints (MCP)
Loose joint capsule allows for free movement Metacarpophalangeal joints (MCP)
Heads of metacarpals articulate with base of proximal phalanx
Deep transverse metacarpal ligaments hold heads of metacarpals 2 through 5 together
Separate joint capsule for each joint
Movements: flexion, extension, abduction, and adduction
 Because the collateral ligaments tighten during flexion, abduction, and adduction are onlypossible in the extended position Interphalangeal joints
Because the collateral ligaments tighten during flexion, abduction, and adduction are onlypossible in the extended position Interphalangeal joints
Proximal interphalangeal joint = PIP Distal interphalangeal joint = DIP Allow flexion and extension
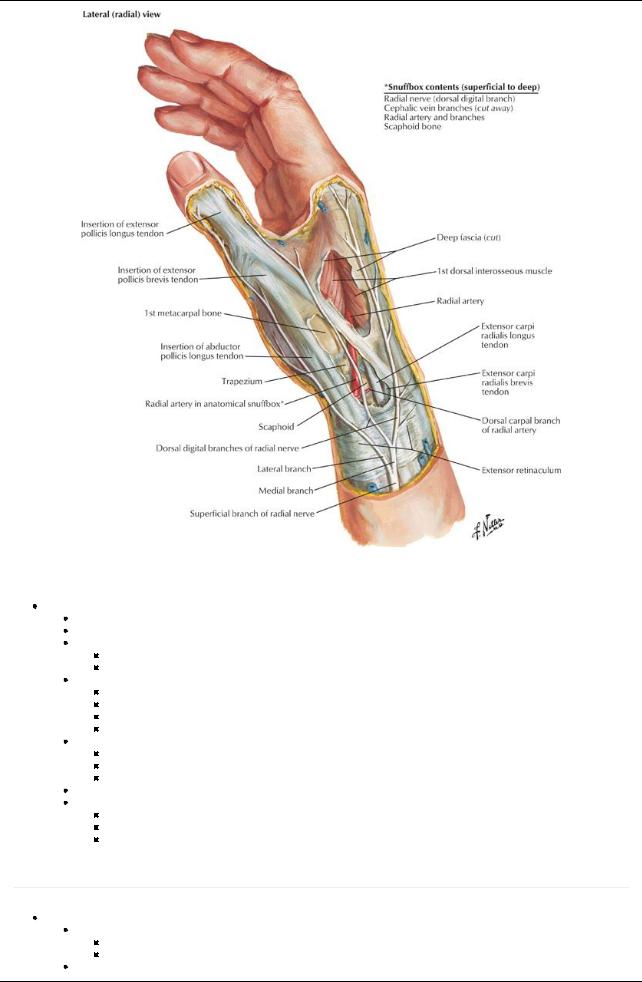
Fascia of the Hand
Extensor and flexor retinaculum continuous with antebrachial fascia
Palmar fascia thickened centrallyas the palmar aponeurosis
Four distinct extensions to the bases of the fingers
Continuous with the fibrous tendon sheaths
Anchored tightlyto skin of palm bynumerous ligamentous bands (retinacula cutis)
Fibrous digital sheaths surround synovial sheaths that enclose superficial and deep flexor tendons
Medial fibrous septum extends from medial border of palmar aponeurosis to fifth metacarpal
Lateral fibrous septum extends from lateral border of palmar aponeurosis to third metacarpal
Septa create compartments within the palm
Muscles of the Hand
page 231 page 232
Adductor pollicis
Thenar (lateral) compartment
Abductor pollicis brevis
Flexor pollicis brevis
Opponens pollicis
Hypothenar (medial) compartment
Abductor digiti minimi
Flexor digiti minimi brevis
Opponens digiti minimi
Short muscles of the hand
Lumbricals-unusual in that theyflexMCP joints and extend IP joints
Palmar interossei-adduct digits
Dorsal interossei-abduct digits
Palmaris brevis
Wrinkles skin of hypothenar eminence
Improves palmar grip
|
Muscle |
Origin |
Insertion |
Innervation |
Action |
Blood |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Supply |
|
|
|
Abductor |
Flexor retinaculum, tubercles of scaphoid |
Lateral side of base |
Recurrent |
Abducts and assists in |
Superficial |
|
|
|
pollicis |
and trapezium |
of proximal phalanx |
branch of |
opposition of thumb |
palmar |
|
|
|
brevis |
|
of thumb (1st digit) |
median |
|
branch of |
|
|
|
|
|
|
nerve (C8- |
|
radial artery |
|
|
|
|
|
|
T1) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
365 / 425 |
||

Flexor |
Flexor retinaculum and trapezium |
Lateral side of base |
Recurrent |
Flexes proximal phalanx |
Superficial |
pollicis |
|
of proximal phalanx |
branch of |
of thumb |
palmar |
brevis |
|
of thumb |
median |
|
branch of |
|
|
|
nerve (C8- |
|
radial artery |
|
|
|
T1) |
|
|
Opponens |
Flexor retinaculum and trapezium |
Lateral side of 1st |
Recurrent |
Draws 1st metacarpal |
Superficial |
pollicis |
|
metacarpal |
branch of |
forward and rotates it |
palmar |
|
|
|
median |
medially |
branch of |
|
|
|
nerve (C8- |
|
radial artery |
|
|
|
T1) |
|
|
Adductor |
Oblique head-bases of second and third |
Medial side of base |
Deep branch |
Adducts thumb |
Deep |
pollicis |
metacarpals capitate and adjacent bones; |
of proximal phalanx |
of ulnar nerve |
|
palmar arch |
|
Transverse head-anterior surface of third |
of thumb |
(C8-T1) |
|
|
|
metacarpal |
|
|
|
|
Palmaris |
Palmar aponeurosis |
Skin of ulnar border |
Superficial |
Deepens the hollow of |
Superficial |
brevis |
|
of palm |
palmar |
the hand |
palmar arch |
|
|
|
branch of |
|
|
|
|
|
ulnar nerve |
|
|
|
|
|
(C8) |
|
|
Abductor |
Pisiform bone, tendon of flexor carpi |
Medial side of base |
Deep branch |
Abducts the little finger |
Deep |
digiti |
ulnaris |
of proximal phalanx |
of ulnar nerve |
(fifth digit) |
palmar |
minimi |
|
of little finger |
(C8-T1) |
|
branch of |
(hand) |
|
|
|
|
ulnar artery |
Flexor digiti |
Flexor retinaculum and hook of hamate |
Medial side of base |
Deep branch |
Flexes proximal phalanx |
Deep |
minimi |
bone |
of proximal phalanx |
of ulnar nerve |
of the little finger |
palmar |
brevis |
|
of little finger |
(C8-T1) |
|
branch of |
(hand) |
|
|
|
|
ulnar artery |
Opponens |
Flexor retinaculum and hook of hamate |
Medial side of fifth |
Deep branch |
Draws fifth metacarpal |
Deep |
digiti |
bone |
metacarpal |
of ulnar nerve |
anteriorlyand rotates it |
palmar |
minimi |
|
|
(C8-T1) |
to face thumb |
branch of |
|
|
|
|
|
ulnar artery |
Lumbricals |
Lateral two tendons of flexor digitorum |
Lateral sides of |
Median nerve |
Extends digits at |
Superficial |
1 and 2 |
profundus |
extensor expansion |
(C8-T1) |
interphalangeal joints |
and deep |
|
|
of digits 2 and 3 |
|
and flexes |
palmar |
|
|
|
|
metacarpophalangeal |
arches |
|
|
|
|
joints |
|
Lumbricals |
Medial three tendons of flexor digitorum |
Lateral sides of |
Deep branch |
Extends digits at |
Superficial |
3 and 4 |
profundus |
extensor expansion |
of ulnar nerve |
interphalangeal joints |
and deep |
|
|
of digits 4 and 5 |
(C8-T1) |
and flexes |
palmar |
|
|
|
|
metacarpophalangeal |
arches |
|
|
|
|
joints |
|
Dorsal |
Adjacent sides of two metacarpal bones |
Base of proximal |
Deep branch |
Abducts digits from axial |
Deep |
interossei |
|
phalanxand extensor |
of ulnar nerve |
line of hand-third digit |
palmar arch |
|
|
expansion of digits 2- |
(C8-T1) |
|
|
|
|
4 |
|
|
|
Palmar |
Palmar surfaces of metacarpals 2, 4, and |
Bases of proximal |
Deep branch |
Adducts digits toward |
Deep |
interossei |
5 |
phalanxand extensor |
of ulnar nerve |
axial line of hand-third |
palmar arch |
|
|
expansion of digits 2, |
(C8-T1) |
digit |
|
|
|
4, and 5 |
|
|
|
366 / 425
