
- •Preface
- •Content
- •Tissues
- •Nerve Tissue
- •Skin - Epidermis
- •Skin - Dermis
- •Skin - Glands
- •Subcutaneous Layer
- •Skeleton
- •Axial Skeleton
- •Cranium
- •Cranial Bones – Inferior Nasal Concha
- •Vertebral Column
- •Sacrum and Coccyx
- •Ribs
- •Sternum
- •Clavicle
- •Scapula
- •Humerus
- •Ulna
- •Radius
- •Metacarpals and Phalanges
- •Pelvis - Male
- •Femur
- •Tibia
- •Fibula
- •Tarsal Bones - Cuboid and Navicular
- •Phalanges
- •Patella
- •Skeletal Muscles
- •Transversospinales Muscles
- •Cervical Hypaxial Muscles
- •Thoracic and Abdominal Hypaxial Muscles
- •Shoulder Muscles - Rotator Cuff
- •Shoulder Muscles - Prime Movers
- •Anterior Brachial Muscles
- •Posterior Brachial Muscles
- •Posterior Thigh Muscles
- •Thigh Muscles
- •Lateral Leg Muscles
- •Posterior Leg Muscles
- •Spinal Nerves
- •Dorsal Rami
- •Intercostal Nerves
- •Cutaneous Nerves
- •Autonomic Nerves
- •Spinal Cord
- •Brain
- •Cerebrum
- •Cerebellum
- •Meninges
- •Hypothalamus
- •Pituitary Gland
- •Pineal Gland
- •Thymus
- •Pancreas
- •Ovaries
- •Testes
- •Blood
- •Heart
- •Lymphatics
- •Larynx
- •Lungs
- •Cast of Trachea and Bronchial Tree
- •Esophagus
- •Stomach
- •Pancreas
- •Large Intestine
- •Mesenteries
- •Omenta
- •Female Reproductive Organs
- •Ovary
- •Vagina
- •Ductus Deferens and Spermatic Cord
- •Penis
- •Index
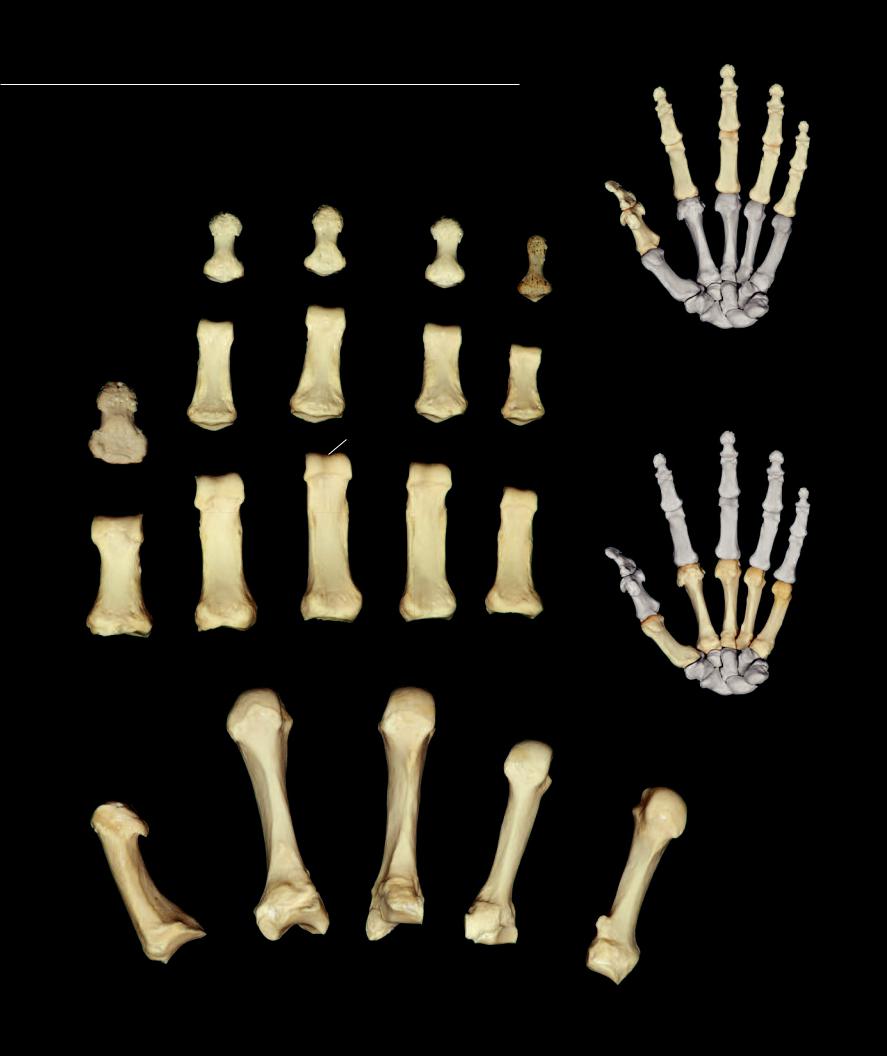
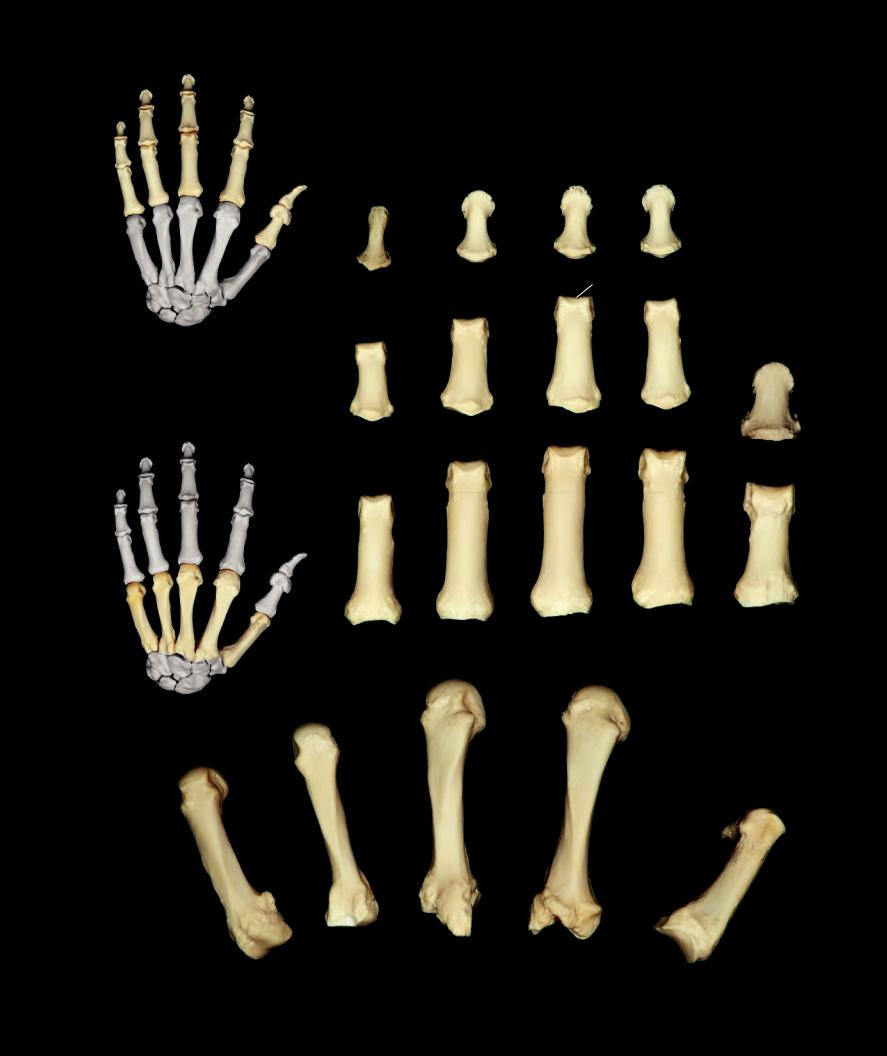
Metacarpals and Phalanges
The fi ve digital rays of the hand consist of a series of four bones, except in the thumb where there are only three bones, that decrease in length from proximal to distal. Forming the skeleton of the palmar region of the hand are the stout metacarpal bones. Note their saddle-like bases and rounded heads. The anterior-posterior fl attened phalanges project into the proper portion of the fingers and thumb from the metacarpal bones.
9 |
9 |
9 |
|
|
|
|
6 |
9 |
5
7
6
9
5
8
6
5
Left phalanges
Anterior view, thumb to left
|
3 |
|
3 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
3 |
|
|
2 |
3 |
3 |
|
2 |
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2 |
2 |
|
|
2 |
|
|
|
1 |
1
1
4
1
1
Left metacarpal bones, numbered I to V from lateral to medial
Anterior view, thumb to left
100
1 |
Base of metacarpal |
5 |
Base of phalanx |
2 |
Shaft or body of metacarpal |
6 |
Shaft or body of phalanx |
3 |
Head of metacarpal |
7 |
Head of phalanx |
4 |
Styloid process of third metacarpal |
8 |
Trochlea of phalanx |
|
|
9 |
Tuberosity of distal phalanx |
6
5
8
7
6
5
7
6
5
Left phalanges
Posterior view, thumb to right
3
3
3
3
|
2 |
|
2 |
2 |
3 |
|
|
|
2 |
|
|
|
|
2 |
1 |
1 |
|
1 |
|
|
1 |
4 |
1 |
|
Left metacarpal bones, numbered I to V from lateral to medial
Posterior view, thumb to right
101
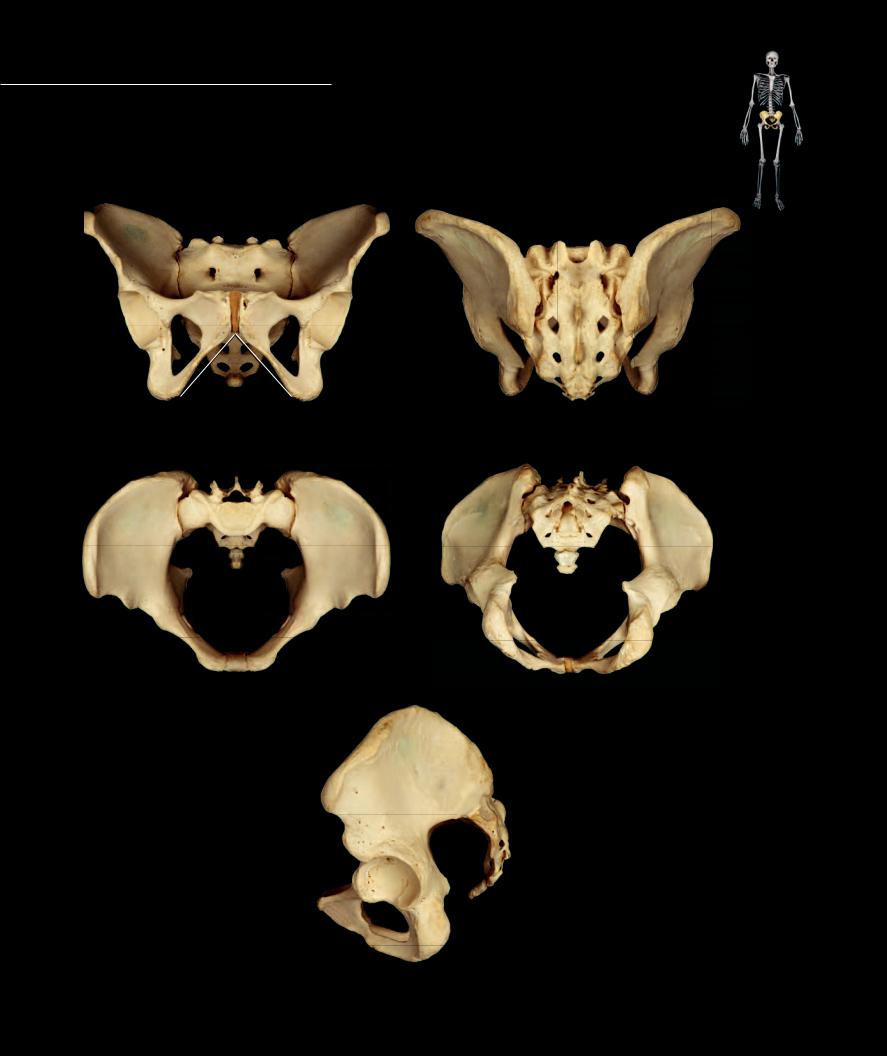
The characteristic features of the female pelvis are related to the role of the female pelvis in childbirth. While there are numerous diagnostic features that help distinguish a female pelvis, some of
the most obvious are those that increase the diameter of the pelvic outlet. For example, note the wider pubic angle (1) and greater sciatic notch (2) of the female pelvis.
1
3
Female pelvis |
Female pelvis |
Anterior view, superior to top |
Posterior view, superior to top |
Female pelvis |
|
Female pelvis |
Superior view, anterior to bottom |
Inferior view, anterior to bottom |
|
2
Female pelvis
Lateral view, anterior to left
102

Pelvis - Male The male pelvis tends to have a more narrow profi le than the pelvis of the female. Compare the diameter of the outlet, the angle of the pubic arch, and the width of the
greater sciatic notch with those of the female pelvis. Also, note the stout, thick ishiopubic ramus (3) of the male compared to the slender ischiopubic ramus of the female pelvis.
1
3
Male pelvis |
Male pelvis |
Anterior view, superior to top |
Posterior view, superior to top |
Male pelvis |
Male pelvis |
|
Superior view, anterior to bottom |
||
Inferior view, anterior to bottom |
||
|
2
Male pelvis
Lateral view, anterior to left
103
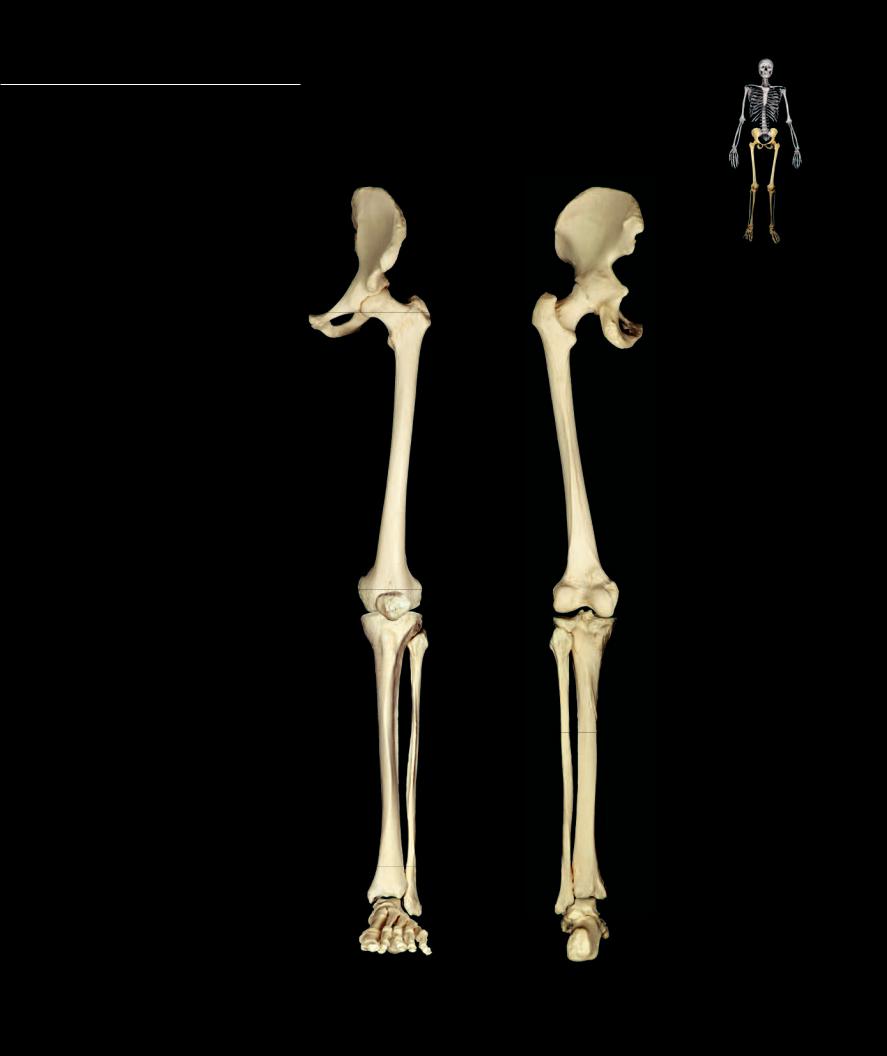
Each inferior appendage consists of 31 bones. The broad base of the inferior limb is the pelvic girdle. This girdle is the strong fusion of three bones, the ilium, ischium, and pubis, to form the os coxae or
hip bone. The os coxae is fi rmly anchored to the sacrum via strong ligaments and a synovial joint. Distal to the girdle is the free part of the lower limb. The bony framework of the thigh is the femur with the sesamoid patella at its distal end. Distal to the femur, the tibia and fi bula form the skeleton of the crus or leg. The distalmost region of the inferior limb is the foot consisting of seven tarsal bones, fi ve metatarsal bones, and fourteen phalanges.
1 |
Os coxae or hip bone |
|
|
2 |
Femur |
1 |
1 |
3 |
Patella |
|
|
|
|
||
4 |
Tibia |
|
|
5 |
Fibula |
|
|
6 |
Tarsal bones |
|
|
7 |
Metatarsal bones |
|
|
8 |
Phalanges |
|
|
2 |
2 |
3
5
5
4 |
4 |
|
7 |
6 |
|
|
|
8 |
Left lower limb |
Left lower limb |
|
Anterior view, lateral to right |
||
Posterior view, lateral to left |
||
|
104

Each os coxae forms from three separate bony elements that fuse during development at their site of union within the acetabulum. The three bony elements are the ilium, ischium, and pubis. This strong girdle of bone unites the inferior limb to the axial skeleton
and transfers the forces of locomotion from the inferior limb to the vertebral column. Each os coxae articulates with three bones — the femur, sacrum, and opposite os coxae. The photo on this page depicts the three bones of the os coxae — the ilium (green), the ischium (blue), and the pubis (red). Landmarks that are shared by the bones are depicted on this image. The following two pages show all the landmarks of the individual bones of the os coxae.
1 Acetabulum
2 Acetabular notch
3 Lunate surface
4 Ischiopubic ramus
5 Obturator foramen
6 Greater sciatic notch
3
1
6
2
5
4
Left os coxae showing individual bones
Lateral view, anterior to left
105

Os Coxae |
1 |
Body of ilium |
8 |
Inner lip of crest |
15 |
Anterior gluteal line |
|
Ilium |
7 |
Intermediate zone of crest |
14 |
Iliac fossa |
|
|
2 |
Supra-acetabular groove |
9 |
Tuberculum of crest |
16 |
Posterior gluteal line |
|
3 |
Ala or wing |
10 |
Anterior superior iliac spine |
17 |
Inferior gluteal line |
|
4 |
Arcuate line |
11 |
Anterior inferior iliac spine |
18 |
Auricular surface |
|
5 |
Iliac crest |
12 |
Posterior superior iliac spine |
19 |
Iliac tuberosity |
|
6 |
Outer lip of crest |
13 |
Posterior inferior iliac spine |
|
|
5
3
19 |
8 |
7 |
|
6 |
|
14
10
|
|
11 |
5 |
|
|
|
4 |
|
1 |
|
|
|
|
3 |
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
9 |
|
|
|
|
|
15 |
|
28 |
29 |
|
|
|
16 |
|
|
|
|
||
|
26 |
|
|
|
|
|
33 |
|
|
|
|
|
25 |
|
|
|
|
|
32 |
|
|
|
12 |
|
21 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Left os coxae |
1 |
13 |
|
|
Anterior view, lateral to right |
|
|
||
28
|
29 |
23 |
25 |
31 |
33
32
21
22
Left os coxae
Posterior view, lateral to right
106

Ischium |
Pubis |
30 |
Pecten pubis or pectineal line |
||
20 |
Body of ischium |
25 |
Body of pubis |
31 |
Obturator groove |
21 |
Ischial ramus |
26 |
Pubic tubercle |
32 |
Inferior pubic ramus |
22 |
Ischial tuberosity |
27 |
Symphysial surface |
33 |
Obturator foramen |
23 |
Ischial spine |
28 |
Pubic crest |
|
|
24 |
Lesser sciatic notch |
29 |
Superior pubic ramus |
|
|
|
5 |
|
|
|
3 |
|
|
|
9 |
|
|
|
15 |
|
|
|
|
16 |
|
10 |
|
|
|
|
17 |
12 |
|
|
|
13 |
|
|
1 |
|
|
|
2 |
|
|
|
|
5 |
|
|
|
3 |
|
|
20 |
23 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
24 |
|
26 |
25 |
19 |
10 |
|
33 |
14 |
|
|
|
||
|
32 |
|
|
|
22 |
18 |
|
|
21 |
|
|
|
12 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
11 |
|
Left os coxae |
13 |
1 |
|
4 |
Lateral view, anterior to left
30
23
31 29
24 20
33 |
|
|
26 |
|
|
||
|
27
21
Left os coxae
Medial view, anterior to right
107
