
- •Table of Contents
- •Congratulations!
- •Scope
- •How to use this manual
- •Prerequisites
- •Conventions and Customer Service
- •What’s New!
- •Precise Point Positioning (PPP) processor
- •Software License
- •Warranty
- •Introduction and Installation
- •1.1 Waypoint Products Group Software Overview
- •1.2 Installation
- •1.2.1 What You Need To Start
- •1.2.2 CD Contents and Installation
- •1.2.3 Upgrading
- •1.3 Processing Modes and Solutions
- •1.4 Overview of the Products
- •1.4.1 GrafNav
- •1.4.2 GrafNet
- •1.4.3 GrafNav Lite
- •1.4.4 GrafNav / GrafNet Static
- •1.4.5 GrafMov
- •1.4.6 GrafNav Batch
- •1.4.7 Inertial Explorer
- •1.5 Utilities
- •1.5.1 Copy User Files
- •1.5.2 Download Service Data
- •1.5.3 GPS Data Logger
- •1.5.4 GPB Viewer
- •1.5.5 Mission Planner
- •1.5.6 Data Converter
- •GrafNav
- •2.1 GrafNav, GrafNav Lite and GrafNav / GrafNet Static Overview
- •2.2 Start a Project with GrafNav
- •2.3 File Menu
- •2.3.1 New Project
- •2.3.2 Open
- •2.3.3 Save Project
- •2.3.4 Save As
- •2.3.5 Print
- •2.3.6 Add Master Files
- •2.3.7 Add Remote Files
- •2.3.8 Alternate Precise / Correction Files
- •2.3.9 Show Master Files
- •2.3.10 Load
- •2.3.12 GPB Utilities
- •2.3.13 Remove Processing Files
- •2.3.15 Recent projects
- •2.3.16 Exit
- •2.4 View Menu
- •2.4.1 GPS Observations
- •2.4.2 Forward and Reverse Solutions
- •2.4.3 Processing History
- •2.4.4 Processing Summary
- •2.4.5 Return Status
- •2.4.6 Features
- •2.4.7 Objects
- •2.4.8 ASCII File (s)
- •2.4.10 Current CFG File
- •2.5 Process Menu
- •2.5.1 Process GNSS (differential)
- •2.5.2 Process PPP (single point)
- •2.5.3 Combine Solutions
- •2.5.4 Launch Batch Processor
- •2.5.5 Stop Auto Run
- •2.5.6 Load GNSS Solution
- •2.5.7 Load PPP Solution
- •2.5.8 Load Any Solution
- •2.5.9 Import Solutions and Setting
- •2.6 Settings Menu
- •2.6.1 GNSS Processing
- •2.6.2 PPP Processing
- •2.6.3 Coordinate
- •2.6.4 Individual
- •2.6.5 Datum
- •2.6.6 DEM Plotting
- •2.6.7 Photogrammetry
- •2.6.8 Manage Profiles
- •2.6.9 Compare Configuration Files
- •2.6.10 Preferences
- •2.7 Output Menu
- •2.7.1 Plot GPS Data
- •2.7.3 Plot Master / Remote Satellite Lock
- •2.7.4 Export Wizard
- •2.7.5 Write Coordinates
- •2.7.6 View Coordinates
- •2.7.7 Export Binary Values
- •2.7.8 Write Combined File
- •2.7.9 Build HTML Report
- •2.7.10 Export to Google Earth
- •2.7.11 Show Map Window
- •2.7.12 Processing Window
- •2.8 Tools Menu
- •2.8.1 Zoom In & Zoom Out
- •2.8.2 Distance & Azimuth Tool
- •2.8.3 Move Pane
- •2.8.4 Find Epoch Time
- •2.8.5 Datum Manager
- •2.8.6 Geoid
- •2.8.7 Grid/Map Projection
- •2.8.8 Convert Coordinate File
- •2.8.9 Time Conversion
- •2.8.10 Favourites Manager
- •2.8.11 Mission Planner
- •2.8.12 Download Service Data
- •2.9 Window Menu
- •2.9.1 Cascade
- •2.9.2 Tile
- •2.9.3 Next and Previous
- •2.9.4 Close Window
- •2.9.5 Close All Windows
- •2.10 Help Menu
- •2.10.1 Help Topics
- •2.10.2 www.novatel.com
- •2.10.3 About GrafNav
- •GrafNet
- •3.1 GrafNet Overview
- •3.1.1 Types of Networks
- •3.1.2 Solution Types
- •3.1.3 Computing Coordinates
- •3.2 Start a Project with GrafNet
- •3.2.1 Fix Bad Baselines
- •3.2.2 Unfixable Data
- •3.3 File
- •3.3.1 New Project
- •3.3.2 Open Project
- •3.3.3 Save Project
- •3.3.4 Save As
- •3.3.5 Print
- •3.3.6 Add / Remove Observations
- •3.3.7 Add / Remove Control Points
- •3.3.8 Add / Remove Check Points
- •3.3.9 Alternate Ephemeris / Correction Files
- •3.3.10 Remove Processing Files
- •3.3.11 Import Project Files
- •3.3.12 View
- •3.3.13 Convert
- •3.3.14 GPB Utilities
- •3.3.15 Recent projects
- •3.3.16 Exit
- •3.4 Process Menu
- •3.4.1 Processing Sessions
- •3.4.2 Rescanning Solution Files
- •3.4.3 Ignore Trivial Sessions
- •3.4.4 Unignore All Sessions
- •3.4.5 Compute Loop Ties
- •3.4.6 Network Adjustment
- •3.4.7 View Traverse Solution
- •3.4.8 View Processing Report
- •3.4.9 View All Sessions
- •3.4.10 View All Observations
- •3.4.11 View All Stations
- •3.5 Options Menu
- •3.5.1 Global Settings
- •3.5.3 Datum Options
- •3.5.4 Grid Options
- •3.5.5 Geoid Options
- •3.5.6 Preferences
- •3.6 Output Menu
- •3.6.1 Export Wizard
- •3.6.2 Write Coordinates
- •3.6.3 View Coordinates
- •3.6.4 Export DXF
- •3.6.5 Show Map Window
- •3.6.6 Show Data Window
- •3.6.7 Baselines Window
- •3.6.8 Processing Window
- •3.7 Tools Menu
- •3.8 Help Menu
- •GrafNav Batch
- •4.1 Overview of GrafNav Batch
- •4.1.1 Getting Started with GrafNav Batch
- •4.2 File Menu
- •4.2.1 New Project
- •4.2.2 Open Project
- •4.2.3 Save Project
- •4.2.4 Save As
- •4.2.5 Print
- •4.2.6 Add Baselines
- •4.2.8 Add Combined Baselines
- •4.2.9 Import CFG Files
- •4.2.10 Edit Selected Baseline Settings
- •4.2.11 Removing Selected Baselines
- •4.2.12 View ASCII Files
- •4.2.13 View Raw GPS Data
- •4.2.14 Convert GPS Data
- •4.2.15 GPB Utilities
- •4.2.16 Remove Process Files
- •4.2.17 Recent Projects
- •4.2.18 Exit
- •4.3 Process Menu
- •4.3.1 Process All Baselines
- •4.3.2 Process Selected
- •4.3.3 GrafNav on Selected Baselines
- •4.3.4 View Selected Processing Summary
- •4.3.5 Load All Solutions
- •4.3.6 Load Selected Solutions
- •4.4 Settings Menu
- •4.4.1 Global
- •4.4.2 Selected
- •4.4.3 Copy Processing Options
- •4.4.4 Load into Selected From
- •4.4.5 Manage
- •4.4.6 Preferences
- •4.5 Output Menu
- •4.5.1 Plot Selected GPS Data
- •4.5.2 View Selected Map
- •4.5.3 Export All
- •4.5.4 Export Selected
- •4.6 Tools Menu
- •4.7 Windows
- •4.8 Help Menu
- •GrafMov
- •5.1 Overview of GrafMov
- •5.2 Getting Started with GrafMov
- •5.3 File Menu
- •5.3.1 Add Master File
- •5.4 View Menu
- •5.5 Process Menu
- •5.6 Setting Menu
- •5.6.1 Moving Baseline Options
- •5.7 Output Menu
- •5.7.1 Plot GPS Data
- •5.8 Tools Menu
- •5.9 Interactive Windows
- •5.10 Help Menu
- •AutoNav
- •6.1 Overview of AutoNav
- •6.2 Getting Started with AutoNav
- •6.3 Base Station Files
- •6.4 Remote Files
- •6.5 Interactive Windows
- •File Formats
- •7.1 Overview of the File Formats
- •7.2 CFG File
- •7.3 GPS Data Files
- •7.3.1 GPB File
- •7.3.2 STA File
- •7.3.3 Old Station File Format
- •7.3.4 EPP File
- •7.4 Output Files
- •7.4.1 FML & RML Files
- •7.4.2 FSS & RSS Files
- •7.4.3 FWD & REV Files
- •7.4.4 FBV & RBV Files
- •Utilities
- •8.1 Utilities Overview
- •8.2 GPB Viewer Overview
- •8.2.1 File
- •8.2.2 Move
- •8.2.3 Edit
- •8.3 Concatenate, Splice and Resample Overview
- •8.3.1 Concatenate, Splice and Resample GPB Files
- •8.4 GPS Data Converter Overview
- •8.4.1 Convert Raw GPS data to GPB
- •8.4.2 Supported Receivers
- •8.5 GPS Data Logger Overview
- •8.5.1 Getting Started with WLOG
- •8.5.2 File
- •8.5.3 Display
- •8.5.4 Plot
- •8.5.5 Zoom Menu
- •8.5.6 Events Menu
- •8.6 WinCE Data Logger Overview
- •8.6.1 Installing CELOG
- •8.6.2 Getting Started with CELOG
- •8.6.3 Variable Display File
- •FAQ and Tips
- •9.1 Overview of FAQ and Tips
- •9.2 General FAQ and Tips
- •9.2.1 How can I store Master Station Coordinates?
- •9.2.2 How can I obtain Master Station Coordinates?
- •9.2.3 How can I customize output formats?
- •9.2.4 How can I download base station data?
- •9.3 Kinematic Processing FAQ and Tips
- •9.3.2 Should I combine forward and reverse solutions?
- •9.3.3 How can I use static / kinematic flags?
- •9.3.4 How do I eliminate problem satellites?
- •9.3.5 How do I set the measurement standard deviations?
- •9.3.6 How do I control bad data?
- •9.3.7 How do I avoid missing epochs?
- •9.3.8 Should I avoid using RINEX for kinematic data?
- •9.3.9 How do I process kinematic data logged during an ionospheric storm?
- •9.3.10 How do I process long kinematic baselines?
- •9.4 Integer Ambiguity Determination Tips
- •9.4.1 How can I detect and fix incorrect integer fixes?
- •9.4.2 How can I help KAR/ARTK find a solution?
- •9.4.3 How can I use KAR and ARTK to improve poor combined separations?
- •9.5 Static Processing FAQ and Tips
- •9.5.1 Can I use GrafNet for static batch processing?
- •9.5.2 Can I use kinematic processing on static baselines?
- •9.5.3 Using KAR or ARTK in GrafNet
- •9.5.4 How can I optimize the fixed static solution?
- •9.5.5 How can I refine L1/L2 integer solutions?
- •9.5.6 Can I use a larger interval for static processing?
- •9.5.7 How do I process static data logged during ionospheric storms?
- •9.5.8 How do I process long static baselines?
- •9.6.1 How should I choose a processing mode?
- •9.6.2 How important are base station coordinates?
- •9.6.3 How can I use the MB Plots?
- •9.6.4 How do I select a data interval?
- •9.6.6 How should I decide which base stations to use?
- •9.6.7 How do I deal with problematic baselines?
- •9.6.9 How can I use the fixed static solution?
- •9.6.10 What is the best way to process data with large base to rover separations?
- •9.6.11 How can I speed up processing?
- •9.7 PPP (Precise Point Positioning)
- •9.7.1 What is Precise Point Positioning?
- •9.7.2 How does PPP differ from differential processing?
- •9.7.3 How accurate is PPP?
- •9.7.4 What is PPP used for?
- •9.7.5 Who should use PPP?
- •9.7.6 Are there any limitations to PPP?
- •9.8 Common Inquiries
- •9.8.1 How can I determine the quality of a final solution?
- •9.8.2 How do I copy user files?
- •9.8.3 How do I update manufacturer files?
- •9.8.4 How do I produce local coordinates?
- •9.8.5 How do I define a local cartesian coordinate system?
- •9.8.6 How do I define a local coordinate grid?
- •9.8.7 How do I process an aerial survey with camera event marks?
- •9.9 Digital Elevation Models (DEM) FAQ and Tips
- •9.9.1 Why would I use a DEM?
- •9.9.2 What are the DEM sources?
- •9.9.3 What DEM formats are supported by GrafNav?
- •9.9.4 How do I handle large DEMs?
- •9.10 Datum FAQ and Tips
- •9.10.1 What are the available datums - related features?
- •9.10.2 How are datums handled within the software?
- •9.10.3 How do I make additional datums available?
- •9.10.4 How do I enter a 7-parameter transformation?
- •9.10.6 How do I use NADCON conversion files?
- •9.10.7 How do I prevent corruption from conversion errors?
- •9.11 Projections FAQ and Tips
- •9.11.1 What features are available with map projections?
- •9.12 Geoid FAQ and Tips
- •9.12.1 What are the available geoid - related features?
- •9.12.2 How can I create a WPG file?
- •A: Output Variables
- •B: Antenna Measurements Diagram
- •C: Summary of Commands
- •Index

Chapter 3 |
GrafNet |
|
|
3.1GrafNet Overview
GrafNet is a static network processing package that creates a single network by tying all the points of static GPS baselines together. Within minutes, GrafNet processes the entire project in a single operation. When the processing is completed, GrafNet color codes the baselines so irregular ones are isolated from the project and can be easily analyzed. GrafNet allows 3 types of static baseline processing solutions, including fixed static, float and ionospheric free.
This chapter tells you about the types of common networks, the different solutions and the methods to produce coordinates for each station in GrafNet. This chapter also describes how to get started with GrafNet, goes through each menu of its interface and provides step-by-step instructions for first-time users.
3.1.1Types of Networks
Closed Loop Network
Surveyors often use this style of network because of increased reliability. Due to the closing of the loops, any baseline determination errors will show up as tie point error. Such closure values can be seen via
Process | View Traverse Solution. If just two GPS receivers are employed, then a method called “leapfrogging” can be used to collect the data. In this procedure, starting from a known point, the lead receiver is placed on the first point to be surveyed. After the first session is complete, the trailing receiver is moved ahead of the lead receiver so that it now becomes the lead. The next baseline is observed and this procedure is repeated until small (4-6) loops are closed.
Radial Network
Also referred to as Single Base Station. Applications where productivity is more important, like GIS, do not need the same degree of reliability as the closed loop network. For these situations, use open loop networks. An example of this a network is in the shaded box. For this method, one receiver is left stationary over a reference or control point. One of more remote GPS receivers are moved from point to point being surveyed.
GPS Baseline
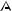 station
station
Figure 1: Closed Loop Network
Antenna height measurement errors will often cancel with this method and should therefore be double-checked. Methods involving more than two receivers become quite complex, and are past the scope of this chapter.
Figure 2: Radial Network
GrafNav / GrafNet 8.10 User Guide Rev 4 |
147 |

Chapter 3 |
GrafNet |
|
|
Table 11: Solution Types
|
Solution |
Fixed |
Ionospheric |
Description |
|
Type |
integer |
Correction |
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
L1 float solution. |
|
|
|
|
Used most often |
|
L1-Float |
N |
N |
with single |
|
frequency receivers |
|||
|
|
|
|
on short |
|
|
|
|
occupations or long |
|
|
|
|
baselines. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Ionospheric-free |
|
|
|
|
float solution. |
|
|
|
|
Requires dual |
|
L3-Float |
N |
Y |
frequency but can |
|
have very good |
|||
|
|
|
|
accuracies on |
|
|
|
|
longer baselines if |
|
|
|
|
occupation is long |
|
|
|
|
enough. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
L1 fixed integer |
|
|
|
|
solution. Can be |
|
|
|
|
very accurate on |
|
|
|
|
shorter baselines. |
|
|
|
|
Solution is |
|
|
|
|
computed from one |
|
|
|
|
continuous period of |
|
L1-Fixed |
Y |
N |
GPS data with the |
|
most satellites |
|||
|
|
|
|
covering the longest |
|
|
|
|
time. The Message |
|
|
|
|
Log (FML / RML) file |
|
|
|
|
can be viewed to |
|
|
|
|
determine how |
|
|
|
|
many satellites are |
|
|
|
|
used and for how |
|
|
|
|
long. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
L1 fixed integer |
|
|
|
|
solution that uses all |
|
|
|
|
of the satellites |
|
|
|
|
tracked. Satellite |
|
L1- |
|
|
tracks that is, |
|
Y |
N |
satellite-base pair |
|
|
NewFixed |
|||
|
|
|
between cycle slips, |
|
|
|
|
|
that fit poorly are |
|
|
|
|
rejected. Look at the |
|
|
|
|
FSS / RSS file to |
|
|
|
|
view each track. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Same as L1-Fixed |
|
|
|
|
except that dual |
|
|
|
|
frequency data is |
|
|
|
|
used. By using the |
|
L1L2-Fixed |
Y |
See Note |
wide-lane, much |
|
shorter fix times are |
|||
|
|
|
|
possible. For longer |
|
|
|
|
baselines, the iono |
|
|
|
|
L2 noise model can |
|
|
|
|
be used to improve |
|
|
|
|
accuracy. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Ionospheric correction is applied if the Iono Noise model is used, which depends on the baseline distance, or if you manually select the L2 Noise model. In such cases, the solution type would appear as L1L2-IonoFixed or L1L2-IonoNewFixed.
3.1.2Solution Types
GrafNet automatically determines concurrent sessions by examining the start and end times of the observation files. GrafNet tries to form sessions using an extended time scale to resolve any conflicts stemming from differing week numbers. This requires that a valid ephemeris file (EPP) be present for each corresponding observation file (GPB). For more than two receivers simultaneously collecting data, unwanted session connections can be ignored using the Session Menu, under Process | View All Sessions. The vector for each session is resolved independently. There are three modes of static processing includes the following:
Fixed Solution
This process uses single or dual frequency data, but assumes integer ambiguities. This mode delivers the best accuracies and is also the default static processing mode. Single frequency will fix reliably on baselines less than 10 km, while dual frequency will work well up to 25 km. Longer baselines will require longer observation times.
Float Solution
This method does not solve for integer ambiguities, and therefore, has no baseline length restrictions. Regardless, long single frequency baselines will have much poorer accuracies than their dual frequency iono-free counterparts. Normally, the float solution is only used when either fixed static solutions cannot be made to pass or for long single frequency baselines of 10 km or more.
Iono-free Solution
This is a float solution with the ionospheric effect largely removed from the carrier phase by combining L1 and L2 carrier phases in the iono-free combination. This option requires dual frequency data at both stations. Iono-free should normally be used if the fixed solution fails (on longer baselines), or on very long baselines (greater than 50km) where fixed static is unreliable.
GrafNet also offers an Automatic mode, which chooses between the three processing modes by examining baseline lengths and the type of measurements available. Table 11, in the shaded box, contains a list of solution types attainable in GrafNet.
148 |
GrafNav / GrafNet 8.10 User Guide Rev 4 |
