
- •Textbook Series
- •Contents
- •1 Definitions
- •Introduction
- •Abbreviations
- •Definitions
- •2 International Agreements and Organizations
- •The Chicago Convention
- •International Law
- •Commercial Considerations
- •Customs and Excise, and Immigration
- •International Obligations of Contracted States
- •Duties of ICAO Member States
- •Status of Annex Components
- •The International Civil Aviation Organization (ICAO)
- •The Organization of ICAO
- •Regional Structure of ICAO
- •Regional Structure and Offices
- •ICAO Publications
- •Other International Agreements
- •The Conventions of Tokyo, the Hague and Montreal
- •The Warsaw Convention
- •The Rome Convention
- •IATA
- •ECAC
- •EASA
- •Eurocontrol
- •World Trade Organization
- •Geneva Convention
- •EU Regulation 261/2004
- •Questions
- •Answers
- •3 Airworthiness of Aircraft
- •Introduction
- •Airworthiness
- •Questions
- •Answers
- •4 Aircraft Nationality and Registration Marks
- •Introduction
- •Nationality and Registration Marks
- •Certification of Registration
- •Aircraft Markings
- •Classification of Aircraft
- •Questions
- •Answers
- •5 Flight Crew Licensing
- •Introduction
- •Definitions
- •General Rules Concerning Licensing
- •Licences and Ratings for Pilots
- •Multi-crew Pilot Licence (MPL)
- •Instrument Rating (Aeroplane) (IR(A))
- •Instructor and Examiner Rating
- •JAR-FCL 3 Medical Requirements
- •Pilot Proficiency
- •EASA Theoretical Knowledge Examinations
- •Questions
- •Answers
- •6 Rules of the Air
- •History
- •Applicability of the Rules of the Air
- •General Rules
- •Visual Flight Rules
- •Instrument Flight Rules
- •Semi-circular Flight Level Rules and RVSM
- •Special VFR
- •Distress and Urgency Signals
- •Restricted, Prohibited or Danger Areas
- •Signals for Aerodrome Traffic
- •Marshalling Signals
- •Flight Deck Signals
- •Questions
- •Answers
- •Instrument Procedures
- •PANS OPS
- •Instrument Departure Procedures
- •Questions
- •Answers
- •8 Approach Procedures
- •Procedure Basics
- •Approach Procedure Design
- •Obstacle Clearance Altitude/Height
- •Operating Minima
- •Descent Gradients
- •Track Reversal and Racetracks
- •Missed Approach Segment and Procedure
- •Published Information
- •RNAV Approach Procedures based on VOR/DME
- •Questions
- •Answers
- •9 Circling Approach
- •Circling Approach
- •Questions
- •Answers
- •10 Holding Procedures
- •Holding Procedures
- •Entry Sectors
- •ATC Considerations
- •Obstacle Clearance
- •Questions
- •Answers
- •11 Altimeter Setting Procedure
- •Altimeter Setting Objectives
- •Transition
- •Phases of Flight
- •Questions
- •Answers
- •12 Parallel or Near-parallel Runway Operation
- •Safety
- •Runway Spacing
- •Questions
- •Answers
- •13 SSR and ACAS
- •Airborne Collision Avoidance System (ACAS)
- •Questions
- •Answers
- •14 Airspace
- •Introduction
- •Control Areas and Zones
- •Classes of Airspace
- •Required Navigation Performance (RNP)
- •Airways and ATS Routes
- •Questions
- •Answers
- •15 Air Traffic Services
- •Introduction
- •Air Traffic Control
- •ATC Clearances
- •Control of Persons and Vehicles at Aerodromes
- •The Flight Information Service
- •The Alerting Service
- •Procedures
- •Questions
- •Answers
- •16 Separation
- •Concept of Separation
- •Vertical Separation
- •Horizontal Separation
- •Radar Separation
- •Procedural Wake Turbulence Separation
- •Radar Wake Turbulence Separation
- •Visual Separation in the Vicinity of Aerodromes
- •Stacking
- •Questions
- •Answers
- •17 Control of Aircraft
- •Procedural ATC
- •Radar Control
- •Radar Identification
- •Radar Service
- •Aerodrome Control
- •Approach Control Service
- •Air Traffic Advisory Service
- •Aircraft Emergencies
- •Questions
- •Answers
- •18 Aeronautical Information Service (AIS)
- •Introduction
- •General
- •The Integrated Aeronautical Information Package
- •The Aeronautical Information Publication (AIP)
- •Notices to Airmen (NOTAM)
- •SNOWTAM
- •ASHTAM
- •Aeronautical Information Circulars (AICs)
- •Pre-flight and Post-flight Information
- •Questions
- •Answers
- •Introduction
- •Aerodrome Reference Code
- •Glossary of Terms
- •Aerodrome Data
- •Runways
- •Taxiways
- •Aprons
- •Questions
- •Answers
- •Requirements
- •Visual Aids for Navigation
- •Runway Markings
- •Taxiway Markings
- •Signs
- •Markers
- •Visual Docking Guidance Systems
- •Questions
- •Answers
- •21 Aerodrome Lighting
- •Aerodrome Lights
- •Approach Lighting Systems
- •Runway Lighting
- •Taxiway Lighting
- •Questions
- •Answers
- •22 Obstacle Marking and Aerodrome Services
- •Introduction
- •Visual Aids for Denoting Obstacles
- •Visual Aids for Denoting Restricted Use Areas
- •Emergency and Other Services
- •Other Aerodrome Services
- •Questions
- •Answers
- •23 Facilitation
- •Entry and Departure of Aircraft
- •Questions
- •Answers
- •24 Search and Rescue
- •Definitions and Abbreviations
- •Establishment and Provision of SAR Service
- •Co-operation between States
- •Operating Procedures
- •Questions
- •Answers
- •25 Security
- •Introduction
- •Objectives
- •Organization
- •Preventative Security Measures
- •Management of Response to Acts of Unlawful Interference
- •Further Security Information
- •Questions
- •Answers
- •26 Aircraft Accident and Incident Investigation
- •Introduction
- •Objective of Investigation
- •Investigations
- •Serious Incidents
- •EU Considerations
- •Questions
- •Answers
- •27 Revision Questions
- •Revision Questions
- •Answers
- •EASA Specimen Examination
- •Answers to Specimen EASA Examination
- •28 Addendum – EASA Part-FCL & Part-MED
- •Chapter Five. Flight Crew Licensing
- •European Aviation Safety Agency (EASA)
- •Licences
- •Ratings
- •Certificates
- •EASA Part-MED
- •29 Index

Chapter
13
SSR and ACAS
SSR and ACAS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
. . . |
. . . |
. . . . . . . . . |
. . . |
. . . |
. . |
|
. 247 |
Secondary Surveillance Radar (SSR) . . . . . . |
. . |
. . |
. . . . . . |
. . |
. . |
. |
. |
247 |
Airborne Collision Avoidance System (ACAS) . . . |
. . |
. . |
. . . . . . |
. . |
. . . . 249 |
|||
Questions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
. . |
. . |
. . . . . . |
. . |
. . |
. |
|
251 |
Answers . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
. . |
. . |
. . . . . . |
. . |
. . |
. |
. |
254 |
245

13 SSR and ACAS
ACAS and SSR 13
246

SSR and ACAS |
|
13 |
|
||
SSR and ACAS |
|||||
|
|
|
|
||
Secondary Surveillance Radar (SSR) |
|
|
|
|
|
13.1 Background. The technical requirements of the EASA Theoretical Knowledge syllabus for |
|
|
|
|
|
SSR, is covered in 062 Radio Navigation. However, the operation of SSR in the ATC environment |
|
|
|
|
|
is within the remit of Air Law. In the chapters of these notes concerning ATC, the use of radar |
|
|
|
|
|
will be discussed and it will be implied that where required, the radar derived information |
|
|
|
|
|
will be enhanced by the use of SSR. The modern SSR systems have been developed from the |
|
|
|
|
|
equipment used in WWII as a means of identifying ‘friend’ from ‘foe’ (IFF). The basic system |
|
|
|
|
|
was rather crude effectively giving the ground station a response from the aircraft indicating |
|
|
|
|
|
that the aircraft was fitted with the then highly secret equipment. As only ‘friendly’ aircraft |
|
|
|
|
|
had the equipment the radar operator could easily distinguish a friendly aircraft radar response |
|
|
|
|
|
from an enemy response. The airborne equipment was given the code name ‘parrot’ which |
|
|
|
|
|
explains some of the rather peculiar phraseology associated with the operation of a modern |
|
|
|
|
|
SSR system. Current SSR systems enable individual aircraft to be identified on a flight by flight |
|
|
|
|
|
basis with the additional facilities to pass data via the SSR system, indicate aircraft altitude |
|
|
|
|
|
and, using the redundant capacity of the SSR system, provide effective collision avoidance |
|
|
|
|
|
enhancement. |
|
|
|
|
|
13.2 Carriage of Transponders. The airborne equipment is called a transponder (because |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
13 |
|
||
it transmits a response to an interrogation). PANS OPS requires that where a serviceable |
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
||
transponder is carried in an aircraft, unless ATC instructs otherwise, it will be used at all |
|
|
ACAS |
||
times. Individual states may specify certain conditions where the carriage and operation of a |
|
|
|||
transponder is mandatory. In either case, the operation of the equipment will be regardless of |
|
|
and |
||
the provision of an ATC service. |
|
|
SSR |
||
|
|
|
|||
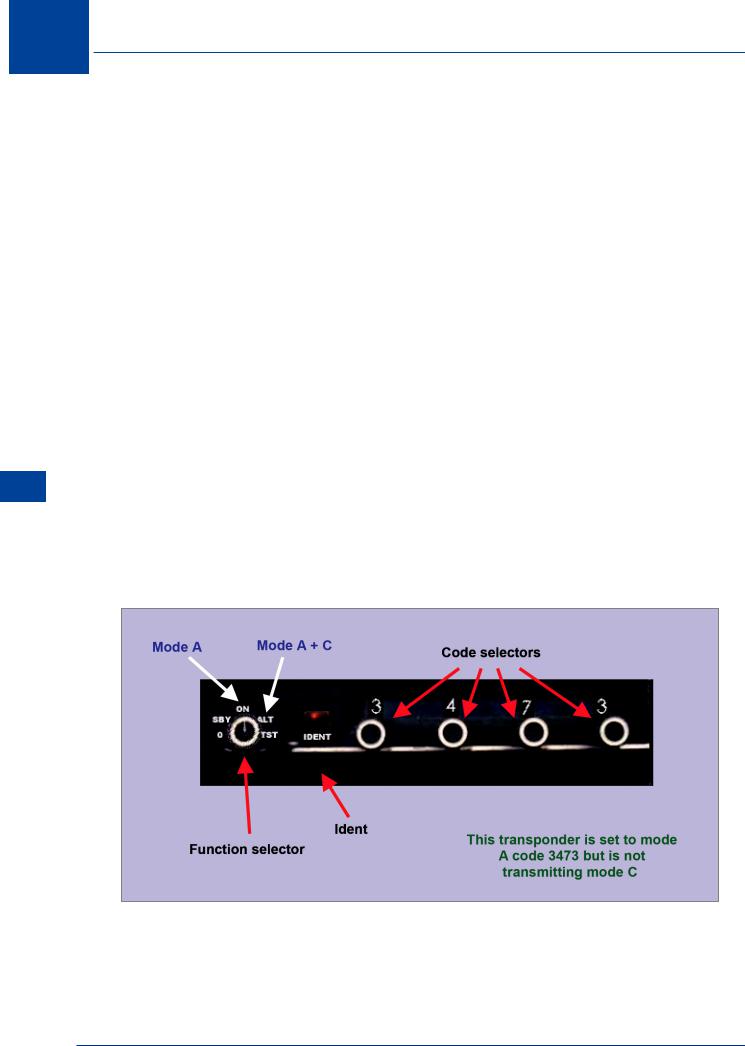
13.3 Mode of Operation. The output codes of the SSR system consist of groups of 4 |
|
|
|
|
|
numbers in the range 0 - 7. The ground station (the interrogator) transmits a coded signal that |
|
|
|
|
|
prompts the aircraft transponder to reply. The overall SSR system has several different ‘modes’ |
|
|
|
|
|
of operation. The response will be mode Alpha with addition of mode Charlie. In addition, |
|
|
|
|
|
the military have other modes of operation of SSR which overlap with civilian usage. In order |
|
|
|
|
|
to correctly indicate the required response code, the mode as well as code should always be |
|
|
|
|
|
specified. The pilot is to respond with the mode and code. Typically a radar controller will |
|
|
|
|
|
request the mode and code as follows: |
|
|
|
|
|
“G-CD, squawk Alpha two one six one” |
|
|
|
|
|
The response to this by the pilot will be (mode and code): |
|
|
|
|
|
“Squawking Alpha two one six one G-CD” |
|
|
|
|
|
13.4 Squawk Ident. The transponder has a facility to enable the radar controller to |
|
|
|
|
|
automatically identify the specific radar contact using SSR other than by reliance on the specific |
|
|
|
|
|
code transmission. This facility may be activated by selection of the ‘Ident’ feature on the |
|
|
|
|
|
transponder controller in response to a request to “squawk Ident.” Pilots are not to squawk |
|
|
|
|
|
Ident except on instruction from the radar controller. |
|
|
|
|
|
247
13
ACAS and SSR 13
SSR and ACAS
13.5 Special Codes. Because the airborne equipment can transmit any of 4096 individual coded responses, certain individual responses have been allocated specific meanings. The following special codes indicate:
• |
Emergency |
A/7700 |
• |
Radio failure |
A/7600 |
• |
Unlawful interference |
A/7500 |
Note : Should an aircraft have been radar identified by a transponder code and subsequently experience an emergency, the pilot should stick to the identified squawk.
In addition, the following reserved codes have the specific meanings:
• A/7000 Conspicuity. This is set when the aircraft is in an area where radar is used to provide ATS, but the pilot is not in receipt of a service (VFR outside CAS).
• A/2000 In the absence of any ATC direction or regional air navigation agreement (or when outside of a radar control/service area). This code is set when eastbound in the NAT region.
• A/0000 Unserviceable transponder. Set as directed by ATC.
13.6 Altitude Reporting Function (Mode Charlie). Mode Charlie encodes and transmits the aircraft altitude with reference to SPS (1013 hPa). Whenever the transponder is operating, mode Charlie should also be selected. At some point during the initial communications with ATC, the pilot will be requested to “say aircraft level for Charlie.” The pilot should report the aircraft level information accurate to the nearest full 100 ft. From this, the ATCO will determine the accuracy of mode Charlie data. If the mode Charlie data is within +/-300 ft of the stated level, mode Charlie is deemed to be accurate.
Figure 13.1
13.7 Transponder Failure. The failure of a transponder in the air will adversely affect the quality of the ATC service provided. Whilst every effort will be made to permit the flight to continue to the destination in accordance with the filed FP, it may be that ATC clearances may be restricted. If a transponder fails before departure and it cannot be rectified, the pilot is to:
248
