
- •Release History
- •Contents
- •List of Figures
- •List of Tables
- •1 TMS320TCI6618 Features
- •1.1 KeyStone Architecture
- •1.2 Device Description
- •1.3 Functional Block Diagram
- •2 Device Overview
- •2.1 Device Characteristics
- •2.2 CPU (DSP Core) Description
- •2.3 Memory Map Summary
- •2.4 Boot Sequence
- •2.5 Boot Modes Supported and PLL Settings
- •2.5.1 Boot Device Field
- •2.5.2 Device Configuration Field
- •2.5.2.1 No Boot Device Configuration
- •2.5.2.2 Serial Rapid I/O Boot Device Configuration
- •2.5.2.3 Ethernet (SGMII) Boot Device Configuration
- •2.5.2.4 PCI Boot Device Configuration
- •2.5.2.5 I2C Boot Device Configuration
- •2.5.2.6 SPI Boot Device Configuration
- •2.5.2.7 HyperLink Boot Device Configuration
- •2.5.3 PLL Settings
- •2.6 Second-Level Bootloaders
- •2.7 Terminals
- •2.8 Terminal Functions
- •2.9 Development
- •2.9.1 Development Support
- •2.9.2 Device Support
- •Related Documentation from Texas Instruments
- •3 Device Configuration
- •3.1 Device Configuration at Device Reset
- •3.2 Peripheral Selection After Device Reset
- •3.3 Device State Control Registers
- •3.3.1 Device Status (DEVSTAT) Register
- •3.3.2 Device Configuration Register
- •3.3.3 JTAG ID (JTAGID) Register Description
- •3.3.4 Kicker Mechanism (KICK0 and KICK1) Register
- •3.3.5 LRESETNMI PIN Status (LRSTNMIPINSTAT) Register
- •3.3.6 LRESETNMI PIN Status Clear (LRSTNMIPINSTAT_CLR) Register
- •3.3.7 Reset Status (RESET_STAT) Register
- •3.3.8 Reset Status Clear (RESET_STAT_CLR) Register
- •3.3.9 Boot Complete (BOOTCOMPLETE) Register
- •3.3.10 Power State Control (PWRSTATECTL) Register
- •3.3.11 NMI Even Generation to CorePac (NMIGRx) Register
- •3.3.12 IPC Generation (IPCGRx) Registers
- •3.3.13 IPC Acknowledgement (IPCARx) Registers
- •3.3.14 IPC Generation Host (IPCGRH) Register
- •3.3.15 IPC Acknowledgement Host (IPCARH) Register
- •3.3.16 Timer Input Selection Register (TINPSEL)
- •3.3.17 Timer Output Selection Register (TOUTPSEL)
- •3.3.18 Reset Mux (RSTMUXx) Register
- •3.4 Pullup/Pulldown Resistors
- •4 System Interconnect
- •4.1 Internal Buses, Bridges, and Switch Fabrics
- •4.2 Data Switch Fabric Connections
- •4.3 Configuration Switch Fabric
- •4.4 Bus Priorities
- •5 C66x CorePac
- •5.1 Memory Architecture
- •5.1.1 L1P Memory
- •5.1.2 L1D Memory
- •5.1.3 L2 Memory
- •5.1.4 MSM SRAM
- •5.1.5 L3 Memory
- •5.2 Memory Protection
- •5.3 Bandwidth Management
- •5.4 Power-Down Control
- •5.5 CorePac Resets
- •5.6 CorePac Revision
- •5.7 C66x CorePac Register Descriptions
- •6 Device Operating Conditions
- •6.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
- •6.2 Recommended Operating Conditions
- •6.3 Electrical Characteristics
- •7 TMS320TCI6618 Peripheral Information and Electrical Specifications
- •7.1 Parameter Information
- •7.1.1 1.8-V Signal Transition Levels
- •7.1.2 Timing Parameters and Board Routing Analysis
- •7.2 Recommended Clock and Control Signal Transition Behavior
- •7.3 Power Supplies
- •7.3.1 Power-Up Sequencing
- •7.3.1.1 Core-Before-IO Power Sequencing
- •7.3.1.2 IO-Before-Core Power Sequencing
- •7.3.1.3 Prolonged Resets
- •7.3.2 Power-Down Sequence
- •7.3.3 Power Supply Decoupling and Bulk Capacitors
- •7.3.4 SmartReflex
- •7.4 Enhanced Direct Memory Access (EDMA3) Controller
- •7.4.1 EDMA3 Device-Specific Information
- •7.4.2 EDMA3 Channel Synchronization Events
- •7.5 Interrupts
- •7.5.1 Interrupt Sources and Interrupt Controller
- •7.5.2 INTC Registers
- •7.5.2.1 INTC0 Register Map
- •7.5.2.2 INTC1 Register Map
- •7.5.2.3 INTC2 Register Map
- •7.5.3 Inter-Processor Register Map
- •7.5.4 NMI and LRESET
- •7.5.5 External Interrupts Electrical Data/Timing
- •7.6 Memory Protection Unit (MPU)
- •7.6.1 MPU Registers
- •7.6.1.1 MPU Register Map
- •7.6.1.2 Device-Specific MPU Registers
- •7.6.2 MPU Programmable Range Registers
- •7.6.2.1 Programmable Range n Start Address Register (PROGn_MPSAR)
- •7.6.2.2 Programmable Range n - End Address Register (PROGn_MPEAR)
- •7.6.2.3 Programmable Range n Memory Protection Page Attribute Register (PROGn_MPPA)
- •7.7 Reset Controller
- •7.7.1 Power-on Reset
- •7.7.2 Hard Reset
- •7.7.3 Soft Reset
- •7.7.4 Local Reset
- •7.7.5 Reset Priority
- •7.7.6 Reset Controller Register
- •7.7.7 Reset Electrical Data/Timing
- •7.8 Main PLL and the PLL Controller
- •7.8.1 Main PLL Controller Device-Specific Information
- •7.8.1.1 Internal Clocks and Maximum Operating Frequencies
- •7.8.1.2 Main PLL Controller Operating Modes
- •7.8.1.3 Main PLL Stabilization, Lock, and Reset Times
- •7.8.2 PLL Controller Memory Map
- •7.8.2.1 PLL Secondary Control Register (SECCTL)
- •7.8.2.2 PLL Controller Divider Register (PLLDIV2, PLLDIV5, PLLDIV8)
- •7.8.2.3 PLL Controller Clock Align Control Register (ALNCTL)
- •7.8.2.4 PLLDIV Divider Ratio Change Status Register (DCHANGE)
- •7.8.2.5 SYSCLK Status Register (SYSTAT)
- •7.8.2.6 Reset Type Status Register (RSTYPE)
- •7.8.2.7 Reset Control Register (RSTCTRL)
- •7.8.2.8 Reset Configuration Register (RSTCFG)
- •7.8.2.9 Reset Isolation Register (RSISO)
- •7.8.3 Main PLL Control Registers
- •7.8.4 Main PLL Controller/SRIO/HyperLink/PCIe Clock Input Electrical Data/Timing
- •7.9.1 DDR3 PLL Control Register
- •7.9.2 DDR3 PLL Device-Specific Information
- •7.9.3 DDR3 PLL Input Clock Electrical Data/Timing
- •7.10 PASS PLL
- •7.10.1 PASS PLL Control Register
- •7.10.2 PASS PLL Device-Specific Information
- •7.10.3 PASS PLL Input Clock Electrical Data/Timing
- •7.11 DDR3 Memory Controller
- •7.11.1 DDR3 Memory Controller Device-Specific Information
- •7.11.2 DDR3 Memory Controller Electrical Data/Timing
- •7.12 I2C Peripheral
- •7.12.1 I2C Device-Specific Information
- •7.12.2 I2C Peripheral Register Description(s)
- •7.12.3 I2C Electrical Data/Timing
- •7.12.3.1 Inter-Integrated Circuits (I2C) Timing
- •7.13 SPI Peripheral
- •7.13.1 SPI Electrical Data/Timing
- •7.13.1.1 SPI Timing
- •7.14 HyperLink Peripheral
- •7.15 UART Peripheral
- •7.16 PCIe Peripheral
- •7.17 Packet Accelerator
- •7.18 Security Accelerator
- •7.19 Ethernet MAC (EMAC)
- •7.20 Management Data Input/Output (MDIO)
- •7.21 Timers
- •7.21.1 Timers Device-Specific Information
- •7.21.2 Timers Electrical Data/Timing
- •7.22 Rake Search Accelerator (RSA)
- •7.23 Enhanced Viterbi-Decoder Coprocessor (VCP2)
- •7.24 Third-Generation Turbo Decoder Coprocessor (TCP3d)
- •7.25 Turbo Encoder Coprocessor (TCP3e)
- •7.26 Bit Rate Coprocessor (BCP)
- •7.27 Serial RapidIO (SRIO) Port
- •7.28 General-Purpose Input/Output (GPIO)
- •7.28.1 GPIO Device-Specific Information
- •7.28.2 GPIO Electrical Data/Timing
- •7.29 Semaphore2
- •7.30 Antenna Interface Subsystem 2
- •7.33 FFTC
- •7.34 Emulation Features and Capability
- •7.34.1 Advanced Event Triggering (AET)
- •7.34.2 Trace
- •7.34.2.1 Trace Electrical Data/Timing
- •7.34.3 IEEE 1149.1 JTAG
- •7.34.3.1 IEEE 1149.1 JTAG Compatibility Statement
- •7.34.3.2 JTAG Electrical Data/Timing
- •8 Mechanical Data
- •8.1 Packaging Information
- •8.2 Package CYP
INFORMATION ADVANCE
TMS320TCI6618 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Communications Infrastructure KeyStone SoC |
|
|
|
|||||
SPRS688—February 2011 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
www.ti.com |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
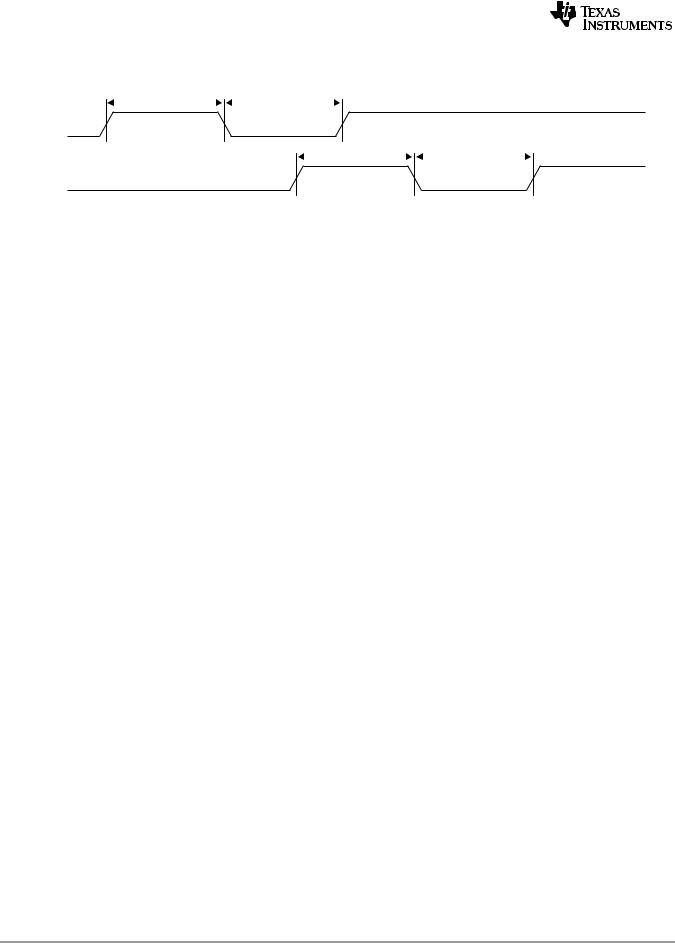
Figure 7-53 Timer Timing |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1 |
2 |
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
TIMIx |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
3 |
4 |
|
||||
TIMOx |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
7.22 Rake Search Accelerator (RSA)
There are four rake search accelerators (RSAs) on the TMS320TCI6618 device. CorePac 1 and CorePac 2 each have one set of directly-connected RSA pairs. The RSA is an extension of the C66x CPU. The CPU performs send/receive to the RSAs via the .L and .S functional units. For more information, see the Rake Search Accelerator (RSA) for KeyStone Devices User Guide in ‘‘Related Documentation from Texas Instruments’’ on page 59.
7.23 Enhanced Viterbi-Decoder Coprocessor (VCP2)
The TMS320TCI6618 device has four high-performance embedded Viterbi decoder coprocessors (VCP2) that significantly speeds up channel-decoding operations on-chip. Each VCP2, operating at CPU clock divided-by-3, can decode more than 694 7.95-Kbps adaptive multi-rate (AMR) [K = 9, R = 1/3] voice channels. The VCP2 supports constraint lengths K = 5, 6, 7, 8, and 9, rates R = 3/4, 1/2, 1/3, 1/4, and 1/5, and flexible polynomials, while generating hard decisions or soft decisions. Communications between the VCP2 and the CPU are carried out through the EDMA3 controller. The VCP2 supports:
•Unlimited frame sizes
•Code rates 3/4, 1/2, 1/3, 1/4, and 1/5
•Constraint lengths 5, 6, 7, 8, and 9
•Programmable encoder polynomials
•Programmable reliability and convergence lengths
•Hard and soft decoded decisions
•Tail and convergent modes
•Yamamoto logic
•Tail biting logic
•Various input and output FIFO lengths
For more information, see the Viterbi Coprocessor (VCP2) for KeyStone Devices User Guide in ‘‘Related Documentation from Texas Instruments’’ on page 59.
7.24 Third-Generation Turbo Decoder Coprocessor (TCP3d)
The TCI6618 device has three high-performance embedded turbo-decoder coprocessors (TCP3d) that significantly speed up channel-decoding operations on-chip for WCDMA, HSPA, HSPA+, TD-SCDMA, LTE, and WiMAX. Operating at CPU clock divided-by-2, the TCP3d is capable of processing data channels at a throughput of >100 Mbps. For more information, see the Turbo Decoder Coprocessor 3 (TCP3d) for KeyStone Devices User Guide
in ‘‘Related Documentation from Texas Instruments’’ on page 59.
188 |
Copyright 2011 Texas Instruments Incorporated |
