
- •About the Authors
- •Dedication
- •Contents at a Glance
- •Table of Contents
- •Introduction
- •About This Book
- •System Requirements
- •How This Book Is Organized
- •Part I: Wireless Networking Fundamentals
- •Part II: Making Plans
- •Part III: Installing a Wireless Network
- •Part IV: Using a Wireless Network
- •Part V: The Part of Tens
- •Icons Used in This Book
- •Where to Go from Here
- •Nothing but Net(work): Why You Need (Or Want) One
- •File sharing
- •Printer and peripheral sharing
- •Internet connection sharing
- •Home arcades and wireless to go
- •Wired versus Wireless
- •Installing wired home networks
- •Installing wireless home networks
- •Picking a Wireless Standard
- •Planning Your Wireless Home Network
- •Workstations and servers
- •Network infrastructure
- •Network interface adapters
- •Get the (Access) Point?
- •Industry Standards
- •Who or What Is Bluetooth?
- •Wi-Fi versus Bluetooth
- •Piconets, Masters, and Slaves
- •Wirelessly synching your PDAs
- •Wireless printing and data transfer
- •Integrating HPNA and HomePlug with Your Wireless Home Network
- •Home Phoning (ET Got It Backward!)
- •Network Power(line)!
- •Deciding What Is Connected to the Network
- •Counting network devices
- •Choosing wired or wireless
- •Choosing a wireless technology
- •Choosing an access point
- •Deciding where to install the AP
- •Adding printers
- •Adding entertainment and more
- •Connecting to the Internet
- •Budgeting for Your Wireless Network
- •Pricing access points
- •Pricing wireless network adapters
- •A sample budget
- •Planning Security
- •Selecting Access Points
- •Certification and Standards Support
- •Compatibility and Form Factor
- •DHCP servers
- •Gateways, NAT, and cable/DSL routers
- •Switches
- •Print servers
- •Operational Features
- •Security
- •Range and Coverage Issues
- •Manageability
- •Web-based configuration
- •Software programming
- •Telnetting to your device
- •Upgradeable firmware
- •Price
- •Warranties
- •Customer and Technical Support
- •Before Getting Started, Get Prepared
- •Setting Up the Access Point
- •Preparing to install a wireless AP
- •Installing the AP
- •Configuring AP parameters
- •Changing the AP Configuration
- •Installing device drivers and client software
- •PC Cards and mini-PCI cards
- •Compact Flash cards
- •PCI and ISA cards
- •USB adapters
- •Modifying Wireless Network Adapters
- •Synchronizing and Internet Access
- •Wireless Zero Configuration with XP
- •Easy installation
- •Automatic network connections
- •Tracking Your Network’s Performance
- •Apple AirPort Hardware
- •Pick an AirPort Card, any card
- •Apple AirPort Software Updates
- •AirPort 2.0 software
- •AirPort 2.0.4 software
- •AirPort 2.0.5 software
- •AirPort 2.1.1 software
- •OS 9 Wireless Networks
- •Installing AirPort software on Mac OS 9
- •Upgrading AirPort Base Station firmware on OS 9
- •OS X Wireless Networks
- •Installing the AirPort software on OS X
- •Upgrading AirPort Base Station firmware on OS X
- •Adding another computer to your AirPort network on OS X
- •Connection sharing
- •Routers and gateways
- •Sharing dialup Internet connections
- •Obtaining an IP Address Automatically
- •Windows 9x
- •Windows 2000
- •Windows XP
- •Setting Up Internet Connection Sharing
- •Windows 98 SE and Windows Me
- •Windows 2000
- •Windows XP
- •Mac OS X v. 10.2 (Jaguar)
- •Assessing the Risks
- •General Internet security
- •Airlink security
- •How about a bit more about WEP?
- •What’s wrong with WEP?
- •Clamping Down on Your Wireless Home Network’s Security
- •Getting rid of the defaults
- •Enabling WEP
- •Closing your network
- •Looking into the Crystal Ball
- •Waiting for WPA
- •The future: 802.11i
- •A Networking Review
- •Basic networking terminology
- •Setting up a workgroup
- •Will You Be My Neighbor?
- •Sharing a document or folder on Windows 95/98/Me
- •Enabling sharing on Windows 2000/XP
- •Setting permissions
- •Accessing shared files
- •Be Economical: Share Those Peripherals
- •Setting up a print server
- •Sharing other peripherals
- •PC Gaming Hardware Requirements
- •Networking Requirements for PC Gaming
- •Console online gaming services and equipment
- •Console wireless networking equipment
- •Dealing with Router Configurations
- •Getting an IP address
- •Dealing with port forwarding
- •Setting Up a Demilitarized Zone (DMZ)
- •Wireless Home Entertainment Gear
- •Expanding Your Home Entertainment Center with Wireless Adapters
- •The Home Media Player
- •The Home Theater PC
- •Internet Content for Your Media Players and HTPCs
- •Making a Connection to Your Car
- •Your car’s path to wireless enlightenment
- •Synching your car stereo with home
- •Getting online with your own car PC
- •Picking wireless gear for your car
- •Using your PDA as a remote control
- •Whole home 802.11-based IR coverage
- •See me, feel me, hear me, touch me
- •Discovering Bluetooth Basics
- •Bluetooth Mobile Phones
- •Bluetooth PDAs
- •Other Bluetooth Devices
- •Printers
- •Digital cameras
- •Keyboards and meeses (that’s plural for mouse!)
- •Bluetooth adapters
- •Discovering Public Hot Spots
- •Freenets and open access points
- •For-pay services
- •Using T-Mobile Hot Spots
- •Using Wayport Hot Spots
- •Using Boingo Hot Spots
- •Tools for Finding Hot Spots
- •Netstumbler.com
- •Boingo
- •Check the Obvious
- •Move the Access Point
- •Move the Antenna(s)
- •Change Channels
- •Check for Dual-Band Interference
- •Check for New Obstacles
- •Install Another Antenna
- •Add a Signal Booster
- •Add a Repeater or Bridge
- •Check Your Cordless Phone Frequencies
- •Your Bath
- •Your Car
- •Your Exercise Gear
- •Your Home Appliances
- •Your Musical Instruments
- •Your Pets
- •Your Phones
- •Your Robots
- •Your Wearing Apparel
- •CNET.com
- •802.11 Planet
- •Broadband Wireless Exchange Magazine
- •80211b.weblogger.com
- •PC Magazine
- •Electronic House Magazine
- •Home Automation Magazine
- •Practically Networked
- •ExtremeTech.com
- •Network World
- •Other Cool Sites
- •Index

164 Part III: Installing a Wireless Network
Connection sharing: All network users access the Internet via one computer that’s specifically set up for doing just that.
A router or an Internet gateway: A router handles the traffic management to enable all network users access to the Internet. An Internet gateway is a broadband modem with a bundled-in router. A wireless Internet gateway adds an access point (AP) to the mix.
Connection sharing
Windows 98 and later versions of Windows enable Internet connection sharing, as does Mac OS X. When using this method to share an Internet connection, each computer in a wired or wireless network is set up to connect to the Internet through the computer that’s connected to the modem that’s connected to the Internet. The disadvantage with this system is that you can’t turn off or remove the computer that’s connected to the modem without also disconnecting all computers from the Internet. In addition, simultaneous usage (several people on the network using the Internet at once) can slow down the computer providing the connection.
Mac OS 9 and Mac OS X v. 10.2 (called Jaguar) or later include a program for the Apple AirPort system called AirPort Software Base Station. The Base Station enables you to share an Internet connection by creating a softwarebased wireless Base Station in one of the computers on your network. Other computers on the network with wireless network adapters can access the Internet through the soft Base Station. Again, the computer that’s running this Base Station software has to be turned on for the other computers in the wireless network to gain access to the Internet, and this Base Station computer is affected by the same performance degradation as in the preceding scenario.
Routers and gateways
By connecting a router between the broadband modem and your home network, all computers on the network can access the Internet without going through another computer. The Internet connection no longer depends on any computer on the network.
The types of routers used in homes are often cable/DSL routers. These devices are also DHCP servers and also include Network Address Translation (NAT) services. The most popular type of device for sharing an Internet connection over a home network, often described as a wireless gateway, combines the features of a router, a DHCP server, a NAT server, and the

Chapter 9: Setting Up Internet Sharing 165
capabilities of a wireless AP. In addition to wireless connectivity, most of these devices also have several Ethernet ports for connecting computers with network cable, giving you the flexibility of adding wired devices and expanding your network connections. Each computer connects to the wireless gateway; the wireless gateway device connects to the broadband (usually DSL or cable) modem; and the modem connects to the Internet.
The nature of the Internet and Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) networking requires that every machine or device connecting has to have a unique IP address. For information to get to its proper destination, every piece of information has to contain the IP address that it came from and the IP address that it’s going to for it to get from one point to another.
A NAT server allows for the conversion of one IP address to one or many other IP addresses. This means that a whole group of computers can look like just one computer to the rest of the Internet. This is becoming more the norm in both home and corporate networks these days because we have many more computers and devices using the Internet today than we have IP addresses to give them. Connecting to an Internet service provider (ISP) will typically deliver one IP address to the device performing the connection. This is true for dialup, cable, and satellite modems as well as DSL. That IP address is used by the computer or Internet gateway that the modem connects to.
If you have one computer, getting an IP address assigned to your computer is very simple because the modem device delivers the IP address to the computer, and the computer uses that address as its own and connects to the Internet. If you have more than one computer or device to connect, you have to share that one IP address that the modem receives among those machines. NAT creates an internal addressing scheme using one of the reserved IP address ranges that the Internet does not use. (192.168.x.x is one of two Class B networks that are used internally to home or office networks using NAT.) Many companies and almost all cable/DSL routers use these address ranges on the networks behind them. In many cases, it’s a given that the IP address of the cable/DSL router will be 192.168.1.1 or 192.168.2.1, depending on which address NAT is configured to use.
After the address translation is in place, a DHCP server then assigns the local IP addresses for all the devices connected inside your home network. The Internet gateway’s NAT function enables all computers connected to the Internet through the Internet gateway device to share the same IP address on the Internet. Figure 9-1 depicts a wireless home network that uses an Internet gateway providing NAT and DHCP to share Internet access to three computers over wireless connections and to two more over wired connections.
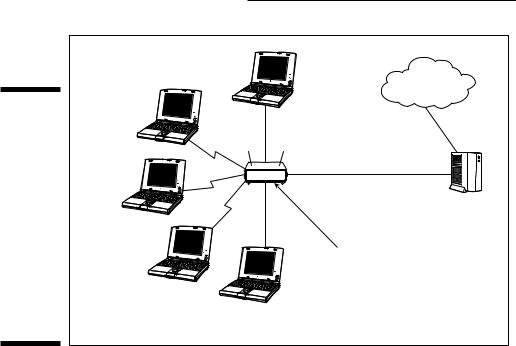
166 Part III: Installing a Wireless Network
|
|
Wired PC |
|
|
|
Wireless |
198.162.1.6 |
Internet |
|
Figure 9-1: |
PC |
|
|
|
198.162.1.5 |
|
|
||
A wireless |
|
|
||
|
|
|
||
home |
|
|
|
|
network |
Wireless |
|
|
|
using a |
209.211.202.11 is delivered |
|||
PC |
||||
wireless |
from the modem. |
|||
198.162.1.4 |
||||
Internet |
|
|
Cable/DSL |
|
gateway |
|
|
||
|
|
modem |
||
device |
|
|
||
|
|
|
||
shares an |
|
|
|
|
Internet |
Wireless |
Wireless |
|
|
connection |
PC |
Internet |
|
|
with wired |
198.162.1.3 |
gateway/DHCP |
|
|
and |
|
(198.162.1.1) |
|
|
wireless |
|
Wired PC |
|
|
computers. |
|
198.162.1.2 |
|
|
Sharing dialup Internet connections
You can use connection sharing and a home network to share a single dialup connection. This would be especially practical if you have a dedicated telephone line for Internet access. You can use a dialup modem to connect to the Internet on the dedicated line, leave the connection running, and then share this connection with all the computers on your home network so that they can access the Internet.
Similarly, if you purchase an Internet gateway that includes a dialup modem, you can use the gateway to share a dialup connection. You can connect the gateway to the Internet using the dialup modem and then use the gateway’s router feature to share this connection with all the networked computers. Some Internet gateways (usually those designed for small businesses) combine both a broadband (DSL usually) modem and a dialup modem in one box. You can use the dialup modem as a backup system if your broadband connection ever goes down.
Apple’s AirPort Base Station does include a dialup modem (standard on older AirPort Base Stations and optional on the AirPort Extreme Base Station) and also includes ISP logon features that can successfully connect to AOL, but you still need multiple AOL accounts for multiple users to access the Internet simultaneously through AOL.
