
- •1. Topographic Surface Anatomy
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •3. Superficial Face
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •4. Neck
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •5. Nasal Region
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •6. Oral Region
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •7. Pharynx
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •13. Cerebral Vasculature
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •14. Topographic Anatomy
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •16. Spinal Cord
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Thorax
- •18. Topographic Anatomy
- •Guides
- •Facts & Hints
- •19. Mammary Gland
- •Guides
- •Facts & Hints
- •20. Body Wall
- •Guides
- •Facts & Hints
- •21. Lungs
- •Guides
- •Facts & Hints
- •22. Heart
- •Guides
- •Facts & Hints
- •23. Mediastinum
- •Guides
- •Facts & Hints
- •Abdomen
- •24. Topographic Anatomy
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •25. Body Wall
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •26. Peritoneal Cavity
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •27. Viscera (Gut)
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •28. Viscera (Accessory Organs)
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •29. Visceral Vasculature
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •30. Innervation
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •32. Topographic Anatomy
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •35. Urinary Bladder
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •39. Testis, Epididymis & Ductus Deferens
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •40. Rectum
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •41. Vasculature
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •42. Innervation
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Upper Limb
- •43. Topographic Anatomy
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •48. Neurovasculature
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Lower Limb
- •49. Topographic Anatomy
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •51. Knee
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •54. Neurovasculature
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints

FACTS & HINTS
HIGH-YIELD FACTS
Clinical Points
Baker's Cyst
Posterior herniation of the synovial membrane through the joint capsule into the popliteal fossa
Swelling appears below joint line and mayextend as far as the midcalf
Large swellings mayinterfere with knee movements but otherwise asymptomatic
Bursitis
Inflammation of the bursa surrounding the knee because of repeated frictional forces In chronic inflammation, bursae become distended and filled with fluid
Prepatellar bursitis (housemaid's knee) and infrapatellar bursitis (clergyman's knee) are most recognized variants
Knee Injury
Knee injuries common, as the knee joint has little external supportive tissue Ligament sprains usuallyself-limiting, but maycause secondarydamage to menisci Tearing of the ligaments often needs surgical correction
Rupture of anterior cruciate ligament occurs when force is directed anteriorlyto the semi-flexed knee, typicallyoccurring in skiers and footballers
Posterior cruciate ligament is more resilient to injury, but mayrupture when force is applied to the tibial tuberositywhile the knee is flexed Collateral ligaments are vulnerable to lateral stresses
MNEMONICS
Memory Aids
Knock-knee and Bowleg: |
Genu valgum vs. Genu vargum |
Knock-knee: |
Genu valgum |
|
Genu valGUM-knees are GUMmed together |
Bowleg: |
Genu vargum |
|
Genu VARgum-VARrhymes with far-knees are VAR(far) apart |
403 / 425

52 Leg
STUDYAIMS
At the end of your study, you should be able to:
Describe the fascial compartments of the leg and understand their importance
Identifythe different parts and surface markings of the tibia and fibula
Know the origins, insertions, and actions of the muscles of the leg
404 / 425
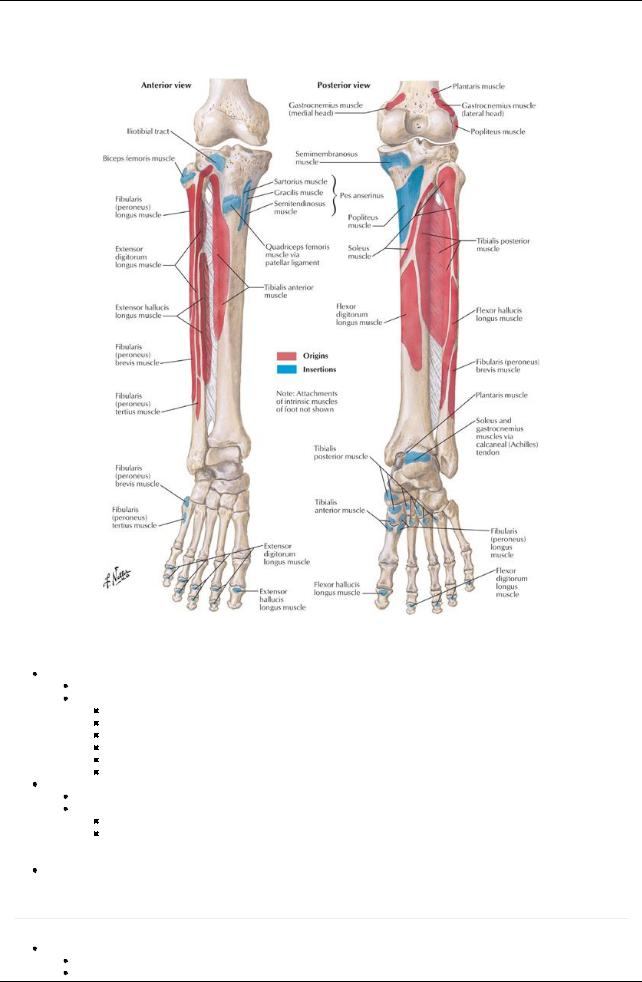
GUIDE
Lower Limb: Leg
[Plate 503, Attachments of Muscles of Leg]
Bones
Tibia
Large, weightbearing
Osteological features
Medial and lateral condyles-medial and lateral protuberances at proximal end articulate with femur
Intercondylar eminence-together with condyles forms tibial plateau, fits into intercondylar fossa of femur
Tibial tuberosity-proximal end of anterior border, broad bump for attachment of patellar ligament
Gerdy's tubercle-Protrusion from lateral condyle to which iliotibial tract attaches
Shaft-or body, with rough diagonal ridge on posterior proximal end: soleal line
Medial malleolus-inferomedial projection at distal end, articulates with talus
Fibula
Slender, nonweightbearing
Osteological features
Head-proximal end with pointed apex, articulates with tibia
Shaft-or body, has three borders (anterior, interosseous, and posterior) and surfaces (anterior, posterior and lateral) for muscle attachments
 Lateral malleolus-distal enlargement, articulates with tibia, contributes to ankle joint Interosseous membrane uniting tibia and fibula
Lateral malleolus-distal enlargement, articulates with tibia, contributes to ankle joint Interosseous membrane uniting tibia and fibula
Fascial Compartments
page 258
page 259
Crural fascia
Deep fascia surrounding leg
Distal continuation of fascia lata
405 / 425
Attaches to anterior and medial borders of tibia
Thicker in proximal leg
Continues as extensor retinaculum distally
 Extensions from deep surface-anterior and posterior intermuscular septa-attach to anterior and posterior margins of fibula Intermuscular septa and interosseous membrane divide leg into three fascial compartments: anterior, lateral, and posterior Muscles in posterior compartment are subdivided into superficial and deep compartments bytransverse intermuscular septum
Extensions from deep surface-anterior and posterior intermuscular septa-attach to anterior and posterior margins of fibula Intermuscular septa and interosseous membrane divide leg into three fascial compartments: anterior, lateral, and posterior Muscles in posterior compartment are subdivided into superficial and deep compartments bytransverse intermuscular septum
Joints
Proximal tibiofibular joint
Plane-type synovial joint
Nonweightbearing
Between head of fibular and lateral condyle of tibia
 Fibrous capsule reinforced byanterior and posterior ligaments of the head of the fibula Distal tibiofibular
Fibrous capsule reinforced byanterior and posterior ligaments of the head of the fibula Distal tibiofibular
Fibrous joint (syndesmosis)
Medial surface of distal fibula articulates with facet on inferior end of tibia
Reinforced byanterior and posterior tibiafibular ligaments and interosseous ligament (extension of interosseous membrane)
Muscles
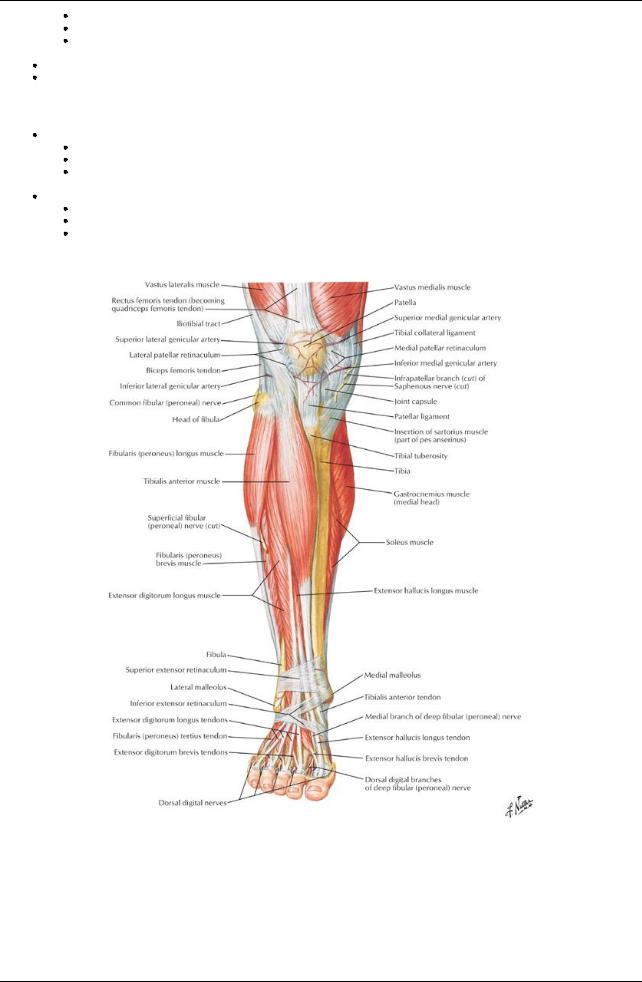
[Plate 507, Muscles of Leg (Superficial Dissection): Anterior View]
406 / 425
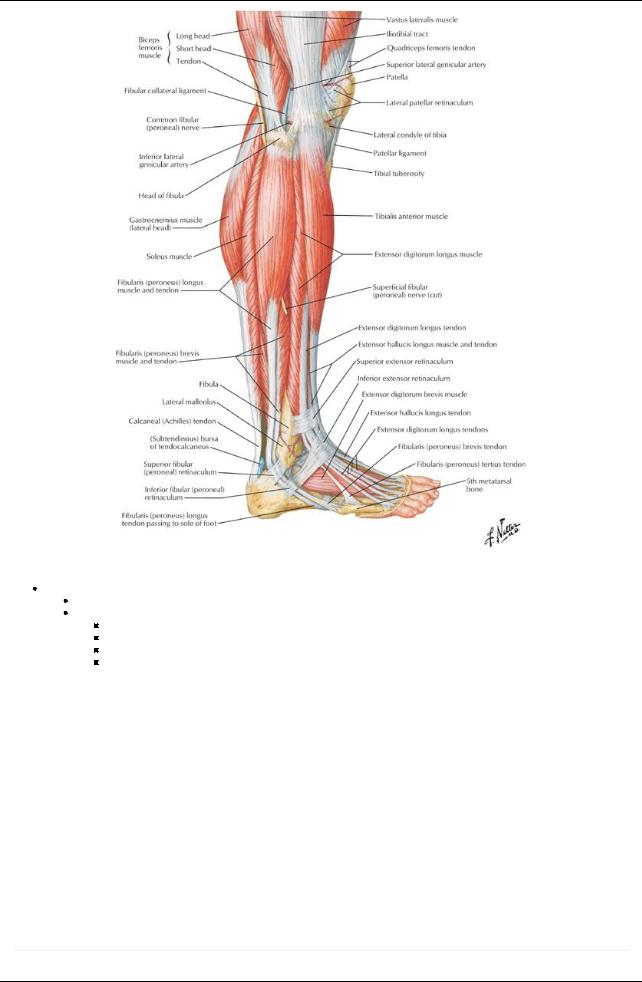
[Plate 509, Muscles of Leg: Lateral View]
Anterior (= extensor) compartment
Primarilydorsiflexors of ankle
Include
Tibialis anterior (also inverts foot and holds up medial longitudinal arch of foot)
Extensor hallucis longus (also dorsiflexes halluxand inverts foot)
Extensor digitorum longus (also dorsiflexes toes)
Peroneus tertius (also everts foot)
Muscles of the Anterior Leg
Muscle |
Origin |
Insertion |
Innervation |
Blood |
Action |
|
|
|
|
Supply |
|
Tibialis |
Lateral condyle and proximal half of |
Medial plantar surfaces of |
Deep |
Anterior |
Dorsiflexes ankle and |
anterior |
lateral tibia, interosseous membrane |
medial cuneiform and base of |
fibular |
tibial |
inverts foot |
|
|
first metatarsal |
nerve (L4- |
artery |
|
|
|
|
L5) |
|
|
Extensor |
Middle part of anterior surface of fibula |
Dorsal aspect of base of distal |
Deep |
Anterior |
Extends great toe and |
hallucis |
and interosseous membrane |
phalanxof great toe |
fibular |
tibial |
dorsiflexes ankle |
longus |
|
|
nerve (L5- |
artery |
|
|
|
|
S1) |
|
|
Extensor |
Lateral condyle of tibia and proximal three |
Middle and distal phalanges of |
Deep |
Anterior |
Extends second |
digitorum |
quarters of anterior surface of |
second through fifth toes |
fibular |
tibial |
through fifth toes and |
longus |
interosseous membrane |
|
nerve (L5- |
artery |
dorsiflexes ankle |
|
|
|
S1) |
|
|
Fibularis |
Distal third of anterior surface of fibula |
Dorsum of base of fifth |
Deep |
Anterior |
Dorsiflexes ankle and |
(peroneus) |
and interosseous membrane |
metatarsal |
fibular |
tibial |
aids in eversion of foot |
tertius |
|
|
nerve (L5- |
artery |
|
|
|
|
S1) |
|
|
page 259 page 260
407 / 425

Lateral (= everter) compartment
Primarilyeverters of the foot
Include
Peroneus longus
Peroneus brevis
Both plantarflexankle, evert foot, and hold up lateral longitudinal arch of foot
Muscles of the Lateral Leg
Muscle |
Origin |
Insertion |
Innervation |
Blood Supply |
Action |
Fibularis |
Head and proximal two |
Plantar base of first |
Superficial fibular |
Anterior tibial |
Everts foot and weakly |
(peroneus) |
thirds of lateral fibula |
metatarsal and medial |
nerve (L5 - S2) |
artery, fibular |
plantarflexes ankle |
longus |
|
cuneiform |
|
artery |
|
Fibularis |
Distal two thirds of |
Dorsal surface of tuberosity |
Superficial fibular |
Fibular artery |
Everts foot and weakly |
(peroneus) |
lateral surface of fibula |
on base of fifth metatarsal |
nerve (L5 - S2) |
|
plantarflexes ankle |
brevis |
|
|
|
|
|
Posterior compartment
Comprised of superficial and deep groups
Separated bytransverse intermuscular septum
Superficial group = plantar flexors of the foot
Gastrocnemius
Soleus
Plantaris
Gastrocnemius and plantaris cross the knee joint and thus also flexknee
All three contribute to calcaneal tendon
Deep group = plantar flexors of the foot
Tibialis posterior (also inverts foot and supports medial longitudinal arch of foot)
Flexor hallucis longus (also plantarflexes interphalangeal joint of halluxand supports medial longitudinal arch of foot)
Flexor digitorum longus (also plantarflexes DIP joints of lateral four toes and supports medial and lateral longitudinal arches of foot)
Popliteus
Forms inferior floor of popliteal fossa
Tendon lies between fibrous capsule and synovial membrane of knee joint
Flexes knee
Rotates femur five degrees laterallyon tibial plateau to unlock knee so flexion can occur
Muscles of the Posterior Leg
page 260
page 261
Muscle |
Origin |
Insertion |
Innervation |
Blood Supply |
Action |
Superficial Muscles |
|
|
|
|
|
Gastrocnemius |
Lateral head: lateral aspect of |
Posterior aspect of calcaneus via |
Tibial |
Popliteal |
Plantarflexes the |
|
lateral condyle of femur. |
the calcaneal tendon |
nerve (S1- |
artery |
ankle joint, |
|
Medial head: popliteal surface |
|
S2) |
|
assists in flexion |
|
above medial condyle of femur |
|
|
|
of the knee joint |
Soleus |
Posterior aspect of head of |
Posterior aspect of calcaneus via |
Tibial |
Posterior tibia |
Plantarflexes the |
|
fibula, proximal fourth of |
the calcaneal tendon |
nerve (S1- |
artery, fibular |
ankle and |
|
posterior surface of fibula, |
|
S2) |
artery, |
stabilizes the leg |
|
soleal line of tibia |
|
|
popliteal |
over the foot |
|
|
|
|
artery |
|
Plantaris |
Popliteal surface of femur |
Calcaneal tendon |
Tibial |
Popliteal |
Weaklyassists |
|
|
|
nerve (L5- |
artery |
gastrocnemius |
|
|
|
S1) |
|
|
Deep Muscles |
|
|
|
|
|
Popliteus |
Lateral aspect of lateral condyle |
Posterior tibia above soleal line |
Tibial |
Popliteal |
Unlocks and |
|
of femur and lateral meniscus |
|
nerve (L4 - |
artery |
weaklyflexes |
|
|
|
S1) |
|
knee joint |
Flexor hallucis |
Distal two-thirds of posterior |
Base of distal phalanxof great toe |
Tibial |
Fibular artery |
Flexes great toe, |
longus |
fibula and inferior part of |
(hallux) |
nerve (L5 - |
|
weakly |
|
interosseous membrane |
|
S2) |
|
plantarflexes the |
|
|
|
|
|
ankle |
Flexor |
Medial part of posterior tibia |
Plantar bases of distal phalanges |
Tibial |
Posterior |
Flexes lateral four |
digitorum |
inferior to soleal line |
of lateral four toes |
nerve (L5- |
tibial artery |
toes, plantarflexes |
longus |
|
|
S1) |
|
ankle |
Tibialis |
Posterior tibia below soleal line, |
Tuberosityof navicular bone, all |
Tibial |
Fibular artery |
Plantarflexes foot |
posterior |
interosseous membrane, |
cuneiforms, cuboid and bases of |
nerve (L4- |
|
at the ankle and |
|
proximal half of posterior fibula |
second through fourth |
L5) |
|
inverts the foot |
|
|
metatarsals |
|
|
|
408 / 425
