
- •Warning and Disclaimer
- •Feedback Information
- •Trademark Acknowledgments
- •About the Author
- •About the Technical Reviewers
- •Dedication
- •Acknowledgments
- •Contents at a Glance
- •Contents
- •Icons Used in This Book
- •Command Syntax Conventions
- •Cisco’s Motivation: Certifying Partners
- •Format of the CCNA Exams
- •What’s on the CCNA Exams
- •ICND Exam Topics
- •Cross-Reference Between Exam Topics and Book Parts
- •CCNA Exam Topics
- •INTRO and ICND Course Outlines
- •Objectives and Methods
- •Book Features
- •How This Book Is Organized
- •Part I: LAN Switching
- •Part II: TCP/IP
- •Part III: Wide-Area Networks
- •Part IV: Network Security
- •Part V: Final Preparation
- •Part VI: Appendixes
- •How to Use These Books to Prepare for the CCNA Exam
- •For More Information
- •Part I: LAN Switching
- •“Do I Know This Already?” Quiz
- •Foundation Topics
- •Brief Review of LAN Switching
- •The Forward-Versus-Filter Decision
- •How Switches Learn MAC Addresses
- •Forwarding Unknown Unicasts and Broadcasts
- •LAN Switch Logic Summary
- •Basic Switch Operation
- •Foundation Summary
- •Spanning Tree Protocol
- •“Do I Know This Already?” Quiz
- •Foundation Topics
- •Spanning Tree Protocol
- •What IEEE 802.1d Spanning Tree Does
- •How Spanning Tree Works
- •Electing the Root and Discovering Root Ports and Designated Ports
- •Reacting to Changes in the Network
- •Spanning Tree Protocol Summary
- •Optional STP Features
- •EtherChannel
- •PortFast
- •Rapid Spanning Tree (IEEE 802.1w)
- •RSTP Link and Edge Types
- •RSTP Port States
- •RSTP Port Roles
- •RSTP Convergence
- •Edge-Type Behavior and PortFast
- •Link-Type Shared
- •Link-Type Point-to-Point
- •An Example of Speedy RSTP Convergence
- •Basic STP show Commands
- •Changing STP Port Costs and Bridge Priority
- •Foundation Summary
- •Foundation Summary
- •Virtual LANs and Trunking
- •“Do I Know This Already?” Quiz
- •Foundation Topics
- •Review of Virtual LAN Concepts
- •Trunking with ISL and 802.1Q
- •ISL and 802.1Q Compared
- •VLAN Trunking Protocol (VTP)
- •How VTP Works
- •VTP Pruning
- •Foundation Summary
- •Part II: TCP/IP
- •IP Addressing and Subnetting
- •“Do I Know This Already?” Quiz
- •Foundation Topics
- •IP Addressing Review
- •IP Subnetting
- •Analyzing and Interpreting IP Addresses and Subnets
- •Math Operations Used to Answer Subnetting Questions
- •Converting IP Addresses from Decimal to Binary and Back Again
- •The Boolean AND Operation
- •How Many Hosts and How Many Subnets?
- •What Is the Subnet Number, and What Are the IP Addresses in the Subnet?
- •Finding the Subnet Number
- •Finding the Subnet Broadcast Address
- •Finding the Range of Valid IP Addresses in a Subnet
- •Finding the Answers Without Using Binary
- •Easier Math with Easy Masks
- •Which Subnet Masks Meet the Stated Design Requirements?
- •What Are the Other Subnet Numbers?
- •Foundation Summary
- •“Do I Know This Already?” Quiz
- •Foundation Topics
- •Extended ping Command
- •Distance Vector Concepts
- •Distance Vector Loop-Avoidance Features
- •Route Poisoning
- •Split Horizon
- •Split Horizon with Poison Reverse
- •Hold-Down Timer
- •Triggered (Flash) Updates
- •RIP and IGRP
- •IGRP Metrics
- •Examination of RIP and IGRP debug and show Commands
- •Issues When Multiple Routes to the Same Subnet Exist
- •Administrative Distance
- •Foundation Summary
- •“Do I Know This Already?” Quiz
- •Foundation Topics
- •Link-State Routing Protocol and OSPF Concepts
- •Steady-State Operation
- •Loop Avoidance
- •Scaling OSPF Through Hierarchical Design
- •OSPF Areas
- •Stub Areas
- •Summary: Comparing Link-State and OSPF to Distance Vector Protocols
- •Balanced Hybrid Routing Protocol and EIGRP Concepts
- •EIGRP Loop Avoidance
- •EIGRP Summary
- •Foundation Summary
- •“Do I Know This Already?” Quiz
- •Foundation Topics
- •Route Summarization and Variable-Length Subnet Masks
- •Route Summarization Concepts
- •VLSM
- •Route Summarization Strategies
- •Sample “Best” Summary on Seville
- •Sample “Best” Summary on Yosemite
- •Classless Routing Protocols and Classless Routing
- •Classless and Classful Routing Protocols
- •Autosummarization
- •Classful and Classless Routing
- •Default Routes
- •Classless Routing
- •Foundation Summary
- •Advanced TCP/IP Topics
- •“Do I Know This Already?” Quiz
- •Foundation Topics
- •Scaling the IP Address Space for the Internet
- •CIDR
- •Private Addressing
- •Network Address Translation
- •Static NAT
- •Dynamic NAT
- •Overloading NAT with Port Address Translation (PAT)
- •Translating Overlapping Addresses
- •Miscellaneous TCP/IP Topics
- •Internet Control Message Protocol (ICMP)
- •ICMP Echo Request and Echo Reply
- •Destination Unreachable ICMP Message
- •Time Exceeded ICMP Message
- •Redirect ICMP Message
- •Secondary IP Addressing
- •FTP and TFTP
- •TFTP
- •MTU and Fragmentation
- •Foundation Summary
- •Part III: Wide-Area Networks
- •“Do I Know This Already?” Quiz
- •Foundation Topics
- •Review of WAN Basics
- •Physical Components of Point-to-Point Leased Lines
- •Data-Link Protocols for Point-to-Point Leased Lines
- •HDLC and PPP Compared
- •Looped Link Detection
- •Enhanced Error Detection
- •Authentication Over WAN Links
- •PAP and CHAP Authentication
- •Foundation Summary
- •“Do I Know This Already?” Quiz
- •Foundation Topics
- •ISDN Protocols and Design
- •Typical Uses of ISDN
- •ISDN Channels
- •ISDN Protocols
- •ISDN BRI Function Groups and Reference Points
- •ISDN PRI Function Groups and Reference Points
- •BRI and PRI Encoding and Framing
- •PRI Encoding
- •PRI Framing
- •BRI Framing and Encoding
- •DDR Step 1: Routing Packets Out the Interface to Be Dialed
- •DDR Step 2: Determining the Subset of the Packets That Trigger the Dialing Process
- •DDR Step 3: Dialing (Signaling)
- •DDR Step 4: Determining When the Connection Is Terminated
- •ISDN and DDR show and debug Commands
- •Multilink PPP
- •Foundation Summary
- •Frame Relay
- •“Do I Know This Already?” Quiz
- •Foundation Topics
- •Frame Relay Protocols
- •Frame Relay Standards
- •Virtual Circuits
- •LMI and Encapsulation Types
- •DLCI Addressing Details
- •Network Layer Concerns with Frame Relay
- •Layer 3 Addressing with Frame Relay
- •Frame Relay Layer 3 Addressing: One Subnet Containing All Frame Relay DTEs
- •Frame Relay Layer 3 Addressing: One Subnet Per VC
- •Frame Relay Layer 3 Addressing: Hybrid Approach
- •Broadcast Handling
- •Frame Relay Service Interworking
- •A Fully-Meshed Network with One IP Subnet
- •Frame Relay Address Mapping
- •A Partially-Meshed Network with One IP Subnet Per VC
- •A Partially-Meshed Network with Some Fully-Meshed Parts
- •Foundation Summary
- •Part IV: Network Security
- •IP Access Control List Security
- •“Do I Know This Already?” Quiz
- •Foundation Topics
- •Standard IP Access Control Lists
- •IP Standard ACL Concepts
- •Wildcard Masks
- •Standard IP ACL: Example 2
- •Extended IP Access Control Lists
- •Extended IP ACL Concepts
- •Extended IP Access Lists: Example 1
- •Extended IP Access Lists: Example 2
- •Miscellaneous ACL Topics
- •Named IP Access Lists
- •Controlling Telnet Access with ACLs
- •ACL Implementation Considerations
- •Foundation Summary
- •Part V: Final Preparation
- •Final Preparation
- •Suggestions for Final Preparation
- •Preparing for the Exam Experience
- •Final Lab Scenarios
- •Scenario 1
- •Scenario 1, Part A: Planning
- •Solutions to Scenario 1, Part A: Planning
- •Scenario 2
- •Scenario 2, Part A: Planning
- •Solutions to Scenario 2, Part A: Planning
- •Part VI: Appendixes
- •Glossary
- •Answers to the “Do I Know This Already?” Quizzes and Q&A Questions
- •Chapter 1
- •“Do I Know This Already?” Quiz
- •Chapter 2
- •“Do I Know This Already?” Quiz
- •Chapter 3
- •“Do I Know This Already?” Quiz
- •Chapter 4
- •“Do I Know This Already?” Quiz
- •Chapter 5
- •“Do I Know This Already?” Quiz
- •Chapter 6
- •“Do I Know This Already?” Quiz
- •Chapter 7
- •“Do I Know This Already?” Quiz
- •Chapter 8
- •“Do I Know This Already?” Quiz
- •Chapter 9
- •“Do I Know This Already?” Quiz
- •Chapter 10
- •“Do I Know This Already?” Quiz
- •Chapter 11
- •“Do I Know This Already?” Quiz
- •Chapter 12
- •“Do I Know This Already?” Quiz
- •Using the Simulation Software for the Hands-on Exercises
- •Accessing NetSim from the CD
- •Hands-on Exercises Available with NetSim
- •Scenarios
- •Labs
- •Listing of the Hands-on Exercises
- •How You Should Proceed with NetSim
- •Considerations When Using NetSim
- •Routing Protocol Overview
- •Comparing and Contrasting IP Routing Protocols
- •Routing Through the Internet with the Border Gateway Protocol
- •RIP Version 2
- •The Integrated IS-IS Link State Routing Protocol
- •Summary of Interior Routing Protocols
- •Numbering Ports (Interfaces)
Foundation Summary 89
Foundation Summary
The “Foundation Summary” section lists the most important facts from the chapter. Although this section does not list everything that will be on the exam, a well-prepared CCNA candidate should at a minimum know all the details in each Foundation Summary before taking the exam.
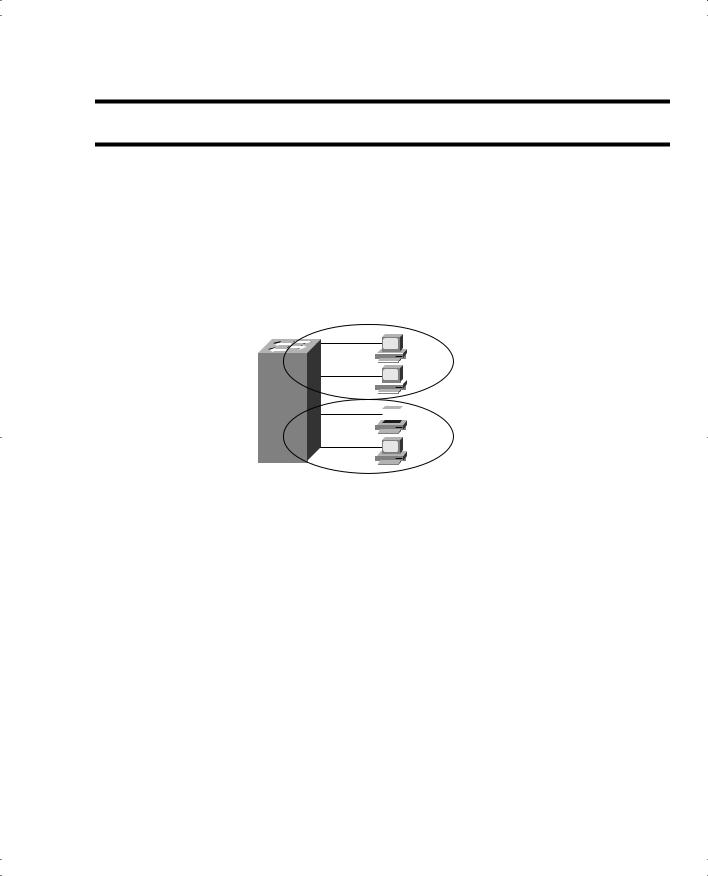
Figure 3-10 shows the general idea of a VLAN, showing two different VLANs/broadcast domains.
Figure 3-10 Network with Two VLANs Using One Switch
Dino
VLAN 1
 Fred
Fred
 Wilma
Wilma
VLAN 2
Table 3-6 summarizes the key features and points of comparison between ISL and 802.1Q.
Table 3-6 |
ISL and 802.1Q Compared |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Function |
ISL |
802.1Q |
|
|
|
|
|
Standards body that defines the protocol |
Cisco-proprietary |
IEEE |
|
|
|
|
|
Encapsulates the original frame |
Yes |
No |
|
|
|
|
|
Allows multiple spanning trees |
Yes |
No |
|
|
|
|
|
Uses a native VLAN |
No |
Yes |
|
|
|
|

90 Chapter 3: Virtual LANs and Trunking
Table 3-7 offers a comparative overview of the three VTP modes.
Table 3-7 VTP Modes
|
Server |
Client |
Transparent |
Function |
Mode |
Mode |
Mode |
|
|
|
|
Originates VTP advertisements |
Yes |
No |
No |
|
|
|
|
Processes received advertisements and synchronizes |
Yes |
Yes |
No |
VLAN configuration information with other switches |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Forwards VTP advertisements received in a trunk |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
|
|
|
|
Saves VLAN configuration in NVRAM |
Yes |
No |
Yes |
|
|
|
|
Can create, modify, or delete VLANs using configuration |
Yes |
No |
Yes |
commands |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Table 3-8 summarizes the different trunking options on the 2950 and their meanings.
Table 3-8 2950 Trunk Configuration Options with the switchport mode Command
Option |
Description |
|
|
access |
Disables port trunk mode and does not even attempt to form a trunk on |
|
the interface. |
|
|
trunk |
Configures the port into permanent trunk mode and negotiates with the |
|
connected device to decide whether to use 802.1Q or ISL. |
|
|
dynamic desirable |
Triggers the port to negotiate the link from nontrunking to trunk mode. |
|
The port negotiates to a trunk port if the connected device is either in the |
|
trunk, dynamic desirable, or dynamic auto state. Otherwise, the port |
|
becomes a nontrunk port. |
|
|
dynamic auto |
Lets a port become a trunk only if the connected device has the state set |
|
to dynamic desirable or trunk. |
|
|

Q&A 91
Q&A
As mentioned in the Introduction, you have two choices for review questions. The following questions give you a bigger challenge than the exam because they are open-ended. By reviewing with this more-difficult question format, you can exercise your memory better and prove your conceptual and factual knowledge of the topics covered in this chapter. The answers to these questions are found in Appendix A.
For more practice with exam-like question formats, including multiple-choice questions and those using a router simulator, use the exam engine on the CD.
1.Define broadcast domain.
2.Define VLAN.
3.If two Cisco LAN switches are connected using Fast Ethernet, what VLAN trunking protocols can be used? If only one VLAN spans both switches, is a VLAN trunking protocol needed?
4.Define VTP.
5.Name the three VTP modes. Which mode does not allow VLANs to be added or modified?
6.What Catalyst 2950 switch command configures ISL trunking on fastethernet port 0/12, so that as long as the switch port on the other end of the trunk is not disabled (off) or configured to not negotiate to become a trunk, the trunk is definitely placed in trunking mode?
7.What type of VTP mode allows a switch to create VLANs and advertise them to other switches?
8.Must all members of the same VLAN be in the same collision domain, the same broadcast domain, or both?
9.What is Cisco’s proprietary trunking protocol over Ethernet?
10.Explain the benefits provided by VTP pruning.
11.Consider the phrase “A VLAN is a broadcast domain is an IP subnet.“ Do you agree or disagree? Why?
12.What fields are added or changed in an Ethernet header when you use 802.1Q? Where is the VLAN ID in those fields?

92Chapter 3: Virtual LANs and Trunking
13.Explain how a switch in VTP transparent mode treats VTP messages received from a VTP server.
14.What command on a 2950 switch creates VLAN 5? What configuration mode is required?
15.What command on a 2950 switch puts an interface into VLAN 5? What configuration mode is required?
16.Describe the basic differences in the processes used by VLAN configuration mode and the normally used configuration mode.
17.Give the correct syntax for the commands that put an interface into the various trunking modes, and identify which commands work when the switch on the other side of the link uses the auto option.
18.What 2950 show commands list trunk status, both configured and operational?


Cisco Published ICND Exam Topics*
Covered in This Part:
2Design an IP addressing scheme to support classful, classless, and private addressing to meet design requirements
3Select an appropriate routing protocol based on user requirements
7Configure routing protocols given user requirements
8Configure IP addresses, subnet masks, and gateway addresses on routers and hosts
9Configure a router for additional administrative functionality
15 Utilize the OSI model as a guide for systematic network troubleshooting
17Troubleshoot routing protocols
18Troubleshoot IP addressing and host configuration
19Troubleshoot a device as part of a working network
24Evaluate the characteristics of routing protocols
* Always re-check www.cisco.com for the latest posted exam topics
