
- •Table of Contents
- •Chapter 1: Probabilistic Design
- •1.1. Understanding Probabilistic Design
- •1.1.1. Traditional (Deterministic) vs. Probabilistic Design Analysis Methods
- •1.1.2. Reliability and Quality Issues
- •1.2. Probabilistic Design Terminology
- •1.3. Using Probabilistic Design
- •1.3.1. Create the Analysis File
- •1.3.1.1. Example Problem Description
- •1.3.1.2. Build the Model Parametrically
- •1.3.1.3. Obtain the Solution
- •1.3.1.4. Retrieve Results and Assign as Output Parameters
- •1.3.1.5. Prepare the Analysis File
- •1.3.2. Establish Parameters for Probabilistic Design Analysis
- •1.3.3. Enter the PDS and Specify the Analysis File
- •1.3.4. Declare Random Input Variables
- •1.3.5. Visualize Random Input Variables
- •1.3.6. Specify Correlations Between Random Variables
- •1.3.7. Specify Random Output Parameters
- •1.3.8. Select a Probabilistic Design Method
- •1.3.8.1. Probabilistic Method Determination Wizard
- •1.3.9. Execute Probabilistic Analysis Simulation Loops
- •1.3.9.1. Probabilistic Design Looping
- •1.3.9.2. Serial Analysis Runs
- •1.3.9.3. PDS Parallel Analysis Runs
- •1.3.9.3.1. Machine Configurations
- •1.3.9.3.1.1. Choosing Slave Machines
- •1.3.9.3.1.2. Using the Remote Shell Option
- •1.3.9.3.1.3. Using the Connection Port Option
- •1.3.9.3.1.4. Configuring the Master Machine
- •1.3.9.3.1.5. Host setup using port option
- •1.3.9.3.1.6. Host and Product selection for a particular analysis
- •1.3.9.3.2. Files Needed for Parallel Run
- •1.3.9.3.3. Controlling Server Processes
- •1.3.9.3.4. Initiate Parallel Run
- •1.3.10. Fit and Use Response Surfaces
- •1.3.10.1. About Response Surface Sets
- •1.3.10.2. Fitting a Response Surface
- •1.3.10.3. Plotting a Response Surface
- •1.3.10.4. Printing a Response Surface
- •1.3.10.5. Generating Monte Carlo Simulation Samples on the Response Surfaces
- •1.3.11. Review Results Data
- •1.3.11.1. Viewing Statistics
- •1.3.11.2. Viewing Trends
- •1.3.11.3. Creating Reports
- •1.4. Guidelines for Selecting Probabilistic Design Variables
- •1.4.1. Choosing and Defining Random Input Variables
- •1.4.1.1. Random Input Variables for Monte Carlo Simulations
- •1.4.1.2. Random Input Variables for Response Surface Analyses
- •1.4.1.3. Choosing a Distribution for a Random Variable
- •1.4.1.3.1. Measured Data
- •1.4.1.3.2. Mean Values, Standard Deviation, Exceedence Values
- •1.4.1.3.3. No Data
- •1.4.1.4. Distribution Functions
- •1.4.2. Choosing Random Output Parameters
- •1.5. Probabilistic Design Techniques
- •1.5.1. Monte Carlo Simulations
- •1.5.1.1. Direct Sampling
- •1.5.1.2. Latin Hypercube Sampling
- •1.5.1.3. User-Defined Sampling
- •1.5.2. Response Surface Analysis Methods
- •1.5.2.1. Central Composite Design Sampling
- •1.5.2.2. Box-Behnken Matrix Sampling
- •1.5.2.3. User-Defined Sampling
- •1.6. Postprocessing Probabilistic Analysis Results
- •1.6.1. Statistical Postprocessing
- •1.6.1.1. Sample History
- •1.6.1.2. Histogram
- •1.6.1.3. Cumulative Distribution Function
- •1.6.1.4. Print Probabilities
- •1.6.1.5. Print Inverse Probabilities
- •1.6.2. Trend Postprocessing
- •1.6.2.1. Sensitivities
- •1.6.2.2. Scatter Plots
- •1.6.2.3. Correlation Matrix
- •1.6.3. Generating an HTML Report
- •1.7. Multiple Probabilistic Design Executions
- •1.7.1. Saving the Probabilistic Design Database
- •1.7.2. Restarting a Probabilistic Design Analysis
- •1.7.3. Clearing the Probabilistic Design Database
- •1.8. Example Probabilistic Design Analysis
- •1.8.1. Problem Description
- •1.8.2. Problem Specifications
- •1.8.2.1. Problem Sketch
- •1.8.3. Using a Batch File for the Analysis
- •1.8.4. Using the GUI for the PDS Analysis
- •Chapter 2: Variational Technology
- •2.1. Harmonic Sweep Using VT Accelerator
- •2.1.1. Structural Elements Supporting Frequency-Dependent Properties
- •2.1.2. Harmonic Sweep for Structural Analysis with Frequency-Dependent Material Properties
- •2.1.2.1. Beam Example
- •Chapter 3: Adaptive Meshing
- •3.1. Prerequisites for Adaptive Meshing
- •3.2. Employing Adaptive Meshing
- •3.3. Modifying the Adaptive Meshing Process
- •3.3.1. Selective Adaptivity
- •3.3.2. Customizing the ADAPT Macro with User Subroutines
- •3.3.2.1. Creating a Custom Meshing Subroutine (ADAPTMSH.MAC)
- •3.3.2.2. Creating a Custom Subroutine for Boundary Conditions (ADAPTBC.MAC)
- •3.3.2.3. Creating a Custom Solution Subroutine (ADAPTSOL.MAC)
- •3.3.2.4. Some Further Comments on Custom Subroutines
- •3.3.3. Customizing the ADAPT Macro (UADAPT.MAC)
- •3.4. Adaptive Meshing Hints and Comments
- •3.5. Where to Find Examples
- •Chapter 4: Rezoning
- •4.1. Benefits and Limitations of Rezoning
- •4.1.1. Rezoning Limitations
- •4.2. Rezoning Requirements
- •4.3. Understanding the Rezoning Process
- •4.3.1. Overview of the Rezoning Process Flow
- •4.3.2. Key Commands Used in Rezoning
- •4.4. Step 1: Determine the Substep to Initiate Rezoning
- •4.5. Step 2. Initiate Rezoning
- •4.6. Step 3: Select a Region to Remesh
- •4.7. Step 4: Perform the Remeshing Operation
- •4.7.1. Choosing a Remeshing Method
- •4.7.1.1. Remeshing Using a Program-Generated New Mesh (2-D)
- •4.7.1.1.1. Creating an Area to Remesh
- •4.7.1.1.2. Using Nodes From the Old Mesh
- •4.7.1.1.3. Hints for Remeshing Multiple Regions
- •4.7.1.1.4. Generating a New Mesh
- •4.7.1.2. Remeshing Using a Generic New Mesh (2-D and 3-D)
- •4.7.1.2.1. Using the REMESH Command with a Generic New Mesh
- •4.7.1.2.2. Requirements for the Generic New Mesh
- •4.7.1.2.3. Using the REGE and KEEP Remeshing Options
- •4.7.1.3. Remeshing Using Manual Mesh Splitting (2-D and 3-D)
- •4.7.1.3.1. Understanding Mesh Splitting
- •4.7.1.3.2. Geometry Details for Mesh Splitting
- •4.7.1.3.3. Using the REMESH Command for Mesh Splitting
- •4.7.1.3.4. Mesh-Transition Options for 2-D Mesh Splitting
- •4.7.1.3.5. Mesh-Transition Options for 3-D Mesh Splitting
- •4.7.1.3.7. Improving Tetrahedral Element Quality via Mesh Morphing
- •4.7.2. Mesh Control
- •4.7.3. Remeshing Multiple Regions at the Same Substep
- •4.8. Step 5: Verify Applied Contact Boundaries, Surface-Effect Elements, Loads, and Boundary Conditions
- •4.8.1. Contact Boundaries
- •4.8.2. Surface-Effect Elements
- •4.8.3. Pressure and Contiguous Displacements
- •4.8.4. Forces and Isolated Applied Displacements
- •4.8.5. Nodal Temperatures
- •4.8.6. Other Boundary Conditions and Loads
- •4.9. Step 6: Automatically Map Variables and Balance Residuals
- •4.9.1. Mapping Solution Variables
- •4.9.2. Balancing Residual Forces
- •4.9.3. Interpreting Mapped Results
- •4.9.4. Handling Convergence Difficulties
- •4.10. Step 7: Perform a Multiframe Restart
- •4.11. Repeating the Rezoning Process if Necessary
- •4.11.1. File Structures for Repeated Rezonings
- •4.12. Postprocessing Rezoning Results
- •4.12.1. The Database Postprocessor
- •4.12.1.1. Listing the Rezoning Results File Summary
- •4.12.1.2. Animating the Rezoning Results
- •4.12.1.3. Using the Results Viewer for Rezoning
- •4.12.2. The Time-History Postprocessor
- •4.13. Rezoning Restrictions
- •4.14. Rezoning Examples
- •4.14.1. Example: Rezoning Using a Program-Generated New Mesh
- •4.14.1.1. Initial Input for the Analysis
- •4.14.1.2. Rezoning Input for the Analysis
- •4.14.2. Example: Rezoning Using a Generic New Mesh
- •4.14.2.1. Initial Input for the Analysis
- •4.14.2.2. Exporting the Distorted Mesh as a CDB File
- •4.14.2.3. Importing the File into ANSYS ICEM CFD and Generating a New Mesh
- •4.14.2.4. Rezoning Using the New CDB Mesh
- •Chapter 5: Mesh Nonlinear Adaptivity
- •5.1. Mesh Nonlinear Adaptivity Benefits, Limitations and Requirements
- •5.1.1. Rubber Seal Simulation
- •5.1.2. Crack Simulation
- •5.2. Understanding the Mesh Nonlinear Adaptivity Process
- •5.2.1. Checking Nonlinear Adaptivity Criteria
- •5.2.1.1. Defining Element Components
- •5.2.1.2. Defining Nonlinear Adaptivity Criteria
- •5.2.1.3. Defining Criteria-Checking Frequency
- •5.3. Mesh Nonlinear Adaptivity Criteria
- •5.3.1. Energy-Based
- •5.3.2. Position-Based
- •5.3.3. Contact-Based
- •5.3.4. Frequency of Criteria Checking
- •5.4. How a New Mesh Is Generated
- •5.5. Convergence at Substeps with the New Mesh
- •5.6. Controlling Mesh Nonlinear Adaptivity
- •5.7. Postprocessing Mesh Nonlinear Adaptivity Results
- •5.8. Mesh Nonlinear Adaptivity Examples
- •5.8.1. Example: Rubber Seal Simulation
- •5.8.2. Example: Crack Simulation
- •Chapter 6: 2-D to 3-D Analysis
- •6.1. Benefits of 2-D to 3-D Analysis
- •6.2. Requirements for a 2-D to 3-D Analysis
- •6.3. Overview of the 2-D to 3-D Analysis Process
- •6.3.1. Overview of the 2-D to 3-D Analysis Process Flow
- •6.3.2. Key Commands Used in 2-D to 3-D Analysis
- •6.4. Performing a 2-D to 3-D Analysis
- •6.4.1. Step 1: Determine the Substep to Initiate
- •6.4.2. Step 2: Initiate the 2-D to 3-D Analysis
- •6.4.3. Step 3: Extrude the 2-D Mesh to the New 3-D Mesh
- •6.4.4. Step 4: Map Solution Variables from 2-D to 3-D Mesh
- •6.4.5. Step 5: Perform an Initial-State-Based 3-D Analysis
- •6.5. 2-D to 3-D Analysis Restrictions
- •Chapter 7: Cyclic Symmetry Analysis
- •7.1. Understanding Cyclic Symmetry Analysis
- •7.1.1. How the Program Automates a Cyclic Symmetry Analysis
- •7.1.2. Commands Used in a Cyclic Symmetry Analysis
- •7.2. Cyclic Modeling
- •7.2.1. The Basic Sector
- •7.2.2. Edge Component Pairs
- •7.2.2.1. CYCOPT Auto Detection Tolerance Adjustments for Difficult Cases
- •7.2.2.2. Identical vs. Dissimilar Edge Node Patterns
- •7.2.2.3. Unmatched Nodes on Edge-Component Pairs
- •7.2.2.4. Identifying Matching Node Pairs
- •7.2.3. Modeling Limitations
- •7.2.4. Model Verification (Preprocessing)
- •7.3. Solving a Cyclic Symmetry Analysis
- •7.3.1. Understanding the Solution Architecture
- •7.3.1.1. The Duplicate Sector
- •7.3.1.2. Coupling and Constraint Equations (CEs)
- •7.3.1.3. Non-Cyclically Symmetric Loading
- •7.3.1.3.1. Specifying Non-Cyclic Loading
- •7.3.1.3.2. Commands Affected by Non-Cyclic Loading
- •7.3.1.3.3. Plotting and Listing Non-Cyclic Boundary Conditions
- •7.3.1.3.4. Graphically Picking Non-Cyclic Boundary Conditions
- •7.3.2. Solving a Static Cyclic Symmetry Analysis
- •7.3.3. Solving a Modal Cyclic Symmetry Analysis
- •7.3.3.1. Understanding Harmonic Index and Nodal Diameter
- •7.3.3.2. Solving a Stress-Free Modal Analysis
- •7.3.3.3. Solving a Prestressed Modal Analysis
- •7.3.3.4. Solving a Large-Deflection Prestressed Modal Analysis
- •7.3.3.4.1. Solving a Large-Deflection Prestressed Modal Analysis with VT Accelerator
- •7.3.4. Solving a Linear Buckling Cyclic Symmetry Analysis
- •7.3.5. Solving a Harmonic Cyclic Symmetry Analysis
- •7.3.5.1. Solving a Full Harmonic Cyclic Symmetry Analysis
- •7.3.5.1.1. Solving a Prestressed Full Harmonic Cyclic Symmetry Analysis
- •7.3.5.2. Solving a Mode-Superposition Harmonic Cyclic Symmetry Analysis
- •7.3.5.2.1. Perform a Static Cyclic Symmetry Analysis to Obtain the Prestressed State
- •7.3.5.2.2. Perform a Linear Perturbation Modal Cyclic Symmetry Analysis
- •7.3.5.2.3. Restart the Modal Analysis to Create the Desired Load Vector from Element Loads
- •7.3.5.2.4. Obtain the Mode-Superposition Harmonic Cyclic Symmetry Solution
- •7.3.5.2.5. Review the Results
- •7.3.6. Solving a Magnetic Cyclic Symmetry Analysis
- •7.3.7. Database Considerations After Obtaining the Solution
- •7.3.8. Model Verification (Solution)
- •7.4. Postprocessing a Cyclic Symmetry Analysis
- •7.4.1. General Considerations
- •7.4.1.1. Using the /CYCEXPAND Command
- •7.4.1.1.1. /CYCEXPAND Limitations
- •7.4.1.2. Result Coordinate System
- •7.4.2. Modal Solution
- •7.4.2.1. Real and Imaginary Solution Components
- •7.4.2.2. Expanding the Cyclic Symmetry Solution
- •7.4.2.3. Applying a Traveling Wave Animation to the Cyclic Model
- •7.4.2.4. Phase Sweep of Repeated Eigenvector Shapes
- •7.4.3. Static, Buckling, and Full Harmonic Solutions
- •7.4.4. Mode-Superposition Harmonic Solution
- •7.5. Example Modal Cyclic Symmetry Analysis
- •7.5.1. Problem Description
- •7.5.2. Problem Specifications
- •7.5.3. Input File for the Analysis
- •7.5.4. Analysis Steps
- •7.6. Example Buckling Cyclic Symmetry Analysis
- •7.6.1. Problem Description
- •7.6.2. Problem Specifications
- •7.6.3. Input File for the Analysis
- •7.6.4. Analysis Steps
- •7.6.5. Solve For Critical Strut Temperature at Load Factor = 1.0
- •7.7. Example Harmonic Cyclic Symmetry Analysis
- •7.7.1. Problem Description
- •7.7.2. Problem Specifications
- •7.7.3. Input File for the Analysis
- •7.7.4. Analysis Steps
- •7.8. Example Magnetic Cyclic Symmetry Analysis
- •7.8.1. Problem Description
- •7.8.2. Problem Specifications
- •7.8.3. Input file for the Analysis
- •Chapter 8: Rotating Structure Analysis
- •8.1. Understanding Rotating Structure Dynamics
- •8.2. Using a Stationary Reference Frame
- •8.2.1. Campbell Diagram
- •8.2.2. Harmonic Analysis for Unbalance or General Rotating Asynchronous Forces
- •8.2.3. Orbits
- •8.3. Using a Rotating Reference Frame
- •8.4. Choosing the Appropriate Reference Frame Option
- •8.5. Example Campbell Diagram Analysis
- •8.5.1. Problem Description
- •8.5.2. Problem Specifications
- •8.5.3. Input for the Analysis
- •8.5.4. Analysis Steps
- •8.6. Example Coriolis Analysis
- •8.6.1. Problem Description
- •8.6.2. Problem Specifications
- •8.6.3. Input for the Analysis
- •8.6.4. Analysis Steps
- •8.7. Example Unbalance Harmonic Analysis
- •8.7.1. Problem Description
- •8.7.2. Problem Specifications
- •8.7.3. Input for the Analysis
- •8.7.4. Analysis Steps
- •Chapter 9: Submodeling
- •9.1. Understanding Submodeling
- •9.1.1. Nonlinear Submodeling
- •9.2. Using Submodeling
- •9.2.1. Create and Analyze the Coarse Model
- •9.2.2. Create the Submodel
- •9.2.3. Perform Cut-Boundary Interpolation
- •9.2.4. Analyze the Submodel
- •9.3. Example Submodeling Analysis Input
- •9.3.1. Submodeling Analysis Input: No Load-History Dependency
- •9.3.2. Submodeling Analysis Input: Load-History Dependency
- •9.4. Shell-to-Solid Submodels
- •9.5. Where to Find Examples
- •Chapter 10: Substructuring
- •10.1. Benefits of Substructuring
- •10.2. Using Substructuring
- •10.2.1. Step 1: Generation Pass (Creating the Superelement)
- •10.2.1.1. Building the Model
- •10.2.1.2. Applying Loads and Creating the Superelement Matrices
- •10.2.1.2.1. Applicable Loads in a Substructure Analysis
- •10.2.2. Step 2: Use Pass (Using the Superelement)
- •10.2.2.1. Clear the Database and Specify a New Jobname
- •10.2.2.2. Build the Model
- •10.2.2.3. Apply Loads and Obtain the Solution
- •10.2.3. Step 3: Expansion Pass (Expanding Results Within the Superelement)
- •10.3. Sample Analysis Input
- •10.4. Top-Down Substructuring
- •10.5. Automatically Generating Superelements
- •10.6. Nested Superelements
- •10.7. Prestressed Substructures
- •10.7.1. Static Analysis Prestress
- •10.7.2. Substructuring Analysis Prestress
- •10.8. Where to Find Examples
- •Chapter 11: Component Mode Synthesis
- •11.1. Understanding Component Mode Synthesis
- •11.1.1. CMS Methods Supported
- •11.1.2. Solvers Used in Component Mode Synthesis
- •11.2. Using Component Mode Synthesis
- •11.2.1. The CMS Generation Pass: Creating the Superelement
- •11.2.2. The CMS Use and Expansion Passes
- •11.2.3. Superelement Expansion in Transformed Locations
- •11.2.4. Plotting or Printing Mode Shapes
- •11.3. Example Component Mode Synthesis Analysis
- •11.3.1. Problem Description
- •11.3.2. Problem Specifications
- •11.3.3. Input for the Analysis: Fixed-Interface Method
- •11.3.4. Analysis Steps: Fixed-Interface Method
- •11.3.5. Input for the Analysis: Free-Interface Method
- •11.3.6. Analysis Steps: Free-Interface Method
- •11.3.7. Input for the Analysis: Residual-Flexible Free-Interface Method
- •11.3.8. Analysis Steps: Residual-Flexible Free-Interface Method
- •11.3.9. Example: Superelement Expansion in a Transformed Location
- •11.3.9.1. Analysis Steps: Superelement Expansion in a Transformed Location
- •11.3.10. Example: Reduce the Damping Matrix and Compare Full and CMS Results with RSTMAC
- •Chapter 12: Rigid-Body Dynamics and the ANSYS-ADAMS Interface
- •12.1. Understanding the ANSYS-ADAMS Interface
- •12.2. Building the Model
- •12.3. Modeling Interface Points
- •12.4. Exporting to ADAMS
- •12.4.1. Exporting to ADAMS via Batch Mode
- •12.4.2. Verifying the Results
- •12.5. Running the ADAMS Simulation
- •12.6. Transferring Loads from ADAMS
- •12.6.1. Transferring Loads on a Rigid Body
- •12.6.1.1. Exporting Loads in ADAMS
- •12.6.1.2. Importing Loads
- •12.6.1.3. Importing Loads via Commands
- •12.6.1.4. Reviewing the Results
- •12.6.2. Transferring the Loads of a Flexible Body
- •12.7. Methodology Behind the ANSYS-ADAMS Interface
- •12.7.1. The Modal Neutral File
- •12.7.2. Adding Weak Springs
- •12.8. Example Rigid-Body Dynamic Analysis
- •12.8.1. Problem Description
- •12.8.2. Problem Specifications
- •12.8.3. Command Input
- •Chapter 13: Element Birth and Death
- •13.1. Elements Supporting Birth and Death
- •13.2. Understanding Element Birth and Death
- •13.3. Element Birth and Death Usage Hints
- •13.3.1. Changing Material Properties
- •13.4. Using Birth and Death
- •13.4.1. Build the Model
- •13.4.2. Apply Loads and Obtain the Solution
- •13.4.2.1. Define the First Load Step
- •13.4.2.1.1. Sample Input for First Load Step
- •13.4.2.2. Define Subsequent Load Steps
- •13.4.2.2.1. Sample Input for Subsequent Load Steps
- •13.4.3. Review the Results
- •13.4.4. Use Analysis Results to Control Birth and Death
- •13.4.4.1. Sample Input for Deactivating Elements
- •13.5. Where to Find Examples
- •Chapter 14: User-Programmable Features and Nonstandard Uses
- •14.1. User-Programmable Features (UPFs)
- •14.1.1. Understanding UPFs
- •14.1.2. Types of UPFs Available
- •14.2. Nonstandard Uses of the ANSYS Program
- •14.2.1. What Are Nonstandard Uses?
- •14.2.2. Hints for Nonstandard Use of ANSYS
- •Chapter 15: State-Space Matrices Export
- •15.1. State-Space Matrices Based on Modal Analysis
- •15.1.1. Examples of SPMWRITE Command Usage
- •15.1.2. Example of Reduced Model Generation in ANSYS and Usage in Simplorer
- •15.1.2.1. Problem Description
- •15.1.2.2. Problem Specifications
- •15.1.2.3. Input File for the Analysis
- •Chapter 16: Soil-Pile-Structure Analysis
- •16.1. Soil-Pile-Structure Interaction Analysis
- •16.1.1. Automatic Pile Subdivision
- •16.1.2. Convergence Criteria
- •16.1.3. Soil Representation
- •16.1.4. Mudslides
- •16.1.5. Soil-Pile Interaction Results
- •16.1.5.1. Displacements and Reactions
- •16.1.5.2. Forces and Stresses
- •16.1.5.3. UNITY Check Data
- •16.2. Soil Data Definition and Examples
- •16.2.1. Soil Profile Data Definition
- •16.2.1.1. Mudline Position Definition
- •16.2.1.2. Common Factors for P-Y, T-Z Curves
- •16.2.1.3. Horizontal Soil Properties (P-Y)
- •16.2.1.3.1. P-Y curves defined explicitly
- •16.2.1.3.2. P-Y curves generated from given soil properties
- •16.2.1.4. Vertical Soil Properties (T-Z)
- •16.2.1.4.1. T-Z curves defined explicitly
- •16.2.1.4.2. T-Z curves generated from given soil properties
- •16.2.1.5. End Bearing Properties (ENDB)
- •16.2.1.5.1. ENDB curve defined explicitly
- •16.2.1.5.2. ENDB curves generated from given soil properties
- •16.2.1.6. Mudslide Definition
- •16.2.2. Soil Data File Examples
- •16.2.2.1. Example 1: Constant Linear Soil
- •16.2.2.2. Example 2: Non-Linear Soil
- •16.2.2.3. Example 3: Soil Properties Defined in 5 Layers
- •16.2.2.4. Example 4: Soil Properties Defined in 5 Layers with Mudslide
- •16.3. Performing a Soil-Pile Interaction Analysis
- •16.3.2. Mechanical APDL Component System Example
- •16.3.3. Static Structural Component System Example
- •16.4. Soil-Pile-Structure Results
- •16.5. References
- •Chapter 17: Coupling to External Aeroelastic Analysis of Wind Turbines
- •17.1. Sequential Coupled Wind Turbine Solution in Mechanical APDL
- •17.1.1. Procedure for a Sequentially Coupled Wind Turbine Analysis
- •17.1.2. Output from the OUTAERO Command
- •Chapter 18: Applying Ocean Loading from a Hydrodynamic Analysis
- •18.1. How Hydrodynamic Analysis Data Is Used
- •18.2. Hydrodynamic Load Transfer with Forward Speed
- •18.3. Hydrodynamic Data File Format
- •18.3.1. Comment (Optional)
- •18.3.2. General Model Data
- •18.3.3. Hydrodynamic Surface Geometry
- •18.3.4. Wave Periods
- •18.3.5. Wave Directions
- •18.3.6. Panel Pressures
- •18.3.7. Morison Element Hydrodynamic Definition
- •18.3.8. Morison Element Wave Kinematics Definition
- •18.3.9. RAO Definition
- •18.3.10. Mass Properties
- •18.4. Example Analysis Using Results from a Hydrodynamic Diffraction Analysis
- •Index
- •ОГЛАВЛЕНИЕ
- •ВВЕДЕНИЕ
- •1.1. Методология проектирования технологических объектов
- •1.2. Компьютерные технологии проектирования
- •1.3. Системы автоматизированного проектирования в технике
- •1.4. Системы инженерного анализа
- •2.2.1. Создание и сохранение чертежа
- •2.2.2. Изменение параметров чертежа
- •2.2.3. Заполнение основной надписи
- •2.2.4. Создание нового вида. Локальная система координат
- •2.2.5. Вычерчивание изображения прокладки
- •2.2.6. Простановка размеров
- •2.2.7. Ввод технических требований
- •2.2.8. Задание материала изделия
- •2.3. Сложные разрезы в чертеже детали «Основание»
- •2.3.1. Подготовка чертежа
- •Cохранить документ.
- •2.3.2. Черчение по сетке из вспомогательных линий
- •2.3.3. Изображение разрезов
- •2.4. Чертежи общего вида при проектировании
- •3.1. Интерфейс программы
- •3.2. Общее представление о трехмерном моделировании
- •3.3. Основные операции геометрического моделирования
- •3.3.1. Операция выдавливания
- •3.3.2. Операция вращения
- •3.3.3. Кинематическая операция
- •3.3.4. Построение тела по сечениям
- •3.4. Операции конструирования
- •3.4.1. Построение фасок и скруглений
- •3.4.2. Построение уклона
- •3.4.3. Сечение модели плоскостью
- •3.4.4. Сечение по эскизу
- •3.4.5. Создание моделей-сборок
- •3.5. Разработка электронных 3D-моделей тепловых устройств
- •3.5.1. Электронные модели в ЕСКД
- •3.5.2. Электронные «чертежи» в ЕСКД
- •3.5.4. Электронная модель сборочного изделия «Газовая горелка»
- •ГЛАВА 4. ИНЖЕНЕРНЫЙ АНАЛИЗ ГАЗОДИНАМИКИ И ТЕПЛООБМЕНА В ANSYS CFX
- •4.1. Область применения ANSYS CFX
- •4.2. Особенности вычислительного процесса в ANSYS CFX
- •4.3. Программы, используемые при расчетах в ANSYS CFX
- •4.4. Организация процесса вычислений в среде пакета Workbench
- •4.4.1. Графический интерфейс пользователя
- •5.1. Постановка теплофизических задач в ANSYS Multiphysics
- •5.2. Решение задач в пакете ANSYS Multiphysics
- •5.2.1. Графический интерфейс пользователя
- •5.2.2. Этапы препроцессорной подготовки решения
- •5.2.3. Этап получения решения и постпроцессорной обработки результатов
- •5.3.5. Нестационарный теплообмен. Нагрев пластины в печи с жидким теплоносителем
- •5.4.1. Температурные напряжения при нагреве
- •БИБЛИОГРАФИЧЕСКИЙ СПИСОК

vk.com/club152685050 | vk.com/id446425943 |
Using Probabilistic Design |
The ANSYS Thin Server will start without any message and will continue running in the background until the machine is restarted or you kill the process. You may close or minimize the window in which the ANSYS Thin Server was started.
Stop the ANSYS Thin Server
The ANSYS Thin Server should be stopped once the parallel process is complete.
Stopping on a PC
You may stop the process by closing the command prompt window or using Ctrl-C.
Stopping on a Linux Machine
On a Linux machine use ps -u UserId | grep tclsh in the command line to determine under which process ID the ANSYS Thin Server is running. Here, UserId is your user account name on the machine. With this "ps" command should get two processes running. Typically, there will be two processes listed, one process for anstclsh and another for tclsh. Use kill -9 process-id to kill both processes. Under certain circumstances, killing the anstclsh process also kills the tclsh process. (Issue the ps command again to verify.) If this does not happen, then kill the tclsh process separately.
1.3.9.3.1.4. Configuring the Master Machine
After you have configured the slave machines you need to configure the master machine for the type of ANSYS Thin Server startup you chose to use on the slave machines. The communication from the master machine to the slave machines is done by the ANSYS Nanny which is a program running in the parent process. It takes care of running the necessary simulations on different slave machines. It will establish the connection to the slave machines, copy the necessary files over to the slave machines,
start and monitor the running simulations and clean up the working directories after the entire sequence of simulations is finished. The ANSYS Nanny will be started automatically as you start executing PDS simulations in parallel, distributed mode.
For parallel processing you need to specify the remote hosts you want to use. This information is placed in a file named hosts150.ans. You can create this file using a text editor or you can use the ANS_ADMIN utility (see the online help available with the ANS_ADMIN utility for more information). This file contains host information for all remote machines on which you may want to run. This file is global and does not contain job-specific information. Typically, your IT administrator would provide
this file, including all the information about the slave machines a typical user can use in your network. If you have multiple users running parallel or distributed jobs at your site, you should have one hosts150.ans file for all users. But you can copy this file to your local working directory and make adjustments. ANSYS searches for this file first in the local directory, followed by the home directory, and finally the apdl directory.
You have two options when setting up the Master Machine to use the ANSYS Thin Server on the slave machines.
Configuration when the Thin Server uses the Remote Shell Option
Let's assume that the slave machine called "MySlaveMachine" has been prepared to work under the remote shell option as outlined above. The slave machine "MySlaveMachine" is an SGI machine and it has 4 CPUs. On the slave machine we also want to use the directory "/tmp/sdr/pds_runs" as the local directory for the remote simulations to run in. In this case your hosts150.ans file must include the lines:
Release 15.0 - © SAS IP, Inc. All rights reserved. - Contains proprietary and confidential information |
|
of ANSYS, Inc. and its subsidiaries and affiliates. |
33 |

vk.com/club152685050Probabi istic Design | vk.com/id446425943
# |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
# |
HOST |
OS |
PORT |
CPU |
TIME |
|
LocPORT |
I/O Directory |
MySlaveMachine |
SGI64 |
0 |
4 |
15 |
0 |
/tmp/sdr/pds_runs |
||
Configuration when the Thin Server uses the Port Option
Assume that you now want to use the same slave machine "MySlaveMachine" using the ANSYS Thin Server. The ANSYS Thin Server has been started on a slave machine called “MySlaveMachine" using the command ansysts150 62000 as shown above. Assume also that the file AnsysClients looks exactly like shown in the section above, i.e. your master machine "MyMasterMachine" can communicate to the ANSYS Thin Server using the communication port numbers 59400-59430. In this case, your hosts150.ans file must include the lines:
# |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
# |
HOST |
OS |
PORT |
CPU |
TIME |
LocPORT |
I/O Directory |
||
MySlaveMachine |
SGI64 |
62000 |
4 |
15 |
59400-59430 |
/tmp/sdr/pds_runs |
|||
This will ensure that the ANSYS Thin Server on the slave machine will be contacted using the same connection port it has been started with, i.e. 62000 in this case. Also the communication will use the same communication port numbers the ANSYS Thin Server accepts from the machine "MyMasterMachine" where you try to connect from.
An example hosts150.ans file looks like this:
#This file is used to specify those hosts that the ANSYS Nanny may
#run children on.
#
#Each host entry is to be on its own line. The host entry consists of
#several fields which are space delimited.
#
#Field 1 - host IP address or name
#Field 2 - host machine type
#Field 3 - execution key (used for Probabilistic Design only):
#0-Use a remote shell to start the child process;
#this requires a remote shell server to be
#running on the host machine.
#>1024-Use a running ANSYS thin server on the host
#which is listening on this port number.
#Field 4 - The default maximum number of jobs to run on this host
#Field 5 - The time in minutes to check again if the host is available.
#If this is zero then the host will not be checked again.
#Field 6 - The local port number to start the communication with the
#ANSYS Thin Server on. This is tied to authentication on the
#ANSYS Thin Server.
#Field 7 - The directory to create the children subdirectories in
#Field 8 - The cluster type. Only valid entry is MPI.
#Field 9 - The speed factor (relative speed to other machines listed).
Only valid entry is 1.
#Field 10 - Number of OpenMP threads. Only valid entry is 1.
#Example:
#
#UNIX box that has five processors
# zeus sgi64 |
0 |
5 30 |
2000 |
/scratch/wjc |
#Microsoft box using the ANSYS Thin Server
# wjcpc |
XP |
2010 |
1 0 |
|
2000 |
C:\TEMP |
|
|
alpha1 |
alpha |
0 |
1 |
15 |
2000 |
/scratch/epc |
MPI 1 1 |
|
athena |
sgi64 |
0 |
1 |
15 |
2000 |
/scratch/epc |
MPI 1 1 |
|
rs43p |
rs6000 |
0 |
1 |
15 |
2000 |
/home/pdstest |
MPI 1 1 |
|
rs260 |
rs64 |
0 |
1 |
15 |
2000 |
/home/pdstest |
MPI 1 1 |
|
snoopy |
hppa8000 |
0 |
1 |
15 |
2000 |
/home/pdstest |
MPI 1 1 |
|
alpha24 |
alpha |
0 |
1 |
15 |
2000 |
/home/pdstest |
MPI 1 |
1 |
hp770 |
hppa8000 |
0 |
1 |
15 |
2000 |
/home/pdstest |
MPI 1 |
1 |
us60 |
usparc |
0 |
1 |
15 |
2000 |
/home/pdstest |
MPI 1 |
1 |
ss60 |
sun64 |
0 |
1 |
15 |
2000 |
/home/pdstest |
MPI 1 |
1 |
|
Release 15.0 - © SAS IP, Inc. All rights reserved. - Contains proprietary and confidential information |
34 |
of ANSYS, Inc. and its subsidiaries and affiliates. |
vk.com/club152685050 | vk.com/id446425943 |
Using Probabilistic Design |
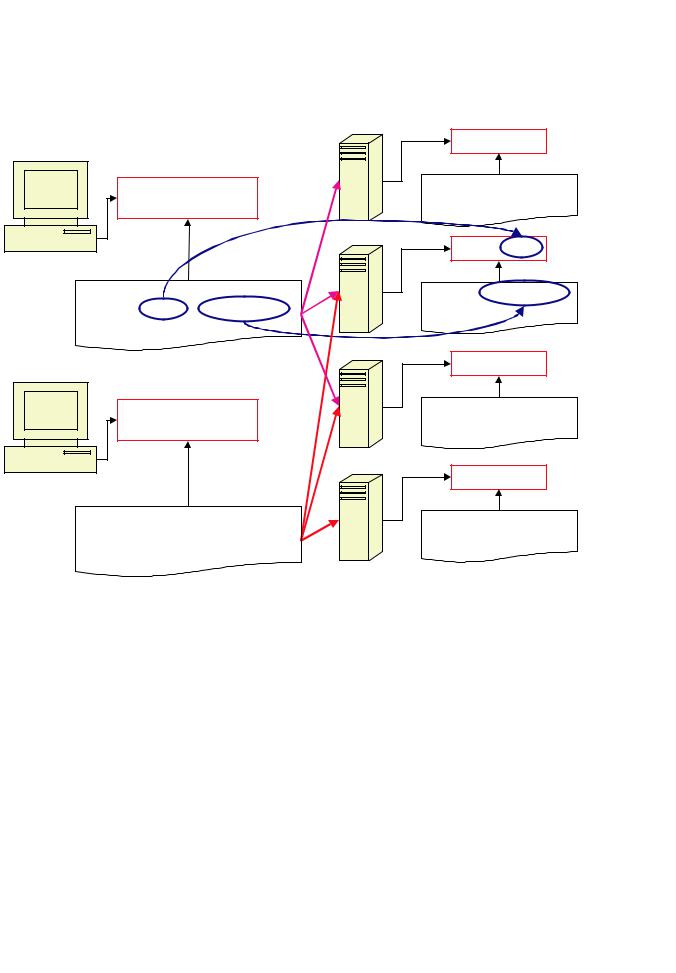
1.3.9.3.1.5. Host setup using port option
The picture below illustrates an example of the set-up of a network with 2 master machines and 4 slave machines using the connection port option. Here, the first master machines uses slave machines 1, 2 and 3, while the second master machine is using only slave machines 2, 3 and 4. In this illustration "NN" represents the revision number of ANSYS.
|
|
|
n y 61111 |
||
|
|
|
A s sClie ts |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Master1 |
51100-51199 |
|
Master1 |
ANSYS sessio |
|
|||
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
||
|
Usi g nny |
|
Master2 |
52100-52199 |
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
n y 62222 |
||
hosts .a s |
|
A s sClie ts |
|
||
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
||
|
Server1 61111 51100 -51199 |
|
Master1 |
51100-51199 |
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Server2 62222 51100 -51199 |
|
Master2 |
52200-52299 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Server3 63333 51100 -51199 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
n y 63333 |
||
|
|
|
A s sClie ts |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
Master2 |
ANSYS sessio |
|
Master1 |
51100-51199 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Usi g nny |
|
Master2 |
52200-52299 |
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
n y 64444 |
||
hosts .a s |
|
|
|
A s sClie ts |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
||
Server2 62222 52200 |
-52299 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Master1 |
51100-51199 |
||||
|
|
|
||||
Server3 63333 52200 |
-52299 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Master2 |
52200-52299 |
||||
|
|
|
|
|||
Server4 64444 52200 |
-52299 |
|
|
|
||
1.3.9.3.1.6. Host and Product selection for a particular analysis
After specifying the hosts145.ans file, provide the specific information that may change from analysis to analysis.
If you are working in interactive mode then select:
Main Menu> Prob Design> Run> Exec Parallel> Host Select
In this menu you can:
•Select the slave machines you want to use for a particular analysis. This is necessary, for example, if you know that some machines in your network are in use by another user at the time you want to start the analysis.
•Select the licenses you want to use for the particular analysis. If there are multiple levels of licenses of ANSYS available in your network, then you should first select the lower license that will be able to run your analysis.
Based on the information provided in the menu, a Jobname.hosts file is created or updated as you press OK in the menu.
Release 15.0 - © SAS IP, Inc. All rights reserved. - Contains proprietary and confidential information |
|
of ANSYS, Inc. and its subsidiaries and affiliates. |
35 |
