
- •1. Topographic Surface Anatomy
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •3. Superficial Face
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •4. Neck
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •5. Nasal Region
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •6. Oral Region
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •7. Pharynx
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •13. Cerebral Vasculature
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •14. Topographic Anatomy
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •16. Spinal Cord
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Thorax
- •18. Topographic Anatomy
- •Guides
- •Facts & Hints
- •19. Mammary Gland
- •Guides
- •Facts & Hints
- •20. Body Wall
- •Guides
- •Facts & Hints
- •21. Lungs
- •Guides
- •Facts & Hints
- •22. Heart
- •Guides
- •Facts & Hints
- •23. Mediastinum
- •Guides
- •Facts & Hints
- •Abdomen
- •24. Topographic Anatomy
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •25. Body Wall
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •26. Peritoneal Cavity
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •27. Viscera (Gut)
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •28. Viscera (Accessory Organs)
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •29. Visceral Vasculature
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •30. Innervation
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •32. Topographic Anatomy
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •35. Urinary Bladder
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •39. Testis, Epididymis & Ductus Deferens
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •40. Rectum
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •41. Vasculature
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •42. Innervation
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Upper Limb
- •43. Topographic Anatomy
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •48. Neurovasculature
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Lower Limb
- •49. Topographic Anatomy
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •51. Knee
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •54. Neurovasculature
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints

FACTS & HINTS
HIGH-YIELD FACTS
Anatomic Points
Functional Overview of the Lower Limb
The lower limb supports the bodyweight and permits locomotion. It is firmlyattached through the rigid pelvis to the vertebral column. The joints are relativelystable and influenced bythe line of gravity; this line passes posterior to the hip joint, anterior to the knee, and anterior to the ankle. Thus onlythe calf muscles need to contract to maintain an upright posture. Clinicallythe limb is divided into four compartments: gluteal, thigh, leg and foot.
page 243
page 244
Lower Limb Development
The general plan of the lower limb is similar to the upper limb; however, during development the lower limb undergoes medial rotation, bringing the extensors of the knee, ankle and toes anteriorlywith the knee pointing forwards. The hip is unaffected, so hip flexors remain anterior and the extensors posterior.
Clinical Points
Varicose Veins
Dilated superficial veins most commonlyseen in the posteromedial parts of the lower limb
Result from absent or faultyvalves in the communicating veins between the deep and superficial venous systems of the limb Secondaryfailure of the saphenofemoral valve mayoccur
Stagnation of blood in these vessels predisposes to thrombosis and subsequent inflammation = thrombophlebitis
380 / 425

50 Hip and Thigh
STUDYAIMS
At the end of your study, you should be able to:
Describe the structure of the hip joint and its movements
Identifythe different parts and surface markings of the femur
Know the origins, insertions and actions of the major muscles of the gluteal region
Know the origins, insertions and actions of the major muscles of the anterior, medial, and posterior thigh
Identifythe margins of the femoral triangle and describe its contents
Describe the course of the adductor canal
381 / 425
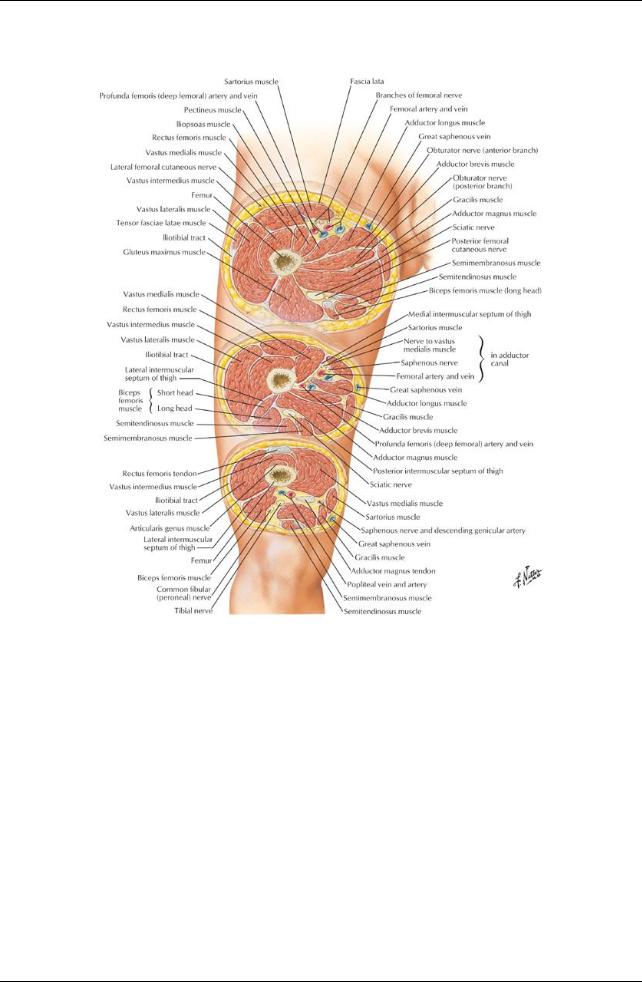
GUIDE
Lower Limb: Hip and Thigh
[Plate 493, Thigh: Serial Cross Sections]
382 / 425
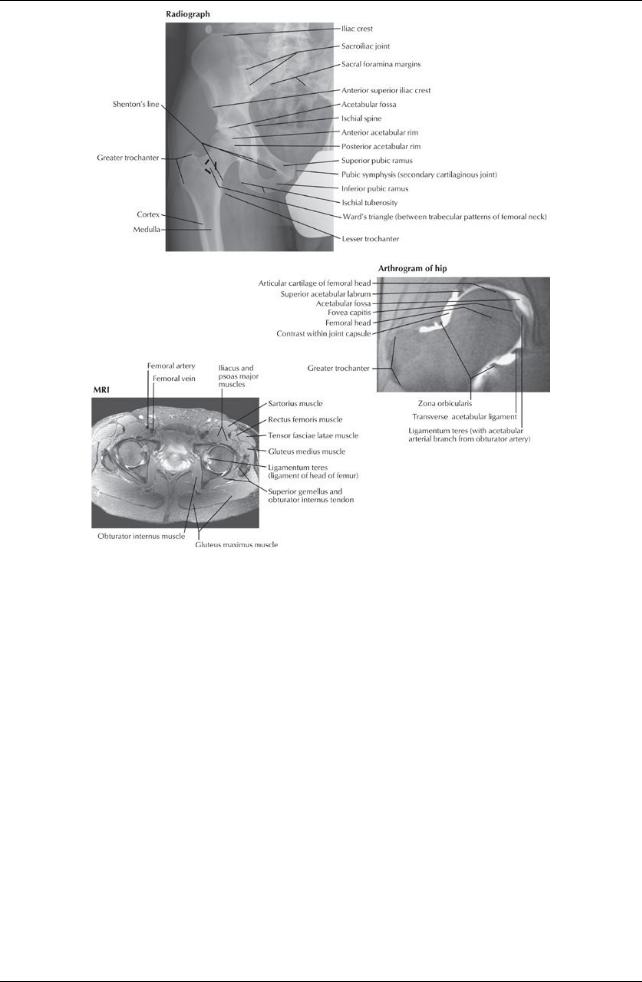
[Plate 531, Hip Radiograph, Arthrogram, and MRI]
Hip Joint
383 / 425
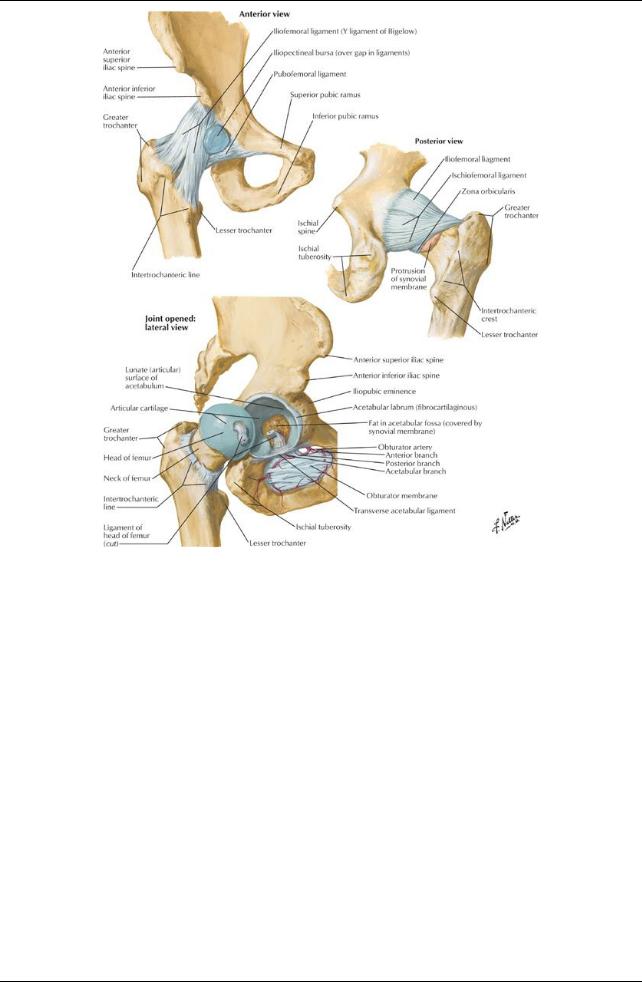
[Plate 475, Hip Joint]
384 / 425
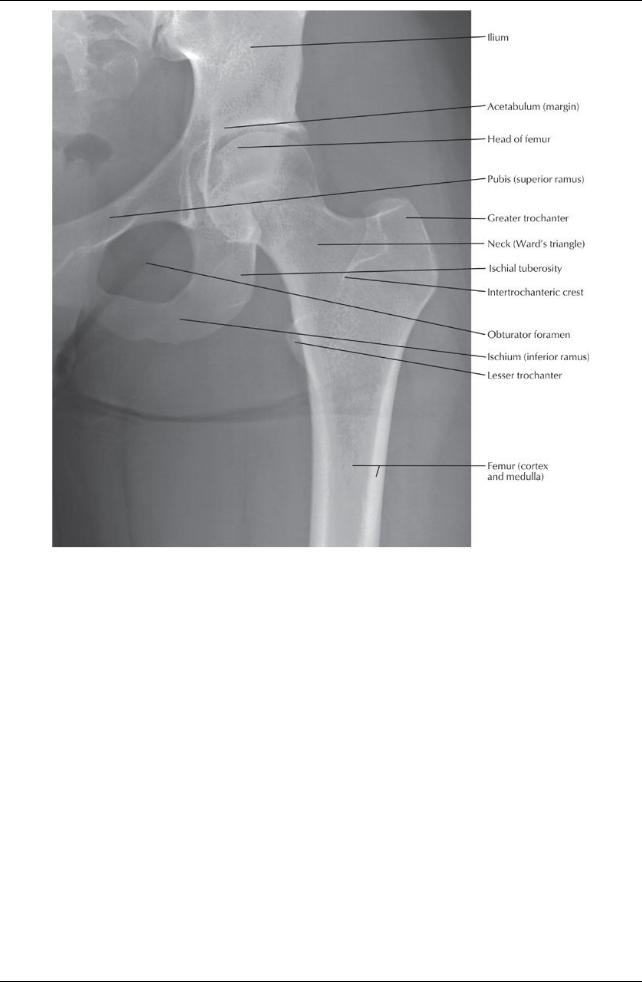
[Plate 476, Hip Joint: Anteroposterior Radiograph]
385 / 425

[Plate 478, Bony Attachments of Muscles of Hip and Thigh: Anterior View]
386 / 425

[Plate 479, Bony Attachments of Muscles of Hip and Thigh: Posterior View]
page 245 page 246
Multiaxial, ball-and-socket synovial joint
Movements
Flexion 140 degrees
Extension 10 degrees
Abduction 45 degrees
Adduction 30 degrees
Internal rotation 40 degrees
External rotation 50 degrees
Acetabulum (see Section 5-2: Pelvis and Perineum: Bones and Ligaments)
Head of femur fits within
Composed of contributions from ilium, ischium, pubis
Deepened byincomplete ring of fibrocartilaginous labrum, which is attached to bonyrim
Ring completed bytransverse acetabular ligament, which spans acetabular notch
Head of femur
Has a ligamentum teres (ligament of the head of the femur)
Attaches fovea (pit) in head of femur to transverse acetabular ligament
Contains branch from obturator artery
Capsule
Strong, fibrous and loose
Attaches to acetabular labrum, transverse acetabular ligament, intertrochanteric line of femur
Lower third of neck of femur is extracapsular.
Strengthened byligaments
Iliofemoral (Y-shaped)
Pubofemoral
Ischiofemoral ligaments
Blood supply(see Section 7-6: Lower Limb: Neurovasculature)
Medial and lateral circumflexarteries from deep branch of femoral or femoral artery
Arteryof head of femur (minor contribution)
Nerve supply
Femoral nerve
387 / 425

Nerve to quadratus femoris (posteriorly)
Articular branch of sciatic nerve
Anterior division of the obturator nerve (inferiorly)
Superior gluteal nerve (posteriorly)
Femur
Longest and heaviest bone in the body
Osteological features
Head with fovea (pit)
Neck-between head and shaft
Greater trochanter-large, lateral, posterosuperior projection from junction of neck and body
Lesser trochanter-rounded medial projection from junction of neck and body
Intertrochanteric line
Ridge running between greater and lesser trochanters
Indicates where neck joins body
Body(shaft)
Smooth and cylindrical
Wide, roughened line posteriorly: linea aspera
Runs vertically
Has medial and lateral lips (margins)
Medial and lateral condyles-medial and lateral rounded projections at its distal end
Medial and lateral epicondyles-central projection from each condyle
Neck is angled at 115 to 140 degrees (average 126 degrees) relative to the long axis of the shaft
Ligaments of the Hip Joint
Ligament |
Attachments |
Function |
Iliofemoral |
ASIS and acetabulum → intertrochanteric line. (Strong; Y-shaped |
Prevents hyperextension |
|
ligament) |
|
Ischiofemoral |
Acetabular rim → circles superiorlyand laterallyto medial base of |
Prevents hyperextension |
|
greater trochanter |
Screws femoral head into acetabulum |
Pubofemoral |
Pubic ramus → laterallyand inferiorlyto joint capsule |
Tightens during extension and |
|
|
abduction |
|
|
Limits abduction |
Transverse |
Joins the inferior ends of the labrum, crosses acetabular notch |
Completes the acetabular ring |
acetabular |
|
|
Ligament of head of |
Acetabular notch → fovea of femur |
Contains arteryto head of femur (minute |
femur |
(Intracapsular but extrasynovial) |
in adults) |
page 246
page 247
Fascial Compartments of the Thigh
Superficial fascia
Contains variable amounts of fat
Cutaneous nerves, such as the saphenous and sural
Superficial veins, such as the great and small saphenous
 Lymphatics Deep fascia = fascia lata
Lymphatics Deep fascia = fascia lata
Separates the subcutaneous tissue from the muscles
Dense strong layer
Prevents bulging of muscles during contraction, which improves efficiencyof pumping blood through veins back to the heart
Attaches to the inguinal ligament, iliac crests, and sacrum superiorly, and is continuous with the crural fascia inferiorly(see Section 7-4: Lower Limb: Leg)
Fascial septa from the fascia lata divide the thigh into three compartments: anterior, medial, and posterior Iliotibial tract
Lateral thickening of fascia lata
Conjoint aponeurosis of tensor fasciae lata and gluteus maximus muscles
 Attaches to tubercle on lateral condyle of the tibia (Gerdytubercle) Saphenous opening in fascia lata
Attaches to tubercle on lateral condyle of the tibia (Gerdytubercle) Saphenous opening in fascia lata
Deficiencyinferior to medial inguinal ligament
Spanned bycribriform fascia
Saphenous vein and efferent lymphatic vessels form superficial inguinal nodes pass through opening and cribriform fascia
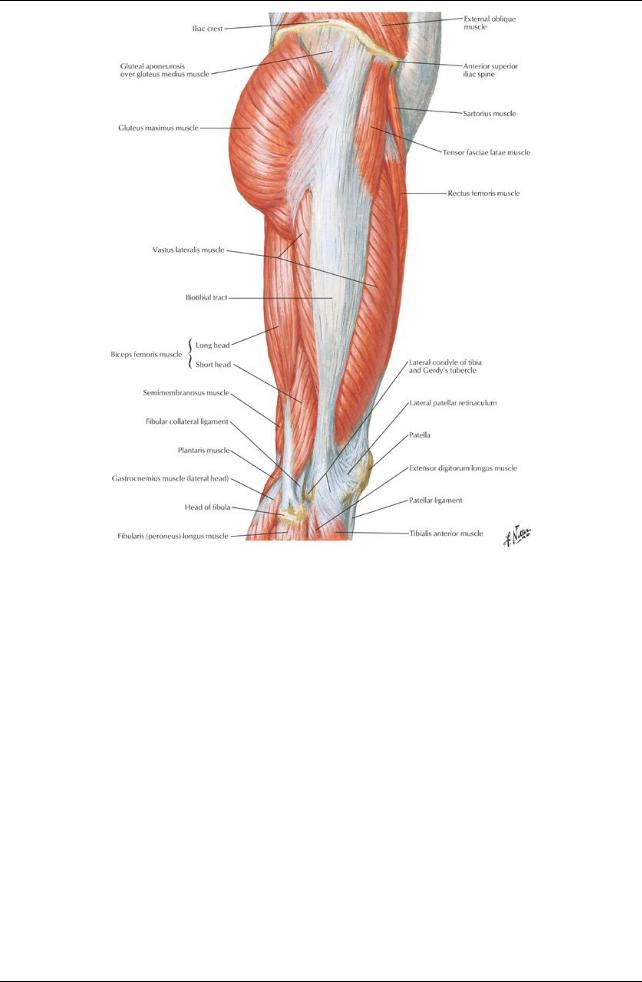
Muscles of the Gluteal Region
Extensor of hip: gluteus maximus
Also laterallyrotates hip
 Through iliotibial tract, extends knee Abductors of hip
Through iliotibial tract, extends knee Abductors of hip
Gluteus medius
Gluteus minimus
Most important function of these muscles: contract to prevent sagging of unsupported side of hip during locomotion, enabling opposite foot to swing through (e.g., Trendelenburg test)
Lateral rotators of hip  Gluteus maximus
Gluteus maximus
388 / 425

Piriformis
Obturator internus
Obturator externus
Gemelli (superior and inferior)
Quadratus femoris
Extensors of knee
Gluteus maximus
Tensor fasciae latae
Muscle |
Origin |
Insertion |
Innervation |
Blood Supply |
Action |
Gluteus |
Ilium posterior to posterior |
Most fibers end in Iliotibial tract that |
Inferior |
Superior and inferior |
Extends |
maximus |
gluteal line dorsal surface of |
inserts into lateral condyle of tibia; |
gluteal |
gluteal arteries, first |
thigh, |
|
sacrum and coccyx, |
some fibers insert gluteal |
nerve (L5 - |
perforating branch of |
assists |
|
sacrotuberous ligament |
tuberosityof femur |
S2) |
deep femoral artery |
lateral |
|
|
|
|
|
rotation |
Gluteus |
Lateral surface of ilium |
Lateral surface of greater |
Superior |
Deep branch of superior |
Abducts |
medius |
between anterior and posterior |
trochanter of femur |
gluteal |
gluteal artery |
thigh, |
|
gluteal lines |
|
nerve (L4 - |
|
rotates thigh |
|
|
|
S1) |
|
medially |
Gluteus |
Lateral surface of ilium |
Anterior border of greater trochanter |
Superior |
Deep branch of superior |
Abducts |
minimus |
between anterior and inferior |
of femur |
gluteal |
gluteal artery |
thigh, |
|
gluteal lines |
|
nerve (L4 - |
|
rotates thigh |
|
|
|
S1) |
|
medially |
Piriformis |
Anterior surface of sacrum and |
Superior border of greater |
Ventral |
Superior and inferior |
Laterally |
|
sacrotuberous ligament |
trochanter of femur |
rami of S1 |
gluteal arteries, internal |
rotates |
|
|
|
and S2 |
pudendal artery |
thigh, |
|
|
|
|
|
abducts |
|
|
|
|
|
flexed thigh |
Obturator |
Pelvic surface of obturator |
Medial surface of greater trochanter |
Nerve to |
Internal pudendal and |
Laterally |
internus |
membrane and margins of |
of femur |
obturator |
superior gluteal arteries |
rotates |
|
obturator foramen |
|
internus |
|
thigh, |
|
|
|
(L5-S2) |
|
abducts |
|
|
|
|
|
flexed thigh |
Gemellus |
Outer surface of ischial spine |
Medial surface of greater trochanter |
Nerve to |
Inferior gluteal artery |
Laterally |
superior |
|
of femur |
obturator |
|
rotates thigh |
|
|
|
internus |
|
|
|
|
|
(L5-S2) |
|
|
Gemellus |
Upper margin of ischial |
Medial surface of greater trochanter |
Nerve to |
Inferior gluteal artery |
Laterally |
inferior |
tuberosity |
of femur |
quadratus |
|
rotates thigh |
|
|
|
femoris |
|
|
|
|
|
(L4-S1) |
|
|
Quadratus |
Lateral margin of ischial |
Quadrate tubercle on |
Nerve to |
Medial circumflex |
Laterally |
femoris |
tuberosity |
intertrochanteric crest of femur |
quadratus |
femoral artery |
rotates thigh |
|
|
|
femoris |
|
|
|
|
|
(L4-S1) |
|
|
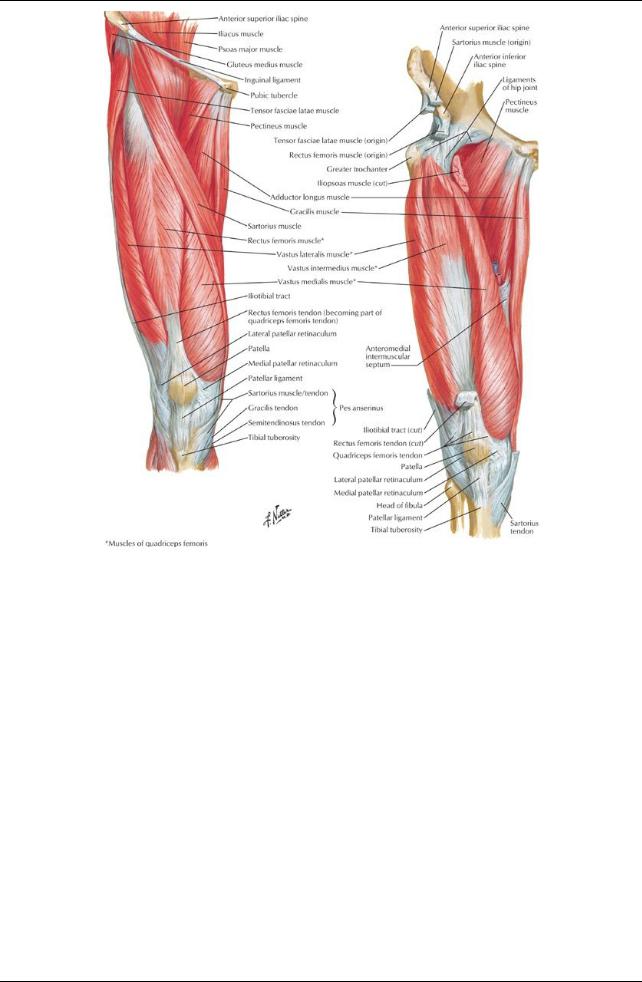
Muscles of the Thigh
389 / 425
[Plate 480, Muscles of Thigh: Anterior Views]
390 / 425
[Plate 482, Muscles of Hip and Thigh: Lateral View]
391 / 425

[Plate 483, Muscles of Thigh: Posterior Views]
Anterior (= extensor) compartment
Flexors of hip
Sartorius (also abducts and laterallyrotates hip and flexes and mediallyrotates knee), Iliopsoas
Pectineus (also adducts hip)
Extensor of knee: quadriceps femoris, composed of
Rectus femoris (also flexes hip)
Vastus lateralis
Vastus intermedius
Vastus medialis (also stabilizes patella)
page 248 page 249
Anterior Thigh Muscles
Muscle |
Origin |
Insertion |
Innervation |
Blood Supply |
Action |
Iliopsoas/psoas |
Sides of vertebra T12 to |
Lesser trochanter of |
Ventral rami of |
Lumbar branches |
Flexes thigh at hip and |
major |
L5 and transverse |
femur |
lumbar spinal |
of iliolumbar artery |
stabilizes the hip |
|
processes of L1-L5 |
|
nerves 1-3 |
|
|
Iliacus |
Iliac crest, iliac fossa, |
Tendon of psoas major |
Femoral nerve |
Iliac branches of |
Flexes thigh at hip and |
|
ala of scrum, and |
and bodyof femur, |
(L2-L3) |
iliolumbar artery |
stabilizes the hip |
|
anterior sacroiliac |
inferior to lesser |
|
|
|
|
ligaments |
trochanter |
|
|
|
Tensor fasciae |
Anterior superior iliac |
Iliotibial tract → lateral |
Superior gluteal |
Superior gluteal |
Abducts, medially |
latae |
spine and anterior part |
condyle of tibia |
nerve (L4-L5) |
arteries, lateral |
rotates and flexes the |
|
of external lip of iliac |
|
|
circumflexfemoral |
thigh, stabilizes trunk |
|
crest |
|
|
artery |
on thigh |
Sartorius |
ASIS and superior part |
Superior part of medial |
Femoral nerve |
Femoral artery |
Abducts, laterally |
|
of notch below it |
surface of tibia |
(L2-L3) |
|
rotates and flexes the |
|
|
|
|
|
thigh |
Quadratus |
Lateral margin of ischial |
Quadrate tubercle on |
Nerve to |
Medial circumflex |
Laterallyrotates thigh |
femoris |
tuberosity |
intertrochanteric crest |
quadratus femoris |
femoral artery |
|
392 / 425

|
|
of femur |
(L4 to S1) |
|
|
Rectus femoris |
Anterior inferior iliac |
Base of patella and to |
Femoral nerve |
Lateral circumflex |
Extends the leg at the |
|
spine and groove |
tibial tuberosityvia |
(L2-L4) |
femoral artery, |
knee joint and flexes |
|
superior to acetabulum |
patellar ligament |
|
deep femoral |
the thigh at the hip joint |
|
|
|
|
artery |
|
Vastus lateralis |
Greater trochanter and |
Base of patella and to |
Femoral nerve |
Lateral circumflex |
Extends the leg at the |
|
lateral lip of linea |
tibial tuberosityvia |
(L2-L4) |
femoral artery, |
knee joint |
|
aspera of femur |
patellar ligament |
|
deep femoral |
|
|
|
|
|
artery |
|
Vastus medialis |
Intertrochanteric line |
Base of patella and to |
Femoral nerve |
Femoral artery, |
Extends the leg at the |
|
and medial lip of linea |
tibial tuberosityvia |
(L2-L4) |
deep femoral |
knee joint |
|
aspera of femur |
patellar ligament |
|
artery |
|
Vastus |
Anterior and lateral |
Base of patella and to |
Femoral nerve |
Lateral circumflex |
Extends the leg at the |
intermedius |
surfaces of bodyof |
tibial tuberosityvia |
(L2-L4) |
femoral artery, |
knee joint |
|
femur |
patellar ligament |
|
deep femoral |
|
|
|
|
|
artery |
|
Pectineus |
Pecten pubis |
Pectineal line of femur |
Femoral nerve |
Medial circumflex |
Adducts and flexes |
|
|
|
(L2-L3) and |
femoral artery, |
thigh |
|
|
|
sometimes |
obturator artery |
|
|
|
|
obturator nerve |
|
|
page 249 page 250
Medial (= adductor) compartment
Adductors of hip
Adductors longus
Adductor brevis
Adductor magnus (also assist lateral rotation of knee)
Gracilis (also flexes knee)
Obturator externus-laterallyrotates hip
Medial Thigh Muscles
|
Muscle |
|
Origin |
Insertion |
|
Innervation |
|
Blood Supply |
Action |
|
||||
|
Adductor |
Bodyof pubis, inferior |
Middle third of linea |
Obturator nerve |
Medial circumflex |
Adducts thigh |
|
|
||||||
|
longus |
to pubic crest |
aspera of femur |
(anterior division) |
femoral artery, |
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(L2-L4) |
obturator artery |
|
|
|
|||
|
Adductor |
Bodyand inferior pubic |
Pectineal line and |
Obturator nerve |
Medial circumflex |
Adducts and flexes thigh |
|
|||||||
|
brevis |
ramus |
|
|
proximal part of linea |
(L2-L4) |
femoral artery, |
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
aspera of femur |
|
|
obturator artery |
|
|
|
|||
|
Adductor |
Inferior pubis ramus, |
Gluteal tuberosity, linea |
Adductor part: |
Deep femoral artery, |
Adducts and flexes thigh |
|
|||||||
|
magnus |
ramus of ischium |
aspera, supracondylar |
obturator nerve |
popliteal artery, |
(adductor part) |
|
|||||||
|
|
Hamstring part: ischial |
line |
|
(L2-L4) |
obturator |
Extends thigh (hamstring |
|
||||||
|
|
tuberosity |
Hamstring part: |
Hamstring part: |
|
|
|
part) |
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
adductor tubercle |
tibial nerve (L4) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
Gracilis |
Bodyof pubis and |
Superior part of medial |
Obturator nerve |
Deep femoral artery, |
Adducts thigh, flexes and |
|
|||||||
|
|
inferior pubic ramus |
surface of tibia |
(L2-L3) |
medial circumflex |
mediallyrotates the leg |
|
|||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
femoral artery |
|
|
|
||
|
Obturator |
Margins of obturator |
Trochanteric fossa of |
Obturator nerve |
Medial circumflex |
Laterallyrotates the thigh and |
|
|||||||
|
externus |
foramen and obturator |
femur |
|
(L2-L3) |
femoral artery, |
stabilizes head of femur in |
|
||||||
|
|
membrane |
|
|
|
|
obturator artery |
acetabulum |
|
|
||||
|
Posterior (= flexor) compartment |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
Hamstrings |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Biceps femoris-also lateral rotates knee |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
Semitendinosus-also medial rotates knee |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
Semimembranosus-also medial rotates knee |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
Together extend hip (except short head of biceps femoris) and flexknee |
|
|
|
|||||||||
|
Hamstring part of adductor magnus-extends hip |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
Posterior Thigh Muscles |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
Muscle |
|
Origin |
Insertion |
|
Innervation |
|
|
Blood Supply |
Action |
|
|||
|
Semitendinosus |
|
Upper and medial |
Superior part |
Tibial division of |
|
Perforating branch of deep |
Flexes leg, |
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
ischial tuberosity |
of medial |
|
sciatic nerve (L5-S2) |
arteryof thigh, superior |
extends thigh |
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
surface of |
|
|
|
|
muscular branches of |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
tibia |
|
|
|
|
popliteal artery |
|
|
|
|
Semimembranosus |
Upper and lateral ischial |
Posterior |
|
Tibial division of |
|
Perforating branch of deep |
Flexes leg, |
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
tuberosity |
|
part of |
|
sciatic nerve (L5-S2) |
arteryof thigh, superior |
extends thigh |
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
medial |
|
|
|
|
muscular branches of |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
condyle of |
|
|
|
|
popliteal artery |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
tibia |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Biceps femoris |
|
Long head-ischial |
Lateral side |
Long head-tibial |
|
Perforating branch of deep |
Flexes and |
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
tuberosity |
|
of head of |
|
division of sciatic |
|
arteryof thigh, superior |
laterallyrotates |
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
fibula |
|
nerve (L5-S2) |
|
|
muscular branches of |
leg, extends |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
393 / 425

Short head-lateral lip of linea aspera, lateral supracondylar line of femur
popliteal artery |
thigh |
Short head-common fibular division of sciatic nerve (L5-S2)
Femoral Triangle
Boundaries
Superiorly: inguinal ligament
Medially: medial border of adductor longus
Laterally: medial border of sartorius
Contents
Femoral nerve (descends outside of femoral sheath)
Femoral sheath
About 4 cm long, extending below inguinal ligament
Subdivided into three compartments
Lateral contains femoral artery
Intermediate contains femoral vein
Medial is femoral canal
Femoral canal
Potential space about 1.5 cm long
Contains loose connective tissue, lymphatic vessels, a deep inguinal lymph node (of Cloquet)
Femoral ring: abdominal entrance to femoral canal, closed byfattytissue and parental peritoneum
Beyond extent of sheath
Femoral arteryand branches
Femoral vein and tributaries
Adductor Canal (= subsartorial canal/Hunter's canal)
page 251 page 252
Boundaries
Superiorly: commences at apexof femoral triangle
Posteriorly: adductors longus and magnus
Anteromedially: sartorius and fascia
Anterolaterally: vastus medialis
Inferiorly: terminates at adductor hiatus (in tendon of adductor magnus)
Contents
Femoral arteryand femoral vein
Pass through adductor hiatus
Become popliteal arteryand vein when theyenter popliteal fossa
Nerves
Saphenous nerve
Nerve to vastus medialis
Lymphatics
394 / 425
