
- •1. Topographic Surface Anatomy
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •3. Superficial Face
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •4. Neck
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •5. Nasal Region
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •6. Oral Region
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •7. Pharynx
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •13. Cerebral Vasculature
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •14. Topographic Anatomy
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •16. Spinal Cord
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Thorax
- •18. Topographic Anatomy
- •Guides
- •Facts & Hints
- •19. Mammary Gland
- •Guides
- •Facts & Hints
- •20. Body Wall
- •Guides
- •Facts & Hints
- •21. Lungs
- •Guides
- •Facts & Hints
- •22. Heart
- •Guides
- •Facts & Hints
- •23. Mediastinum
- •Guides
- •Facts & Hints
- •Abdomen
- •24. Topographic Anatomy
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •25. Body Wall
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •26. Peritoneal Cavity
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •27. Viscera (Gut)
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •28. Viscera (Accessory Organs)
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •29. Visceral Vasculature
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •30. Innervation
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •32. Topographic Anatomy
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •35. Urinary Bladder
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •39. Testis, Epididymis & Ductus Deferens
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •40. Rectum
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •41. Vasculature
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •42. Innervation
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Upper Limb
- •43. Topographic Anatomy
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •48. Neurovasculature
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Lower Limb
- •49. Topographic Anatomy
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •51. Knee
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •54. Neurovasculature
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints

42 Innervation
STUDYAIMS
At the end of your study, you should be able to:
Describe the formation of the sacral plexus
Know the main branches of this plexus and what theysupply
Describe the parasympathetic innervation of the pelvis
Describe the sympathetic innervation of the pelvis
Describe the innervation of the perineum
320 / 425
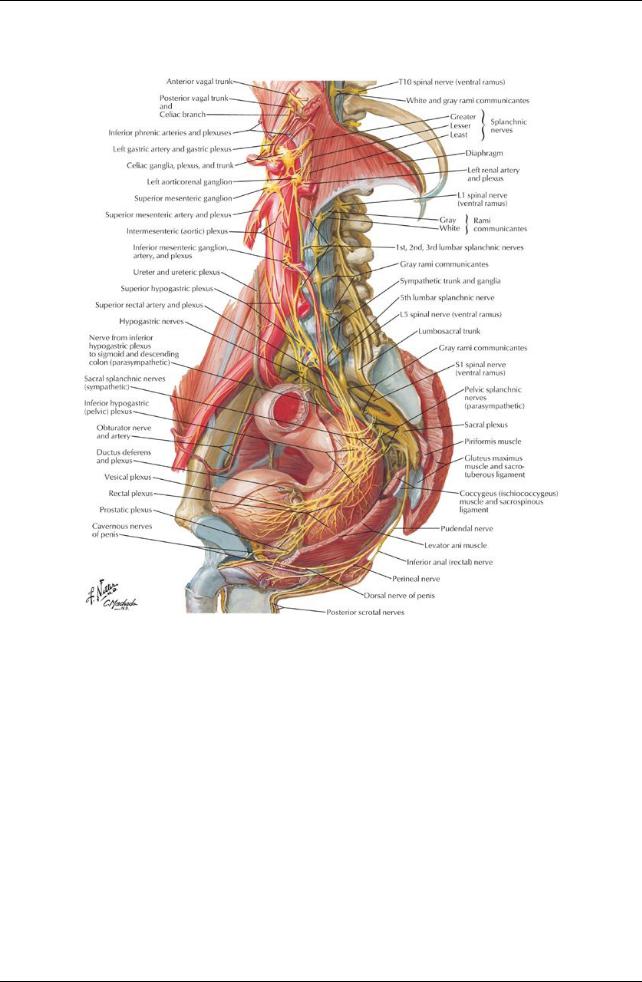
GUIDE
Pelvis and Perineum: Innervation
[Plate 390, Nerves of Pelvic Viscera: Male]
321 / 425
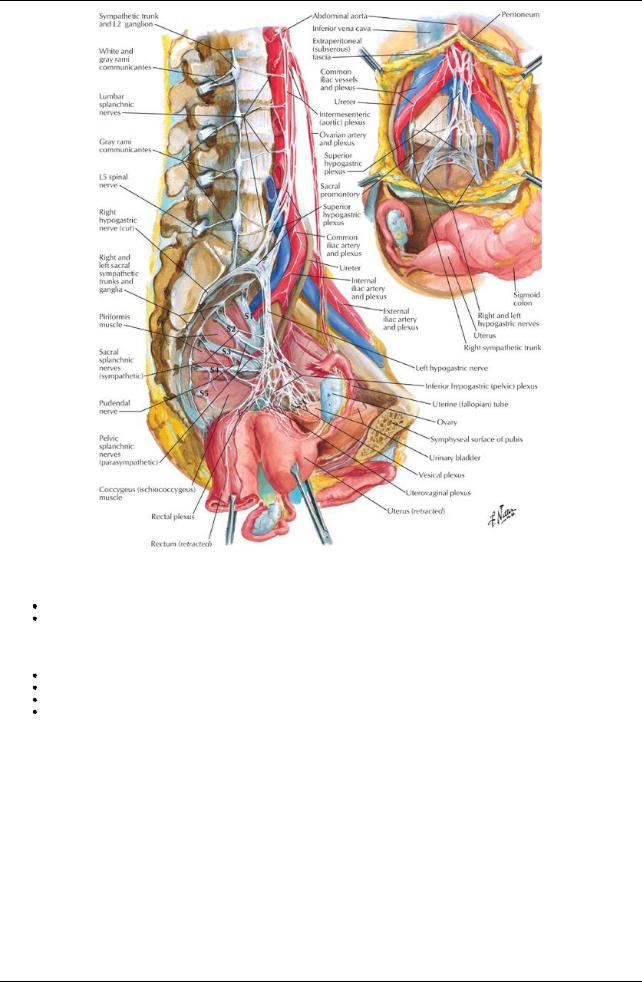
[Plate 392, Nerves of Pelvic Viscera: Female]
Innervation of the Pelvis
Pelvic innervation is both somatic and autonomic
Manynerves pass through the pelvis without innervating anystructures
Sacral plexus (somatic contribution)
Located on posterior wall of true pelvis on anterior surface of piriformis muscle
Formed byventral rami of S1-S4 spinal nerves and the lumbosacral trunk, formed from fibers from the ventral rami of L4-L5 spinal nerves Branches supply: lower limb; pelvic floor and wall and perineum; most branches leave the pelvis through greater sciatic foramina
Two major branches are the sciatic nerve and pudendal nerve
Branches of the Sacral Plexus
Nerve |
Structures Supplied |
Spinal nerve origin |
Major branches |
|
|
Sciatic |
Hip joint |
L4-L5, S1-S3 |
|
Flexor muscles of knee |
|
|
Muscles of leg and foot |
|
Pudendal |
Sensoryand motor to all structures in the perineum |
S2-S4 |
Superior gluteal |
Gluteus medius and minimus muscles |
L4-L5, S1 |
Inferior gluteal |
Gluteus maximus muscle |
L5, S1-S2 |
Posterior femoral cutaneous |
Sensoryto buttock, superior medial, and posterior thigh |
S2-S3 |
Minor branches |
|
|
Nerve to piriformis |
Piriformis muscle |
S1-S1 |
Nerve to obturator internus and superior gemellus mm |
Obturator internus and superior gemellus muscles |
L5, S1-S2 |
Nerve to quadratus femoris and inferior gemellus mm |
Quadratus femoris and inferior gemellus muscles |
L4-L5, S1 |
Nerve to levator ani and coccygeus |
Pelvic diaphragm |
S3-S4 |
page 208
322 / 425

page 209
Autonomic nerves
Sympathetic innervation
Sympathetic trunks
Contain fibers from lower thoracic and upper lumbar spinal segments Descend on posterior abdominal wall on either side of the vertebral bodies Descend behind common iliac artery, in front of sacrum and piriformis muscle Fuse on anterior surface of coccyxas ganglion impar
Are source of sacral splanchnic nerves that join inferior hypogastric (pelvic) plexus in pelvis
Contain either postsynaptic fibers from synapses in ganglia superiorlyor presynaptic fibers that will synapse in one of four sympathetic ganglia in pelvis
Primaryfunction is to send postsynaptic fibers to sacral spinal nerves via greyrami communicantes
No white rami communicantes associated with sacral sympathetic trunks because sympathetic outflow is thoracolumbar Lumbar splanchnics join superior hypogastric plexus
Superior hypogastric plexus
Is located just below the bifurcation of the aorta
Is a continuation of the intermesenteric/aortic plexus Contains no parasympathetic fibers
Contains visceral afferents ascending from the pelvis
Continues into the pelvis as loose collections of fibers in either side of the anterior sacrum = right and left hypogastric nerves Spreads out in pelvis as inferior hypogastric (pelvic) plexus
Functions
Vasomotor, pilomotor, secretoryto sweat glands to skin of perineum and lower limb Controls ejaculation (in males)
Innervates smooth muscle of blood vessels in pelvis and smooth muscle of some organs Parasympathetic innervation
From pelvic splanchnic nerves
Outflow from 2nd to 4th sacral spinal cord segment Contain visceral afferents
Controls micturition, erection, and defecation
Innervates descending and sigmoid colon via fibers ascending in the sigmoid mesenteryand the parietal peritoneum of the left side of the posterior abdominal wall
Inferior Hypogastric (Pelvic) Plexus
General structure
Formed from fibers of hypogastric nerves, sacral splanchnic nerves, and pelvic splanchnic nerves Lies on posterolateral pelvic wall internal to internal iliac arteries and their branches
Gives off
Middle rectal plexus
Uterovaginal plexus (females)
Vesical plexus
Deferential plexus
Prostatic plexus (males
Cavernous nerves (nervi erigentes) to erectile tissue of penis and clitoris
Except for cavernous nerves, nerves in the various plexuses reach the viscera in companywith relevant branches of the internal iliac artery Branches transmit efferents from both sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous systems and visceral afferents
page 209 page 210
Contents
Preand postsynaptic sympathetic fibers from superior hypogastric plexus via hypogastric nerves Postsynaptic sympathetic fibers from sacral splanchnic nerves
Sympathetic ganglia
Visceral afferent fibers that either ascend along the hypogastric nerves or return to the CNS via the pelvic splanchnic nerves, depending on the information carried.
Presynaptic parasympathetic fibers from the pelvic splanchnic nerves
Enteric parasympathetic ganglia where the plexus lies on or near a pelvic viscus Postsynaptic parasympathetic fibers from the enteric ganglia to the viscus innervated
323 / 425
