
- •Preface
- •Content
- •Tissues
- •Nerve Tissue
- •Skin - Epidermis
- •Skin - Dermis
- •Skin - Glands
- •Subcutaneous Layer
- •Skeleton
- •Axial Skeleton
- •Cranium
- •Cranial Bones – Inferior Nasal Concha
- •Vertebral Column
- •Sacrum and Coccyx
- •Ribs
- •Sternum
- •Clavicle
- •Scapula
- •Humerus
- •Ulna
- •Radius
- •Metacarpals and Phalanges
- •Pelvis - Male
- •Femur
- •Tibia
- •Fibula
- •Tarsal Bones - Cuboid and Navicular
- •Phalanges
- •Patella
- •Skeletal Muscles
- •Transversospinales Muscles
- •Cervical Hypaxial Muscles
- •Thoracic and Abdominal Hypaxial Muscles
- •Shoulder Muscles - Rotator Cuff
- •Shoulder Muscles - Prime Movers
- •Anterior Brachial Muscles
- •Posterior Brachial Muscles
- •Posterior Thigh Muscles
- •Thigh Muscles
- •Lateral Leg Muscles
- •Posterior Leg Muscles
- •Spinal Nerves
- •Dorsal Rami
- •Intercostal Nerves
- •Cutaneous Nerves
- •Autonomic Nerves
- •Spinal Cord
- •Brain
- •Cerebrum
- •Cerebellum
- •Meninges
- •Hypothalamus
- •Pituitary Gland
- •Pineal Gland
- •Thymus
- •Pancreas
- •Ovaries
- •Testes
- •Blood
- •Heart
- •Lymphatics
- •Larynx
- •Lungs
- •Cast of Trachea and Bronchial Tree
- •Esophagus
- •Stomach
- •Pancreas
- •Large Intestine
- •Mesenteries
- •Omenta
- •Female Reproductive Organs
- •Ovary
- •Vagina
- •Ductus Deferens and Spermatic Cord
- •Penis
- •Index
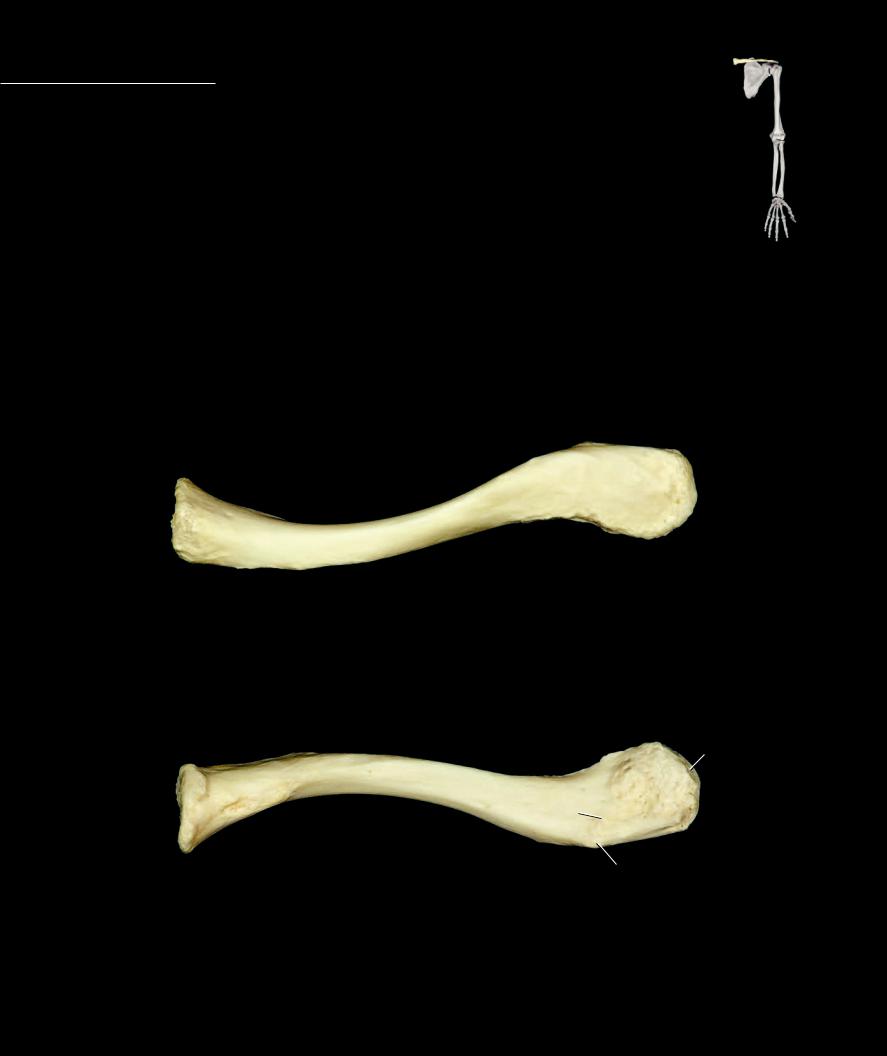
Clavicle The clavicle has an S-shaped appearance that can range from an almost straight, shallow S-curve shape to a deeper, more prominent S-curve shape. The curve at
the medial or sternal end of the bone is concave posteriorly, while the curve at the lateral or acromial end is concave anteriorly. This is one of the more variable bones of the skeleton. It is typically smooth and straight in females and rougher and more curved in males. The bone forms the ventral strut of the pectoral girdle that props the shoulder joint away from the rib cage. It is subcutaneous and easily palpable throughout its length. This combination of features makes it susceptible to fracture from falls onto the limb. The clavicle articulates with the three bones — the scapula, sternum, and first rib.
1 Sternal end
2 Sternal facet
3 Impression for costoclavicular ligament
4 Shaft or body
5 Subclavian groove
6 Acromial end
7 Acromial facet
8 Tuberosity for coracoclavicular ligament
9 Conoid tubercle
10 Trapezoid line
6
1
4
Left clavicle
Superior view, lateral to right
7
|
5 |
|
1 |
8 |
6 |
3 |
10 |
|
Left clavicle |
9 |
Inferior view, lateral to right
86

4 |
6 |
1
Left clavicle
Anterior view, lateral to right
6
4
1
9
Left clavicle
Posterior view, lateral to left
7 |
6 |
2 |
|
Left clavicle |
Left clavicle |
|
Lateral view, anterior to left |
||
Medial view, anterior to right |
||
|
87
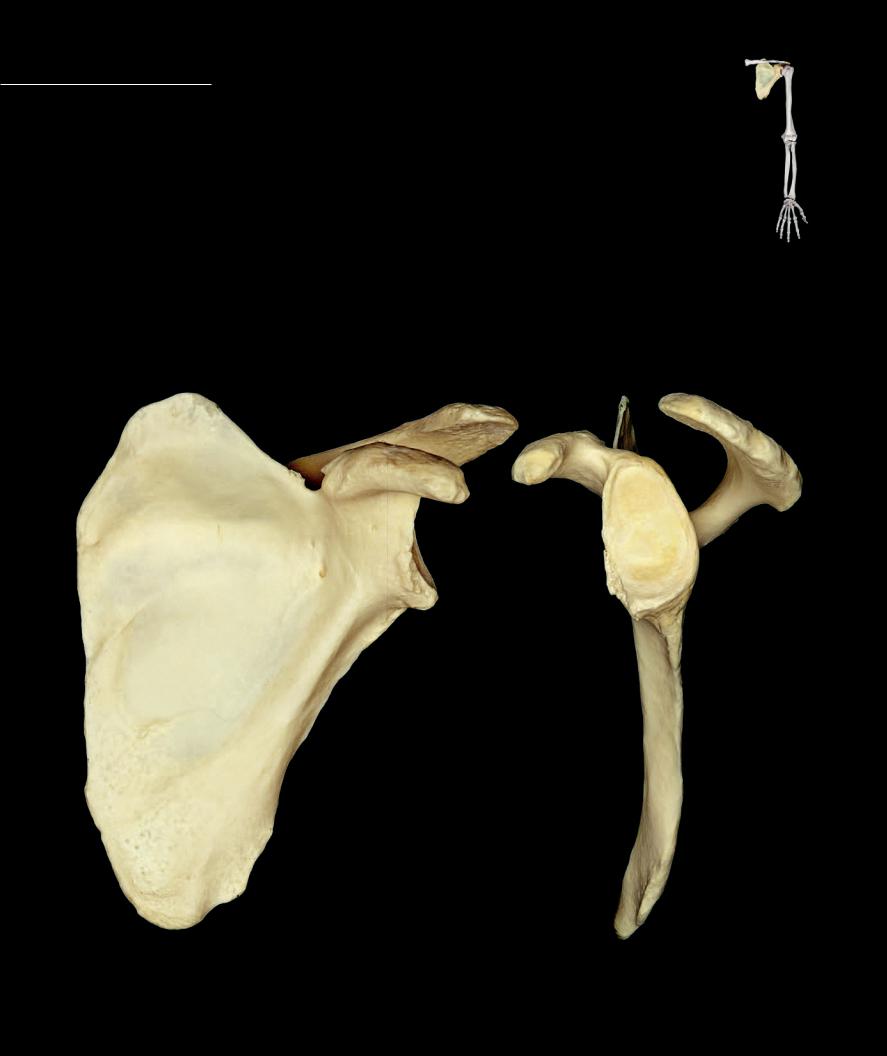
Scapula The scapula is a fl at, triangular bone with three prominent projections. The fl attened triangular portion of the bone, the body, spans from the second to the seventh rib and
consists of three borders (superior, lateral, and medial) and three angles (superior, inferior, and lateral) and is typically a very thin plate of bone. Its lateral angle is conspicuous as it forms the glenoid fossa, or shoulder socket that articulates with the head of the humerus. Its three prominent projections are the anterior projecting coracoid process, the posterior projecting ridge called the spine, and the fl at laterally projecting acromion, which forms the lateral expansion of the spine. The scapula articulates with two bones — the clavicle and the humerus.
1 |
Subscapular fossa |
11 |
Superior border |
2 |
Spine |
12 |
Suprascapular notch |
3 |
Deltoid tubercle |
13 |
Inferior angle |
4 |
Supraspinous fossa |
14 |
Superior angle |
5 |
Infraspinous fossa |
15 |
Glenoid cavity |
6 |
Acromion |
16 |
Supraglenoid tubercle |
7 |
Clavicular facet |
17 |
Infraglenoid tubercle |
8 |
Acromial angle |
18 |
Neck |
9 |
Medial border |
19 |
Coracoid process |
10 |
Lateral border |
|
|
14 |
14 |
7 |
6 |
|
|
11 |
|
19 |
16 |
19
12
2
15
18
1
17 |
17 |
9
10
13
|
13 |
Left scapula |
Left scapula |
Anterior view, lateral to right |
|
|
Lateral view, anterior to right |
88

14
11
6
12
2
8
3
18
17 |
5 |
|
9
10
13
Left scapula
Posterior view, Lateral to left
19
16
12
15
4
6
2
8
Left scapula
Superior view, lateral to left
89
