- •1 Structure of a business letter
- •1 This is how a business school teacher is explaining the parts of a business letter to a student:
- •2 Now read the letter and name its elements:
- •Grammar: The Sequence of Tenses – Узгодження часів
- •2 Writing a business e-mail
- •1 Why do people use e-mail in business? Make a list of reasons.
- •2 Read some 'rules' for writing good business e-mails. Which rules do you follow?
- •3 Read the e-mail below from a student to a company about their work experience programme. Which rules in ex 2 does he break?
- •4 Look al the phrases in italics (1-6) in the e-mail. Match them with the formal phrases (a-f) below:
- •5 Here are some phrases to use in e-mails. Write starting (s), ending (e), saying why you are writing (w) or requesting (r) after each one and the ones in ex 4:
- •6 Rewrite Luigi’s e-mail using the rules in ex 2 and some of the phrases in ex 5. Grammar: Reported Speech (statements) – Непряма мова (стверджувальні речення)
- •3 Doing Business on the Internet
- •1 Match words that have a similar meaning:
- •Grammar: Reported Questions, Requests, Orders – Непрямі питання, прохання, накази
- •4 Business across Cultures
- •1 Match words that have a similar meaning:
- •2 Match the words and phrases in the box with the correct definition:
- •5 Put these statements about customs and culture into the correct order. Translate the sentences:
- •Grammar: First Conditional – Умовні речення і типу
- •5 What is Economics About?
- •1 Read the following words and try to guess their meaning. Mind the stress!
- •2 Match English and Ukrainian equivalents:
- •3 Choose the correct word:
- •4 Complete the sentences:
- •Grammar Second Conditional – Умовні речення іі типу
- •6 Products, Goods and Services
- •1 Match words that have a similar meaning:
- •3 Match the words and phrases in the box with the correct definition:
- •Grammar: Third Conditional – Умовні речення ііі типу
- •7 Markets
- •I. Give English equivalents of the following:
- •III. Answer the questions:
- •IV. Translate into English:
- •Grammar: Modals – Модальні дієслова (1) Ability (здатність, спроможність): can, could, be able to
- •Permission (дозвіл): can, could, may, be allowed to
- •8 Export and Import
- •1 Match words that have a similar meaning:
- •4 Fill in the missing prepositions: (of (2), in, at (2), by (3), on (2), for, through, to)
- •5 Translate into English:
- •Grammar: Modals – Модальні дієслова (2)
- •9 Money and its functions
- •1 Match words that have a similar meaning:
- •2 Translate the sentences into Ukrainian. Define the part of speech of the underlined words:
- •3 The words in the box frequently occur before "money". Find combinations that mean:
- •4 Match the words and phrases in the box with the correct definition:
- •Grammar: Modals with the Perfect Infinitive – Модальні дієслова з перфектним інфінітивом
- •10 Aggregate supply
- •I. Find equivalents:
- •II. Match the synonyms:
- •III. Fill in the blanks with prepositions or adverbs if necessary:
- •IV. Match the terms with their definitions:
- •V. Define which of the following items best completes the statement:
- •VI. Complete the following sentences:
- •VIII. Translate into English:
- •Grammar: The Infinitive – Інфінітив
- •11 Aggregate demand
- •I. Match the antonyms:
- •V. Complete the following sentences:
- •VI. Translate into English:
- •VII. Replace the Ukrainian words and phrases by their English equivalents in the correct form:
- •Grammar: The Gerund – Герундій
- •(12) Grammar: The Participle – Дієприкметник
3 The words in the box frequently occur before "money". Find combinations that mean:
1) money that is being used by the public as opposed to money left in bank accounts; 2) money easily available on loan at a low rate of interest; 3) extra money or high wages paid to people working in dangerous conditions; 4) money that is difficult to borrow because of high interest rates; 5) money that is not circulated or invested and does not earn interest; 6) an item that can be easily exchanged in the |
|
way that money can, although it is not money itself. It includes cheques and postal orders but not banknotes or coins; 7) money lent on condition that it must be repaid immediately if necessary; 8) money offered by someone to show that he/she is honest and truthful and will keep to all agreed terms and conditions; 9) the reward paid by the owners of a rescued ship or goods to the person or organization that saved it / them; 10) change for small purchases; 11) money which is moved from country to country to get the best return; 12) money paid to someone in return for keeping silent about a crime.
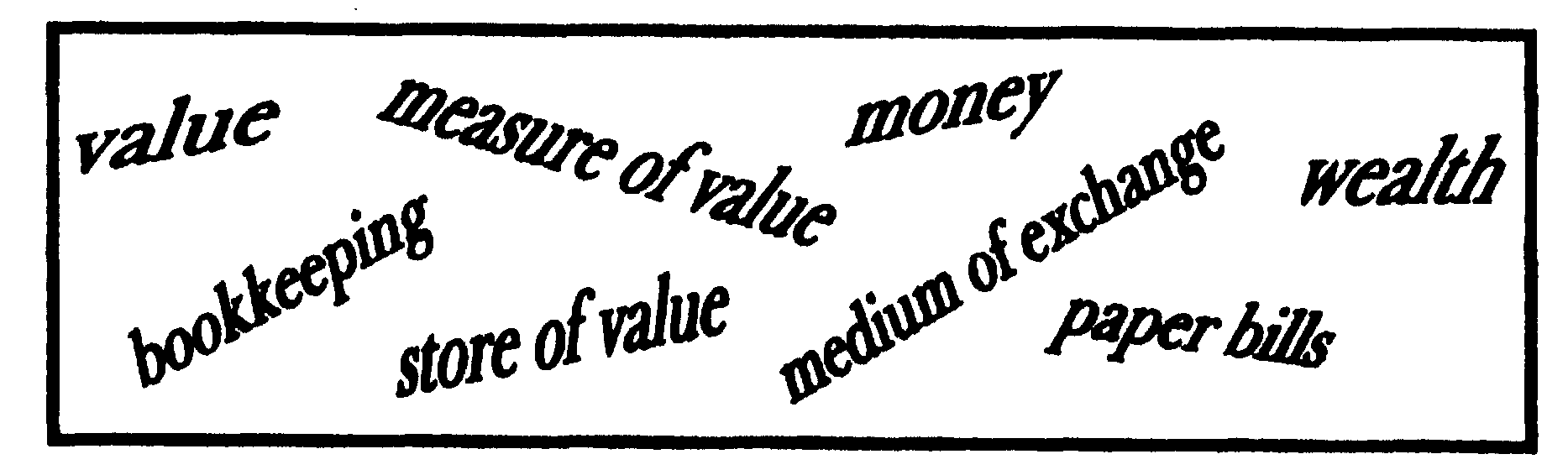
4 Match the words and phrases in the box with the correct definition:
1) banknotes; 2) a means of payment, esp. coins and banknotes, given and accepted in buying and selling; 3) a means for retaining and accumulating wealth; 4) a single standard or "yardstick" that is used to assign values to, and compare the values of products and resources; 5) anything that is accepted as payment for products and resources; 6) the |
|
recording of all money received into and paid out of a company in a book or on a computer file; 7) the worth of something in terms of the money or goods for which it can be exchanged; 8) a large amount of money, goods or property.
5 Choose the correct word from the box to complete the gaps. Translate the sentences into Ukrainian:
spent; functions; a yardstick; accumulating; trust; exchange; retained; value; the medium of exchange; money |
1 Our central aim is to make.... 2 Credit cards and cheques are increasingly used as.... 3 Returned goods can be exchanged for goods of an equivalent.... 4 You will be given a higher salary in... for doing a more responsible job. 5 I... my business partner completely. 6 She... most of her parents' property, but some went to her children. 7 My savings are... interest. 8 A 10% profit after taxes is widely seen as... for making money in a business. 9 One of the most important... of my job is to see that goods are delivered on time. 10 He... $200 to fix his car.
Grammar: Modals with the Perfect Infinitive – Модальні дієслова з перфектним інфінітивом
Can, may, might, must, could, should, ought to are also used to talk about possibility, probability and certainty in the past.
Must + Perfect Infinitive expresses the speaker's certainty that something has happened.
If she is not here by now, something must have happened.
Could / may / might + Perfect Infinitive express the idea that there is a possibility that something has
happened: She looks miserable. She could / may / might have lost her job. (Perhaps she has lost her job)
Can't / couldn't + Perfect Infinitive express the speaker's certainty that something has not happened:
She can't / couldn't have gone; her coat is still here. (I’m sure she’s still here.)
May not / might not + Perfect Infinitive express the idea that it is possible that something didn't happen:
Nobody is in the office. They may not / might not have received our message.
Should / ought to + Perfect Infinitive indicate that an action considered desirable was not carried out:
You ought to / should have warned your employer. (I think it was a good idea to warn your employer.)
Shouldn't / oughtn't to + Perfect Infinitive indicate that an action considered undesirable was carried out:
You shouldn’t / oughtn't to have told her this news. (I think it was a bad idea to tell her the news.)
Ex.1. Complete the following sentences with an appropriate modal verb from the box below:
should, couldn't, ought to, must, can't, shouldn't, may |
1 She ______ have lost her way; she must have missed the train. 2 Has she phoned yet? She ______ have phoned two hours ago. 3 I'm not waiting much longer. He ______ have been here hours ago. 4 The bus ______ have been at the airport. He promised to meet us. 5 He is back already. He ______ have started very early. 6 Do you remember reading about it in the newspapers? No, I ______ have been abroad at the time. 7 We had a very good dinner for $10 at a restaurant yesterday. You ______ have had a very good dinner if you only paid $10. 8 I saw your boss in the theatre yesterday. You _____ have seen him; he is still abroad. 9 The letter ______ have been posted long ago. 10 You _______ have greeted him first. 11 She _______ have made such a mistake. 12 You _______ have left your glasses in the car. 13 Give him a ring. He _______ have arrived by now. 14 They______have followed her advice. Now they regret not to have done so. 15 You _______ have spoken to your employee in such a tone. I am sure, you have hurt him. 16 He ______ have left without saying good-bye. 17 He ______ have concealed something from his employer. 18 They _______ have delayed the discussion of the problem.
Ex.2. Complete the sentences with should (shouldn’t), could, may (may not), needn't, can't + have:
1 You ………………. been here a week ago. 2 He ……………….. signed that contract. He was on business trip last week. 3 If he needed money, he ……………… asked me. 4 "Where’s the secretary?" "No idea. She ……………….. gone home." 5 He ………………… got a new job. I'll phone him tonight. 6 She hasn't come. But she ……………. got your message. 7 You ………… made that speech in front of an audience; nobody appreciated it. 8 You really ………………… informed your employer of those changes! 9 The de-legation ………………. arrived yet. 10 You ………………. warned him. Why didn't you? 11 He ………… spoken to the manager. I've already spoken to him. 12 You ………….. bought that house. 13 I …..………... borrowed him money. It was my mistake. 14 He …………….. invested all the money. I’m sure he hasn't.
Ex.3. Translate into English:
1 He може бути, щоб він дав згоду виконати таку кількість роботи за такий короткий строк. 2 Не може бути, щоб вони досі не вирішили цього питання. 3 Зараз вони, можливо, вже закінчили свій дослід. 4 Тобі потрібно було зателефонувати йому вчора; ти знав що він хворий. 5 Звичайно, ти повинна була попередити їх раніше. Чому ти цього не зробила? 6 Його здоров'я покращилося. Він, можливо, кинув палити. 7 Він, можливо, не усвідомив одразу всієї важливості повідомлення. 8 Щось, можливо, затримало його. Він повинен був вже повернутися. 9 Можливо ти не зрозумів її. Вона не хотіла образити тебе. 10 Вони, можливо, не скоротили свої витрати. Ось чому вони зараз є боржниками. 11 В неї, мабуть, не було жодного шансу попередити мене заздалегідь. 12 До цього часу він, можливо, сплатив вже всі борги.