
- •1. Topographic Surface Anatomy
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •3. Superficial Face
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •4. Neck
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •5. Nasal Region
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •6. Oral Region
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •7. Pharynx
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •13. Cerebral Vasculature
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •14. Topographic Anatomy
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •16. Spinal Cord
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Thorax
- •18. Topographic Anatomy
- •Guides
- •Facts & Hints
- •19. Mammary Gland
- •Guides
- •Facts & Hints
- •20. Body Wall
- •Guides
- •Facts & Hints
- •21. Lungs
- •Guides
- •Facts & Hints
- •22. Heart
- •Guides
- •Facts & Hints
- •23. Mediastinum
- •Guides
- •Facts & Hints
- •Abdomen
- •24. Topographic Anatomy
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •25. Body Wall
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •26. Peritoneal Cavity
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •27. Viscera (Gut)
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •28. Viscera (Accessory Organs)
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •29. Visceral Vasculature
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •30. Innervation
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •32. Topographic Anatomy
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •35. Urinary Bladder
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •39. Testis, Epididymis & Ductus Deferens
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •40. Rectum
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •41. Vasculature
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •42. Innervation
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Upper Limb
- •43. Topographic Anatomy
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •48. Neurovasculature
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Lower Limb
- •49. Topographic Anatomy
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •51. Knee
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •54. Neurovasculature
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints

48 Neurovasculature
STUDYAIMS
At the end of your study, you should be able to:
Describe the arterial supplyof the arm, forearm, and hand, distinguishing the arteries supplying each of the compartments Know the locations of the brachial, radial, and ulnar pulses
Describe the venous drainage of the hand, forearm, and arm Describe the lymphatic drainage of the upper limb Understand the organization of the brachial plexus
Know the innervation to the compartments of the arm and forearm Recognize the course of the major nerves of the upper limb
Understand the dermatome map of the upper limb and its cutaneous innervation
369 / 425

GUIDE
Upper Limb: Neurovasculature
Vascular Supply to the Upper Limb
[Plate 421, Brachial Artery in Situ]
Arterial Supply to the Arm
page 236
page 237
Axillaryartery
Begins at lateral border of first rib and ends at inferior border of teres major
Divided into three descriptive parts bypectoralis minor muscle
First part
First rib to medial border of pectoralis minor
Is enclosed in axillarysheath
One branch-superior thoracic arterysupplying serratus anterior
Second part
Posterior to pectoralis minor
Two branches
Thoracoacromial artery
Lateral thoracic artery
Both supplythe pectoral muscles and breast
Third part
Lateral border of pectoralis minor to inferior border of teres major
Three branches
Subscapular artery
Largest branch
Divides into circumflexscapular and thoracodorsal arteries
Supplies serratus anterior, teres major, subscapularis, and latissimus dorsi muscles
Anterior and posterior circumflexhumeral arteries
Brachial artery
370 / 425

Continuation of the axillaryartery, ends in cubital fossa
Lies anterior to triceps and brachialis throughout its course
Accompanied bymedian nerve, which crosses anterior to arteryand lies mediallyin cubital fossa
Divides into ulnar and radial arteries under bicipital aponeurosis
Branches
Manymuscular branches
Profunda brachii arteryfrom medial aspect
Superior and inferior ulnar collateral branches
Profunda brachii (deep arteryof the arm)
Accompanies radial arteryin radial groove
Divides into anterior and posterior descending branches to elbow
Arterial Supply to the Forearm
Ulnar artery
Larger of two terminal branches of brachial artery
Begins medial to biceps tendon and descends through anterior compartment deep to pronator teres
Branches
Anterior ulnar recurrent
Posterior ulnar recurrent
Common interosseus, which branches into
Anterior interosseus artery
Posterior interosseus artery
Muscular branches to muscles of medial side of forearm
Branches to the hand
Radial artery
Begins in cubital fossa at neck of radius
Passes distallydeep to brachioradialis muscle
Palpable throughout lateral forearm (best felt at the wrist)
Branches
Supplies flexor and extensor muscles on lateral side of forearm
Radial recurrent artery
Branches to the hand
Arterial Supply to the Hand
Branches from the ulnar artery
Palmar carpal branch
Runs across anterior wrist deep to tendons of flexor digitorum profundus (FDP)
Anastomoses with palmar carpal branch of radial arteryto form palmar carpal arch
Dorsal carpal branch
Arises proximal to pisiform
Crosses dorsal to wrist
Anastomoses with dorsal carpal branch of radial arteryto form dorsal carpal arch
Superficial branch of ulnar arteryin hand-continues into palm as superficial palmar arch
Deep (palmar) branch of ulnar arteryin the hand
Anastomoses with radial artery
Forms deep palmar arch
Venous Drainage of Hand and Forearm
page 237 page 238
Veins of hand
Superficial and deep palmar venous arches
Dorsal venous network (arch)
Both drain to cephalic and basilic veins
Superficial veins of forearm
Basilic vein ascends posteromediallyon forearm
Cephalic vein ascends on lateral border of forearm
Median cubital vein connects cephalic and basilic over cubital fossa
Deep veins of forearm
Paired radial and ulnar veins and interosseus veins accompanyarteries of same name
All communicate with superficial veins and median cubital vein
Venous Drainage of Arm
Superficial veins (drain into axillaryvein)
Cephalic vein
On anterolateral surface
Enters groove between deltoid and pectoralis major (deltopectoral groove)
Then deltopectoral triangle
Empties into termination of axillaryvein
Basilic vein
Medial side, inferior arm
Pierces deep fascia at junction of inferior and middle third of arm
Runs superiorlyto axillaryvein
371 / 425

Deep veins
Paired, accompanybrachial artery(venae comitantes)
Form at elbow from radial and ulnar veins
Have valves
Merge with basilic vein to form axillaryvein
Lymphatics
All lymph from the arm drains to the axillarynodes
Lymph from breasts and thoraxalso drains to the nodes
Nerve Supply to Upper Limb
Brachial Plexus [C5-T1]
page 238
page 239 page 239
page 240
Composed of
Roots (5)
Trunks (3)
Divisions (6)
Cords (3)
Branches (13+4 from roots)
Roots
Ventral rami of spinal nerves C5-T1
Give rise to
Dorsal scapular nerve (C5, possible contribution from C4)
Long thoracic nerve (C5-C7) to serratus anterior muscle
Trunks
Superior from ventral rami of C5 and 6
Branches
a.Nerve to subclavius muscle
b.Suprascapular nerve to supraand infraspinatus, shoulder joint
Middle from ventral ramus of C7
 Inferior from ventral rami of C8 and T1 Divisions
Inferior from ventral rami of C8 and T1 Divisions
Anterior divisions of superior and middle trunks form lateral cord
Anterior division of inferior trunk continues as medial cord
 Posterior divisions of all three trunks for posterior cord Cords
Posterior divisions of all three trunks for posterior cord Cords
Named byrelationship to axillaryartery, which theysurround
Lateral
Medial
Posterior
Branches
Branches from lateral cord
Lateral pectoral nerve (C5-C7) to pectoralis major and minor muscles
Musculocutaneous (C5-C7)
Lateral root of median nerve (C6-C7)
Branches from medial cord
Medial pectoral nerve (C8-T1) to pectoralis minor and major
Ulnar nerve (C8-T1)
Medial brachial cutaneous nerve (C8-T1) supplies skin over medial surface of arm and proximal surface of forearm
Medial antebrachial cutaneous nerve (C8-T1) to skin over medial forearm
Median root of median nerve (C8-T1)
Branches from the posterior cord
Upper subscapular nerve (C5-C6) to subscapularis
Lower subscapular nerve (C5-C6) to teres major and subscapularis
Thoracodorsal nerve (C6-C8) to latissimus dorsi
Axillarynerve (C5-C6) to teres minor and deltoid (ends as the upper lateral brachial cutaneous nerve)
Radial nerve (C5-T1) supplies all extensors of the upper limb and sensation to skin overlying extensor region, including hand
Other facts
Anterior divisions supplythe flexor parts of the upper limb
Posterior divisions supplythe extensor parts of the upper limb
Each cord divides into two main terminal branches
Posterior→axillaryand radial
Lateral→musculocutaneous and median
Medial→Median and ulnar
Supraclavicular part of plexus
Arises from roots and trunks
Approachable through posterior triangle of the neck
Dorsal scapular nerve
Nerve to subclavius
Suprascapular nerve
Long thoracic nerve
Infraclavicular part (cords and their branches) is in the axilla 
 Arise from cords
Arise from cords
372 / 425

Approachable through axilla
All the rest of the nerve branches from brachial plexus
Ulnar nerve supplies
Flexor carpi ulnaris
Medial half of FDP
Hypothenar muscles
Third and fourth lumbricals
All interossei muscles
Skin over the medial hand and 1½ digits
Median nerve supplies
Forearm flexors (except flexor carpi ulnaris and the lateral half of flexor digitorum profundus)
Thenar muscles and first and second lumbricals
Skin over the lateral hand and 3½ digits
Musculocutaneous nerve supplies
Flexor muscles of arm (anterior compartment)
Skin over lateral aspect of forearm (lateral antebrachial cutaneous)
Radial nerve supplies
Triceps
Anconeus
Extensor muscles of forearm
Skin over posterior arm and forearm
Axillarynerve supplies
Teres minor
Deltoid
Shoulder joint
Skin over inferior deltoid
Dermatomes and Cutaneous Innervation of the Upper Limb
[Plate 401, Dermatomes of Upper Limb]
373 / 425
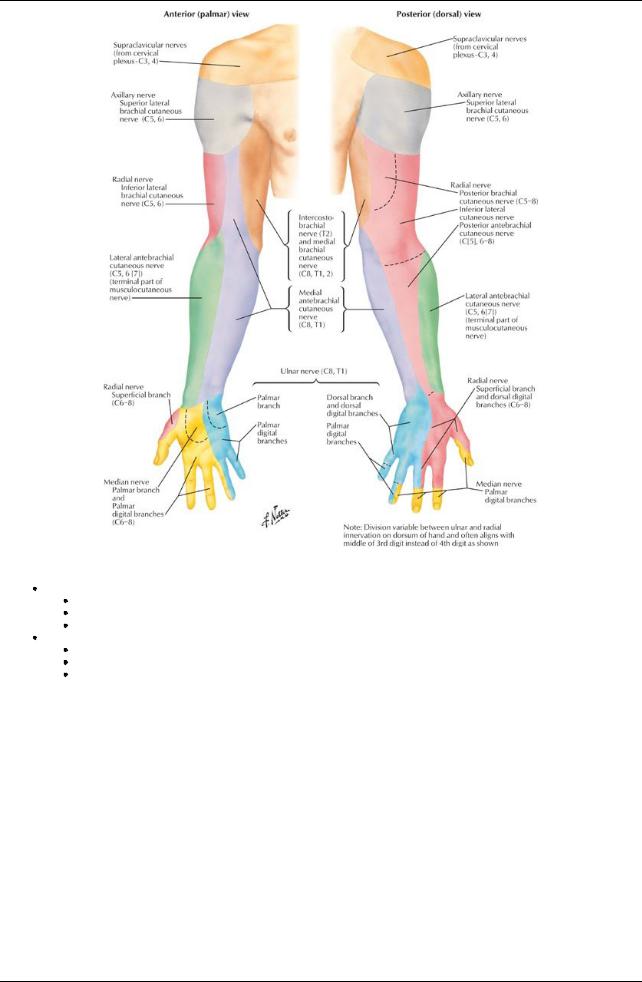
[Plate 402, Cutaneous Innervation of Upper Limb]
Dermatomes
Band-like areas of skin
Each supplied bya single spinal nerve through dorsal and ventral rami
Arranged in segmental fashion
Cutaneous innervation of the upper limb
Follows segmental arrangement of spinal nerve contributions to the brachial plexus
No representation of C7 on anterior aspect of arm and forearm
No representation of T1 on palmar or dorsal surface of hand
374 / 425
