
- •О.И. Сафроненко, к.С.Петросян, с.Ю. Резникова learning to learn in english
- •Методическая записка
- •Contents
- •Unit 1 Learn How to Learn
- •What do you think?
- •Focus on Language
- •Focus on language
- •What do you think?
- •Keep learning? Keep earning!
- •Comprehension check
- •What do you think?
- •Unit 2 Study Smart, Not Hard
- •What do you think?
- •Focus on language
- •What do you think?
- •What are effective study habits?
- •Focus on language
- •Practice
- •Unit 3 Revise & Practise
- •Progress Test
- •Unit 1 Making the Choice of Your Life
- •What do you think?
- •Focus on Language
- •First degree courses in the uk
- •Comprehension check
- •What do you think?
- •Unit 2 Your Personal Science Odyssey
- •What do you think?
- •Comprehension check
- •Focus on Language
- •Practice
- •Unit 3 Revise & Practise
- •Game “Why physics or math, etc.?”
- •Progress Test
- •Unit 1 Secret of Success
- •What do you think?
- •Focus on language
- •Practice
- •Thinking about what we have found!
- •Comprehension check
- •Focus on language
- •“The World Wide Web: the battle for your mind at your fingertips”
- •Unit 2 Hunting for Treasures
- •Comprehension check
- •What do you think?
- •Focus on Language
- •Practice
- •Technology and Libraries
- •Comprehension check
- •What do you think?
- •Unit 3 Revise & Practise
- •Progress Test
- •Unit 1 Scientific Milestones
- •Metric system telescope compass thermometer microscope
- •Comprehension check
- •Focus on Language
- •Practice
- •Practice
- •Invention /discovery
- •Unexpected Discoveries
- •Comprehension check
- •What do you think?
- •Focus on language
- •Practice
- •What do you think?
- •Unit 2 Scientific Revolution
- •Breakthroughs of the 20th century
- •What do you think?
- •Focus on language
- •Verb Suffixes
- •Practice
- •What do you think?
- •Unit 3 Revise & Practise
- •Progress Test
- •Rules of the Lab
- •Unit 1 Global Issues
- •Comprehension check
- •Focus on language
- •Practice
- •Practice
- •What do you think?
- •Global Warming: Facts vs. Myths myths:
- •Comprehension check
- •Focus on language
- •Practice
- •Comprehension check
- •Focus on Language
- •Work in teams of 3. Make as many words as possible using the prefixes re-, dis-, over-, sub-, en-, up- . Compare as a class.
- •Practice
- •Unit 3 Revise & Practise
- •Progress Test
- •Unit 1 The 20th Century and Beyond
- •Science for the Twenty-First Century
- •Focus on language
- •Practice
- •As old as writing
- •What do you think?
- •Unit 2 Into the Future
- •What do you think?
- •Focus on the language
- •Practice
- •Practice
- •What do you think?
- •Unit 3 Revise & Practise
- •Progress Test
- •Unit 1 Job Opportunities for Students
- •Part-time Jobs vs. Holiday Jobs
- •Comprehension check
- •What do you think?
- •Focus on language
- •Practice
- •What do you think?
- •Focus on language
- •Unit 2 On the Job
- •What do you think?
- •Focus on language
- •Practice
- •What can I do with a Science degree?
- •What do you think?
- •Unit 3 Revise & Practise
- •Progress Test
- •Scripts Module 1 Unit 1 Five New Year's Resolutions for English Learners
- •Module 1 Unit 2
- •Module 2 Unit 1 a Look at Washington University
- •Module 2 Unit 1
- •Module 3 Unit 1
- •Module 3 Unit 2 Website of the Week — Universal Digital Library
- •Module 4 Unit 1
- •Module 4 Unit2 The Discoveries Behind This Year's Nobel Prizes for Science
- •Module 5 Unit 1 Cities Around the World Are 'Going Green'
- •Module 5 Unit 2 Electronic Waste
- •Is it illegal to dispose of computers in the trash?
- •Module 6 Unit 1 Scientists Receive National Medals of Science and Technology
- •Module 6 Unit 2
- •Module 7 Unit 1 Job Centre
- •Module 7 Unit 2
- •Interns Provide Free Labor, But Internships Are Not Always Free
- •Keys Module 1 Unit 1
- •Module 1 Unit 2
- •In the Realm of Science 1
- •Module 1 Unit 3
- •Module 2 Unit 1
- •Module 2 Unit 2
- •Module 2 Unit 3
- •Модуль 3 Unit 1
- •Module 3 Unit 2
- •Module 3 Unit 3
- •Module 4 Unit 1
- •Module 4 Unit 2
- •In the Realm of Science 2
- •In the Realm of Science 3
- •Module 4 Unit 3
- •Module 5 Unit 1
- •Module 5 Unit 2
- •Module 5 Unit 3
- •Module 6 Unit 1
- •In the Realm of Science 1
- •Module 6 Unit 2
- •Module 6 Unit 3
- •Module 7 Unit 1
- •Module 7 Unit 2
- •Module 7 Unit 3
- •List of materials used
- •Part-time Jobs vs. Holiday Jobs// Retrieved from e4s:co uk http://www.E4s.Co.Uk/docs/part-time-jobs.Htm
- •Internet recourses
What do you think?
-
Do you agree with the expert’s advice?
-
Does every student with good memory make a successful learner? Why?/Why not?
-
Do you think you are a successful learner? Why?/Why not?
-
How do you think you can improve your learning strategies?
|
Reading |
-
Read what some former students say about how to study effectively. Write out the recommendations and advice they give.
What are effective study habits?
No two people study the same way, and there is little doubt that what works for one person may not work for another. However, there are some general techniques that seem to produce good results. Our reporter, Barbara Brown, interviewed some former students about their effective study habits.












2. Which of the recommendations do you follow? Why?
Focus on language
-
Study these examples of advice.
-
Giving advice
To give advice we can use
-
imperative:
Express your goals positively.
Do not set goals too low or too high.
Avoid setting general, intricate or unclear goals.
-
modals should or ought to:
You should be honest about how plans are going.
(=You ought to be …)
-
had better - advice close to warning:
If you want other people really help you, you’d better inform them in advance.
-
Second Conditionals:
If I were you, I would set priorities first.
-
Practice
-
What other ways to give advice do you know? Give your own examples.
Example: It’s a good idea to set priorities when you have several goals.
|
“In high school I was able to get all or most of my work done without much of a problem. But here in college, there’s so much material to read and absorb, and papers and exams take longer to finish and study for that sometimes I feel like I can hardly keep my head above this pool of work.” – Kathy Brown |
-
Read Kathy Brown’s letter
describing the problem she faces
with her studies. As a class give her some helpful advice.
|
Get real |
|
|
Carry out some self exploratory work. Take the time management test to see where your time goes and report results in class. Do the tasks on your own daily, weekly and semester schedules. Choose the one you find the most significant and present it in class.
-
Useful sites to search
http://www.studygs.net/timman.htm
http://www.ucc.vt.edu/stdysk/stdyhlp.html
|
Speaking |
In groups of 3-4 think of any other tips how to arrange your day to get maximum
output. Compare with the other groups. Which of these do you follow?
e.g.: write down daily tasks
………………………
………………………
|
Tool box: Giving advice Avoid … You/one should … Don’t … If … , you’d better … I recommend/advice … It’s a good idea/technique/… If I were you, I would … |
|
Writing |
|
|
|
Managing your learning It is useful to keep a record of what you study. This might be a record for your work and a record for your feelings about the course. The latter will allow you to see whether you are progressing, what your difficulties are, as well as formulate your objectives and analyze your distractions. |
-
Answer the questions.
-
What kind of records do students usually keep?
-
Have you ever kept a diary?
-
Do you think it can help in studies? In what way?
-
Look at the mind map and discuss possible contents for a learner diary. How would you like to organize your learner diary?
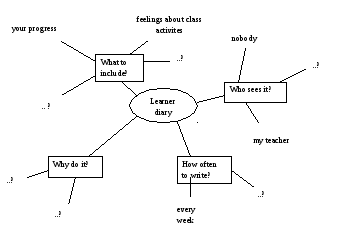
-
Think about what you have done in the last week in your English classes and write an entry for your learner diary.
|
In the Realm of Science |
Words of the Latin origin are widely used in many languages. English and Russian are not the exceptions, e.g.: консенсус, кворум, P.S., quantum, etc.
-
Think of the other Latin words used in the Russian and English languages.
-
Pay attention to the correct pronunciation in English of the following abbreviations:
|
Abbreviation |
Latin |
Russian equivalent |
|
A.C. |
Ante Christum |
до нашей эры |
|
A.D. |
anno Domini |
нашей эры |
|
vs |
versus |
против |
|
et al. |
et alii |
и другие |
|
P.S. |
post scriptum |
постскриптум |
|
etc. |
et cetera |
и так далее |
|
i.e. |
id est |
то есть |
|
p.m. |
post meridiem |
пополудни |
|
NB |
nota bene |
обрати особое внимание |
|
e.g. |
exempli gratia |
например |
|
v.v |
vice versa |
наоборот |
|
a.m. |
ante meridiem |
до полудня |
-
Match Latin and English equivalents. Should go away!!!
i.e for example
e.g. B.C. (before Christ)
etc. that is
at al. and so on
A.C. and the others
-
Many English words and word parts can be traced back to Latin. The
following table lists some common Latin roots.
|
Latin root |
Basic meaning |
Example words |
|
-dict- |
to say |
contradict, dictate, predict |
|
-duc- |
to lead, bring, take |
deduce, produce, reduce |
|
-gress- |
to walk |
digress, progress, transgress |
|
-ject- |
to throw |
project, reject, subject |
|
-pel- |
to drive |
compel, dispel, repel |
|
-pend- |
to hang |
depend, impend, pendulum |
|
-port- |
to carry |
export, report, support |
|
-scrib-, -script- |
to write |
describe, subscription, transcribe |
|
-tract- |
to pull, drag, draw |
attract, contract, extract |
|
-vert- |
to turn |
convert, divert, invert |
-
Read the most famous Latin sayings. Which one do you like most of all.
Comment on it.
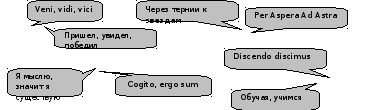
|
Unit 2. Progress Monitoring In this unit you have worked on the following vocabulary related to the topic “Ways of learning”
Tick (V) the points you are confident about and cross (X) the ones you need to revise. |
