
- •Т.В. Барамикова, л.П. Ільєнко, к.Б. Кугай, а.В. Спіжова, н.В. Зимнікова, а.М. Ткаленко
- •Передмова
- •Unit 1 history of arts Part I
- •I Listen and remember the following words:
- •III Read and translate the following text: History of Arts
- •V Complete the sentences with the words from the text:
- •X Speak on the topic using the following words and word-combinations:
- •I Read and remember:
- •Renaissance
- •III Make up a plan of the text.
- •VIII Give the main idea of the dialogue in your own words.
- •V Complete the sentences with the words from the text:
- •X Speak on the topic using the following words and word-combinations:
- •I Read and remember:
- •The History of Arts. Brief Overview
- •III Make up a plan of the text.
- •IV Translate the paragraph in italics in a written form.
- •V Render the text in brief in a written form.
- •VI Work in pairs. Discuss the questions :
- •VII Practice reading the dialogue with your partner:
- •VIII Make up your own dialogues using the key words and expressions from the unit.
- •IV Answer the questions:
- •X Speak on the topic using the following words and word-combinations:
- •I Read and remember:
- •II Read the text and define the main idea of it: World War I and after the War
- •III Make up a plan of the text.
- •VIII Give the main idea of the dialogue in your own words.
- •IV Answer the questions:
- •X Speak on the topic using the following words and word-combinations:
- •I Read and remember:
- •II Read the text and define the main idea of it: Charles Frederick Worth Industrializes Fashion
- •III Make up a plan of the text.
- •I Mind the following words and word-combinations:
- •Unit 5 design elements
- •I Listen and remember the following words:
- •Design Elements
- •V Complete the sentences with the words from the text:
- •X Speak on the topic using the following words and word-combinations:
- •I Read and remember:
- •Design Principles
- •III Make up a plan of the text.
- •VIII Make up your own dialogues using the key words and expressions from the unit.
- •IV Answer the questions:
- •X Speak on the topic using the following words and word-combinations:
- •I Read and remember:
- •II Read the text and define the main ideaof it: The World Famous Designers
- •III Make up a plan of the text.
- •IV Answer the questions:
- •V Complete the sentences with the words from the text.
- •X Speak on the topic using the following words and word combinations:
- •I Read and remember:
- •II Read the text and define the main idea of it: Dance Costume
- •III Make up a plan of the text.
- •VIII Give the main idea of the dialogue in your own words.
- •III Match the words in the left column with their definitions:
- •IV Answer the questions:
- •X Speak on the topic using the following words and word combinations:
- •I Read and remember:
- •II Read the text and define the main idea of it: Scenic Makeup
- •III Make up a plan of the text.
- •VIII Give the main idea of the dialogue in your own words.
- •IV Answer the questions:
- •V Complete the sentences with the words from the text:
- •III Make up a plan of the text.
- •IV Translate the paragraph in italics in a written form.
- •V Render the text in brief in a written form.
- •VI Work in pairs. Discuss the questions.
- •VII Practice reading the dialogues with your partner:
- •VIII Make up your own dialogues using the key words and expressions from the unit.
- •Unit 10
- •IV Answer the questions:
- •V Complete the sentences with the words from the text:
- •III Make up a plan of the text.
- •VIII Give the main idea of the dialogue in your own words.
- •IX Make up your own dialogues using the key-words and expressions from the unit.
- •I Mind the following words and word-combinations
- •III Listen to the text again and be ready to answer the questions:
- •IV Answer the questions:
- •V Complete the sentences with the words from the text:
- •VI Find the English equivalents to the words:
- •VII Make up sentences with the terms:
- •VIII Give definitions to the words and word-combinations:
- •IX Translate the sentences into English:
- •X Speak on the topic using the following words and word combinations:
- •I Read and learn:
- •II Read the text and define the main idea of it: Flower Symbolism
- •III Make up a plan of the text.
- •IV Translate the paragraph in italics in a written form.
- •V Render the text in brief in a written form.
- •VI Work in pairs. Discuss the questions.
- •VII Practise reading the dialogue with your partner:
- •VIII Give the main idea of the dialogue in your own words.
- •IX Make up your own dialogues using the key words and expressions from the unit.
- •I Mind the following words and word-combinations:
- •II Listen to the text and decide if the statements are true or false:
- •IV Answer the questions:
- •V Complete the sentences with the words from the text:
- •VI Find the English equivalents to the words:
- •III Make up a plan of the text.
- •VIII Give the main idea of the dialogue in your own words.
- •Unit 13
- •IV Answer the questions:
- •X Speak on the topic using the following words and word-combinations:
- •I Read and remember:
- •II Read the text and define the main idea of it: Raymond Loewy. The Father of Industrial Design
- •III Make up a plan of the text.
- •VIII Give the main idea of the dialogue in your own words.
- •IV Answer the questions:
- •V Complete the sentences with the words from the text:
- •VI Find the English equivalents to the words:
- •VII Make up sentences with the terms:
- •VIII Give definitions to the words and word-combinations:
- •IX Translate the sentences into English:
- •X Speak on the topic using the following words and word combinations:
- •I Read and learn:
- •II Read the text and define the main idea of it: The Importance of Colour
- •III Make up a plan of the text.
- •IV Translate the paragraph in italics in a written form.
- •V Render the text in brief in a written form.
- •VI Work in pairs. Discuss the questions.
- •VII Practise reading the dialogue with your partner:
- •VIII Give the main idea of the dialogue in your own words.
- •IV Answer the questions:
- •V Complete the sentences with the words from the text:
- •VI Find the English equivalents to the words:
- •VII Make up sentences with the terms:
- •VIII Give definitions to the words and word-combinations:
- •IX Translate the sentences into English:
- •X Speak on the topic using the following words and word combinations:
- •I Read and remember:
- •II Read the text and define the main idea of it:
- •Video Design
- •III Make up a plan of the text.
- •VIII Give the main idea of the dialogue in your own words.
- •IV Answer the questions:
- •V Complete the sentences with the words from the text:
- •VI Find the English equivalents to the words:
- •VII Make up sentences with the terms:
- •VIII Give definitions to the words:
- •IX Translate the sentences into English:
- •X Speak on the topic using the following words and word-combinations:
- •I Read and remember:
- •II Read the text and define the main idea of it: The History of Logo Design
- •III Make up a plan of the text.
- •IV Translate the paragraph in italics in a written form.
- •V Render the text in brief in a written form.
- •VI Work in pairs. Discuss the questions:
- •VII Practice reading the dialogue with your partner:
- •VIII Give the main idea of the dialogue in your own words.
- •Texts for additional reading the origins of costume
- •1. Read the text. What is the main idea of the text?
- •2. Find unknown terms and words in the text and give their translations?
- •3. Make up a plan of the text in the form of questions.
- •3. Make up a plan of the text in the form of questions.
- •3. Make up a plan of the text in the form of questions.
- •3. Make up a plan of the text in the form of questions.
- •3. Answer the following questions:
- •3. Make up a plan of the text in the form of questions.
- •4. Answer the following questions :
- •5. Translate the last paragraph of the text in a written form.
- •Interior design. Style selection
- •1. Read and translate the text. What is the main idea of the text?
- •2. Find unknown terms and words in the text and give their translations?
- •3. Make up a plan of the text in the form of questions.
- •3. Make up a plan of the text in the form of questions.
- •3. Answer the questions:
- •3. Make up a plan of the text in the form of questions.
- •3. Make up a plan of the text in the form of questions.
- •3. Make up a plan of the text in the form of questions and ask your groupmates to find answers in the text.
- •3. Answer the following questions:
- •3. Answer the following questions:
- •3. Answer the following questions:
- •3. Answer the questions:
- •3. Make up a plan of the text in the form of questions and ask your groupmates to find answers in the text.
- •3. Make up a plan of the text in the form of questions and ask your groupmates to find answers in the text.
- •Українсько-Англійський словник а
- •Glossary a
- •Список використаної літератури
- •Introductory horticulture by h. Edward Reiley, Carroll l. Shry – Albany, ny: Delmar Thomson Learning, 2002. – 564 p.
III Make up a plan of the text.
IV Translate the paragraph in italics in a written form.
V Questions for discussion:
What is the Renaissance?
What did the Renaissance affect?
What did some historians postulate?
What were the other opinions as to the origin of the Renaissance?
What is one of the distinguishing features of the art cultural movement?
Who are the most famous representatives of the artistic pinnacles?
How did the Renaissance spread to Europe?
What do you know about the English Renaissance?
VI Render the text in brief in a written form.
VII Practise reading the dialogue with your partner.
J. Heavens, what sparkling eyes that lady on the portrait has! And what a graceful pose!
H. Isn't it lovely! Her face is gentle, she looks as if she was alive.
J. And the texture of her dress! It looks so soft and silky as if you could feel it with your hand.
H. You like realist portraits, don't you?
J. I like pictures that are true to life, where every leaf and flower is depicted exactly.
H. Like in still life? Look, at this one. Flowers in a vase, watermelons, grapes and cherries. Doesn't it look nice?
J. Wow, it makes me feel really hungry. Do we call this art realism?
H. Well, realism artists' ideal was a truthful depiction of what laid before their eyes and precise drawing of a landscape or a portrait.
O. There is nothing like landscapes to me. I like nature depicted as mysterious and majestic.
H. You seem to like romanticism, don't you?
O. How can you tell a realistic landscape from a romantic one?
H. Romantic artists used exaggerations: the hills and trees are higher, the sea is bluer than in real life. Artists stressed the wild character of the place and the drama of contrasts.
J. Look over there. That calm sea shore will make you feel happy. The rocks and blue water are flooded with sunlight. And the delicate white figure of a lady in the wide-brim hat conveys the spirit of leisure, harmony and optimism.
O. And I see the brushwork here is unlike those we have seen. The trace of the brush is left and the character of the work is rapid and sketch-like.
H. Naturally, another style – another expression. This is piece of impressionism. Impressionists tried to capture one instant in time.
J. The moment, stop! You are a wonder!
H. Right you are. Emphasis was placed on capturing the first impression of the subject, it was painted on the spot, in a state of great emotional excitement at the sight of a wonderful world.
O. What do you know about contemporary art?
H. There are a great number of styles both of realistic and formalistic trends, and a great deal of masterpieces.
J. We'll see some of them in the Museum of Modern Art, I believe. Let’s go there next week.
VIII Give the main idea of the dialogue in your own words.
IX Make up your own dialogues using the key words and expressions from the unit.
Text C
I Mind the following words and word-combinations:
inventor

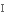



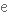
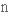
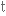

 винахідник
винахідникarchetype





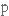
 прообраз
прообраз infinite



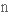
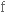

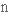
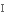
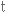
 безмежний
безмежний curiosity




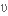

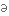

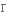





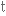
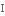
 цікавість
цікавість to equal






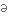
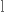
 дорівнювати
дорівнювати diversely

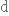
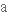


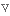



 різноманітно
різноманітно renowned



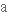
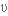

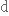
 визнаний
визнаний primarily



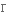

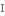
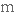







 в першу чергу
в першу чергуvastly


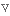
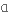

 широко
широко
to conceptualise

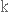
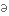
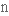



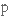




 замислювати
замислювати
solar




 сонячний
сонячний
tensile strength


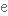
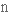

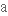
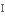



 сила
натягування
сила
натягування
II Listen to the text. Decide if the statements are true or false:
Leonardo da Vinci was an Italian scientist, engineer, anatomist, painter, sculptor, botanist, musician and writer.
He is perhaps the most diversely talented person to have ever lived.
Leonardo is renowned primarily as a musician.
As an engineer, Leonardo conceptualised a plane.
As a scientist, he greatly advanced the state of knowledge in the fields of anatomy and hydrodynamics.
III Listen to the text again and be ready to answer the questions:
What is the most famous portrait by Leonardo da Vinci?
How is Leonardo da Vinci often described?
REVIEW ASSIGNMENTS
I Revise the vocabulary minimum of Unit 1 to be checked up.
II Match the words:
1 valuable a) сучасний
2 contemporary b) поява
3 ancient c) середньовічний
4 to depict d) майстерність
5 medieval e) середньовічний
6 manuscript f) цiнний
7 features g) зображувати
8 workmanship h) столiття
9 advent i) древній
10 century j) рукопис
III Match the words in the left column with their definitions:
1 sculpture a) outstanding work, achievement or performance
2 mosaic b) art or process of applying paints to a surface such as canvas, to make a picture or other artistic composition
3 jewellery c) art of making three-dimensional or relief forms by chiselling, carving, modelling
4 painting d) design or decoration made up of small pieces of coloured glass, stone, etc.
5 masterpiece e) objects that are worn for personal adornment such as bracelets, rings, necklaces, etc.
UNIT 2
HISTORY OF ARTS
Part II
TEXT A
I Listen and remember the following words:
to impose

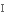
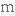



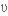
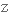
 накладати
накладатиto execute


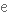


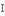
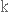

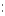
 виконувати
виконуватиto view



 дивитися,
поглядати
дивитися,
поглядатиto embody



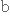

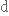

 втілювати
втілюватиto intersect


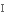
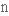
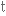
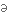


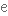


 перетинати
перетинатиto supersede


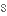





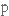


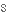
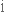

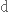
 замінювати,
заміщати
замінювати,
заміщатиto merge

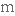


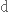

 змінюватися,
зливатися
змінюватися,
зливатисяsilverwork [’sɪlvər wɜ:rk] вироби із срібла
refinement

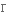
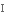



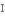
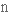

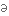
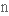
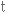
 витонченість,
удосконалення
витонченість,
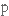
удосконаленняpre-eminence


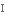


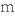
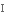

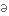
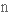

 перевага
перевага
II Read and remember the following phrases:
defining statement – вирішальний фактор
extra-sculptural elements – додаткові скульптурні елементи
concealed lighting – приховане освітлення
excessive ornamentation – надмірний орнамент
complexity of lines – складність ліній
engraved publications – фоліанти
III Read and translate the following text:
Baroque and Rococo
 Baroque
is an artistic style of unity imposed upon rich heavy detail.
Baroque
is an artistic style of unity imposed upon rich heavy detail.
A defining statement of what Baroque signifies in painting is provided by the series of paintings executed by Peter Paul Rubens for Marie de Medici at the Luxembourg Palace in Paris.
In Baroque sculpture was a dynamic movement and energy of human forms. These sculptures often had multiple ideal viewing angels. The characteristic Baroque sculpture added extra-sculptural elements, for example concealed lighting, or water fountains.
Baroque architecture was taken up with enthusiasm in central Germany (Ludwigsburg Palace and Zwinger Dresden), Austria and Russia (Peterhof). In England the culmination of Baroque architecture was embodied in works by Sir Christopher Wren, Sir John Vanburgh and Nicholas Hawksmoor. Many examples of Baroque architecture and town planning are found in other European towns, and in Latin America. Town planning of this period featured radiating avenues intersecting in squares, which took ones from Baroque garden plans.
In modern usage, the term “Baroque” may still be used, usually describing works of art, craft, or design that are thought to have excessive ornamentation or complexity of line.
Baroque was superseded in many centres by the Rococo style, beginning in France in the late 1720s, especially for interiors, paintings and the decorative arts.
 The
1730 represented the height of Rococo development in France. The
style had spread beyond architecture and furniture to painting and
sculpture.
The
1730 represented the height of Rococo development in France. The
style had spread beyond architecture and furniture to painting and
sculpture.
 The
Rococo style spread with French artists and engraved publications. It
was readily received in the Catholic parts of Germany, Bohemia, and
Austria, where it was merged with the lively German Baroque
traditions. In Great Britain Rococo was always thought of as the
“French taste”. It was never widely adopted as an architectural
style, although its influence was strongly felt in such areas as
silverwork, porcelain, and silk. Thomas Chippendale transformed
British furniture design through his adaptation and refinement of the
style.
The
Rococo style spread with French artists and engraved publications. It
was readily received in the Catholic parts of Germany, Bohemia, and
Austria, where it was merged with the lively German Baroque
traditions. In Great Britain Rococo was always thought of as the
“French taste”. It was never widely adopted as an architectural
style, although its influence was strongly felt in such areas as
silverwork, porcelain, and silk. Thomas Chippendale transformed
British furniture design through his adaptation and refinement of the
style.
 It
is not surprising, that French Rococo art was at home indoors.
Metalwork, porcelain figures, frills and especially furniture rose to
new pre-eminence as the French upper class thought to outfit their
homes in the new fashionable style.
It
is not surprising, that French Rococo art was at home indoors.
Metalwork, porcelain figures, frills and especially furniture rose to
new pre-eminence as the French upper class thought to outfit their
homes in the new fashionable style.
Rococo style took pleasure in asymmetry, a taste that was new to European style.
During the Rococo period, furniture was lightened, physically and visually. The idea of furniture had evolved to a symbol of status and took on a role in comfort and versatility. Furniture could be easily moved around for gatherings.
In general, Rococo is an entirely interior style because the wealthy and aristocratic moved back to Paris from Versailles.
 Though
Rococo originated in the purely decorative arts, the style showed
clearly in painting. The painters used delicate colours and curving
forms, decorating their canvases with cherubs and myths of love.
Portraiture was also popular among Rococo painters.
Though
Rococo originated in the purely decorative arts, the style showed
clearly in painting. The painters used delicate colours and curving
forms, decorating their canvases with cherubs and myths of love.
Portraiture was also popular among Rococo painters.
Sculpture was another area where the Rococo was widely adopted. Etienne-Maurice Falconet is widely considered as one of the best representatives of French Rococo. This style was best expressed through delicate porcelain sculpture. Falconet himself was a director of a famous porcelain factory.
ІV Answer the questions:
What kind of style is Baroque?
Whose works signify the Baroque style in painting?
Where was Baroque architecture taken up with enthusiasm?
Where can examples of Baroque architecture be found?
What does the term “Baroque” mean in modern usage?
What style was Baroque superseded by?
Who promoted the Rococo style spreading?
Where was this style popular?
How was Rococo embodied in furniture?
Why is Rococo considered to be an entirely interior style?
