
- •Contents
- •Preface
- •How to use this book
- •Chapter 1 Units, constants, and conversions
- •1.1 Introduction
- •1.2 SI units
- •1.3 Physical constants
- •1.4 Converting between units
- •1.5 Dimensions
- •1.6 Miscellaneous
- •Chapter 2 Mathematics
- •2.1 Notation
- •2.2 Vectors and matrices
- •2.3 Series, summations, and progressions
- •2.5 Trigonometric and hyperbolic formulas
- •2.6 Mensuration
- •2.8 Integration
- •2.9 Special functions and polynomials
- •2.12 Laplace transforms
- •2.13 Probability and statistics
- •2.14 Numerical methods
- •Chapter 3 Dynamics and mechanics
- •3.1 Introduction
- •3.3 Gravitation
- •3.5 Rigid body dynamics
- •3.7 Generalised dynamics
- •3.8 Elasticity
- •Chapter 4 Quantum physics
- •4.1 Introduction
- •4.3 Wave mechanics
- •4.4 Hydrogenic atoms
- •4.5 Angular momentum
- •4.6 Perturbation theory
- •4.7 High energy and nuclear physics
- •Chapter 5 Thermodynamics
- •5.1 Introduction
- •5.2 Classical thermodynamics
- •5.3 Gas laws
- •5.5 Statistical thermodynamics
- •5.7 Radiation processes
- •Chapter 6 Solid state physics
- •6.1 Introduction
- •6.2 Periodic table
- •6.4 Lattice dynamics
- •6.5 Electrons in solids
- •Chapter 7 Electromagnetism
- •7.1 Introduction
- •7.4 Fields associated with media
- •7.5 Force, torque, and energy
- •7.6 LCR circuits
- •7.7 Transmission lines and waveguides
- •7.8 Waves in and out of media
- •7.9 Plasma physics
- •Chapter 8 Optics
- •8.1 Introduction
- •8.5 Geometrical optics
- •8.6 Polarisation
- •8.7 Coherence (scalar theory)
- •8.8 Line radiation
- •Chapter 9 Astrophysics
- •9.1 Introduction
- •9.3 Coordinate transformations (astronomical)
- •9.4 Observational astrophysics
- •9.5 Stellar evolution
- •9.6 Cosmology
- •Index
172 |
Optics |
|
|
8.7Coherence (scalar theory)
Mutual |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(t)ψ (t+ τ) |
|
|
|
|
||||||||||
coherence |
|
Γ12(τ) = |
|
ψ |
1 |
|
|
|
(8.97) |
||||||||||||||||||||||
function |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
ψ |
1 |
(t)ψ (t+ τ) |
|
||||||||||||||||
|
|
γ12(τ) = |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
(8.98) |
||||||||||||
Complex degree |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2 |
|
|
|
2 |
|
1/2 |
|
||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
[|ψ1| |
|ψ2| |
] |
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||
of coherence |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
= |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Γ12(τ) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
(8.99) |
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
[Γ11(0)Γ22(0)]1/2 |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
Combined |
|
Itot = I1 + I2 + 2(I1I2) |
1/2 |
[γ12 |
(τ)] |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
intensitya |
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(8.100) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
Fringe visibility |
|
|
|
|
|
2(I1I2)1/2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|γ12(τ)| |
(8.101) |
||||||||
V (τ) = |
|
|
|
I1 + I2 |
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
if |γ12(τ)| is a |
V = |
Imax − Imin |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(8.102) |
|||||||||||||||||||
constant: |
|
Imax + Imin |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||
if I1 = I2: |
V (τ) = |γ12(τ)| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(8.103) |
|||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
ψ |
1 |
(t)ψ (t+ τ) |
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||
Complex degree |
γ(τ) = |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(8.104) |
||||||
|
|
|
|
|ψ1(t)2| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||
of temporal |
|
= % |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||
b |
|
|
|
|
I(ω)e−iωτ dω |
|
|
|
|
(8.105) |
|||||||||||||||||||||
coherence |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
I(ω) dω |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
% |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Coherence time |
∆τc = |
∆lc |
|
|
|
1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(8.106) |
|||||||||||||||
and length |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
|
|
|
c |
|
∆ν |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
ψ |
1 |
ψ |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
Complex degree |
γ(D) = |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
(8.107) |
||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
of spatial |
|
|
|
|
|
|
[|ψ1|2 |ψ2|2 ]1/2 |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||
c |
|
|
= % |
I(sˆ)eikD sˆ dΩ |
|
|
|
|
(8.108) |
||||||||||||||||||||||
coherence |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
I(sˆ) dΩ· |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
% |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
Intensity |
d |
|
I1I2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
= 1 + γ2(D) |
(8.109) |
||||||||||||||||
correlation |
|
2 |
|
|
|
1/2 |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
[ I1 |
2 |
I2 |
] |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
Speckle |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
intensity |
|
pr(I) = |
|
|
|
|
|
|
e−I/ I |
|
|
|
|
|
|
(8.110) |
|||||||||||||||
|
|
I |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||
distributione |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
Speckle size |
|
|
|
|
λ |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
(coherence |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
∆wc α |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(8.111) |
||||||||
width) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Γij mutual coherence function
τtemporal interval
ψi (complex) wave disturbance at spatial point i
ttime
· |
mean over time |
γij |
complex degree of coherence |
complex conjugate
Itot |
combined intensity |
Ii |
intensity of disturbance at |
|
point i |
real part of
Imax max. combined intensity
Imin min. combined intensity
γ(τ) degree of temporal coherence
I(ω) specific intensity
ωradiation angular frequency
cspeed of light
∆τc coherence time ∆lc coherence length
∆ν spectral bandwidth
γ(D) degree of spatial coherence
Dspatial separation of points 1 and 2
I(sˆ) specific intensity of distant extended source in direction sˆ
dΩ di erential solid angle
sˆ unit vector in the direction of dΩ
kwavenumber
pr probability density
∆wc characteristic speckle size
λwavelength
αsource angular size as seen from the screen
aFrom interfering the disturbances at points 1 and 2 with a relative delay τ. bOr “autocorrelation function.”
cBetween two points on a wavefront, separated by D. The integral is over the entire extended source.
dFor wave disturbances that have a Gaussian probability distribution in amplitude. This is “Gaussian light” such as from a thermal source.
eAlso for Gaussian light.

8.8 Line radiation |
173 |
|
|
8.8 Line radiation
Spectral line broadening
Natural |
I(ω) = |
|
|
|
|
(2πτ)−1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(8.112) |
||||||||
broadeninga |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||
(2τ)−2 + (ω − ω0)2 |
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||
Natural |
1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(8.113) |
|||||
half-width |
∆ω = |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
2τ |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Collision |
I(ω) = |
|
|
|
|
(πτc)−1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(8.114) |
||||||||
broadening |
(τc)−2 + (ω − ω0)2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||
Collision and |
|
1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
πmkT |
|
|
|
−1/2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
pressure |
|
|
|
|
2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
∆ω = τc |
= pπd |
|
|
16 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
(8.115) |
||||||||||||
half-widthc |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
mc2 |
1/2 |
|
− |
2 |
( |
ω |
− |
ω |
0) |
2 |
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||
Doppler |
I(ω) = |
|
|
|
|
|
|
exp |
mc |
|
|
|
|||||||||||
|
|
|
2 |
|
|
|
|
2 |
|
|
|||||||||||||
broadening |
|
2kT ω0 π |
|
|
2kT |
|
|
ω0 |
|
|
|||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(8.116) |
|||
Doppler |
|
|
|
|
|
|
kT ln2 1/2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
half-width |
∆ω = ω0 |
|
2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(8.117) |
|||||||||
mc2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||
I(ω) normalised intensityb
τlifetime of excited state
ωangular frequency (= 2πν)
∆ω half-width at half-power
ω0 centre frequency
τc mean time between collisions
ppressure
de ective atomic diameter
mgas particle mass
kBoltzmann constant
Ttemperature
cspeed of light
I(ω) |
∆ω |
ω0 |
aThe transition probability per unit time for the state is = 1/τ. In the classical limit of a damped oscillator, the
e-folding time of the electric field is 2τ. Both the natural and collision profiles described here are Lorentzian.
%
bThe intensity spectra are normalised so that I(ω) dω = 1, assuming ∆ω/ω0 1.
cThe pressure-broadening relation combines Equations (5.78), (5.86) and (5.89) and assumes an otherwise perfect gas of finite-sized atoms. More accurate expressions are considerably more complicated.
Einstein coe cientsa
Absorption |
|
R12 = B12Iν n1 |
(8.118) |
Rij |
transition rate, level i → j (m−3 s−1) |
|
|
|||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||||||||
|
Bij |
Einstein B coe cients |
|
8 |
||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Iν |
specific intensity of radiation field |
|
|
Spontaneous |
R21 |
= A21n2 |
|
(8.119) |
A21 |
Einstein A coe cient |
|
|
||||||||||
|
ni |
number density of atoms in quantum |
|
|
||||||||||||||
emission |
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
level i (m−3) |
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Stimulated |
|
R21 = B21Iν n2 |
(8.120) |
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
emission |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
A21 |
= |
|
2hν3 |
|
g1 |
(8.121) |
h |
Planck constant |
|
|
|
Coe cient |
|
|
B12 |
|
c2 |
g2 |
ν |
frequency |
|
|
||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||
ratios |
|
|
|
|
B21 |
g1 |
|
|
c |
speed of light |
|
|
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
= |
|
|
|
(8.122) |
gi |
degeneracy of ith level |
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
B12 |
g2 |
|
|
|
|||||||
aNote that the coe cients can also be defined in terms of spectral energy density, uν = 4πIν /c rather than Iν . In this |
|
|||||||||||||||||
case |
A21 |
= |
8πhν3 |
g1 |
. See also Population densities on page 116. |
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
B12 |
|
c3 |
g2 |
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
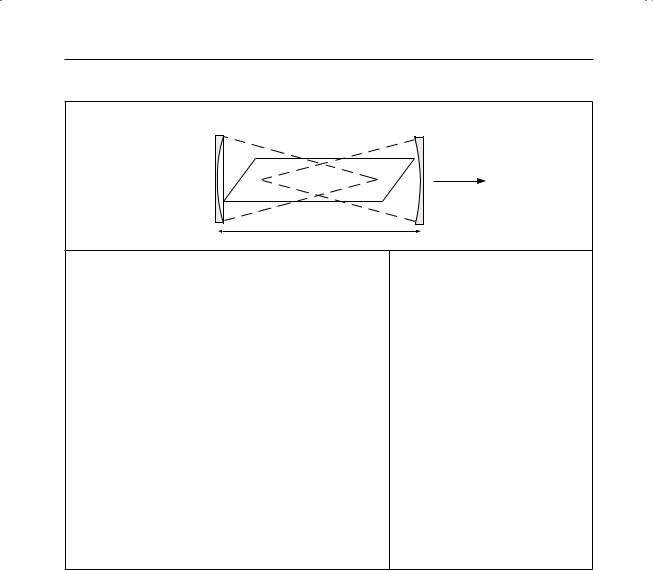
174 Optics
Lasersa
R1 |
R2 |
|
r1 |
light out
L r2
Cavity stability |
0 ≤ |
|
1 − |
L |
1 |
− |
L |
|
≤ |
1 (8.123) |
|||||||||||||
condition |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||
r1 |
r2 |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||
Longitudinal |
νn = |
|
|
c |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(8.124) |
|||||
cavity modesb |
|
|
|
n |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
2L |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
|
Q = |
|
2πL(R1R2)1/4 |
|
|
|
(8.125) |
||||||||||||||||
Cavity Q |
λ[1 − (R1R2)1/2] |
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
4πL |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(8.126) |
|||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||
|
λ(1 |
− |
R1R2) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
Cavity line |
∆νc = |
|
νn |
|
= 1/(2πτc) |
|
|
(8.127) |
|||||||||||||||
width |
|
Q |
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||
Schawlow– |
∆ν |
|
|
2πh(∆νc)2 |
|
|
|
|
glNu |
||||||||||||||
Townes line |
|
|
= |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
νn |
|
|
|
|
|
|
P |
|
|
glNu |
− |
guNl |
||||||||||
width |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(8.128) |
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Threshold |
R1R2 exp[2(α− β)L] > 1 |
(8.129) |
|||||||||||||||||||||
lasing condition |
|||||||||||||||||||||||
r1,2 radii of curvature of end-mirrors
Ldistance between mirror centres
νn mode frequency
ninteger
cspeed of light
Qquality factor
R1,2 |
mirror (power) reflectances |
λ |
wavelength |
∆νc |
cavity line width (FWHP) |
τc |
cavity photon lifetime |
∆ν |
line width (FWHP) |
Plaser power
gu,l |
degeneracy of upper/lower levels |
Nu,l |
number density of upper/lower |
|
levels |
αgain per unit length of medium
βloss per unit length of medium
aAlso see the Fabry-Perot etalon on page 163. Note that “cavity” refers to the empty cavity, with no lasing medium present.
bThe mode spacing equals the cavity free spectral range.
