- •О.И. Сафроненко, к.С.Петросян, с.Ю. Резникова learning to learn in english
- •Методическая записка
- •Contents
- •Unit 1 Learn How to Learn
- •What do you think?
- •Focus on Language
- •Focus on language
- •What do you think?
- •Keep learning? Keep earning!
- •Comprehension check
- •What do you think?
- •Unit 2 Study Smart, Not Hard
- •What do you think?
- •Focus on language
- •What do you think?
- •What are effective study habits?
- •Focus on language
- •Practice
- •Unit 3 Revise & Practise
- •Progress Test
- •Unit 1 Making the Choice of Your Life
- •What do you think?
- •Focus on Language
- •First degree courses in the uk
- •Comprehension check
- •What do you think?
- •Unit 2 Your Personal Science Odyssey
- •What do you think?
- •Comprehension check
- •Focus on Language
- •Practice
- •Unit 3 Revise & Practise
- •Game “Why physics or math, etc.?”
- •Progress Test
- •Unit 1 Secret of Success
- •What do you think?
- •Focus on language
- •Practice
- •Thinking about what we have found!
- •Comprehension check
- •Focus on language
- •“The World Wide Web: the battle for your mind at your fingertips”
- •Unit 2 Hunting for Treasures
- •Comprehension check
- •What do you think?
- •Focus on Language
- •Practice
- •Technology and Libraries
- •Comprehension check
- •What do you think?
- •Unit 3 Revise & Practise
- •Progress Test
- •Unit 1 Scientific Milestones
- •Metric system telescope compass thermometer microscope
- •Comprehension check
- •Focus on Language
- •Practice
- •Practice
- •Invention /discovery
- •Unexpected Discoveries
- •Comprehension check
- •What do you think?
- •Focus on language
- •Practice
- •What do you think?
- •Unit 2 Scientific Revolution
- •Breakthroughs of the 20th century
- •What do you think?
- •Focus on language
- •Verb Suffixes
- •Practice
- •What do you think?
- •Unit 3 Revise & Practise
- •Progress Test
- •Rules of the Lab
- •Unit 1 Global Issues
- •Comprehension check
- •Focus on language
- •Practice
- •Practice
- •What do you think?
- •Global Warming: Facts vs. Myths myths:
- •Comprehension check
- •Focus on language
- •Practice
- •Comprehension check
- •Focus on Language
- •Work in teams of 3. Make as many words as possible using the prefixes re-, dis-, over-, sub-, en-, up- . Compare as a class.
- •Practice
- •Unit 3 Revise & Practise
- •Progress Test
- •Unit 1 The 20th Century and Beyond
- •Science for the Twenty-First Century
- •Focus on language
- •Practice
- •As old as writing
- •What do you think?
- •Unit 2 Into the Future
- •What do you think?
- •Focus on the language
- •Practice
- •Practice
- •What do you think?
- •Unit 3 Revise & Practise
- •Progress Test
- •Unit 1 Job Opportunities for Students
- •Part-time Jobs vs. Holiday Jobs
- •Comprehension check
- •What do you think?
- •Focus on language
- •Practice
- •What do you think?
- •Focus on language
- •Unit 2 On the Job
- •What do you think?
- •Focus on language
- •Practice
- •What can I do with a Science degree?
- •What do you think?
- •Unit 3 Revise & Practise
- •Progress Test
- •Scripts Module 1 Unit 1 Five New Year's Resolutions for English Learners
- •Module 1 Unit 2
- •Module 2 Unit 1 a Look at Washington University
- •Module 2 Unit 1
- •Module 3 Unit 1
- •Module 3 Unit 2 Website of the Week — Universal Digital Library
- •Module 4 Unit 1
- •Module 4 Unit2 The Discoveries Behind This Year's Nobel Prizes for Science
- •Module 5 Unit 1 Cities Around the World Are 'Going Green'
- •Module 5 Unit 2 Electronic Waste
- •Is it illegal to dispose of computers in the trash?
- •Module 6 Unit 1 Scientists Receive National Medals of Science and Technology
- •Module 6 Unit 2
- •Module 7 Unit 1 Job Centre
- •Module 7 Unit 2
- •Interns Provide Free Labor, But Internships Are Not Always Free
- •Keys Module 1 Unit 1
- •Module 1 Unit 2
- •In the Realm of Science 1
- •Module 1 Unit 3
- •Module 2 Unit 1
- •Module 2 Unit 2
- •Module 2 Unit 3
- •Модуль 3 Unit 1
- •Module 3 Unit 2
- •Module 3 Unit 3
- •Module 4 Unit 1
- •Module 4 Unit 2
- •In the Realm of Science 2
- •In the Realm of Science 3
- •Module 4 Unit 3
- •Module 5 Unit 1
- •Module 5 Unit 2
- •Module 5 Unit 3
- •Module 6 Unit 1
- •In the Realm of Science 1
- •Module 6 Unit 2
- •Module 6 Unit 3
- •Module 7 Unit 1
- •Module 7 Unit 2
- •Module 7 Unit 3
- •List of materials used
- •Part-time Jobs vs. Holiday Jobs// Retrieved from e4s:co uk http://www.E4s.Co.Uk/docs/part-time-jobs.Htm
- •Internet recourses
What do you think?
-
Do you think ‘green’ initiatives will become popular all over the world? Why?/Why not?
-
Would you like to live in an eco-city?
-
Have you ever participated in any ‘green’ activity?
-
Do you think such initiatives can help to improve the community?
|
|
Speaking |
|
|---|---|---|
|
|
||
|
Tool box: Presenting another point of view Some of the people think that … Each of the interviewees believes that … Most of the people agree/disagree that … Hardly anybody/Nobody feels that … According to the majority of people … Two of ten interviewees say … 50% of people point out that… Very few people/All the people claim that … etc. |
|
Writing |
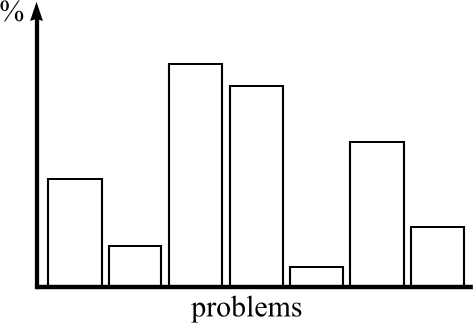
Complete the bar chart below marking each bar with the results of your interviews. Summarize your findings in a paragraph.
|
|
|
|
|
Reading |
|
|
-
Do you know what a greenhouse is? What for do we use it? What is the
Greenhouse effect and how is it related to global warming?
-
Work in groups. Brainstorm ideas about global warming: signs, causes and consequences. Discuss your ideas as a class.
-
Before you read the text match each word in A with its definition in B.
|
A |
B |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
-
There are some well-known facts as well as myths about the problem of global warming. Match each myth with the right fact below.
Global Warming: Facts vs. Myths myths:



FACTS:
1. Over millions of years, animals and plants lived, died and were compressed to form huge deposits of oil, gas and coal. In little more than 300 years, however, we have burned a large amount of this storehouse of carbon to supply energy. Today, the by-products of fossil fuel use - billions of tons of carbon (in the form of carbon dioxide), methane, and other greenhouse gases - form a blanket around the Earth, trapping heat from the sun, raising temperatures on the ground, and steadily
changing our climate.
2. The slow heating of the oceans creates a significant delay between the time when carbon dioxide and other greenhouse gases are emitted into the atmosphere and the moment when changes in temperature occur. This is one of the main reasons why we don't see changes in temperature at the same time as changes in greenhouse gas emissions. In addition, there are many other factors that affect year-to-year variation in the Earth's temperature such as volcanic eruptions, etc. Still, scientific evidence points clearly to anthropogenic (i.e. human-made) greenhouse gases as the main reason for climate change.
3. Carbon dioxide, a gas created by the burning of fossil fuels (like gasoline and coal), is the most important human-made greenhouse gas. Carbon dioxide from fossil fuel use is produced in huge quantities and can stay in the atmosphere for as long as 200 years. Thus we need to act now if we want to avoid the increasingly dangerous consequences of climate change in the future.
4. Before human activities began to dramatically increase carbon dioxide levels in the atmosphere, the amount of carbon dioxide emitted from natural sources closely matched the amount that was absorbed through natural processes, for example, through photosynthesis. Some carbon is later released back to the atmosphere. This balance has now been upset by human activities, which since the Industrial Revolution, have put twice as much carbon dioxide into the atmosphere than can be naturally removed by the oceans and forests. This has resulted in carbon dioxide levels higher than they have been in the last 420,000 years.
5. Carbon dioxide can act as a fertilizer for some plant species under some conditions. However, in nature, plant nutrients like nitrogen as well as water are often in short supply. Thus, even if plants have extra carbon dioxide available, their growth might be limited by a lack of water and nutrients. Finally, climate change itself could lead to decreased plant growth in many areas because of increased drought, flooding and heat waves.
(Adapted from IPCC, 2001. Climate Change 2001: The Scientific Basis)