
- •Table of Contents
- •Congratulations!
- •Scope
- •How to use this manual
- •Prerequisites
- •Conventions and Customer Service
- •What’s New!
- •Precise Point Positioning (PPP) processor
- •Software License
- •Warranty
- •Introduction and Installation
- •1.1 Waypoint Products Group Software Overview
- •1.2 Installation
- •1.2.1 What You Need To Start
- •1.2.2 CD Contents and Installation
- •1.2.3 Upgrading
- •1.3 Processing Modes and Solutions
- •1.4 Overview of the Products
- •1.4.1 GrafNav
- •1.4.2 GrafNet
- •1.4.3 GrafNav Lite
- •1.4.4 GrafNav / GrafNet Static
- •1.4.5 GrafMov
- •1.4.6 GrafNav Batch
- •1.4.7 Inertial Explorer
- •1.5 Utilities
- •1.5.1 Copy User Files
- •1.5.2 Download Service Data
- •1.5.3 GPS Data Logger
- •1.5.4 GPB Viewer
- •1.5.5 Mission Planner
- •1.5.6 Data Converter
- •GrafNav
- •2.1 GrafNav, GrafNav Lite and GrafNav / GrafNet Static Overview
- •2.2 Start a Project with GrafNav
- •2.3 File Menu
- •2.3.1 New Project
- •2.3.2 Open
- •2.3.3 Save Project
- •2.3.4 Save As
- •2.3.5 Print
- •2.3.6 Add Master Files
- •2.3.7 Add Remote Files
- •2.3.8 Alternate Precise / Correction Files
- •2.3.9 Show Master Files
- •2.3.10 Load
- •2.3.12 GPB Utilities
- •2.3.13 Remove Processing Files
- •2.3.15 Recent projects
- •2.3.16 Exit
- •2.4 View Menu
- •2.4.1 GPS Observations
- •2.4.2 Forward and Reverse Solutions
- •2.4.3 Processing History
- •2.4.4 Processing Summary
- •2.4.5 Return Status
- •2.4.6 Features
- •2.4.7 Objects
- •2.4.8 ASCII File (s)
- •2.4.10 Current CFG File
- •2.5 Process Menu
- •2.5.1 Process GNSS (differential)
- •2.5.2 Process PPP (single point)
- •2.5.3 Combine Solutions
- •2.5.4 Launch Batch Processor
- •2.5.5 Stop Auto Run
- •2.5.6 Load GNSS Solution
- •2.5.7 Load PPP Solution
- •2.5.8 Load Any Solution
- •2.5.9 Import Solutions and Setting
- •2.6 Settings Menu
- •2.6.1 GNSS Processing
- •2.6.2 PPP Processing
- •2.6.3 Coordinate
- •2.6.4 Individual
- •2.6.5 Datum
- •2.6.6 DEM Plotting
- •2.6.7 Photogrammetry
- •2.6.8 Manage Profiles
- •2.6.9 Compare Configuration Files
- •2.6.10 Preferences
- •2.7 Output Menu
- •2.7.1 Plot GPS Data
- •2.7.3 Plot Master / Remote Satellite Lock
- •2.7.4 Export Wizard
- •2.7.5 Write Coordinates
- •2.7.6 View Coordinates
- •2.7.7 Export Binary Values
- •2.7.8 Write Combined File
- •2.7.9 Build HTML Report
- •2.7.10 Export to Google Earth
- •2.7.11 Show Map Window
- •2.7.12 Processing Window
- •2.8 Tools Menu
- •2.8.1 Zoom In & Zoom Out
- •2.8.2 Distance & Azimuth Tool
- •2.8.3 Move Pane
- •2.8.4 Find Epoch Time
- •2.8.5 Datum Manager
- •2.8.6 Geoid
- •2.8.7 Grid/Map Projection
- •2.8.8 Convert Coordinate File
- •2.8.9 Time Conversion
- •2.8.10 Favourites Manager
- •2.8.11 Mission Planner
- •2.8.12 Download Service Data
- •2.9 Window Menu
- •2.9.1 Cascade
- •2.9.2 Tile
- •2.9.3 Next and Previous
- •2.9.4 Close Window
- •2.9.5 Close All Windows
- •2.10 Help Menu
- •2.10.1 Help Topics
- •2.10.2 www.novatel.com
- •2.10.3 About GrafNav
- •GrafNet
- •3.1 GrafNet Overview
- •3.1.1 Types of Networks
- •3.1.2 Solution Types
- •3.1.3 Computing Coordinates
- •3.2 Start a Project with GrafNet
- •3.2.1 Fix Bad Baselines
- •3.2.2 Unfixable Data
- •3.3 File
- •3.3.1 New Project
- •3.3.2 Open Project
- •3.3.3 Save Project
- •3.3.4 Save As
- •3.3.5 Print
- •3.3.6 Add / Remove Observations
- •3.3.7 Add / Remove Control Points
- •3.3.8 Add / Remove Check Points
- •3.3.9 Alternate Ephemeris / Correction Files
- •3.3.10 Remove Processing Files
- •3.3.11 Import Project Files
- •3.3.12 View
- •3.3.13 Convert
- •3.3.14 GPB Utilities
- •3.3.15 Recent projects
- •3.3.16 Exit
- •3.4 Process Menu
- •3.4.1 Processing Sessions
- •3.4.2 Rescanning Solution Files
- •3.4.3 Ignore Trivial Sessions
- •3.4.4 Unignore All Sessions
- •3.4.5 Compute Loop Ties
- •3.4.6 Network Adjustment
- •3.4.7 View Traverse Solution
- •3.4.8 View Processing Report
- •3.4.9 View All Sessions
- •3.4.10 View All Observations
- •3.4.11 View All Stations
- •3.5 Options Menu
- •3.5.1 Global Settings
- •3.5.3 Datum Options
- •3.5.4 Grid Options
- •3.5.5 Geoid Options
- •3.5.6 Preferences
- •3.6 Output Menu
- •3.6.1 Export Wizard
- •3.6.2 Write Coordinates
- •3.6.3 View Coordinates
- •3.6.4 Export DXF
- •3.6.5 Show Map Window
- •3.6.6 Show Data Window
- •3.6.7 Baselines Window
- •3.6.8 Processing Window
- •3.7 Tools Menu
- •3.8 Help Menu
- •GrafNav Batch
- •4.1 Overview of GrafNav Batch
- •4.1.1 Getting Started with GrafNav Batch
- •4.2 File Menu
- •4.2.1 New Project
- •4.2.2 Open Project
- •4.2.3 Save Project
- •4.2.4 Save As
- •4.2.5 Print
- •4.2.6 Add Baselines
- •4.2.8 Add Combined Baselines
- •4.2.9 Import CFG Files
- •4.2.10 Edit Selected Baseline Settings
- •4.2.11 Removing Selected Baselines
- •4.2.12 View ASCII Files
- •4.2.13 View Raw GPS Data
- •4.2.14 Convert GPS Data
- •4.2.15 GPB Utilities
- •4.2.16 Remove Process Files
- •4.2.17 Recent Projects
- •4.2.18 Exit
- •4.3 Process Menu
- •4.3.1 Process All Baselines
- •4.3.2 Process Selected
- •4.3.3 GrafNav on Selected Baselines
- •4.3.4 View Selected Processing Summary
- •4.3.5 Load All Solutions
- •4.3.6 Load Selected Solutions
- •4.4 Settings Menu
- •4.4.1 Global
- •4.4.2 Selected
- •4.4.3 Copy Processing Options
- •4.4.4 Load into Selected From
- •4.4.5 Manage
- •4.4.6 Preferences
- •4.5 Output Menu
- •4.5.1 Plot Selected GPS Data
- •4.5.2 View Selected Map
- •4.5.3 Export All
- •4.5.4 Export Selected
- •4.6 Tools Menu
- •4.7 Windows
- •4.8 Help Menu
- •GrafMov
- •5.1 Overview of GrafMov
- •5.2 Getting Started with GrafMov
- •5.3 File Menu
- •5.3.1 Add Master File
- •5.4 View Menu
- •5.5 Process Menu
- •5.6 Setting Menu
- •5.6.1 Moving Baseline Options
- •5.7 Output Menu
- •5.7.1 Plot GPS Data
- •5.8 Tools Menu
- •5.9 Interactive Windows
- •5.10 Help Menu
- •AutoNav
- •6.1 Overview of AutoNav
- •6.2 Getting Started with AutoNav
- •6.3 Base Station Files
- •6.4 Remote Files
- •6.5 Interactive Windows
- •File Formats
- •7.1 Overview of the File Formats
- •7.2 CFG File
- •7.3 GPS Data Files
- •7.3.1 GPB File
- •7.3.2 STA File
- •7.3.3 Old Station File Format
- •7.3.4 EPP File
- •7.4 Output Files
- •7.4.1 FML & RML Files
- •7.4.2 FSS & RSS Files
- •7.4.3 FWD & REV Files
- •7.4.4 FBV & RBV Files
- •Utilities
- •8.1 Utilities Overview
- •8.2 GPB Viewer Overview
- •8.2.1 File
- •8.2.2 Move
- •8.2.3 Edit
- •8.3 Concatenate, Splice and Resample Overview
- •8.3.1 Concatenate, Splice and Resample GPB Files
- •8.4 GPS Data Converter Overview
- •8.4.1 Convert Raw GPS data to GPB
- •8.4.2 Supported Receivers
- •8.5 GPS Data Logger Overview
- •8.5.1 Getting Started with WLOG
- •8.5.2 File
- •8.5.3 Display
- •8.5.4 Plot
- •8.5.5 Zoom Menu
- •8.5.6 Events Menu
- •8.6 WinCE Data Logger Overview
- •8.6.1 Installing CELOG
- •8.6.2 Getting Started with CELOG
- •8.6.3 Variable Display File
- •FAQ and Tips
- •9.1 Overview of FAQ and Tips
- •9.2 General FAQ and Tips
- •9.2.1 How can I store Master Station Coordinates?
- •9.2.2 How can I obtain Master Station Coordinates?
- •9.2.3 How can I customize output formats?
- •9.2.4 How can I download base station data?
- •9.3 Kinematic Processing FAQ and Tips
- •9.3.2 Should I combine forward and reverse solutions?
- •9.3.3 How can I use static / kinematic flags?
- •9.3.4 How do I eliminate problem satellites?
- •9.3.5 How do I set the measurement standard deviations?
- •9.3.6 How do I control bad data?
- •9.3.7 How do I avoid missing epochs?
- •9.3.8 Should I avoid using RINEX for kinematic data?
- •9.3.9 How do I process kinematic data logged during an ionospheric storm?
- •9.3.10 How do I process long kinematic baselines?
- •9.4 Integer Ambiguity Determination Tips
- •9.4.1 How can I detect and fix incorrect integer fixes?
- •9.4.2 How can I help KAR/ARTK find a solution?
- •9.4.3 How can I use KAR and ARTK to improve poor combined separations?
- •9.5 Static Processing FAQ and Tips
- •9.5.1 Can I use GrafNet for static batch processing?
- •9.5.2 Can I use kinematic processing on static baselines?
- •9.5.3 Using KAR or ARTK in GrafNet
- •9.5.4 How can I optimize the fixed static solution?
- •9.5.5 How can I refine L1/L2 integer solutions?
- •9.5.6 Can I use a larger interval for static processing?
- •9.5.7 How do I process static data logged during ionospheric storms?
- •9.5.8 How do I process long static baselines?
- •9.6.1 How should I choose a processing mode?
- •9.6.2 How important are base station coordinates?
- •9.6.3 How can I use the MB Plots?
- •9.6.4 How do I select a data interval?
- •9.6.6 How should I decide which base stations to use?
- •9.6.7 How do I deal with problematic baselines?
- •9.6.9 How can I use the fixed static solution?
- •9.6.10 What is the best way to process data with large base to rover separations?
- •9.6.11 How can I speed up processing?
- •9.7 PPP (Precise Point Positioning)
- •9.7.1 What is Precise Point Positioning?
- •9.7.2 How does PPP differ from differential processing?
- •9.7.3 How accurate is PPP?
- •9.7.4 What is PPP used for?
- •9.7.5 Who should use PPP?
- •9.7.6 Are there any limitations to PPP?
- •9.8 Common Inquiries
- •9.8.1 How can I determine the quality of a final solution?
- •9.8.2 How do I copy user files?
- •9.8.3 How do I update manufacturer files?
- •9.8.4 How do I produce local coordinates?
- •9.8.5 How do I define a local cartesian coordinate system?
- •9.8.6 How do I define a local coordinate grid?
- •9.8.7 How do I process an aerial survey with camera event marks?
- •9.9 Digital Elevation Models (DEM) FAQ and Tips
- •9.9.1 Why would I use a DEM?
- •9.9.2 What are the DEM sources?
- •9.9.3 What DEM formats are supported by GrafNav?
- •9.9.4 How do I handle large DEMs?
- •9.10 Datum FAQ and Tips
- •9.10.1 What are the available datums - related features?
- •9.10.2 How are datums handled within the software?
- •9.10.3 How do I make additional datums available?
- •9.10.4 How do I enter a 7-parameter transformation?
- •9.10.6 How do I use NADCON conversion files?
- •9.10.7 How do I prevent corruption from conversion errors?
- •9.11 Projections FAQ and Tips
- •9.11.1 What features are available with map projections?
- •9.12 Geoid FAQ and Tips
- •9.12.1 What are the available geoid - related features?
- •9.12.2 How can I create a WPG file?
- •A: Output Variables
- •B: Antenna Measurements Diagram
- •C: Summary of Commands
- •Index
GrafNav |
Chapter 2 |
|
|
|
|
Antenna Models
The simple model, and generic profile, for the advanced method are identical. They assume that the L1 and L2 phase centers are coincident and have no offsets from the antenna height measurement. For each antenna profile, the following information can be edited:
•The antenna model
•The manufacturer
•The horizontal distance from the phase centre to the edge of the ground plane
•The L1 and L2 phase offsets from the origin
•The location of the origin on the antenna
To measure to the ground plane, enter a slant distance instead of a vertical antenna height. GrafNav uses Pythagorean Theorem to calculate the antenna height using the slant distance and the horizontal distance in the antenna profile. However, this requires the creation of a profile, as those loaded with the software are obtained from the NGS (National Geodetic Survey), who do not often measure the ground plane radius. See Section 2.4.7, on Page 57 for information about antenna heights for static sessions.
The antenna origin must be moved to antenna ground plane. Refer to http:// www.novatel.com/products/ waypoint_faqs.htm for more information.
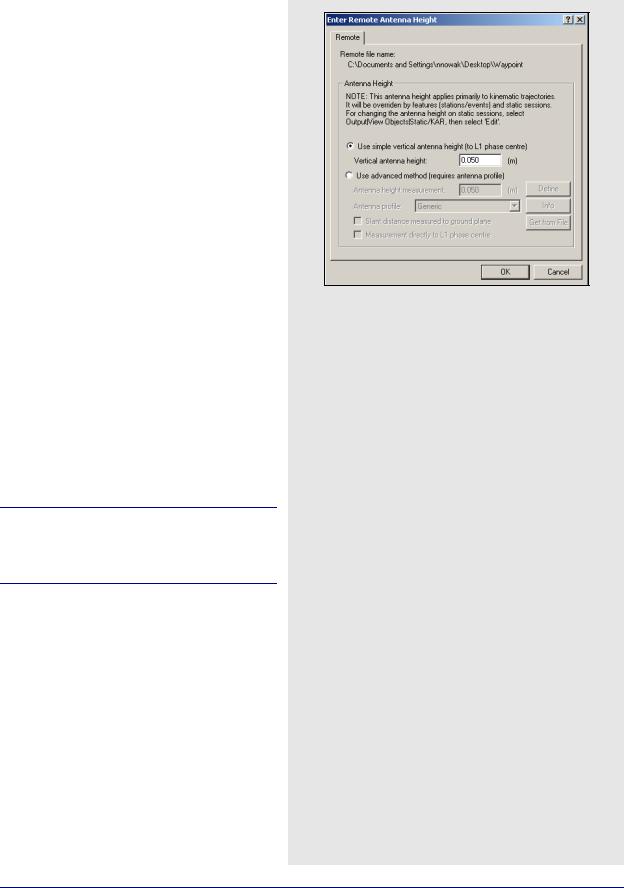
2.3.7Add Remote Files
When starting a new project, the program needs the data collected from the remote station.
This antenna height applies primarily to kinematic trajectories and features, such as stations or events, and static sessions override it.
If an antenna height is not entered, the program assumes that the height was zero and calculates heights based on this information. If an STA (station) file exists and a station mark is present in that file, the last antenna height shows up by default.
See Section 2.3.6, on Page 36 for information regarding antenna height models.
How to add a remote file
1.Select File | Add Remote File after giving the new project a name and adding the master GPB file(s). From the list of available GPB files, choose the file collected at the remote station.
2.When prompted, enter the remote station antenna height.
How to change the remote antenna height on specific static sessions
1.Select View | Objects | KAR/Static.
2.Click Edit for each static session.
GrafNav / GrafNet 8.10 User Guide Rev 4 |
37 |

Chapter 2 |
GrafNav |
|
|
How to specify alternate ephemeris files
1.Go to File | Alternate Ephemeris Files. The program displays a list of ephemeris files (EPP), precise ephemeris files (SP3/ SP3c), IONEX files (yyI), and clock files (CLK).
2.Select the appropriate EPP file.
How to load ephemerides from different stations
1.Select Tools | Download Service Data.
2.Download data from the nearest station for the day of interest.
3.For precise ephemeris, select the Options tab and enable precise ephemeris download.
2.3.8Alternate Precise / Correction Files
Broadcast Ephemeris
The ephemeris file contains trajectory information used to reconstruct the orbit of each satellite. This data is necessary for GPS positioning.
Generally, the GNSS receiver includes broadcast ephemeris data with its raw data files. Either the decoder or the logging software converts these files into EPP format. You should monitor data logging to ensure that enough ephemerides are being saved. Ephemeris information is usually updated every 1- 2 hours. Receivers will also output ephemerides at startup or as satellites rise into view.
GrafNav overcomes missing ephemeris data by searching all EPP files associated with the master, or remote, files in the project. If none of the EPP files in the project contain the necessary ephemeris, you can obtain them from a specified alternate source, for instance, CORS or IGS. See the shaded box for steps on how to specify alternate ephemeris files.
Ephemerides from different stations, or precise ephemerides that span over a day, can be added to the list to be included with the processing. See the shaded box for steps on how to load ephemerides from different stations.
38 |
GrafNav / GrafNet 8.10 User Guide Rev 4 |

GrafNav |
Chapter 2 |
|
|
|
|
Precise Ephemerides
Precise ephemerides are satellite trajectories computed post-mission. They are much more accurate than broadcast ephemerides but for differential processing, this accuracy improvement is not noticeable and is generally lost in the noise. However, for PPP processing, precise ephemerides are required.
A precise ephemeris is useful for single point processing. Geodetic services such as National Geodetic Survey (NGS) in the United States, the Geodetic Survey of Canada and some European agencies compute these orbits on a continual basis. In most cases, this data is available at a few days latency. The easiest way to download SP3 files is via Waypoint’s download program. See Chapter 7 on Page 207 for details.
Waypoint software only supports precise orbits stored in the SP3 format (most agencies use this format). Orbits which have been optimized for the United States are available free of charge from NGS via their website (www.nga.mil).
Waypoint software’s precise orbit implementation requires that a broadcast ephemeris orbit is available. Precise ephemerides cannot be used to circumvent missing broadcast orbit information. If a broadcast ephemeris is missing, consider downloading data from the nearest CORS or IGS station. See Section 2.8.12, on Page 140 for help.
IONEX and Satellite Clock Files
IONEX (Ionosphere Map Exchange files) contain information concerning the Total Electron Count (TEC) in a two-dimensional grid. For single frequency long-range differential or single point processing, the information in an IONEX file adds corrections helpful to the L1 frequency and are available through the Download Service Data utility.
Satellite clock files can also be downloaded using the Download Service Data utility. These files contain a list of biases that can assist single point positioning because the clock bias is only differenced out in differential positioning. For PPP, these files are required.
How to load a precise ephemeris file in the SP3 format
1.Go to File | Alternate Ephemeris Files. The program displays a list of ephemeris files (EPP), precise ephemeris files (SP3), IONEX files (yyI), and clock files (CLK).
2.Select the appropriate SP3 file.
How to load IONEX files and satellite clock files
1.Go to File | Alternate Ephemeris Files.The program displays a list of ephemeris files (EPP), precise ephemeris files (SP3), IONEX files (yyI), and clock files (CLK).
2.Select the appropriate yyI and/or CLK file.
GrafNav / GrafNet 8.10 User Guide Rev 4 |
39 |

Chapter 2 |
GrafNav |
|
|
View/Edit GPS option settings
Show Station Info
Displays information about the station.
Show GPB Info
Displays information about the GPB file.
Show Time Gaps
Displays information about any time gaps in the data.
View Raw GPS Data
Opens the master file in GPB Viewer.
View Ephemeris File
Opens the EPP file in the internal viewer.
View Station File
Opens the STA file in the internal viewer.
Insert Static/Kinematic Markers
Opens up the menu to insert static/kinematic markers in the file.
Resample/Fill Gaps using the following options
•File Interval – fills all gaps by resampling using the data interval.
•Processing Interval – fills gaps and lowers or raises the data rate in accordance with the specified processing interval.
•Remote File Times – produces a GPB file with epoch times that match the remote file. Any data gap present in the remote file is also present in the new master GPB file. This method of resampling removes unneeded data logged before, and after, the observation time period at the remote. It allows resampling of GPB files that do not sample at a constant rate, examples of these files include SiRF, GSU and I/II.
Resampling can cause additional errors. If you are resampling intervals of 5 seconds or less, the error is negligible for kinematic processing but for 30 second data, this error is 1-2 cm and hampers integer ambiguity resolution. Resampling should not be performed for static processing.
Disable
Disables the selected master station from being used for processing.
Remove
Removes the master file completely from the project.
Plot L1 Locktime
Launches the L1 Satellite Lock/Elevation plot.
Plot L2 Locktime
Launches the L2 Satellite Lock/Elevation plot.
2.3.9 Show Master Files
Object
This command brings up the Object menu for the base stations, where the following features are available:
View
Brings up the Object Info message box for the selected base station.
Edit
Allows you to edit the name, coordinates, and antenna height of the selected base station.
View/Edit GPS
Displays a list of actions that are listed in the shaded box.
Disable
Disables the selected master station from being used for processing.
Remove
Removes the master file from the project.
Add to Favourites
This adds the object with solution to the list of Favourites. See Section 2.8.10, on Page 135 for more details.
40 |
GrafNav / GrafNet 8.10 User Guide Rev 4 |
