
- •Preface
- •Content
- •Tissues
- •Nerve Tissue
- •Skin - Epidermis
- •Skin - Dermis
- •Skin - Glands
- •Subcutaneous Layer
- •Skeleton
- •Axial Skeleton
- •Cranium
- •Cranial Bones – Inferior Nasal Concha
- •Vertebral Column
- •Sacrum and Coccyx
- •Ribs
- •Sternum
- •Clavicle
- •Scapula
- •Humerus
- •Ulna
- •Radius
- •Metacarpals and Phalanges
- •Pelvis - Male
- •Femur
- •Tibia
- •Fibula
- •Tarsal Bones - Cuboid and Navicular
- •Phalanges
- •Patella
- •Skeletal Muscles
- •Transversospinales Muscles
- •Cervical Hypaxial Muscles
- •Thoracic and Abdominal Hypaxial Muscles
- •Shoulder Muscles - Rotator Cuff
- •Shoulder Muscles - Prime Movers
- •Anterior Brachial Muscles
- •Posterior Brachial Muscles
- •Posterior Thigh Muscles
- •Thigh Muscles
- •Lateral Leg Muscles
- •Posterior Leg Muscles
- •Spinal Nerves
- •Dorsal Rami
- •Intercostal Nerves
- •Cutaneous Nerves
- •Autonomic Nerves
- •Spinal Cord
- •Brain
- •Cerebrum
- •Cerebellum
- •Meninges
- •Hypothalamus
- •Pituitary Gland
- •Pineal Gland
- •Thymus
- •Pancreas
- •Ovaries
- •Testes
- •Blood
- •Heart
- •Lymphatics
- •Larynx
- •Lungs
- •Cast of Trachea and Bronchial Tree
- •Esophagus
- •Stomach
- •Pancreas
- •Large Intestine
- •Mesenteries
- •Omenta
- •Female Reproductive Organs
- •Ovary
- •Vagina
- •Ductus Deferens and Spermatic Cord
- •Penis
- •Index
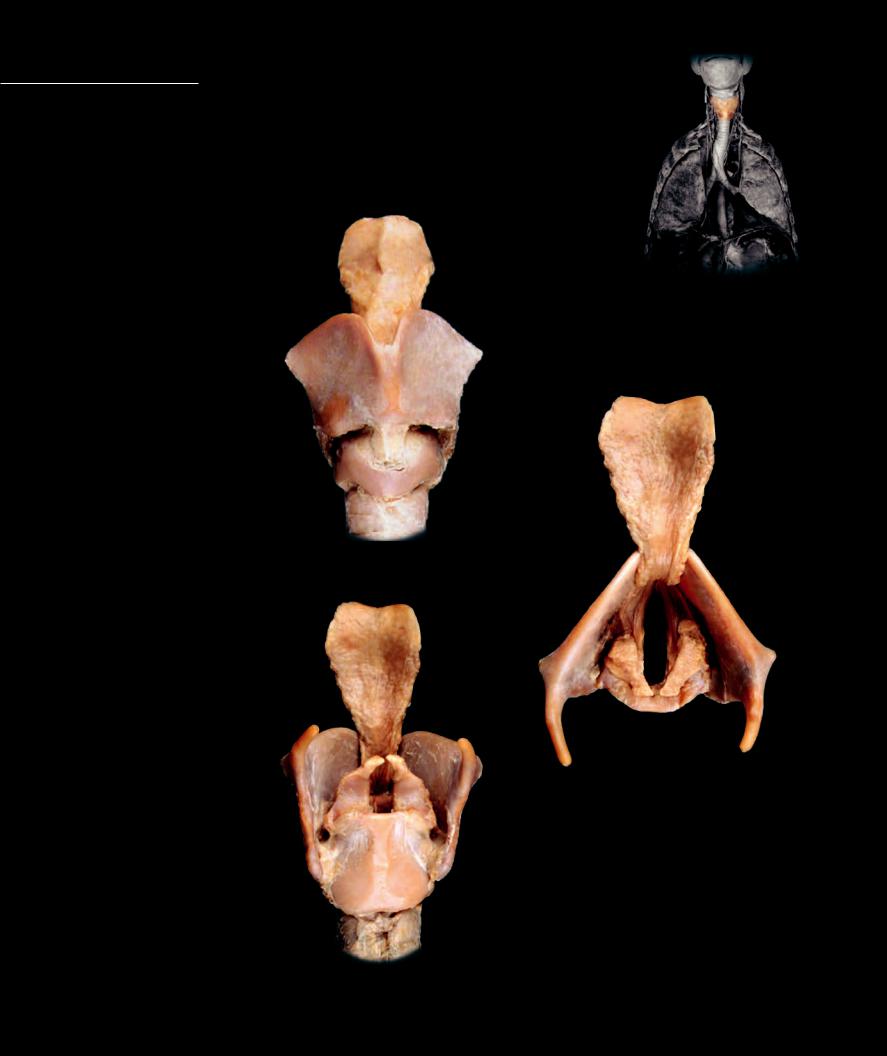
Larynx The entrance to the trachea is an expanded region called the larynx, or voice box. A series of large cartilages form the walls of this region. The soft tissue lining of the laryngeal cartilages folds into the larynx to form the vocal folds, fl aps of
tissue that lie across the opening of the larynx. Within the edges of the vocal folds are the vocal cords, two bands of elastic tissue that can be stretched and positioned in different shapes by laryngeal cartilages and muscles. As air is moved past the taut vocal cords, they vibrate to produce the many different sounds of speech. During swallowing, the vocal cords assume a function not related to speech; they are brought into tight apposition to each other to close off the rima glottidis, the entrance to the lower larynx and trachea.
|
|
|
1 |
1 |
Epiglottis |
|
|
2 |
Thyroid cartilage |
|
|
3 |
Thyroid tubercle (Adam’s apple) |
|
|
4 |
Superior cornu |
|
|
5 |
Inferior cornu |
|
|
6 |
Cricothyroid membrane |
|
3 |
7 |
Cricoid cartilage |
2 |
|
8 |
Arytenoid cartilage |
|
|
9 |
Corniculate cartilage |
|
|
10Trachea
11Vocal fold
12Vocal ligament
13 Rima glottidis |
6 |
7
10
Laryngeal cartilages
Anterior view
1
4
2 9
8
1
11
2
12
13 8
4
Laryngeal cartilages
Superior view
5
7
10
Laryngeal cartilages
Posterior view
294
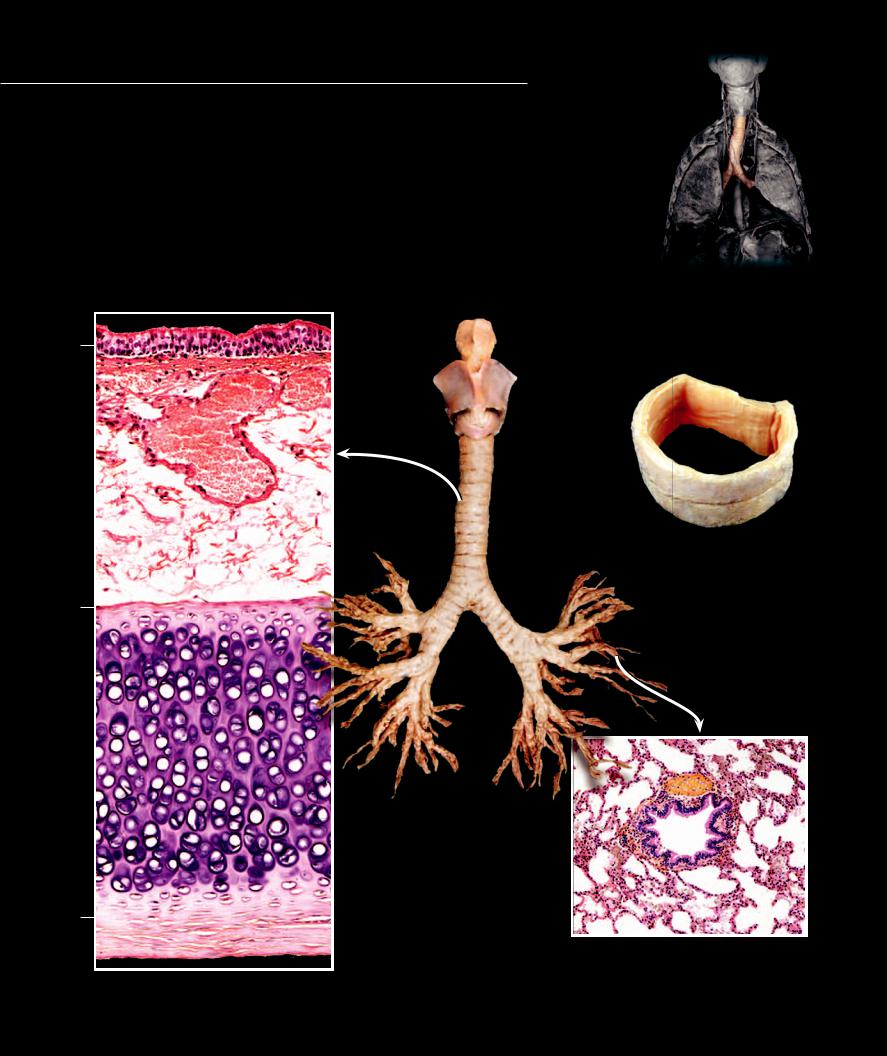
The trachea, “windpipe,” is the conduction tube that
transports the air to and from the lungs. It is reinforced by U-shaped cartilages.The trachea branches into two tubes called bronchi that enter the lungs. Each bronchus serves as the trunk of a highly branched, tree-like network of bronchial tubes that become progressively narrower, shorter, and more numerous as they spread throughout the tissues of the lung. These small tubes eventually terminate as the small, dead-end air sacs called alveoli, the principal site of gas exchange between air and blood.
1 |
Epiglottis |
8 |
Segmental (tertiary) bronchus |
14 |
Tela submucosa (areolar ct) |
2 |
Thyroid cartilage |
9 |
Bronchiole |
15 |
Tunica adventitia (dense ct) |
3 |
Cricoid cartilage |
10 |
Fibromuscular membrane |
16 |
Bronchiole cartilage (hyaline) |
4 |
Trachea |
11 |
Tracheal ring |
17 |
Alveolar spaces |
5 |
Right main (primary) bronchus |
12 |
Hyaline cartilage of tracheal ring |
18 |
Vein with red blood cells (rbc) |
6 |
Left main (primary) bronchus |
13 |
Tunica mucosa (pseudostratified) |
19 |
Pulmonary vein with rbcs |
7 |
Lobar (secondary) bronchus |
|
|
|
|
13 |
1 |
|
2
10
3
18
14
11
4
Section of trachea
Anterolateral view
|
8 |
5 |
|
9 |
|
8 |
7 |
6 |
|||
|
|||||
|
8 |
||||
|
|
|
|
||
|
7 |
|
|
7 |
|
|
|
|
|
8 |
98
7
8
8
12
9 |
9 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
16 |
|
|
17 |
|
Dissection of lower |
9 |
|
respiratory tract |
|
|
|
|
|
Anterior view |
|
19
17
15
|
Photomicrograph of alveoli and |
|
small bronchial tube |
Photomicrograph of tracheal wall |
100x |
100x |
295 |
|
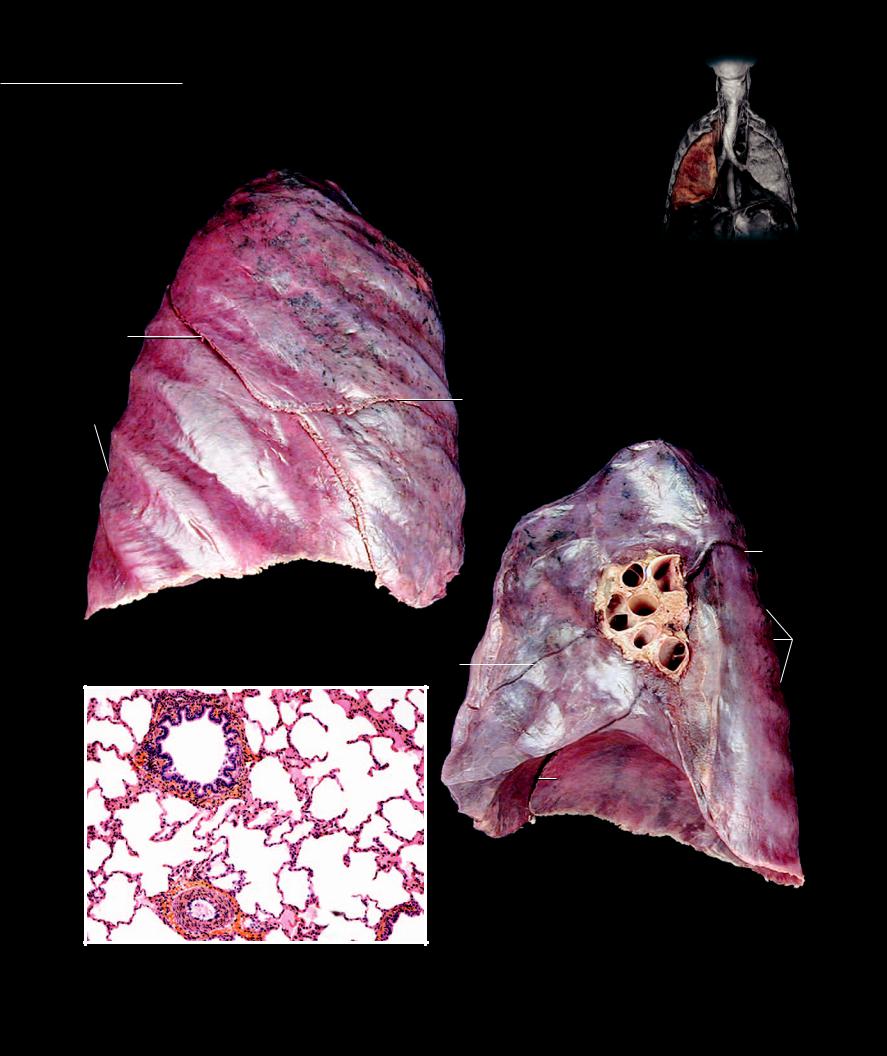
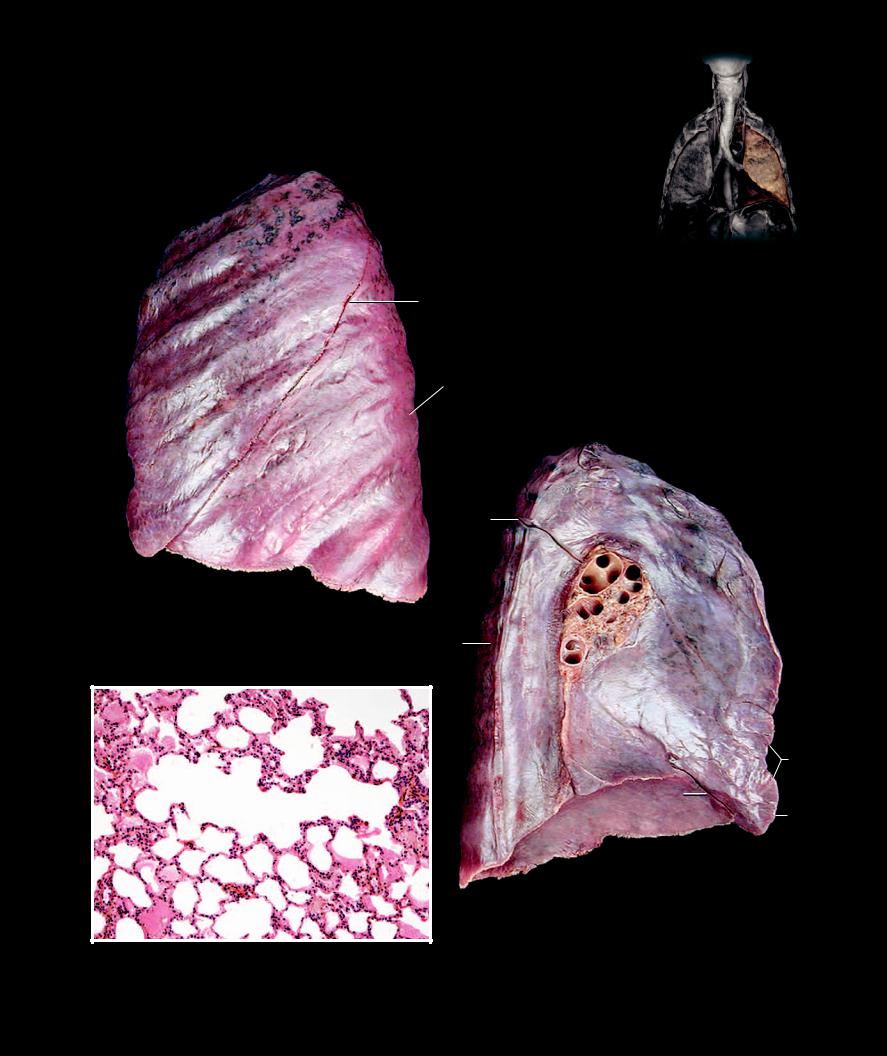
Lungs The lungs are the spongy, pyramidal-shaped organs that house the bronchial tree and the extensive pulmonary vascular network. Each lung is surrounded by a thin mesothelial covering, the visceral pleura, and sits on either side of
the heart within the thoracic cavity. The vascular and respiratory passageways enter each lung on its medial aspect at the hilum. The wide base of the lung sits on the diaphragm inferiorly and tapers to a narrow apex superiorly. The right lung has three lobes and the left lung two lobes.
1
2
5
6
10 
4
3
2 |
|
|
|
|
|
||
8 |
7 |
|
5 |
|
|
||
|
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||
9 |
14 |
|
|
|
|
||
Right lung |
7 |
|
|
|
10 |
||
|
|||||||
Lateral view, anterior to the right |
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|||
6 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
3 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
18 |
|
|
4 |
|
|
|
|
15
17
5 11
17
|
17 |
16 |
Right lung |
18 |
Medial view, anterior to the left |
Photomicrograph of lung tissue
100x
296
1 |
Apex |
8 |
Pulmonary artery |
14 |
Hilum |
2 |
Superior lobe |
9 |
Pulmonary vein |
15 |
Bronchiole |
3 |
Middle lobe |
10 |
Costal impression |
16 |
Small artery |
4 |
Inferior lobe |
11 |
Diaphragmatic surface |
17 |
Alveolar spaces |
5 |
Oblique fissure |
12 |
Aortic impression |
18 |
Blood vessels with rbcs |
6 |
Transverse fissure |
13 |
Cardiac notch |
19 |
Lingula |
7 |
Segmental (tertiary) bronchus |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1 |
|
|
2
5
 10
10
|
4 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
5 |
|
|
2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
8 |
9 |
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
7 |
7 |
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
Left lung |
14 |
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
Lateral view, anterior to the left |
4 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
12 |
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
17 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
18 |
18 |
|
|
|
|
5 |
|
|
13 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
11 |
|
|
19 |
|
|
17 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
17 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
18 |
|
|
|
Left lung |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Medial view, anterior to the right |
|
|
|
|
||
Photomicrograph of lung tissue
100x
297
