
- •Preface
- •Content
- •Tissues
- •Nerve Tissue
- •Skin - Epidermis
- •Skin - Dermis
- •Skin - Glands
- •Subcutaneous Layer
- •Skeleton
- •Axial Skeleton
- •Cranium
- •Cranial Bones – Inferior Nasal Concha
- •Vertebral Column
- •Sacrum and Coccyx
- •Ribs
- •Sternum
- •Clavicle
- •Scapula
- •Humerus
- •Ulna
- •Radius
- •Metacarpals and Phalanges
- •Pelvis - Male
- •Femur
- •Tibia
- •Fibula
- •Tarsal Bones - Cuboid and Navicular
- •Phalanges
- •Patella
- •Skeletal Muscles
- •Transversospinales Muscles
- •Cervical Hypaxial Muscles
- •Thoracic and Abdominal Hypaxial Muscles
- •Shoulder Muscles - Rotator Cuff
- •Shoulder Muscles - Prime Movers
- •Anterior Brachial Muscles
- •Posterior Brachial Muscles
- •Posterior Thigh Muscles
- •Thigh Muscles
- •Lateral Leg Muscles
- •Posterior Leg Muscles
- •Spinal Nerves
- •Dorsal Rami
- •Intercostal Nerves
- •Cutaneous Nerves
- •Autonomic Nerves
- •Spinal Cord
- •Brain
- •Cerebrum
- •Cerebellum
- •Meninges
- •Hypothalamus
- •Pituitary Gland
- •Pineal Gland
- •Thymus
- •Pancreas
- •Ovaries
- •Testes
- •Blood
- •Heart
- •Lymphatics
- •Larynx
- •Lungs
- •Cast of Trachea and Bronchial Tree
- •Esophagus
- •Stomach
- •Pancreas
- •Large Intestine
- •Mesenteries
- •Omenta
- •Female Reproductive Organs
- •Ovary
- •Vagina
- •Ductus Deferens and Spermatic Cord
- •Penis
- •Index
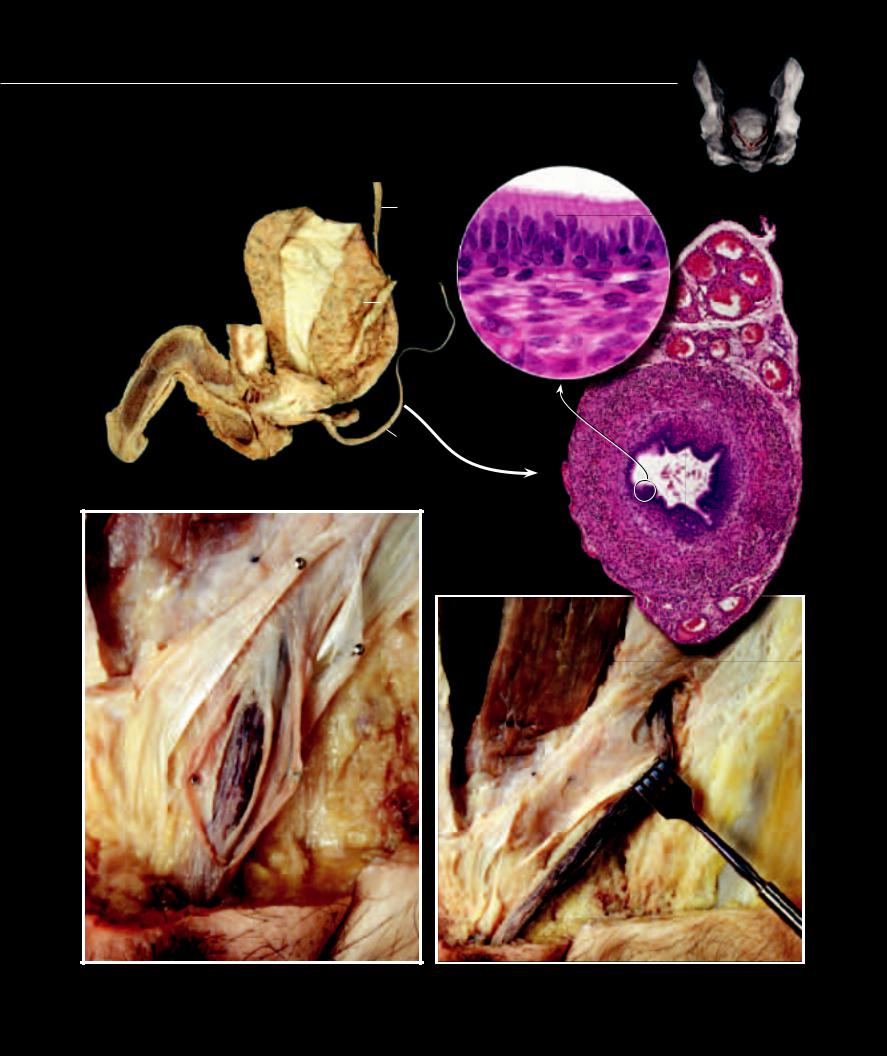
Ductus Deferens and Spermatic Cord
The ductus (vas) deferens is the muscular tube that transports sperm from the epididymis to the ejaculatory duct within the prostate gland. Peristaltic muscle contractions in the tube move the sperm. The ductus deferens accompanies the testicular vessels and nerves within a wrapping of fascia and muscle, called the spermatic cord. The cord extends from the testis to the superficial inguinal ring in the abdominal wall.
|
|
|
19 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2 |
7 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
19 |
|
|
3 |
7 |
|
|
|
|
|
||
15 |
|
|
|
|
|
18 |
|
|
|
7 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
14 |
|
|
|
|
7 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
16 |
|
|
|
|
|
17 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1 |
|
|
Dissection of male genital structures |
|
4 |
5 6 |
||
|
|
||||
Medial view
Photomicrograph of ductus deferens
30x, callout 400x
8
20
8 |
13 |
10
9
9
7
12
11
Dissection of spermatic cord exiting superficial inguinal ring |
Dissection of inguinal canal and spermatic cord |
Anterior view |
Anterior view |
330
1 |
Ductus deferens |
10 |
Internal spermatic fascia |
19 |
Ureter |
28 |
Psoas major muscle |
||
2 |
Pseudostratified columnar epithelium |
11 |
Superficial inguinal ring |
20 |
Rectus abdominis |
29 |
Iliacus muscle |
||
3 |
Lamina propria |
12 |
Inguinal canal |
21 |
Superior ramus of pubis (cut) |
30 |
Sacrum |
||
4 |
Inner longitudinal muscle layer |
13 |
Deep inguinal ring |
22 |
Inferior ramus of pubis (cut) |
31 |
Levator ani muscle |
||
5 |
Middle circular muscle layer |
14 |
Penis |
23 |
Body of pubis (cut) |
32 |
Sciatic nerve |
||
6 |
Outer longitudinal muscle layer |
15 |
Bladder |
24 |
Pudendal nerve and vessels |
33 |
Testis |
||
7 |
Testicular blood vessels |
16 |
Prostate gland |
25 |
Rectum (enlarged) |
34 |
Obturator internus muscle |
||
8 |
External spermatic fascia |
17 |
Seminal vesicle |
26 |
Internal iliac artery |
35 |
Tendinous arch of levator ani |
||
9 |
Cremaster fascia |
18 |
Pubic symphysis |
27 |
External iliac artery (cut) |
36 |
Ampulla of ductus deferens |
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
27 |
|
|
|
27 |
|
|
|
30 |
|
26 |
30 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
26 |
|
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
25 |
|
|
32 |
25 |
32 |
1 |
|
|
21 |
|
|
1 |
|
24 |
734
|
31 |
|
23 |
|
22 |
14 |
8 |
|
14 |
|
33 |
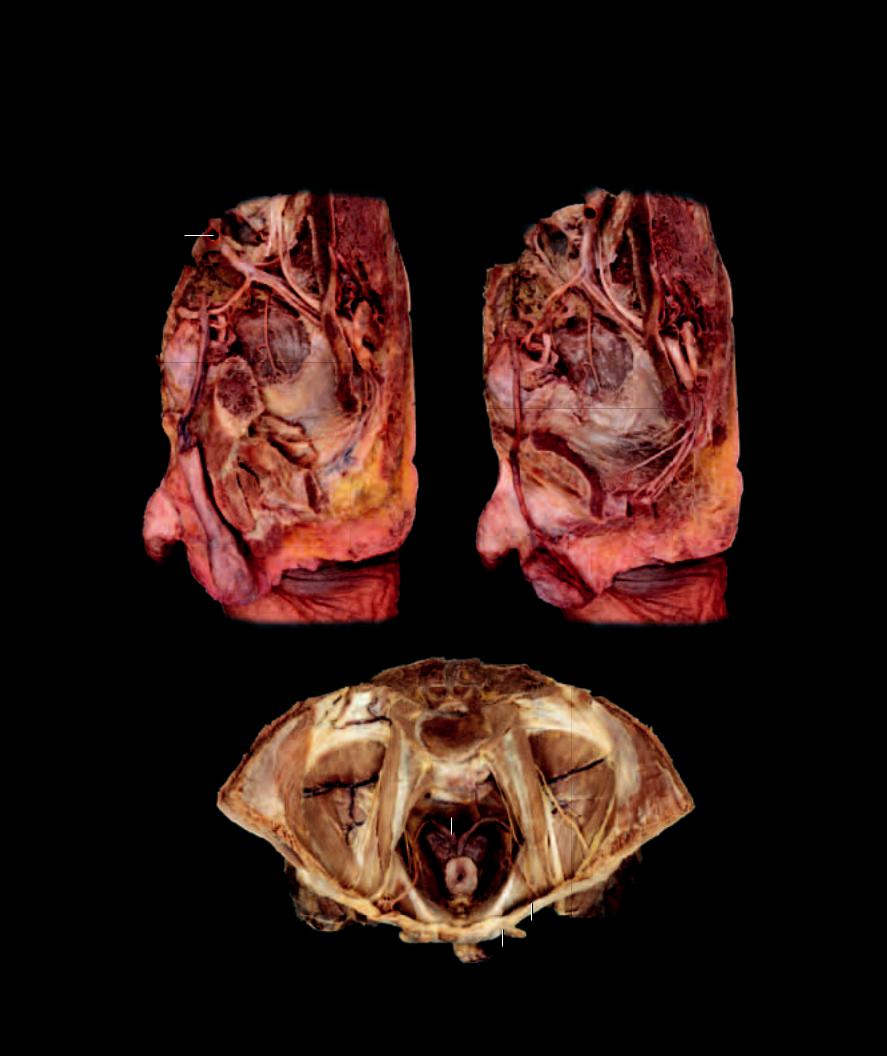
Lateral dissection of male pelvis |
Lateral disscetion of male pelvis |
Lateral view |
Lateral view |
28
29 |
36 |
17
15
31
35
13
14 11
Dissection of male pelvic cavity
Superior view, bladder removed
331

Associated with the male ducts of egress are three glands, often referred to as the accessory sex glands
of the male. The three named glands are the paired seminal glands (vesicles), the unpaired prostate gland, and the paired bulbourethral glands. They arise as epithelial outgrowths of terminal end of the male ducts of egress at the base of the bladder. They produce secretions that protect and nourish the sperm.
1 |
Seminal vesicle |
7 |
Bladder |
13 |
Crus of penis |
2 |
Prostate gland |
8 |
Ductus deferens |
14 |
Ilium |
3 |
Bulbourethral gland |
9 |
Ampulla of ductus deferens |
15 |
Ischial tuberosity |
4 |
Secretory epithelium |
10 |
Rectum |
16 |
Obturator internus muscle |
5 |
Trabecula |
11 |
Pubic symphysis |
17 |
Levator ani muscle |
6 |
Blood vessel |
12 |
Bulb of penis |
18 |
Deep transverse perineal muscle |
5 |
6 |
6 |
14 |
5
4
4
Photomicrograph of seminal vesicle
50x
7
9
1
2 |
10 |
11
3
13
12
Parasagittal section revealing prostate and bulbourethral glands
7
8
16 1
9
17
2
15
18
Dissection of pelvic region
Posterior view
4
4
6
Photomicrograph of prostate gland
Medial view |
200x |
332
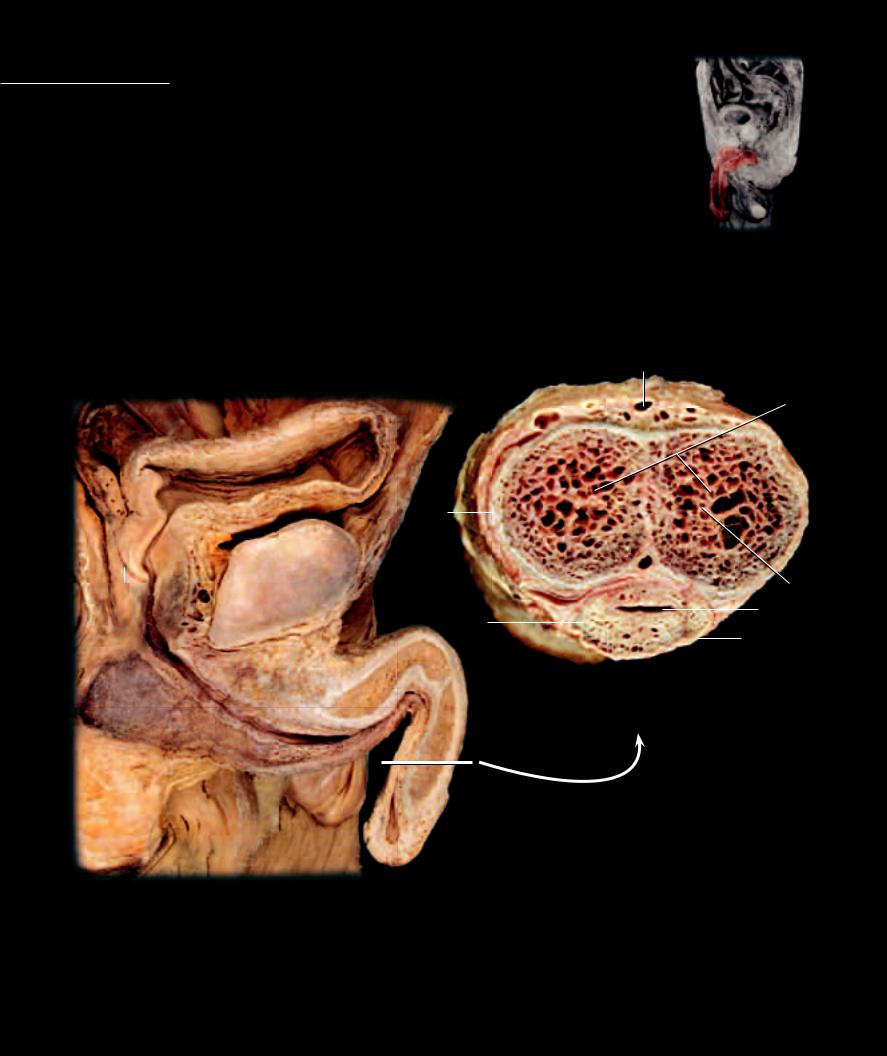
Penis The penis is the intromittent organ of the male external genitalia through which the long urethra, in comparison to the female, courses as it transports both urine and semen from the male body. Along with the urethra, the penis consists of three masses of erectile tis-
sue. On the dorsal aspect of the body of the penis are the paired corpora cavernosae. These erectile tissue bodies are the principal tissues of penile erection. At the base of the penis each corpus cavernosum extends laterally to form the crura of the penis. Each crus attaches to the inferior pubic ramus. On the ventral aspect of the penis is the slender unpaired corpus spongiosum, which surrounds the spongy urethra. The corpus spongiosum expands distally as the glans penis, which forms the expanded tip of the penis. It expands proximally to form the bulb of the penis in the perineum beneath the prostate gland. The glans is covered by a hood of skin, the prepuce, which can be removed via circumcision.
1 |
Glans penis |
7 |
Deep dorsal vein |
13 |
Ampula of ductus deferens |
2 |
Corpus cavernosum penis |
8 |
Tunica albuginea of corpus spongiosum |
14 |
Pubic symphysis |
3 |
Corpus spongiosum penis |
9 |
Tunica albuginea of corpus cavernosum |
15 |
Testis |
4 |
Crus of penis |
10 |
Deep (cavernous) artery of penis |
16 |
Ejaculatory duct |
5 |
Bulb of penis |
11 |
Intermediate (membranous) urethra |
17 |
Bladder |
6 |
Spongy urethra |
12 |
Prostatic urethra |
18 |
Suspensory ligament of penis |
7
2
13
|
|
12 |
14 |
|
9 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
16 |
|
|
10 |
||||||||||
|
|
|
|||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
6 |
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
11 |
18 |
|
3 |
|
|
|
|
|
8 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Transverse section of penis |
|||||
5 |
|
4 |
|
|
|
|
|
Superior view |
|||||
|
|
|
6 |
3 |
2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
3 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
15 6
1
Sagittal section of penis in situ
Medial view
333
This page intentionally left blank
