
- •Preface
- •Content
- •Tissues
- •Nerve Tissue
- •Skin - Epidermis
- •Skin - Dermis
- •Skin - Glands
- •Subcutaneous Layer
- •Skeleton
- •Axial Skeleton
- •Cranium
- •Cranial Bones – Inferior Nasal Concha
- •Vertebral Column
- •Sacrum and Coccyx
- •Ribs
- •Sternum
- •Clavicle
- •Scapula
- •Humerus
- •Ulna
- •Radius
- •Metacarpals and Phalanges
- •Pelvis - Male
- •Femur
- •Tibia
- •Fibula
- •Tarsal Bones - Cuboid and Navicular
- •Phalanges
- •Patella
- •Skeletal Muscles
- •Transversospinales Muscles
- •Cervical Hypaxial Muscles
- •Thoracic and Abdominal Hypaxial Muscles
- •Shoulder Muscles - Rotator Cuff
- •Shoulder Muscles - Prime Movers
- •Anterior Brachial Muscles
- •Posterior Brachial Muscles
- •Posterior Thigh Muscles
- •Thigh Muscles
- •Lateral Leg Muscles
- •Posterior Leg Muscles
- •Spinal Nerves
- •Dorsal Rami
- •Intercostal Nerves
- •Cutaneous Nerves
- •Autonomic Nerves
- •Spinal Cord
- •Brain
- •Cerebrum
- •Cerebellum
- •Meninges
- •Hypothalamus
- •Pituitary Gland
- •Pineal Gland
- •Thymus
- •Pancreas
- •Ovaries
- •Testes
- •Blood
- •Heart
- •Lymphatics
- •Larynx
- •Lungs
- •Cast of Trachea and Bronchial Tree
- •Esophagus
- •Stomach
- •Pancreas
- •Large Intestine
- •Mesenteries
- •Omenta
- •Female Reproductive Organs
- •Ovary
- •Vagina
- •Ductus Deferens and Spermatic Cord
- •Penis
- •Index
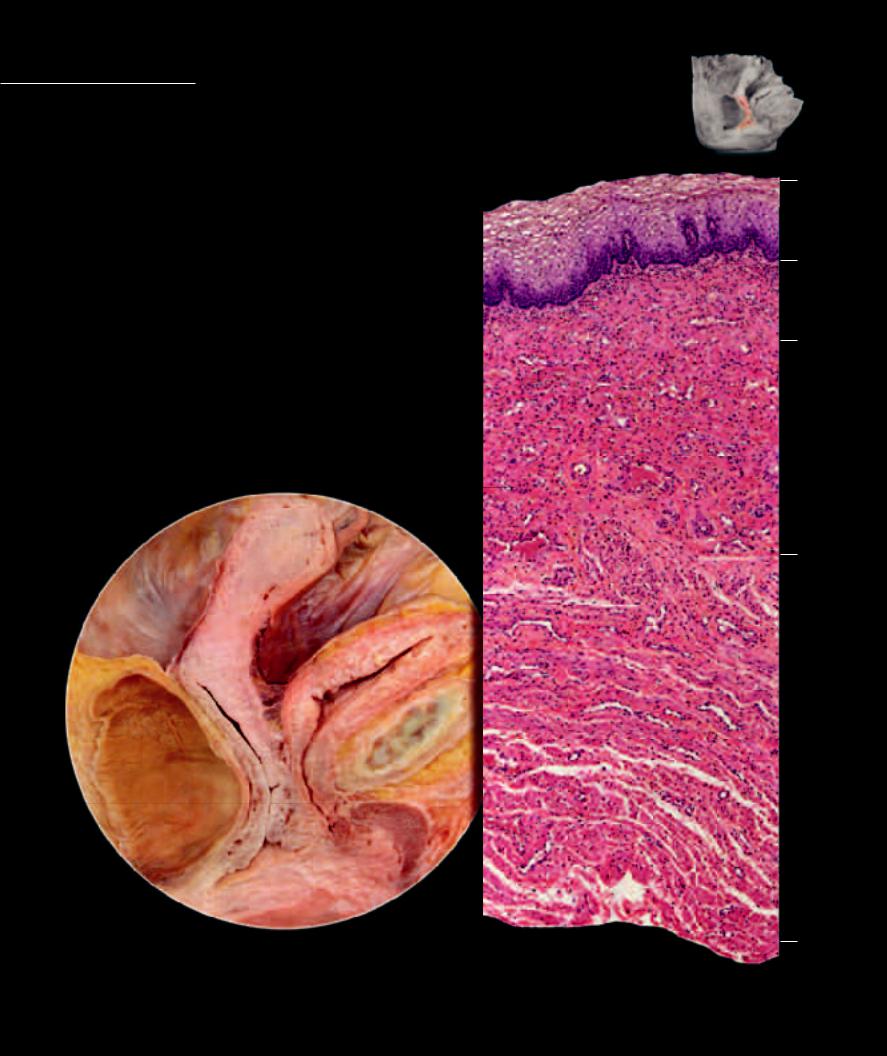
Vagina The vagina, from the Latin word meaning sheath, is the receptacle for the penis during sexual intercourse, the birth canal, and the outlet for the menstrual fl ow.
This muscular tube has a protective mucosal lining of stratifi ed squamous epithelium. Approximately 10 cm (4 inches) in length, it expands at its superior end to form a cuffl ike wrapping around the cervix of the uterus. The caverns of the cuffl ike superior end are called the fonices, and it is in this region that the sperm are deposited during intercourse.
1 Vagina
2 Nonkeratinized stratified squamous epithelium of the mucosa
3 Lamina propria of the mucosa
4 Inner circular layer of tunica muscularis
5 Outer longitudinal layer of tunica muscularis
6 Adventitia
7 Fundus of uterus
8 Body of uterus
9 Cervix of uterus
10Bladder
11Urethra
12Rectum
13Rectouterine pouch
14Vesicouterine pouch
15Pubic symphysis
16Clitoris
7
8
13
914
10
1
15
 11
11
12
16
Sagittal section showing vagina in situ
Medial view
Photomicrograph of vaginal wall
25x
2
3
4
5
6
326

Surrounding the openings of the vagina and ure-
thra in the perineum of the female are the external genital structures. Bounding the openings on either side are the folds of skin called the labia majora and labia minora. Between these folds is the common entry way to both urethra and vagina, the vestibule. Deep to the labial skin are the erectile tissues of the female, the clitoris and bulb of the vestibule. The greater vestibular glands empty their lubricating secretions into the vestibule and opening of the vagina.
1 |
Body of clitoris |
7 |
Ischiocavernosus muscle |
13 |
Gluteus maximus muscle |
2 |
Crura of clitoris |
8 |
Bulbospongiosus muscle |
14 |
Gluteus medius muscle |
3 |
Bulb of vestibule |
9 |
Ischioanal fossa |
15 |
Ischium |
4 |
Greater vestibular gland |
10 |
Perineal membrane |
16 |
Gracilis muscle |
5 |
Vestibule |
11 |
Deep perineal fascia |
17 |
Adductor muscles |
6 |
Transverse perenei superficialis |
12 |
Head of femur |
18 |
Femoral artery |
1
18
16
2
17
83
|
12 |
5 |
|
|
|
7 |
|
|
|
14 |
|
|
4 |
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
10
11
|
6 |
15 |
9 |
|
|
13 |
|
Perineal dissection revealing details of external genitalia
Inferior view
327
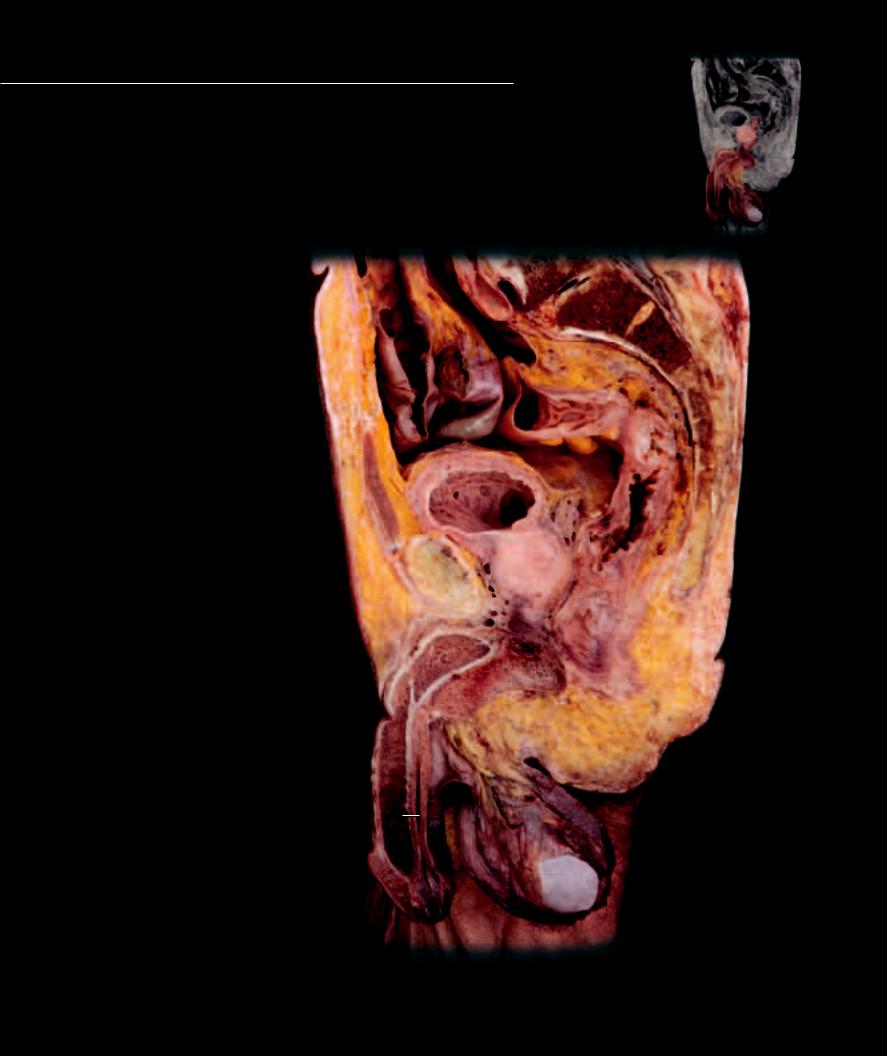
Like the female, there are both internal and external genital organs in the male.
The major difference between the sexes is the enlargement of the erectile tissue organs of the male and the descent of the gonads, the testes, from an internal position to a suspended position outside the body cavity. The male genital organs include the testes suspended in the scrotum. The testes consist of an extensive tubular system that gives rise to the sperm, which then pass through the tubular ducts of egress — the rete testis, epididymis, ductus deferens, ejaculatory duct, and urethra — to exit from the male body. Accessory glands of the male join the ducts of egress and add secretions to the sperm, and the erectile intromittant organ, the penis, introduces the sperm into the female system.
1 |
Scrotum |
18 |
2 |
Testis |
|
3 |
Glans penis |
|
4 |
Corpus cavernosum penis |
|
5 |
Corpus spongiosum penis |
17 |
6 |
Bulb of penis |
|
7 |
Spongy urethra |
|
8 |
Crus of penis |
|
9 |
Bulbourethral gland |
16 |
10Prostate gland
11Seminal vesicle
12Bladder
13Pubic symphysis
14 |
Rectus abdominis |
14 |
|
15 |
Rectum |
|
12 |
16 |
Sigmoid colon |
|
11 |
17 |
Small intestine |
|
|
|
|
||
18 |
Sacrum |
|
15 |
|
|
13 |
10 |
9
8
6
5
4
7
1
2
3
Parasagittal section of male pelvis
Medial view
328
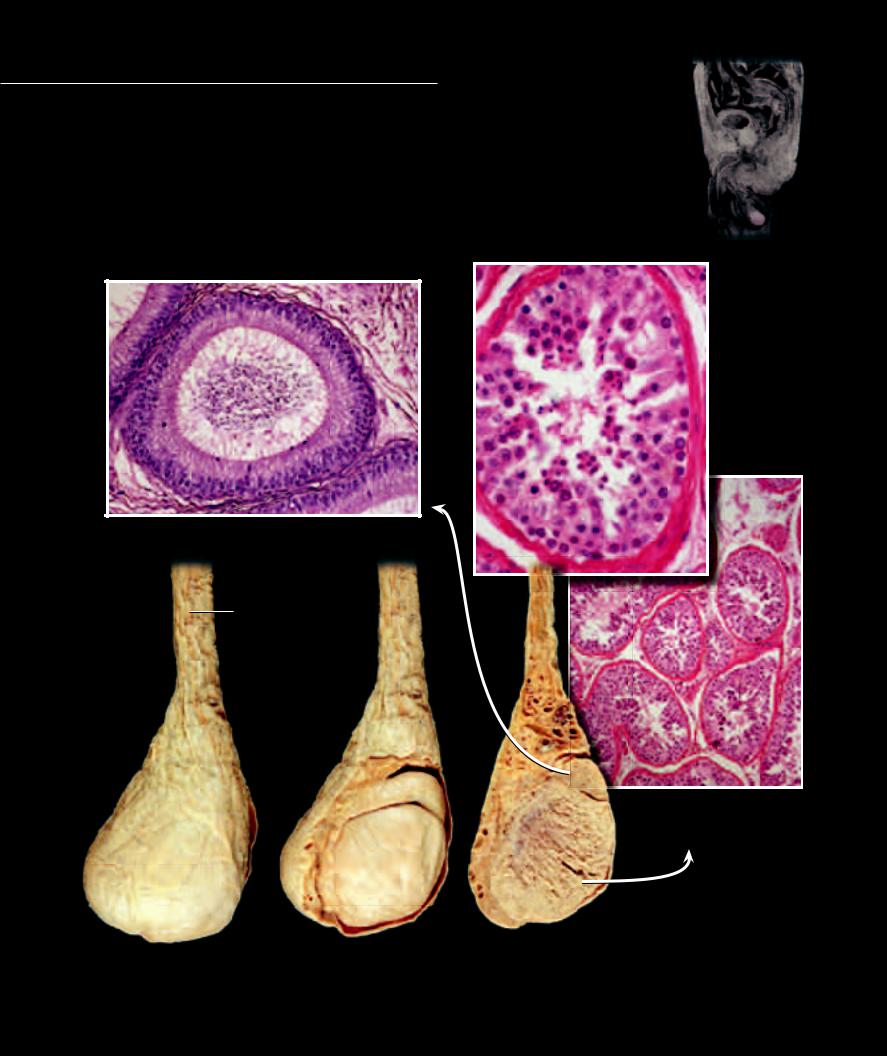
The testes are the site of sperm production in the male. Unlike the solid, cellular ovaries, the testes are collec-
tions of small, highly coiled tubes, the seminiferous tubules. Beginning at puberty the spermatogonia, sperm stem cells, in the walls of the seminiferous tubules begin meiosis and produce hundreds of millions of sperm cells daily. From the testis the sperm are moved into the epididymis where they are stored and reach maturity prior to passing into the ductus deferens.
1 |
Coelom of testis |
7 |
Rete testis |
13 |
Sertoli cell |
2 |
External spermatic fascia |
8 |
Spermatic cord |
14 |
Basement membrane |
3 |
Cremaster muscle |
9 |
Spermatogonium |
15 |
Interstitial cells (of Leydig) |
4 |
Tunica albuginea of testis |
10 |
Primary spermatocyte |
16 |
Sperm in lumen of epididymis |
5 |
Epididymis |
11 |
Secondary spermatocyte |
17 |
Mucosa of epididymis |
6 |
Seminiferous tubules |
12 |
Spermatid |
18 |
Stereocilia |
16
18
17
Photomicrograph of epididymis
200x
8
8
3
|
2 |
|
3 |
2 |
5 |
|
4
1
Testis and spermatic cord |
Testis and spermatic cord |
|
with fascia removed |
||
with fascial coverings |
||
Medial view |
||
Medial view |
||
|
12
11
10
9
8
5
7
6
14
13
13
15
15
Photomicrograph of seminiferous tubules
40x, callout 160x
Sagittal section of testis and spermatic cord
Medial view
329
