
- •Using Help
- •About online Help
- •Navigating in Help
- •Using bookmarks, the table of contents, the index, and Find
- •Contents
- •Introduction
- •Welcome
- •Registration
- •Installing Adobe Photoshop and ImageReady
- •Getting started
- •If you are new to Photoshop:
- •If you are an experienced Photoshop user:
- •If you want to focus on Web features:
- •If you want to concentrate on photo editing and retouching:
- •If you want to focus on productivity features:
- •Using the printed documentation
- •Using online Help
- •Using tool tips
- •Using Web resources
- •About Adobe Online
- •Using Adobe Online
- •Accessing Adobe Online through the Help menu
- •Other learning resources
- •Customer support
- •Customer support on Adobe Online
- •Additional customer support resources
- •An Overview of Adobe Photoshop
- •Explore state-of-the-art tools
- •Edit images with ease
- •Enjoy unlimited creative options
- •Create compelling Web designs
- •Enjoy precise typographic control
- •Stay ahead of deadlines
- •Automate repetitive tasks
- •Maintain color precisely
- •What’s New in Photoshop 7.0
- •Meet every challenge
- •Stay competitive
- •Take advantage of tighter-than-ever integration
- •Looking at the Work Area
- •About the work area
- •Using the toolbox
- •Toolbox overview (1 of 3)
- •Toolbox overview (2 of 3)
- •Toolbox overview (3 of 3)
- •Using the tools
- •Using the tool pointers
- •Using the tool options bar
- •Using the palette well (Photoshop)
- •Using tool presets (Photoshop)
- •Using palettes
- •Changing the palette display
- •Docking palettes together
- •Customizing your workspace
- •Using pop-up sliders
- •Using pop-up palettes
- •Using the Info palette (Photoshop)
- •Using context menus
- •Viewing images
- •Changing the screen display mode
- •Using the document window
- •Navigating the view area
- •Magnifying and reducing the view
- •Correcting mistakes
- •Reverting to a previous version of an image
- •About the History palette
- •Using the History palette
- •Setting history options (Photoshop)
- •Making a snapshot of an image (Photoshop)
- •Painting with a state or snapshot of an image (Photoshop)
- •Duplicating images
- •Using rulers
- •Using columns (Photoshop)
- •Using the measure tool (Photoshop)
- •Using guides and the grid
- •Working with Extras
- •Displaying status information (Photoshop)
- •Annotating images (Photoshop)
- •Adding notes and audio annotations
- •Opening and editing annotations
- •Jumping between applications
- •Jumping between Photoshop and ImageReady
- •Jumping to other applications (ImageReady)
- •Previewing an image in a browser
- •Managing libraries with the Preset Manager (Photoshop)
- •Setting preferences
- •Resetting all warning dialogs
- •Monitoring operations
- •Using plug-in modules
- •Assigning scratch disks
- •Getting Images into Photoshop and ImageReady
- •About bitmap images and vector graphics
- •About image size and resolution
- •Changing image size and resolution
- •Displaying image size information
- •About resampling
- •Choosing an interpolation method
- •Changing the pixel dimensions of an image
- •Changing the print dimensions and resolution of an image (Photoshop)
- •Determining a recommended resolution for an image (Photoshop)
- •Scanning images
- •Importing scanned images
- •Importing an image using the TWAIN interface
- •Importing images using WIA (Windows Image Acquisition) Support
- •Scanning using the resolution setting (Photoshop)
- •Optimizing the dynamic range of the scan (Photoshop)
- •Eliminating unwanted color casts (Photoshop)
- •Creating new images
- •Opening and importing images
- •Opening PostScript artwork
- •Importing PICT resources (Mac OS)
- •Using the File Browser (Photoshop)
- •About workgroup management
- •Getting started with workgroup management
- •Logging on and off WebDAV servers
- •Saving changes to the server
- •Working with Color
- •About color modes and models (Photoshop)
- •HSB model
- •RGB model
- •RGB mode
- •CMYK model
- •CMYK mode
- •L*a*b model
- •Lab mode
- •Bitmap mode
- •Grayscale mode
- •Duotone mode
- •Indexed Color mode
- •Multichannel mode
- •Color gamuts (Photoshop)
- •Adjusting the monitor display
- •Specifying 8-bit color display (Photoshop)
- •Making previews display more quickly (Photoshop)
- •Adjusting color display for cross-platform variations
- •Channels and bit depth (Photoshop)
- •About color channels
- •About bit depth
- •Converting between bit depths
- •Converting between color modes (Photoshop)
- •Converting between Grayscale and Bitmap modes (Photoshop)
- •Making Grayscale and Bitmap mode conversions
- •Converting to indexed color (Photoshop)
- •Conversion options for indexed-color images (Photoshop)
- •Palette type
- •Number of colors
- •Color inclusion and transparency
- •Dithering
- •Customizing indexed color tables (Photoshop)
- •Using the color table to edit colors and assign transparency
- •Saving and loading color tables
- •Producing Consistent Color (Photoshop)
- •About color management
- •Do you need color management?
- •Creating a viewing environment for color management
- •Setting up color management
- •About working spaces
- •About color management policies
- •Working with policy warnings and messages
- •Customizing color management settings
- •Specifying working spaces
- •Specifying color management policies
- •Customizing advanced color management settings
- •Specifying a color management engine
- •Specifying a rendering intent
- •Using dither
- •Desaturating monitor colors
- •Blending RGB colors
- •Saving and loading color management settings
- •Synchronizing color management between applications
- •Calibrating versus characterizing a monitor
- •About monitor calibration settings
- •Calibrating with Adobe Gamma (Windows)
- •Entering custom CMYK settings
- •Specifying ink colors
- •Specifying dot gain
- •Adjusting the separation type and black generation
- •Printing a hard proof
- •Making Color and Tonal Adjustments
- •Basic steps for correcting images
- •1. Calibrate your monitor.
- •2. Check the scan quality and tonal range.
- •3. Adjust the tonal range.
- •4. Adjust the color balance.
- •5. Make other special color adjustments.
- •6. Sharpen the edges of the image.
- •Checking scan quality and tonal range (Photoshop)
- •Using the color adjustment tools
- •Making color adjustments
- •Seeing the color values of pixels (Photoshop)
- •Saving and reapplying settings
- •Comparing corrections in CMYK and RGB (Photoshop)
- •Identifying out-of-gamut colors (Photoshop)
- •Using the Levels dialog box
- •Using Levels to set highlights, shadows, and midtones
- •Using Levels to adjust color (Photoshop)
- •Using the Curves dialog box (Photoshop)
- •Using target values to set highlights and shadows (Photoshop)
- •Setting auto correction options (Photoshop)
- •Adjusting the gamma value of an image (ImageReady)
- •About the color wheel
- •Using the Color Balance command (Photoshop)
- •Using the Hue/Saturation command
- •Using the Replace Color command (Photoshop)
- •Using the Selective Color command (Photoshop)
- •Making quick overall adjustments to an image
- •Using the Brightness/Contrast command
- •Using the Auto Levels command
- •Using the Auto Contrast command
- •Using the Auto Color command (Photoshop)
- •Using the Variations command
- •Applying special color effects to images
- •Using the Desaturate command
- •Using the Invert command
- •Using the Equalize command (Photoshop)
- •Using the Threshold command (Photoshop)
- •Using the Posterize command (Photoshop)
- •Using the Gradient Map command (Photoshop)
- •Sharpening images
- •Selecting
- •About selections
- •Making pixel selections
- •Using the Select menu
- •Using the marquee tools
- •Using the lasso, polygonal lasso, and magnetic lasso tools
- •Setting options for the lasso, polygonal lasso, and magnetic lasso tools
- •Using the magic wand tool
- •Using the Color Range command (Photoshop)
- •Creating selections from slices (ImageReady)
- •Adjusting pixel selections
- •Moving, hiding, or inverting a selection
- •Adjusting selections manually
- •Adjusting selections numerically
- •Softening the edges of a selection
- •Moving, copying, and pasting selections and layers
- •Copying selections or layers
- •Using drag and drop to copy between applications
- •Using the Clipboard to copy between applications
- •Using the Snap command
- •Saving and loading selections
- •Deleting selections
- •Removing fringe pixels from a selection (Photoshop)
- •Extracting objects from their background (Photoshop)
- •Transforming and Retouching
- •Changing the size of the work canvas
- •Cropping images
- •Transforming perspective while cropping (Photoshop)
- •Transforming objects in two dimensions
- •Specifying what to transform
- •Setting the reference point
- •Applying transformations
- •Using the Free Transform command
- •Transforming objects in three dimensions
- •Transforming and manipulating objects
- •Modifying the preview image
- •Setting 3D rendering options
- •Cloning and repairing images
- •Using the clone stamp tool
- •Using the pattern stamp tool
- •Using the healing brush tool (Photoshop)
- •Using the patch tool (Photoshop)
- •Retouching images
- •Using the smudge tool
- •Using the focus tools
- •Using the toning tools
- •Using the sponge tool
- •Using the Liquify command
- •Using the Liquify dialog box
- •Distorting images
- •Freezing and thawing areas
- •Reconstructing distortions
- •Saving and loading distortions
- •Drawing
- •About drawing and painting
- •Drawing shapes and paths
- •About the drawing tools
- •Creating shape layers
- •Creating a work path (Photoshop)
- •Creating rasterized shapes
- •Using the shape tools
- •Setting shape tool options
- •Using preset shapes (Photoshop)
- •Controlling a shape as you draw it
- •Using the pen tools (Photoshop)
- •Drawing with the pen tool
- •Drawing curves with the pen tool
- •Drawing with the freeform pen tool
- •Editing shape layers
- •Using the Paths palette (Photoshop)
- •Editing paths (Photoshop)
- •About anchor points, direction lines, direction points, and components
- •Selecting paths (Photoshop)
- •Moving, reshaping, and deleting path segments
- •Moving, reshaping, copying, and deleting path components
- •Aligning and distributing path components
- •Adding, deleting, and converting anchor points
- •Managing paths (Photoshop)
- •Converting between paths and selection borders (Photoshop)
- •Converting paths to selection borders
- •Converting selection borders to paths
- •Adding color to paths (Photoshop)
- •Filling paths with color
- •Stroking to paint path borders
- •Painting
- •Using the painting tools (Photoshop)
- •Using the painting tools (ImageReady)
- •Erasing
- •Using the eraser tool
- •Using the magic eraser tool
- •Using the background eraser tool (Photoshop)
- •Using the Auto Erase option
- •Using the art history brush tool (Photoshop)
- •Working with brushes
- •Using the Brushes palette (Photoshop)
- •Selecting preset brushes
- •Customizing brush tips (Photoshop)
- •About brush dynamics (Photoshop)
- •Specifying brush shape dynamics (Photoshop)
- •Specifying brush scattering (Photoshop)
- •Creating textured brushes (Photoshop)
- •Creating dual brushes (Photoshop)
- •Specifying color dynamics (Photoshop)
- •Specifying paint dynamics (Photoshop)
- •Adding noise to brush strokes (Photoshop)
- •Using wet brush edges (Photoshop)
- •Creating airbrush effects (Photoshop)
- •Smoothing brush strokes (Photoshop)
- •Protecting texture in brush strokes (Photoshop)
- •Copying textures between tools (Photoshop)
- •Clearing brush options (Photoshop)
- •Creating and managing preset brushes (Photoshop)
- •Setting options for painting and editing tools
- •Selecting a blending mode
- •Using the gradient tool (Photoshop)
- •Specifying the gradient transparency
- •Managing gradients
- •Using the paint bucket tool
- •Filling and stroking selections and layers
- •Filling a selection or layer with colors or patterns
- •Stroking a selection or layer with color
- •Creating and managing patterns
- •Managing patterns (Photoshop)
- •Using the Pattern Maker
- •Generating patterns
- •Previewing patterns
- •Reviewing tiles and pattern previews
- •Specifying pattern smoothness and detail
- •Choosing foreground and background colors
- •Using color settings in the toolbox
- •Using the eyedropper tool
- •Using the Color palette
- •Using the Swatches palette
- •Using the Adobe Color Picker
- •Specifying a color using numeric values
- •Using Web-safe colors
- •Recognizing nonprintable colors (Photoshop)
- •Choosing custom colors (Photoshop)
- •Choosing a custom color system (Photoshop)
- •Using other color pickers
- •Using Channels and Masks
- •About channels
- •Using the Channels palette (Photoshop)
- •Viewing channels
- •Changing the display of the palette
- •Selecting and editing channels
- •Managing channels (Photoshop)
- •Rearranging and renaming channels
- •Duplicating channels
- •Splitting channels into separate images
- •Merging channels
- •Deleting channels
- •Mixing color channels (Photoshop)
- •Adding spot colors (Photoshop)
- •About spot colors
- •Creating spot channels
- •Modifying spot channels
- •Adjusting overlapping spot colors
- •Using channel calculations to blend layers and channels (Photoshop)
- •Using the Apply Image command
- •Using the Calculations command
- •About the Add and Subtract blending modes
- •About masks (Photoshop)
- •Creating temporary masks in Quick Mask mode (Photoshop)
- •Storing masks in alpha channels
- •About alpha channels (Photoshop)
- •Creating alpha channels (Photoshop)
- •Saving a mask selection
- •Modifying alpha channels (Photoshop)
- •Loading a selection into an image
- •Using Layers
- •About layers
- •Using the Layers palette
- •Creating layers and layer sets
- •About the background layer
- •Adding layers and layer sets
- •Working with layered images
- •Selecting layers
- •Displaying the contents of layers
- •Duplicating layers
- •Changing the stacking order of layers
- •Linking layers
- •Repositioning the contents of layers
- •Locking layers
- •Unifying layers (ImageReady)
- •Sampling from layers
- •Managing layers
- •Renaming layers
- •Color coding layers
- •Rasterizing layers
- •Deleting layers
- •Merging layers
- •Flattening all layers
- •Setting opacity and blending options
- •Setting layer opacity
- •Choosing a blending mode
- •Filling new layers with a neutral color
- •Specifying knockout options
- •Restricting blending to channels (Photoshop)
- •Grouping blend effects
- •Specifying a range for blending layers (Photoshop)
- •Using layer effects and styles
- •About layer effects and styles
- •Applying preset styles
- •Creating custom styles
- •Displaying layer styles
- •Editing styles
- •Modifying layer effects with contours (Photoshop)
- •Applying global lighting
- •Creating and managing preset styles
- •Copying and pasting styles
- •Scaling layer effects (Photoshop)
- •Removing layer effects
- •Converting layer styles to layers
- •Masking layers
- •About masking layers
- •Creating and editing layer masks
- •Creating and editing vector masks
- •Unlinking layers and masks
- •Applying and discarding layer masks
- •Selecting opaque areas on a layer
- •Creating clipping groups
- •Applying Filters for Special Effects
- •Loading images and textures
- •Using texture and glass surface controls
- •Tips for creating special effects
- •Choosing a Lighting Effects type
- •Choosing a Lighting Effects style
- •Using a Lighting Effects texture
- •Using Type
- •About type
- •Creating type
- •About using the type tools (Photoshop)
- •Entering point type
- •Entering paragraph type
- •Creating a type selection border (Photoshop)
- •Working with type layers
- •Editing text in type layers
- •Rasterizing type layers
- •Changing type layer orientation
- •Specifying anti-aliasing
- •Converting between point type and paragraph type
- •Warping type layers
- •Creating a work path from type (Photoshop)
- •Converting type to shapes (Photoshop)
- •Formatting characters
- •Selecting characters
- •Using the Character palette
- •Choosing a font
- •Choosing a type size
- •Changing the type color
- •Specifying leading
- •Specifying kerning and tracking
- •Adjusting horizontal or vertical scale
- •Specifying baseline shift
- •Changing case
- •Making characters superscript or subscript
- •Applying underline and strikethrough
- •Using ligatures and old style numerals
- •Using fractional character widths
- •Viewing text using the operating system layout
- •Rotating vertical type
- •Checking for spelling errors (Photoshop)
- •Finding and replacing text (Photoshop)
- •Formatting paragraphs
- •Selecting paragraphs and showing the Paragraph palette
- •Aligning and justifying type
- •Indenting paragraphs
- •Changing space above or below paragraphs
- •Specifying hanging punctuation
- •Adjusting hyphenation
- •Preventing unwanted word breaks
- •Adjusting spacing
- •Working with composition
- •About composition methods
- •Choosing a composition method
- •Setting options for Chinese, Japanese, and Korean type (Photoshop)
- •Displaying CJK type options
- •Adjusting tsume
- •Specifying how leading is measured
- •Using tate-chuu-yoko
- •Specifying left and right underlining
- •Working with Japanese composition
- •Using burasagari
- •Designing Web Pages
- •About designing Web pages with Photoshop and ImageReady
- •Creating and viewing slices
- •About slices
- •Types of slices
- •Creating user slices
- •Creating layer-based slices
- •Converting auto slices to user slices
- •Viewing slices
- •Selecting and modifying slices
- •Using the Slice palette (ImageReady)
- •Selecting slices
- •Moving and resizing user slices
- •Dividing user slices and auto slices
- •Duplicating slices
- •Combining slices (ImageReady)
- •Arranging user slices and layer-based slices
- •Aligning user slices (ImageReady)
- •Distributing user slices (ImageReady)
- •Deleting user slices and layer-based slices
- •Locking slices (Photoshop)
- •Specifying slice options
- •Viewing slice options
- •Choosing a content type
- •Specifying slice names
- •Specifying slice background colors
- •Assigning a URL to an Image slice
- •Resizing and moving slices using numeric coordinates
- •Specifying browser messages
- •Adding HTML text to a slice
- •Optimizing slices
- •Linking slices (ImageReady)
- •Creating and viewing image maps (ImageReady)
- •Creating image maps
- •Converting layer-based image maps to tool-based image maps
- •Viewing image maps
- •Selecting and modifying image maps (ImageReady)
- •Using the Image Map palette (ImageReady)
- •Selecting image maps
- •Duplicating image maps
- •Arranging image maps
- •Aligning tool-based image maps
- •Distributing tool-based image maps
- •Deleting image maps
- •Specifying image map options (ImageReady)
- •Selecting an image map type (ImageReady)
- •Creating Web photo galleries (Photoshop)
- •Customizing and creating Web photo gallery styles (Photoshop)
- •About Web photo gallery styles
- •Customizing Web photo gallery styles
- •Creating new Web photo gallery styles
- •Using tokens in Web photo gallery styles
- •Creating Rollovers and Animations (ImageReady)
- •About working with layers in rollovers and animations
- •Editing layers in rollover states and animation frames
- •Unifying and matching layers rollovers and animations
- •Using the Rollovers palette
- •Creating and editing rollovers
- •About rollovers
- •Creating slices for rollovers
- •Creating rollover states
- •Editing rollover states
- •Previewing rollover states
- •Adding animation to rollover states
- •Applying and creating rollover styles
- •Copying and pasting rollover states
- •Duplicating rollover states
- •Rearranging and deleting rollover states
- •Creating and editing animations
- •About animation
- •Using the Animation palette
- •Adding frames
- •Selecting frames
- •Editing frames
- •Rearranging and deleting frames
- •Copying and pasting frames
- •Tweening frames
- •Specifying looping
- •Specifying delay for frames
- •Adding layers to frames
- •Setting the frame disposal method
- •Flattening frames into layers
- •Viewing animations
- •Optimizing animations
- •Viewing animated images in Photoshop
- •Saving animations
- •Saving animations as animated GIFs
- •Saving animations as QuickTime movies
- •Opening animated GIFs
- •Opening QuickTime movies as animations
- •About optimization
- •Optimizing images
- •Using the Save for Web dialog box (Photoshop)
- •Working with slices in the Save for Web dialog box (Photoshop)
- •Using the Optimize palette (ImageReady)
- •Viewing optimized images (ImageReady)
- •Applying optimization settings
- •Optimization options for GIF and PNG-8 formats
- •Optimization options for JPEG format
- •Optimization options for PNG-24 format
- •Optimization options for WBMP format
- •Saving and resetting optimization settings
- •Resizing the image during optimization (Photoshop)
- •Controlling optimization (ImageReady)
- •Setting optimization preferences (ImageReady)
- •Using weighted optimization
- •About masks and weighted optimization
- •Using masks to modify JPEG quality
- •Using masks to modify GIF lossiness
- •Using masks to modify dithering
- •Using masks to modify color reduction
- •Optimizing colors in GIF and PNG-8 images
- •Viewing a color table
- •Generating a color table
- •Changing the display of the color table
- •Adding new colors to the color table
- •Including black and white in a color table
- •Selecting colors
- •Shifting colors
- •Shifting to Web-safe colors
- •Mapping colors to transparency
- •Locking colors in the color table
- •Deleting colors from the color table
- •Loading and saving color tables
- •Using master palettes (ImageReady)
- •Working with hexadecimal values for color
- •Viewing hexadecimal values for colors in the Info palette
- •Copying colors as hexadecimal values
- •Using a droplet to automate optimization settings (ImageReady)
- •Saving optimized images
- •Setting output options
- •Using the Output Settings dialog box
- •Setting HTML output options
- •Setting slice output options
- •Setting image map output options (ImageReady)
- •Setting background options
- •Adding title and copyright information to Web pages
- •Saving and Exporting Images
- •Saving images
- •Exporting images in ZoomView format (Photoshop)
- •Photoshop format
- •Photoshop 2.0 (Photoshop)
- •AVI (ImageReady)
- •Photoshop EPS
- •Photoshop DCS 1.0 and 2.0 (Photoshop)
- •EPS TIFF or EPS PICT Preview (Photoshop)
- •Filmstrip
- •JPEG
- •PICT File
- •PICT Resource
- •Pixar
- •QuickTime Movie (ImageReady)
- •Raw (Photoshop)
- •Scitex CT (Photoshop)
- •Targa
- •TIFF
- •Adding digital copyright information
- •Before adding a watermark
- •Embedding digital watermarks
- •Using the Watermark Durability setting
- •Using the signal strength meter
- •Creating multiple-image layouts (Photoshop)
- •Creating contact sheets
- •Creating picture packages
- •Customizing picture package layouts
- •Placing Photoshop images in other applications (Photoshop)
- •Using image clipping paths to create transparency
- •Printing image clipping paths
- •Exporting paths to Adobe Illustrator
- •Object linking and embedding (OLE) (Windows only)
- •Printing (Photoshop)
- •About printing
- •Printing images
- •Positioning and scaling images
- •Setting output options
- •Selecting halftone screen attributes
- •Printing part of an image
- •Choosing a print encoding method
- •Printing vector graphics
- •Using color management when printing
- •Creating color traps
- •Printing duotones
- •About duotones
- •Modifying the duotone curve
- •Specifying overprint colors
- •Saving and loading duotone settings
- •Viewing individual printing plates
- •Printing duotones
- •Exporting duotone images to other applications
- •Printing color separations
- •Automating Tasks
- •About actions
- •Using the Actions palette
- •Recording actions
- •Creating a new action
- •Recording paths (Photoshop)
- •Inserting stops
- •Setting modal controls
- •Excluding commands
- •Inserting nonrecordable commands (Photoshop)
- •Specifying an output folder (ImageReady)
- •Recording image size options (ImageReady)
- •Inserting optimization settings for selected slices (ImageReady)
- •Playing actions
- •Setting playback options (Photoshop)
- •Editing actions
- •Rearranging actions and commands
- •Recording additional commands
- •Rerecording and duplicating actions and commands
- •Deleting actions and commands
- •Changing action options
- •Managing actions in the Actions palette
- •Saving and loading actions (Photoshop)
- •Saving actions (ImageReady)
- •Organizing sets of actions (Photoshop)
- •Using the Batch command (Photoshop)
- •Using droplets
- •Creating a droplet from an action
- •Creating droplets for use on different operating systems
- •Editing droplets (ImageReady)
- •Using droplets to automate optimization settings (ImageReady)
- •Using the Automate commands (Photoshop)
- •External automation
- •Creating templates for data-driven graphics (ImageReady)
- •About data-driven graphics
- •Using variables
- •Using data sets
- •Previewing data-driven graphics
- •Saving templates for use with other Adobe products
- •Macintosh Shortcuts
- •Viewing
- •Selecting and moving objects
- •Painting
- •Editing
- •Path editing*
- •Slicing and Optimizing
- •Windows Shortcuts
- •Viewing
- •Selecting and moving objects
- •Painting
- •Editing
- •Path editing*
- •Slicing and Optimizing
- •Legal Notices
- •Copyright
- •Index

Adobe Photoshop Help |
Making Color and Tonal Adjustments |
|
|
|
|
Using Help | Contents | Index |
Back |
144 |
Setting auto correction options (Photoshop)
The Auto Correction Options dialog box lets you automatically adjust the overall tonal range of an image, specify clipping percentages, and assign color values to shadows, midtones, and highlights. You can apply the settings during a single use of the Levels dialog box or Curves dialog box, or you can save the settings for future use with the Levels, Auto Levels, Auto Contrast, Auto Color, and Curves commands.
To set auto correction options:
1Click Options in the Levels dialog box or Curves dialog box.
2Specify the algorithm you want Photoshop to use to adjust the overall tonal range of an image:
•Enhance Monochromatic Contrast clips all channels identically. This preserves the overall color relationship while making highlights appear lighter and shadows appear darker. The Auto Contrast command uses this algorithm.
•Enhance Per Channel Contrast maximizes the tonal range in each channel to produce a more dramatic correction. Because each channel is adjusted individually, Enhance Per Channel Contrast may remove or introduce color casts. The Auto Levels command uses this algorithm.
•Find Dark & Light Colors finds the average lightest and darkest pixels in an image and uses them to maximize contrast while minimizing clipping. The Auto Color command uses this algorithm.
3Select Snap Neutral Midtones if you want Photoshop to find an average nearly neutral color in an image and then adjust the gamma values to make the color neutral. The Auto Color command uses this algorithm.
4To specify how much to clip black and white pixels, enter percentages in the Clip text boxes. A value between 0.5% and 1% is recommended.
By default, Photoshop clips the black and white pixels by 0.5%—that is, it ignores the first 0.5% of either extreme when identifying the lightest and darkest pixels in the image. This ensures that white and black values are based on representative rather than extreme pixel values.
5To assign color values to the darkest, neutral, and lightest areas of an image, click a color swatch. For guidelines on setting color values, see “Using target values to set highlights and shadows (Photoshop)” on page 141.
6Do one of the following:
•To save the settings for use in the current Levels or Curves dialog box, click OK. If you subsequently click the Auto button, Photoshop will reapply the same settings to the image.
•To save the settings as the default, select Save as Defaults, then click OK. The next time you open the Levels or Curves dialog box, you can apply the same setting by clicking the Auto button.The default clipping percentages are also used by the Auto Level, Auto Contrast, and Auto Color commands.
Using Help | Contents | Index |
Back |
144 |

Adobe Photoshop Help |
Making Color and Tonal Adjustments |
|
|
|
|
Using Help | Contents | Index |
Back |
145 |
Adjusting the gamma value of an image (ImageReady)
Gamma measures the brightness of midtone values produced by a device (often a monitor). A higher gamma value yields an overall darker image. Windows systems use a higher gamma value than Mac OS systems, with the result that the same image is noticeably darker on a Windows system than on a Mac OS system.
Image with Windows gamma and Mac OS gamma
Designers, particularly those who use Mac OS systems to create images that will be viewed primarily on Windows systems, must consider the issue of cross-platform gamma. You can modify the gamma value of an image to compensate for the differences between Windows and Mac OS monitors.
Note: The Gamma dialog box modifies the pixel values in an image. By contrast, the View > Preview commands adjust the appearance of the image on your monitor but do not change the image’s pixel values.
To adjust the gamma value automatically:
1Choose Image > Adjustments > Gamma.
2Select Preview to preview the adjustment in the image.
3Adjust the gamma:
•Select Windows to Macintosh to adjust gamma for display in Mac OS.
•Select Macintosh to Windows to adjust gamma for display in Windows.
Note: Images created in Photoshop 4.0 or earlier use Mac OS gamma value (1.8) by default and should be adjusted for display in Windows (unless gamma was adjusted when the image was created). Images created in Photoshop 5.0 or later use Windows gamma value (2.2) by default and will be at the correct gamma for display in Windows with no adjustment.
To adjust the gamma value manually:
1Choose Image > Adjustments > Gamma.
2Select Preview to preview the adjustment in the image.
3Drag the Gamma slider, or enter a value in the text box between 0.1 and 9.99. The Gamma slider measures the amount of change from the current gamma value. (The slider does not indicate the actual gamma value.)
Using Help | Contents | Index |
Back |
145 |

Adobe Photoshop Help |
Making Color and Tonal Adjustments |
|
|
|
|
Using Help | Contents | Index |
Back |
146 |
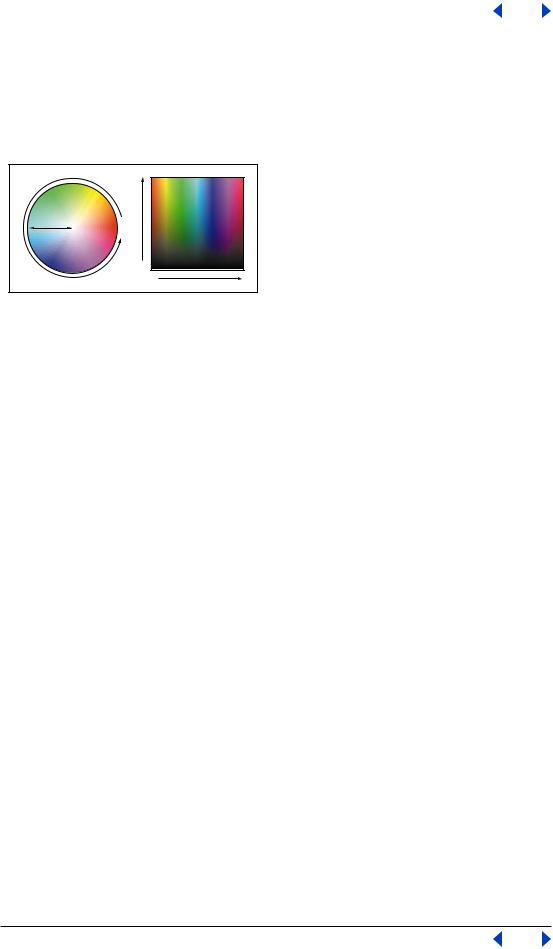
About the color wheel
Because there are numerous ways to achieve similar results in color balance, it’s useful to consider the type of image you have and the effect you want to produce. If you’re new to adjusting color components, it helps to keep a diagram of the color wheel on hand. You can use the color wheel to predict how a change in one color component affects other colors and also how changes translate between RGB and CMYK color models.
A
F 
 C
C
D
Color wheel:
A. Green B.Yellow C. Red D. Magenta E. Blue F. Cyan
For example, you can decrease the amount of any color in an image by increasing the amount of its opposite on the color wheel—and vice versa. Similarly, you can increase and decrease a color by adjusting the two adjacent colors on the wheel, or even by adjusting the two colors adjacent to its opposite.
In a CMYK image, you can decrease magenta either by decreasing the amount of magenta or its complement (by adding cyan and yellow). You can even combine these two corrections, minimizing their effect on overall lightness. In an RGB image, you can decrease magenta by removing red and blue or by adding green. All of these adjustments result in an overall color balance containing less magenta.
Using the Color Balance command (Photoshop)
The Color Balance command changes the overall mixture of colors in an image for generalized color correction.
To use the Color Balance command:
1Make sure the composite channel is selected in the Channels palette. This command is available only when you’re viewing the composite channel.
2Open the Color Balance dialog box. (See “Making color adjustments” on page 132.)
3Select Shadows, Midtones, or Highlights to select the tonal range on which you want to focus the changes.
4Select Preserve Luminosity to prevent changing the luminosity values in the image while changing the color. This option maintains the tonal balance in the image.
5Drag a slider toward a color you want to increase in the image; drag a slider away from a color you want to decrease in the image.
The values above the color bars show the color changes for the red, green, and blue channels. (For Lab images, the values are for the a and b channels.) Values can range from –100 to +100.
Using Help | Contents | Index |
Back |
146 |
Adobe Photoshop Help |
Making Color and Tonal Adjustments |
|
|
|
|
Using Help | Contents | Index |
Back |
147 |
Using the Hue/Saturation command
The Hue/Saturation command lets you adjust the hue, saturation, and lightness of the entire image or of individual color components in an image. Adjusting the hue, or color, represents a move around the color wheel. Adjusting the saturation, or purity of the color, represents a move across its radius.
A
B
C
D
Color wheel and radius of color wheel:
A. Saturation B. Hue C. Brightness D. Hues
You can also use the Colorize option to add color to a grayscale image converted to RGB, or to an RGB image—for example, to make it look like a duotone by reducing its color values to one hue.
To use the Hue/Saturation command:
1 Open the Hue/Saturation dialog box. (See “Making color adjustments” on page 132.)
The two color bars in the dialog box represent the colors in their order on the color wheel. The upper color bar shows the color before the adjustment; the lower bar shows how the adjustment affects all of the hues at full saturation.
2 (Photoshop) For Edit, choose which colors to adjust:
•Choose Master to adjust all colors at once.
•Choose one of the other preset color ranges listed for the color you want to adjust. An adjustment slider appears between the color bars, which you can use to edit any
range of hues. (For information on how to modify the slider’s range, see the instructions following this procedure.)
3 For Hue, enter a value or drag the slider until the colors appear as you want.
The values displayed in the text box reflect the number of degrees of rotation around the wheel from the pixel’s original color. A positive value indicates clockwise rotation, a negative value counterclockwise rotation. Values can range from –180 to +180.
4 For Saturation, enter a value or drag the slider to the right to increase the saturation or to the left to decrease it.
The color shifts away from or toward the center of the wheel, relative to the beginning color values of the selected pixels. Values can range from –100 to +100.
5 For Lightness, enter a value or drag the slider to the right to increase the lightness or to the left to decrease it. Values can range from –100 to +100.
Using Help | Contents | Index |
Back |
147 |

Adobe Photoshop Help |
Making Color and Tonal Adjustments |
|
|
|
|
Using Help | Contents | Index |
Back |
148 |
To modify the range of an adjustment slider (Photoshop):
1Choose an individual color from the Edit menu in the dialog box.
2Do any of the following to the adjustment slider:
•Drag one of the white triangles to adjust the amount of color fall-off without affecting the range.
•Drag the area between the triangle and the vertical bar to adjust the range without affecting the amount of fall-off.
•Drag the center area to move the entire adjustment slider, selecting a different
color area.
•Drag one of the vertical white bars next to the dark gray area to adjust the range of the color component. Increasing the range decreases the fall-off, and vice versa.
•Ctrl-drag (Windows) or Command-drag (Mac OS) the color bar so that a different color is in the center of the bar.
A B C D
Hue/Saturation adjustment slider:
A.Adjusts fall-off without affecting range B.Adjusts range without affecting fall-off C.Moves entire slider D. Adjusts range of color component
If you modify the adjustment slider so that it falls into a different color range, the name changes to reflect this. For example, if you choose Yellow and alter its range so that it falls in the red part of the color bar, the name changes to Red 2.You can convert up to six of the individual color ranges to varieties of the same color range (for example, Red through Red 6).
Note: By default, the range of color selected when you choose a color component is 30° wide, with 30° of fall-off on either side. Setting the fall-off too low can produce banding in the image.
3 To edit the range by choosing colors from the image, select the eyedropper tool  in the dialog box and click in the image. Use the eyedropper + tool to add to the range; use the eyedropper – tool to subtract from the range.
in the dialog box and click in the image. Use the eyedropper + tool to add to the range; use the eyedropper – tool to subtract from the range.
While the eyedropper tool is selected, you can also press Shift to add to the range or Alt (Windows) or Option (Mac OS) to subtract from it.
To colorize a grayscale image or create a monotone effect:
1(Photoshop) If you are colorizing a grayscale image, choose Image > Mode > RGB Color to convert the image to RGB.
2Open the Hue/Saturation dialog box. (See “Making color adjustments” on page 132.)
3Select Colorize.The image is converted to the hue of the current foreground color, if the foreground color is not black or white. The lightness value of each pixel does not change.
4Use the Hue slider to select a new color if desired. Use the Saturation and Lightness sliders to adjust the saturation and lightness of the pixels.
Using Help | Contents | Index |
Back |
148 |
