
- •Preface
- •Content
- •Tissues
- •Nerve Tissue
- •Skin - Epidermis
- •Skin - Dermis
- •Skin - Glands
- •Subcutaneous Layer
- •Skeleton
- •Axial Skeleton
- •Cranium
- •Cranial Bones – Inferior Nasal Concha
- •Vertebral Column
- •Sacrum and Coccyx
- •Ribs
- •Sternum
- •Clavicle
- •Scapula
- •Humerus
- •Ulna
- •Radius
- •Metacarpals and Phalanges
- •Pelvis - Male
- •Femur
- •Tibia
- •Fibula
- •Tarsal Bones - Cuboid and Navicular
- •Phalanges
- •Patella
- •Skeletal Muscles
- •Transversospinales Muscles
- •Cervical Hypaxial Muscles
- •Thoracic and Abdominal Hypaxial Muscles
- •Shoulder Muscles - Rotator Cuff
- •Shoulder Muscles - Prime Movers
- •Anterior Brachial Muscles
- •Posterior Brachial Muscles
- •Posterior Thigh Muscles
- •Thigh Muscles
- •Lateral Leg Muscles
- •Posterior Leg Muscles
- •Spinal Nerves
- •Dorsal Rami
- •Intercostal Nerves
- •Cutaneous Nerves
- •Autonomic Nerves
- •Spinal Cord
- •Brain
- •Cerebrum
- •Cerebellum
- •Meninges
- •Hypothalamus
- •Pituitary Gland
- •Pineal Gland
- •Thymus
- •Pancreas
- •Ovaries
- •Testes
- •Blood
- •Heart
- •Lymphatics
- •Larynx
- •Lungs
- •Cast of Trachea and Bronchial Tree
- •Esophagus
- •Stomach
- •Pancreas
- •Large Intestine
- •Mesenteries
- •Omenta
- •Female Reproductive Organs
- •Ovary
- •Vagina
- •Ductus Deferens and Spermatic Cord
- •Penis
- •Index
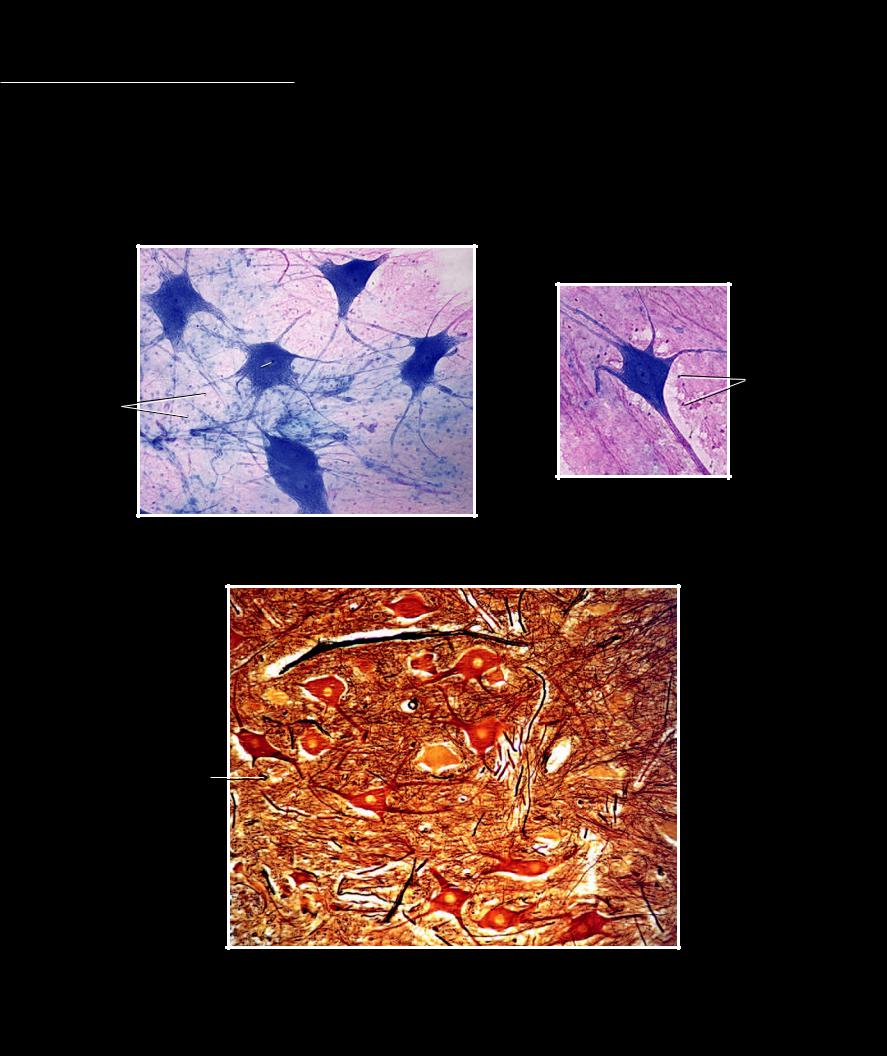
Nervous tissue forms the complex electrical computing system of the body. The cells that characterize nervous tissue are the branched, wire-like cells called neurons. Surrounding the neurons of the nervous tissue are the smaller, more numerous glial cells
that are involved in protecting, insulating, and nourishing the neurons. The neurons can be grouped together in long slender structures called nerves, or they can form the complex circuit boards we call the spinal cord and brain.
1 Nucleus of multipolar neuron
2 Cell body of multipolar neuron
3 Nucleus of glial cell
4 Axon
5 Dendrite
4
|
5 |
5 |
|
5 |
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
5 |
2 |
5 |
1 |
|
|
||
|
1 |
3 |
||
|
|
|||
|
|
|
||
3 |
|
5 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
4 |
2
Neuron
400x
Nerve tissue
Multipolar neuron smear, 400x
1
2 |
5 |
5
1
3 |
5 |
|
4
2
Nerve tissue
Section of ventral horn of spinal cord, 200x
16
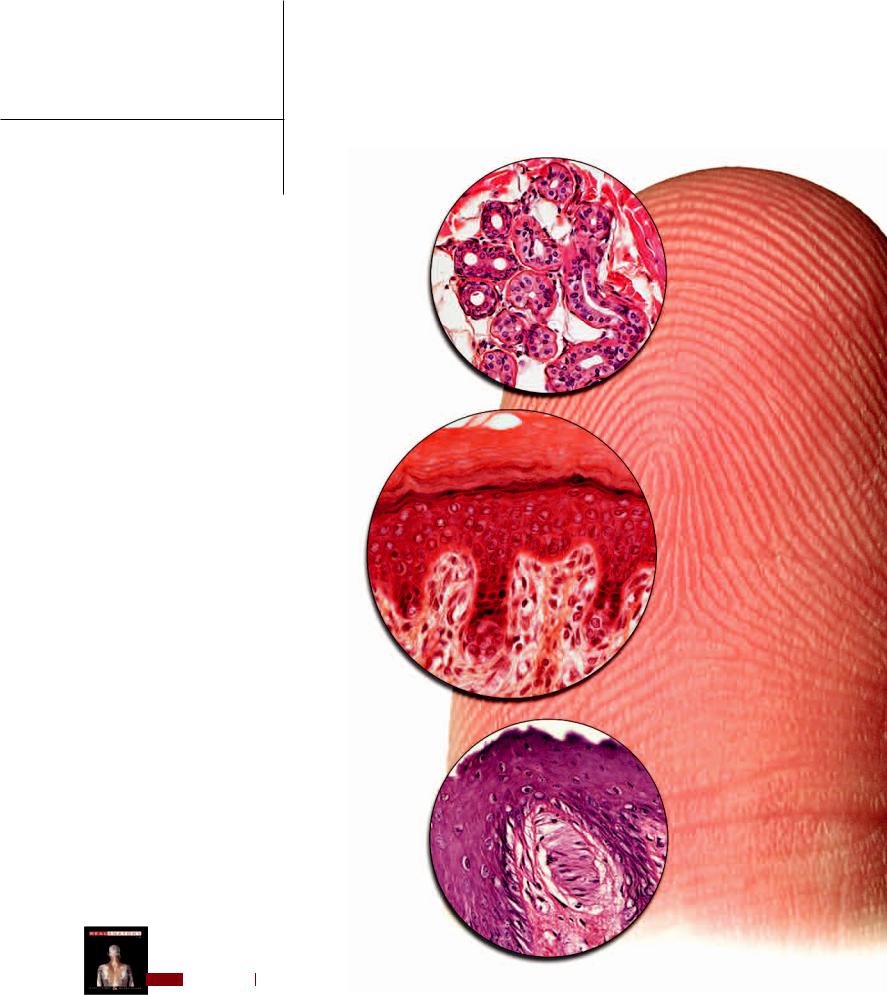
3 Integument
The integument forms the organ system that covers the body. From the Latin meaning to cover inward, the integument is an important system that performs a variety of functions that are essential to life. The outer layers of the integument called
the epidermis and dermis form the skin, which is an important protective layer. The skin protects the body in a number of ways. Its tough, outer-covering of dead cells protects the more delicate deeper layers from friction and abrasion. The pigment cells in the epidermis produce
melanin, a protective pigment that absorbs damaging ultraviolet radiation from the sun, to protect the rapidly dividing keratinocytes that make up the majority of the epidermal layer of the skin. The structure of the epidermal layer of the
skin and its secretions also protect the body from excessive water loss or gain. The large network of blood vessels and numerous sweat glands form
an evaporative cooling system that help to protect the body from overheating in warm conditions or during exercise. Additionally, the impenetrable skin and some of its special cells form a first line of defense against bacterial invasion.
These are just some of the functions of the integument. Other important functions are the following: it is a major surface for sensory perception to receive input or stimuli from the environment, it is an excretory surface to help rid
the body of metabolic wastes, it plays an important role in energy storage and metabolism, it provides an
important site for the production of vitamin D and various growth factors, and it plays a major role in sociosexual communication and identification. This chapter will depict the structural features of the integument that account for this wide variety of important functions.
Find more information about the integument in
R E A L A N AT O M Y
17
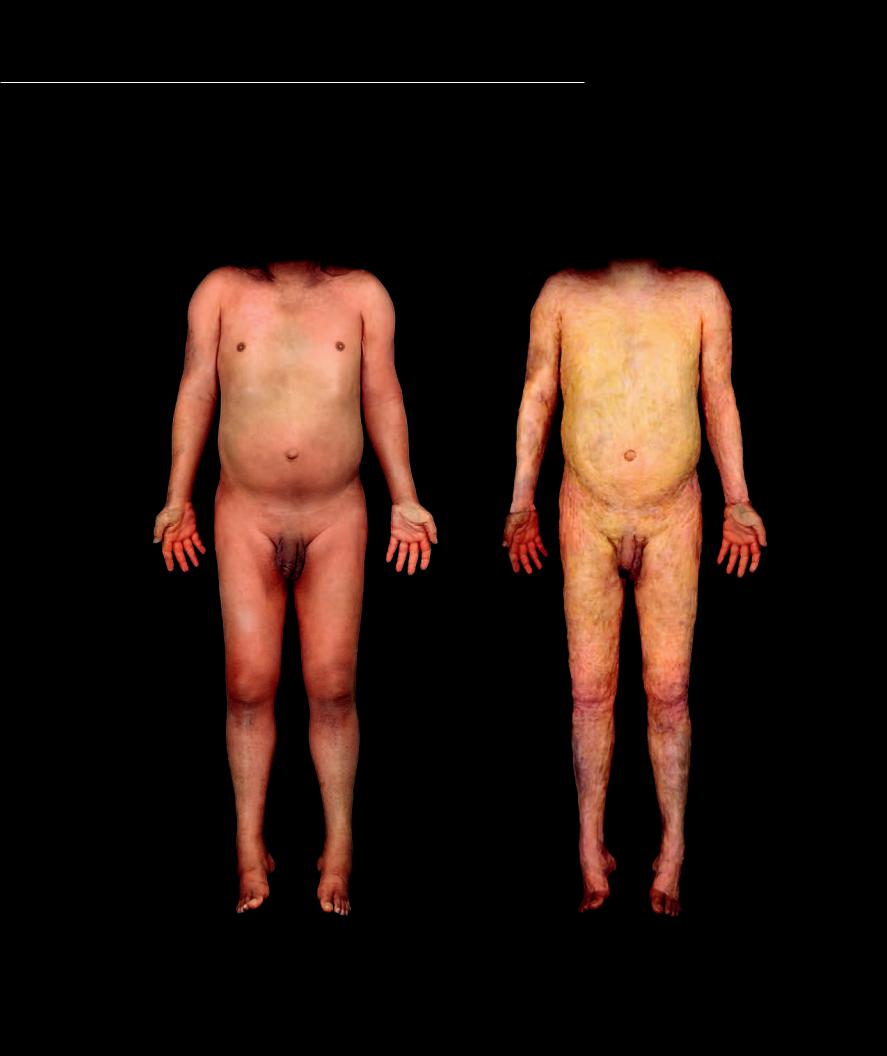
The integument consists of two major parts or layers of anatomy, the skin and the subcutaneous layer, or hy-
podermis. The cadaver and histology images on this and the facing page illustrate these two layers of anatomy. The skin, consisting of the superficial epidermis and the deeper dermis, structurally combines an epithelial tissue and connective tissue to form the body’s covering organ. The skin is an organ that produces hairs, various glands, fi nger and toe nails, and accounts for the majority of the functions of the integument. The subcutaneous layer is a variable layer that can consist of fat, fibrous connective tissue, loose connective tissue, and smooth muscle.
Epidermal layer of the skin |
Subcutaneous layer of the integument |
Anterior view |
Anterior view |
18
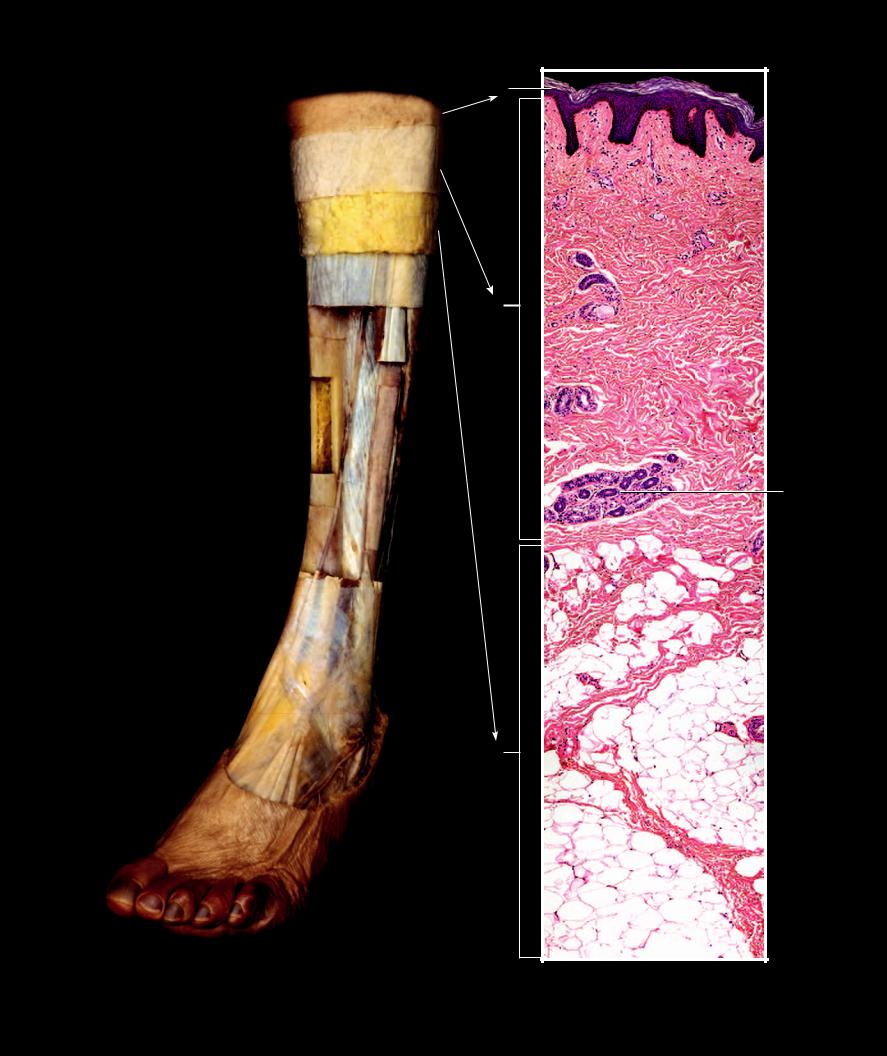
|
|
1 |
|
|
2 |
1 |
Epidermis |
|
2 |
Dermis |
|
3 |
Subcutaneous layer |
3 |
4 |
Fascia |
|
5 |
Periosteum |
|
6 |
Compact bone of tibia |
|
7 |
Fibula |
|
8 |
Medullary cavity |
4 |
9 |
Interosseous membrane |
|
10Tendon
11Muscle
12 |
Stratified squamous epithelium |
5 |
11 |
13 |
Dense irregular connective tissue |
|
10 |
14 |
Adipose tissue |
|
|
|
|
||
15 |
Retinaculum cutis |
|
5 |
16 |
Secretory coils of sweat gland |
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
8 |
|
|
|
|
6 |
|
|
|
7 |
9
5
5
4
1
Step dissection of leg showing layers of the integument
Anterolateral view
1
12
13
2
16
15
15
3
14
15
Integument
Section of integument, 100x
19
