
- •1. Topographic Surface Anatomy
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •3. Superficial Face
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •4. Neck
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •5. Nasal Region
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •6. Oral Region
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •7. Pharynx
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •13. Cerebral Vasculature
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •14. Topographic Anatomy
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •16. Spinal Cord
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Thorax
- •18. Topographic Anatomy
- •Guides
- •Facts & Hints
- •19. Mammary Gland
- •Guides
- •Facts & Hints
- •20. Body Wall
- •Guides
- •Facts & Hints
- •21. Lungs
- •Guides
- •Facts & Hints
- •22. Heart
- •Guides
- •Facts & Hints
- •23. Mediastinum
- •Guides
- •Facts & Hints
- •Abdomen
- •24. Topographic Anatomy
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •25. Body Wall
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •26. Peritoneal Cavity
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •27. Viscera (Gut)
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •28. Viscera (Accessory Organs)
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •29. Visceral Vasculature
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •30. Innervation
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •32. Topographic Anatomy
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •35. Urinary Bladder
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •39. Testis, Epididymis & Ductus Deferens
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •40. Rectum
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •41. Vasculature
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •42. Innervation
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Upper Limb
- •43. Topographic Anatomy
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •48. Neurovasculature
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Lower Limb
- •49. Topographic Anatomy
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •51. Knee
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints
- •54. Neurovasculature
- •Guide
- •Facts & Hints

35 Urinary Bladder
STUDYAIMS
At the end of your study, you should be able to:
Describe the course of the pelvic ureters
Outline the gross structure of the bladder
Describe the relations of the bladder
Describe the structure of the male urethra
Describe the structure of the female urethra
277 / 425

GUIDE
Pelvis and Perineum: Urinary Bladder
[Plate 348, Urinary Bladder: Orientation and Supports]
278 / 425
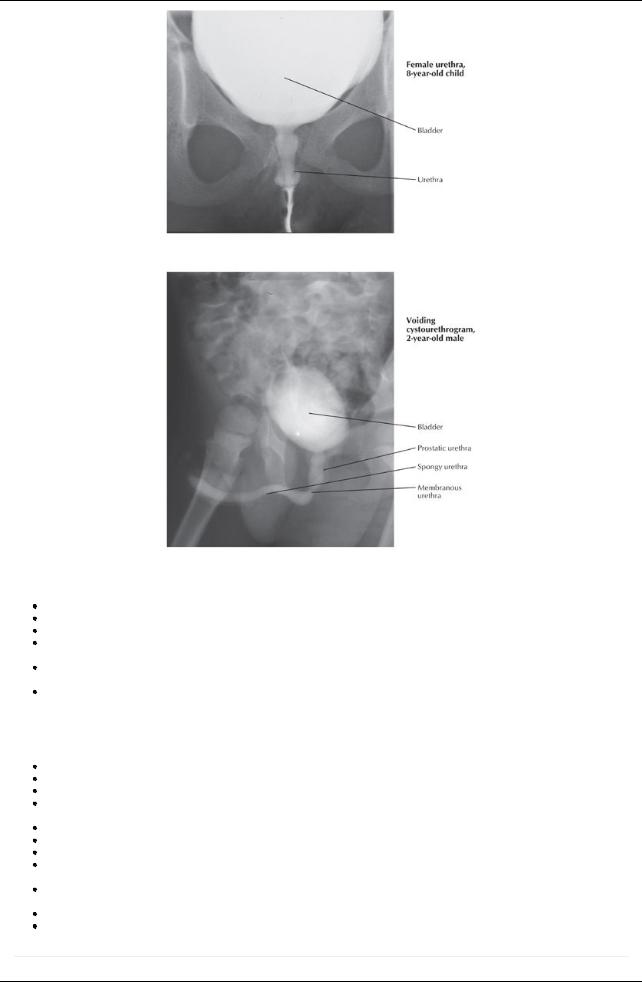
[Plate 351, Male and Female Cystourethrograms]
Ureters
Cross pelvic brim at the level of sacroiliac joint, anterior to the bifurcation common iliac arteryto pierce the posterior surface of the bladder Enters the posterolateral surface of the bladder and runs obliquelythrough the bladder wall, creating a flap valve
In males: the ureter passes under the ductus deferens, superior to the seminal vesicles
In women: the ureter descends posterior to the ovaryand into the base of the broad ligament passing under the uterine artery("water under the bridge")
Supplied bybranches of common and internal iliac arteries and uterine artery(inferior vesicle arteryin males) and drained byveins with same names.
Innervated byfibers from adjacent autonomic plexuses
Urinary Bladder
General structure
Lies posterior to pubic bones and pubic symphysis
When emptyis tetrahedron in shape and lies entirelywithin true pelvic cavity; spherical when full and mayreach as high as umbilicus When emptyhas a base (posterior surface) and a superior and two inferolateral surfaces.
Base (posterior surface) of bladder defined internallybytwo ureteric openings at superolateral corners and internal urethral opening inferiorly
Triangular area defined bythese openings is the vesicle trigone Ridge between two urethral openings is the interureteric fold
Neck of bladder is where base and inferolateral sides meet, inferiorly
Anterior angle or apexis site of attachment of urachus-fibrous remnant of fetal allantois, which is seen as the median umbilical ligament on the anterior abdominal wall
Bladder wall is composed of a thick layer of interwoven bundles of smooth muscle running transversely, longitudinally, and obliquelydetrusor muscle
In region of neck, detrusor muscle runs circularlyas involuntaryinternal sphincter Bladder mucosa is thrown into rugae except within trigone, which is smooth
page 176 page 177
279 / 425

Relations of the Urinary Bladder
|
Border |
Structure |
|
Superior |
Peritoneum |
|
|
Ileum |
|
|
Sigmoid colon |
|
Inferolateral |
Obturator internus muscle |
|
|
Levator ani muscle |
|
|
Obturator nerve |
|
|
Obturator arteryand vein |
|
|
Superior vesical arteryand vein |
|
Anterior |
Retropubic space-containing adipose tissue and veins |
|
|
Pubic crest |
|
Posterior-male |
Seminal vesicles |
|
|
Ampulla of ductus deferens |
|
|
Rectovesical pouch |
|
|
Ampulla of rectum |
|
Posterosuperior-female |
Vesicouterine pouch |
|
|
Bodyof uterus |
|
Posterior-female |
Cervix |
|
|
Anterior wall vagina |
|
Inferior-male |
Prostate |
|
|
Prostatic venous plexus |
Arterial supply |
|
|
Superior vesicle arteries (branches of internal iliac artery) supplyapexand superior part of bladder
Inferior vesical arteries supplyfundus and neck in males
Vaginal arteries (branches of uterine arteries) supplyfundus and neck in females
Obturator arteries (branches of internal iliac artery) provide arterial twigs
Venous drainage
Vesical venous plexus drains to internal iliac plexus via inferior vesical veins
Communicates with prostatic venous plexus in males and uterovaginal venous plexus in females
Female urethra
Threeto 4-cm long fibromuscular tube, bound to anterior vaginal wall
Extends from internal urethral meatus of bladder to external meatus situated just anterior to the vaginal opening in the vestibule Descends with vagina through urogenital hiatus and pelvic diaphragm and through perineal membrane where it is surrounded byexternal sphincter urethrae
Paraurethral glands, homologs to the prostate, open on either side near external urethral orifice Supplied byinternal pudendal and vaginal arteries
Drained byveins of same name
Innervated bybranches of pudendal nerve via S2-S4 spinal cord segments and afferents run with pelvic splanch
page 177
page 178
Male urethra
Twenty-cm fibromuscular tube
Conveys both urine and semen
Extends from internal urethral meatus of bladder to external urethral meatus in glans penis
Divided into three parts: prostatic; membranous and spongyurethra
Comparison of Prostatic, Membranous and Spongy Parts of the Male Urethra
|
|
Prostatic Urethra |
Membranous Urethra |
SpongyUrethra |
|
|
Length |
3 cm |
2 cm |
15 cm |
|
|
Extent |
Internal urethral meatus to apexof prostate |
Apexof prostate to perineal |
Bulb of penis to glans |
|
|
|
|
membrane |
penis |
|
|
Key |
Urethral crest (midline ridge) |
Surrounded bystriated muscle of |
|
|
|
Anatomical |
Prostatic sinuses (site of opening prostatic ducts) |
external urethral sphincter |
|
|
|
Features |
Prostatic utricle (blind-ending sac on urethral crest; |
Bulbourethral glands lie |
|
|
|
|
remnant of fetal duct forming uterus in females) |
posterolaterally |
|
|
|
|
Ejaculatoryduct (opens either side of the utricle) |
Pubic symphysis lies anteriorly |
|
|
|
|
|
attaching via pubourethral |
|
|
|
|
|
ligaments |
|
|
|
Blood |
Inferior vesical and rectal arteries |
Inferior vesical and rectal arteries |
Internal pudendal arteryvia |
|
|
Supply |
|
|
dorsal arteries of penis |
|
|
Venous |
Veins of same names and prostatic venous plexus |
Veins of same names and prostatic |
Prostatic venous plexus |
|
|
Drainage |
|
venous plexus |
and internal pudendal |
|
|
|
|
|
veins |
|
|
Nerve |
Pudendal nerve (S2-S4) and prostatic plexus |
Pudendal nerve (S2-S4) and |
Pudendal nerve (S2-S4) |
|
280 / 425

Supply |
|
prostatic plexus |
and prostatic plexus |
281 / 425
