
- •O. Pisotska
- •Передмова
- •Lesson 39
- •Vocabulary
- •Word-building
- •Grammar:
- •Forms of participle
- •Reading and developing speaking skills
- •Respiratory system
- •Normal ventilation
- •Smoking
- •Overview
- •Vocabulary
- •Word-building
- •Grammar
- •Absolute participle construction
- •Reading and developing speaking skills
- •Respiratory disorders
- •Tracheobronchitis and bronchitis
- •Disorders of the sinuses and throat
- •Vocabulary
- •Word-building
- •Grammar:
- •Construction “it is (was, will be ) … that (who, whom)”
- •Reading and developing speaking skills
- •Overview
- •Lesson 42
- •Vocabulary
- •Reading and developing speaking skills
- •Infectious diseases and their types
- •Subgroups of the infectious diseases
- •Overview
- •Immune system
- •Vocabulary
- •Word-building
- •Grammar:
- •Simple tenses (revision)
- •Reading and developing speaking skills
- •Immune system
- •Immunity
- •Overview
- •Lesson 44
- •Vocabulary
- •Word-building
- •Grammar:
- •Functions of “one”
- •Reading and developing speaking skills
- •Overview
- •Lesson 45
- •Vocabulary
- •Word-building
- •Grammar:
- •Infinitive and its forms
- •Інфінітив у формі|у формі| Continuous| виражає тривалу дію, що відбувається одночасно з дією, вираженою дієсловом-присудком:
- •Інфінітив у формі|у формі| Perfect| виражає|виказує,висловлює| дію, що передує дії, вираженій дієсловом-присудком:
- •Subjective infinitive construction
- •Reading and developing speaking skills
- •Endocrine system
- •Ex. 16. Translate the text “Endocrine System” into Ukrainian.
- •Endocrine glands
- •Functions of hormones
- •Ex. 34. Speak on the some endocrine glands using obtained data. You may use the following expressions:
- •Thyroid gland
- •Overview
- •Vocabulary
- •Reading and developing speaking skills
- •Hormonal problems
- •Ex. 7. Translate the text “Hormonal Problems” into Ukrainian.
- •Overview
- •Vocabulary
- •Grammar:
- •Objective infinitive construction
- •Reading and developing speaking skills
- •Diabetes mellitus
- •Insulin injection
- •Medication
- •Overview
- •Lesson 48
- •I. Read and translate one of the following texts: Text a thyroid diseases
- •Allergy
- •Text c tuberculosis
- •II. Speak on the following topics:
- •Word-building
- •Nervous system
- •Various forms of nerve cells.
- •Spinal cord
- •Overview
- •Lesson 50
- •Vocabulary
- •Word-building
- •Grammar:
- •Sequence of tenses
- •Reading and developing speaking skills
- •Ex. 20. Read the following abstract and write down all unknown medical terms. Translate them with the aid of dictionary. Tell about the hypothalamic functions: hypothalamus
- •Human brain and its functions
- •What is wonderful about the brain?
- •Overview
- •Lesson 51
- •Vocabulary
- •Reading and developing speaking skills
- •Disorders of nervous system
- •Infections
- •Ex. 8. Read and memorize the following words:
- •Degenerative disorders
- •Ex. 16. Write the summary of the text "Degenerative Disorders" overview
- •Lesson 52
- •Vocabulary
- •Word-building
- •Grammar:
- •Adverbs
- •Reading and developing speaking skills Ex. 4. Read the vocabulary and memorize new words. Ex. 5. Insert the missing letters, read the following words and translate them:
- •Accessory structures
- •Eye placement
- •Overview
- •Lesson 53
- •Vocabulary
- •Word-building
- •Grammar:
- •Noun as attribute
- •Reading and developing speaking skills
- •Ear disorders
- •Communicating with a hearing-impaired person
- •Vocabulary
- •Word-building
- •Reading and developing speaking skills
- •What is your skin type
- •Ex. 22. Read and translate the following text: skin disorders
- •Text a disorders of vision
- •Bronchitis
- •Vocabulary
- •Word-building
- •Grammar:
- •Objective participle construction
- •The Objective Participle Construction перекладається підрядним реченням зі сполучником “як”: I saw them walking along the street.Я бачив, як вони йшли по вулиці.
- •Reading and developing speaking skills
- •Urinary system
- •Ex. 20. Make up a dialogue on the urinary system.
- •Functions of urinary system
- •Fluid excretion
- •Kidneys
- •Ex. 26. Describe the structure of kidney using the following figure:
- •Ex. 27 Describe kidneys’ functions. The following expressions may be helpful:
- •Ex. 28. Write the summary of the text "Kidneys".
- •Overview
- •Lesson 57
- •Vocabulary
- •Word-building
- •Grammar:
- •Functions of the verb “to have”
- •Reading and developing speaking skills
- •Kidneys disorders
- •Kidney stones
- •Ex. 23. Pronounce and memorize the words to the theme studied:
- •Kidney transplantation
- •Overview
- •Lesson 58
- •Vocabulary
- •Word-building
- •Grammar:
- •Functions of the verb “to be”
- •Reading and developing speaking skills
- •Ex. 8. Read and memorize the following terms:
- •Ex. 21. Write the summary of the text “Cancer”.
- •New methods to fight cancer
- •Overview
- •Vocabulary
- •Word-building
- •Grammar:
- •Interrogative form (Revision)
- •Reading and developing speaking skills
- •Ex. 8. Translate the following words into English:
- •Stomach tumor
- •Ex. 18. Give a summary of the text “Stomach Tumor”.
- •Lung cancer
- •Tumors of the small intestine
- •Cancer of the kidney
- •Vocabulary
- •Word-building
- •Grammar:
- •Reading and developing speaking skills
- •Pregnancy
- •Food and nutrition during pregnancy
- •Development of the organ systems
- •Signs of pregnancy
- •Vocabulary
- •Word-building
- •Grammar: simple tenses (revision)
- •Reading and developing skills
- •Death; embryo; adolescent; occur; amount; achieve; subsequent; myelin sheath; push; raise; grasp; listen; quietly; laugh; loud.
- •First year after birth
- •Development during the preschool years
- •School years
- •Vocabulary
- •Word-building
- •Interrogative form
- •Reading and developing reading skills
- •Newborn’s nutrition
- •Breast feeding
- •Infant’s nutrition
- •Nutrition of preschool child
- •Vocabulary
- •Grammar: modal verbs (revision)
- •Reading and developing speaking skills
- •Childhood infectious diseases
- •Chickenpox
- •Immunization
- •Overview
- •Vocabulary
- •Grammar:
- •Infinitive constructions and participles (revision)
- •Reading and developing speaking skills
- •Measles
- •Complications of measles
- •Some notions about measles
- •I. Read and translate one of the following texts: Text a female reproductive system
- •Male reproductive system
- •Infertility
- •Breast cancer
- •Whooping cough
- •Treatment for whooping cough
- •II. Speak on the following topics:
- •Appendix 1
- •Irregular verbs
- •Appendix 2 suffixes and term-elements
- •Term elements of greek and latin origin greek, latin, english and ukrainian equivalents
- •Короткий довідник з правил словотворення
- •Найуживаніші суфікси англійської мови:
- •Основні префікси:
- •Practical grammar guide
- •(Короткий граматичний довідник)
- •Іменник
- •(Cases)
- •Артикль (article)
- •Займенники (pronouns)
- •Прикметник (adjective)
- •Найвищий ступінь порівняння прикметників (Superlative Degree)
- •Порядок слів у реченні.
- •Побудова розповідних і питальних речень
- •Способи визначення присудка в англійському реченні
- •Неозначено-особові речення
- •Безособові речення.
- •Форми дієслова forms of the verb
- •Часи групи simple (indefinite) present simple
- •Past simple
- •Future simple
- •Simple tenses
- •Часи групи continuous
- •Present continuous
- •Past continuous
- •Future continuous
- •Continuous tenses
- •Perfect tenses
- •Present perfect
- •Past perfect
- •Future perfect
- •Perfect tenses
- •Стан дієслова
- •Passive voice
- •Зведена таблиця часів стверджувальної форми
- •Зведена таблиця питальної форми
- •Interrogative form
- •Дієслова to be та to have
- •Ознаки функціональної відмінності дієслова to be
- •Модальні дієслова (modal verbs)
- •Модальне дієслово can
- •Модальне дієслово could
- •Модальне дієслово may
- •Модальне дієслово must
- •Ознаки розпізнавання граматичних форм, утворених за допомогою допоміжних дієслів should I would
- •Підрядні додаткові та означальні речення (object clauses)
- •Виділення членів речення за допомогою підсилювальної конструкції it is (was, will be) ... That (who, which)
- •Умовний спосіб
- •(Infinitive)
- •Об’єктний інфінітивний комплекс (Objective Infinitive Construction)
- •Дієприкметник
- •Об’єктний дієприкметниковий комплекс (Objective Participle Construction)
- •The Objective Participle Construction перекладається підрядним реченням зі сполучником “як”: I saw them walking along the street. – я бачив, як вони йшли по вулиці. Герундій (gerund)
- •Форми герундія
- •Герундіальний комплекс (зворот) (Gerund Construction)
- •Узгодження часів у підрядному додатковому реченні
- •Vocabulary список використаної літератури
Reading and developing speaking skills
Ex. 6. Read VOCABULARY and memorize new words.
Ex. 7. Compose 2-3 sentences using the words of the VOCABULARY.
Ex. 8. Insert the missing letters:
Diap_ragm; ex_ale; bre_the; na_es; bron_hi; aver_ge; pl_ura; cil_a; ape_; pas_ageway; d_nse; capil_ary; alve_lus; bronchiol_; exp_nd.
Ex. 9. Translate the following words and word-combinations into Ukrainian:
Ciliated columnar epithelium; larynx; pharynx; include; perform; individual cell; nares; cilia; pass; separate openings; nasopharynx; oropharynx; laryngopharynx; casing; cartilage; propel; apex of the lung.
Ex. 10. Read the following words and word-combinations:
Bronchi; associated; trachea; diaphragm; oxygen; release; atmosphere; moisten; adenoids; tonsils; unpaired cartilage; swallow; primary; superiorly; weight.
Ex. 11. Read the following text:
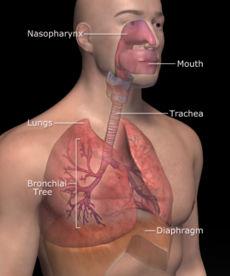
Respiratory system
|
The respiratory system consists of the nasal cavity, pharynx, larynx, trachea (windpipe), bronchi, and lungs. The upper respiratory tract includes the nasal cavity, pharynx, and associated structures, and the lower one involves the larynx, trachea, bronchi, and lungs. Respiratory movements are realized by the diaphragm and the muscles of the thoracic wall. All cells of the body perform aerobic metabolism for which oxygen is essential. The respiratory system and the cardiovascular system take oxygen from the air and transport it to individual cells. They then transport carbon dioxide from cells and release it from the body into the air. The respiratory system plays an important role in regulating pH of the body fluids. Respiration is the exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide between the atmosphere and body cells. Air enters the nasal cavity located inside the external nose and joined the pharynx through the |
|
external nares.
A mucous membrane and cilia warm the air and filter out foreign bodies. Then the air passes into the pharynx. Pharynx (throat) is the common opening of both the digestive and respiratory systems. Inferiorly, the pharynx leads to the separate openings of the respiratory system (opening into the larynx) and the digestive system (i.e. the esophagus). The pharynx can be divided into three regions, the nasopharynx, the oropharynx, and the laryngopharynx. The adenoids and the tonsils are located in the pharynx. Then the air reaches the larynx (voice box). The larynx consists of an outer casing of nine cartilages that are connected to each other by muscles and ligaments. Six of the nine cartilages are paired, and three are unpaired. The largest and most superior cartilage is unpaired thyroid cartilage, or Adam's apple. After that the air passes through the trachea and bronchi. The trachea is a membranous tube that consists of dense connective tissue and smooth muscle. The cilia propel mucus and foreign particles toward the larynx where they can enter the esophagus and be swallowed. The trachea connects the larynx to the primary bronchi. They go to each lung.
The lungs are the principal organs of the respiration and the largest organs of the body. Each lung is conical in shape, its base is on the diaphragm and its apex extends superiorly to a point approximately 2.5 cm superior to each clavicle. The right lung is larger than the left and weights an average of 620 g, whereas the left lung weights 560 g. The right lung has three lobes, and the left lung has two. The alveoli located in the lungs allow for the exchange of gases. The blood absorbs the oxygen from the alveoli and gives carbon dioxide away, which is exhaled (breathed out).
NOTES:
nasopharynx носоглотка
oropharynx ротова частина глотки
laryngopharynxгортаноглотка, гортанна частинаглотки
Ex. 12. Translate the following words and word-combinations into English:
Верхівка; видихати; складатися з; для якого необхідний кисень; прохід; капіляр; середнє число, середня величина; зовнішня частина|частка| носа; щільний; війки; діафрагма; ніздрі; зволожувати; хрящ щитовидної залози; аденоїди; альвеола; плевра; розтягувати(ся|ся|), розширювати(ся|ся|), збільшувати(ся|ся|).
Ex. 13. Translate the text “Respiratory System” into Ukrainian.
Ex. 14. Insert the missing words:
1. The respiratory system consists of the nasal cavity, pharynx, larynx, trachea, _, and lungs. 2. The respiratory system and the cardiovascular system transport oxygen to _ cells. 3. Respiration is the _ of oxygen and carbon dioxide between the atmosphere and body cells. 4. Air enters the _ cavity. 5. Then the air passes into the _. 6. After that the air passes through the trachea and _. 7. The trachea connects the larynx to the primary _. 8. The lungs are the principal organs of the _. 9. The right lung is larger than the _. 10. The right lung has _ lobes, and the left lung has two.
Ex. 15. Answer the following questions:
1. What does the respiratory system consist of? 2. What is the major function of the respiratory system? 3. What parts is the respiratory tract divided into? 4. Where does air enter? 5. What is pharynx? 6. What is trachea? 7. What are the lungs? 8. What is the difference between right and left lungs?
Ex. 16. Describe the picture above.
Ex. 17. Read the following sentence and learn it by heart:
Respiration involves several important processes: 1) ventilation, the movement of air into and out of the respiratory passages and the lungs; 2) gas exchange between the air in the lungs and the blood; 3) transport of oxygen and carbon dioxide in the blood; and 4) gas exchange between the blood and the tissues.
Ex. 18. Read the following words and word-combinations and translate them into Ukrainian:
Fissure; lobule; visible; primary bronchi; secondary bronchi; respective lung; point of entry; hilum; tertiary bronchi; terminal bronchioles; duct; cluster; medial border; parietal pleura; to become continuous with; visceral pleura; fluid; lubricant; slide.
Ex. 19. Read the following abstract and entitle it:
The lobes are separated by deep, prominent fissures on the surface of the lung. The primary bronchi divide into secondary bronchi. The point of entry for the bronchi, vessels, and nerves in each lung is called the hilum, or root, of the lung. The secondary bronchi conduct air to each lobe. The secondary bronchi give rise to tertiary bronchi, which extend to the lobules. The bronchial tree continues to branch several times, finally giving rise to bronchioles. They also subdivide numerous times to become terminal bronchioles, which then divide into respiratory bronchioles. Each respiratory bronchiole divides to form alveolar ducts that end as clusters of air sac called alveoli. The lungs contain over 300 million such alveoli. If they could be stretched out on a flat surface, they would cover an area approximately the size of tennis court.
Ex. 20. Speak on the structure of the respiratory system.
Ex. 21. Read the following text and get ready to narrate it:
LUNGS
The lungs are the principal organs of respiration. They occupy the major part of the cavity on both sides of the chest. The two lungs are not equal in size. The right lung is divided into three lobes and is a bit larger. The left lung is divided into two lobes. The lobes are separated by deep, prominent fissures on the surface of the lung. Each lobe is divided into lobules that are separated from each other by connective tissue.
The primary bronchi divide into secondary bronchi as they enter their respective lungs. The point of entry for the bronchi, vessels, and nerves in each lung is called the hilum, or root, of the lung. The secondary bronchi, two in the left lung and three in the right lung, conduct air to each lobe. The secondary bronchi, in turn, give rise to tertiary bronchi, which extend to the lobules. The bronchial tree continues to branch several times, finally giving rise to bronchioles. The bronchioles also subdivide numerous times to become terminal bronchioles, which then divide into respiratory bronchioles. Each respiratory bronchiole divides to form alveolar ducts that end as clusters of air sacs called alveoli. An alveolar sac is composed of two or more alveoli.
Each lung is surrounded by a separate pleural cavity, attached only along its medial border at the hilum. Each pleural cavity is lined with a serous membrane called the parietal pleura. At the hilum the parietal pleura becomes continuous with a serous membrane, the visceral pleura, which covers the surface of the lung.
The pleural cavity is filled with pleural fluid that is produced by the pleural membranes. The pleural fluid performs two functions: it acts as a lubricant, allowing the pleural membranes to slide past each other as the lungs and thorax change shape during respiration; and it helps hold the pleural membranes together.
Deoxygenated blood is transported to the lungs through the pulmonary arteries, and oxygenated blood leaves through the pulmonary veins. Oxygenated blood is mixed with a small amount of deoxygenated blood returning from the bronchi.
Ex. 22. Answer the following questions:
1. What are the lungs? 2. How many lobes do the right and left lungs have? 3. What is each lobe divided into? 4. Where do the primary bronchi divide into secondary ones? 5. What is hilum of the lung? 6. What does each respiratory bronchiole form? 7. What is the lung surrounded by? 8. What is the parietal pleura? 9. What is the visceral pleura? 10. What is the pleural cavity filled with? 11. What are the functions of the pleural fluid? 12. What are the two major routes of blood flow to and from the lungs?
Ex. 23. Give a summary of the text “Lungs”.
Ex. 24. Make up the dialogue on the structure and functions of the lungs.
Ex. 25. Read the following words and word-combinations and memorize their meaning:
Branch| розгалужуватися; create| створювати; adjacent| розташований|схильний| поряд|поруч|, суміжний, сусідній; inhale| вдихати; push| down| натискати|натискувати|, тискнути; suck| всмоктувати, засмоктувати; similar| подібний, схожий; file| ряд|лава,низка|, колона; merge| зливати(ся|ся|), сполучати|з'єднувати|(ся|ся|).
Ex. 26. Read and translate the following text:

 Respiratory
System
Respiratory
System