
- •Contents
- •Preface
- •How to use this book
- •Chapter 1 Units, constants, and conversions
- •1.1 Introduction
- •1.2 SI units
- •1.3 Physical constants
- •1.4 Converting between units
- •1.5 Dimensions
- •1.6 Miscellaneous
- •Chapter 2 Mathematics
- •2.1 Notation
- •2.2 Vectors and matrices
- •2.3 Series, summations, and progressions
- •2.5 Trigonometric and hyperbolic formulas
- •2.6 Mensuration
- •2.8 Integration
- •2.9 Special functions and polynomials
- •2.12 Laplace transforms
- •2.13 Probability and statistics
- •2.14 Numerical methods
- •Chapter 3 Dynamics and mechanics
- •3.1 Introduction
- •3.3 Gravitation
- •3.5 Rigid body dynamics
- •3.7 Generalised dynamics
- •3.8 Elasticity
- •Chapter 4 Quantum physics
- •4.1 Introduction
- •4.3 Wave mechanics
- •4.4 Hydrogenic atoms
- •4.5 Angular momentum
- •4.6 Perturbation theory
- •4.7 High energy and nuclear physics
- •Chapter 5 Thermodynamics
- •5.1 Introduction
- •5.2 Classical thermodynamics
- •5.3 Gas laws
- •5.5 Statistical thermodynamics
- •5.7 Radiation processes
- •Chapter 6 Solid state physics
- •6.1 Introduction
- •6.2 Periodic table
- •6.4 Lattice dynamics
- •6.5 Electrons in solids
- •Chapter 7 Electromagnetism
- •7.1 Introduction
- •7.4 Fields associated with media
- •7.5 Force, torque, and energy
- •7.6 LCR circuits
- •7.7 Transmission lines and waveguides
- •7.8 Waves in and out of media
- •7.9 Plasma physics
- •Chapter 8 Optics
- •8.1 Introduction
- •8.5 Geometrical optics
- •8.6 Polarisation
- •8.7 Coherence (scalar theory)
- •8.8 Line radiation
- •Chapter 9 Astrophysics
- •9.1 Introduction
- •9.3 Coordinate transformations (astronomical)
- •9.4 Observational astrophysics
- •9.5 Stellar evolution
- •9.6 Cosmology
- •Index

7.6 LCR circuits |
147 |
|
|
7.6 LCR circuits
LCR definitions
Current |
I = |
dQ |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(7.139) |
||||||
|
dt |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
Ohm’s law |
V = IR |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(7.140) |
||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Ohm’s law (field |
J = σE |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(7.141) |
||||||||
form) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
Resistivity |
ρ = |
1 |
|
= |
RA |
(7.142) |
|||||||||||
σ |
|
|
|
|
l |
|
|||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
Capacitance |
C = |
|
Q |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(7.143) |
|||||
|
V |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
Current through |
I = C |
dV |
|
|
|
|
(7.144) |
||||||||||
capacitor |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||
|
|
dt |
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
Self-inductance |
L = |
Φ |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(7.145) |
|||||||
|
I |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
Voltage across |
V = −L |
dI |
(7.146) |
||||||||||||||
inductor |
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
dt |
|||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
Mutual |
L12 = |
|
Φ1 |
= L21 |
(7.147) |
||||||||||||
inductance |
|
|
I2 |
|
|
|
|||||||||||
|
| |
L12 |
| |
= k |
|
|
|
|
|
(7.148) |
|||||||
Coe cient of |
|
|
|
|
L1L2 |
||||||||||||
coupling |
|
|
|
( |
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
Linked magnetic |
Φ = Nφ |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(7.149) |
||||||||
flux through a coil |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Icurrent
Qcharge
Rresistance
Vpotential di erence over R
Icurrent through R
Jcurrent density
Eelectric field
σconductivity
ρresistivity
Aarea of face (I is normal to face)
llength
Ccapacitance
Vpotential di erence across C
Icurrent through C
ttime
Φtotal linked flux
Icurrent through inductor
Vpotential di erence over L
Φ1 |
total flux from loop 2 |
|
linked by loop 1 |
L12 |
mutual inductance |
I2 |
current through loop 2 |
kcoupling coe cient
between L1 and L2 (≤ 1)
Φlinked flux
Nnumber of turns around φ
φflux through area of turns
|
|
|
|
l |
|
A |
||
|
7

148 |
Electromagnetism |
|
|
Resonant LCR circuits
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
ω0 |
resonant |
Phase |
|
|
|
|
1/LC |
|
|
|
(series) |
|
|
angular |
||||
2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
frequency |
||||||||
resonant |
ω0 = "1/LC |
− |
R2 |
/L2 |
(parallel) |
|
L |
inductance |
||||||||
frequencya |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(7.150) |
C |
capacitance |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
R |
resistance |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
δω |
half-power |
|
|
|
|
1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
Tuningb |
|
δω |
= |
= |
|
R |
|
|
|
|
(7.151) |
|
bandwidth |
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
ω0 |
Q |
|
ω0L |
|
|
|
|
Q |
quality |
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
factor |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
Quality |
Q = 2π |
|
|
stored energy |
(7.152) |
|
|
|||||||||
factor |
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||
energy lost per cycle |
|
|
||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
aAt which the impedance is purely real.
bAssuming the capacitor is purely reactive. If L and R are parallel, then 1/Q = ω0L/R.
series
RL C
parallel
Energy in capacitors, inductors, and resistors
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
U |
stored energy |
Energy stored in a |
|
|
1 |
|
|
|
|
|
1 |
|
|
|
|
|
1 Q2 |
|
C |
capacitance |
|||||||
capacitor |
U = |
|
|
CV |
2 = |
|
|
QV = |
|
|
|
|
|
(7.153) |
Q |
charge |
|||||||||
2 |
|
|
2 C |
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
V |
potential di erence |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
L |
inductance |
Energy stored in an |
|
|
1 |
|
|
|
|
|
1 |
|
|
1 Φ2 |
|
||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||
|
U = |
|
|
LI |
= |
|
|
ΦI = |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(7.154) |
Φ |
linked magnetic flux |
||||||
inductor |
|
2 |
|
2 |
2 |
|
L |
|
|||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
I |
current |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Power dissipated in |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
V 2 |
|
|
W |
power dissipated |
|||||||
a resistora (Joule’s |
W = IV = I |
2 |
|
|
|
|
(7.155) |
||||||||||||||||||
|
R = R |
R |
resistance |
||||||||||||||||||||||
law) |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
τ |
relaxation time |
|
|
0 r |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
Relaxation time |
τ = |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(7.156) |
r |
relative permittivity |
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
|
|
|
|
σ |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
σ |
conductivity |
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
aThis is d.c., or instantaneous a.c., power.
Electrical impedance
Impedances in series |
Z tot = |
n |
Z n |
−1 |
(7.157) |
|||
Impedances in parallel |
Z tot = n |
Z n−1 |
(7.158) |
|||||
Impedance of capacitance |
|
|
i |
|
|
|
|
|
Z C = − ωC |
|
|
(7.159) |
|||||
|
|
|
||||||
Impedance of inductance |
Z L = iωL |
|
|
|
|
(7.160) |
||
|
|
|
|
|||||
Impedance: Z |
Capacitance: C |
|
|
|||||
Inductance: L |
Resistance: R = Re[Z ] |
|
||||||
Conductance: G = 1/R |
Reactance: X = Im[Z ] |
|
||||||
Admittance: Y = 1/Z |
Susceptance: S = 1/X |
|
||||||
7.6 LCR circuits |
149 |
|
|
Kirchho ’s laws
|
|
|
Ii |
currents impinging |
Current law |
Ii = 0 |
(7.161) |
|
on node |
|
node |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Vi |
potential di erences |
Voltage law |
Vi = 0 |
(7.162) |
|
around loop |
|
loop |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
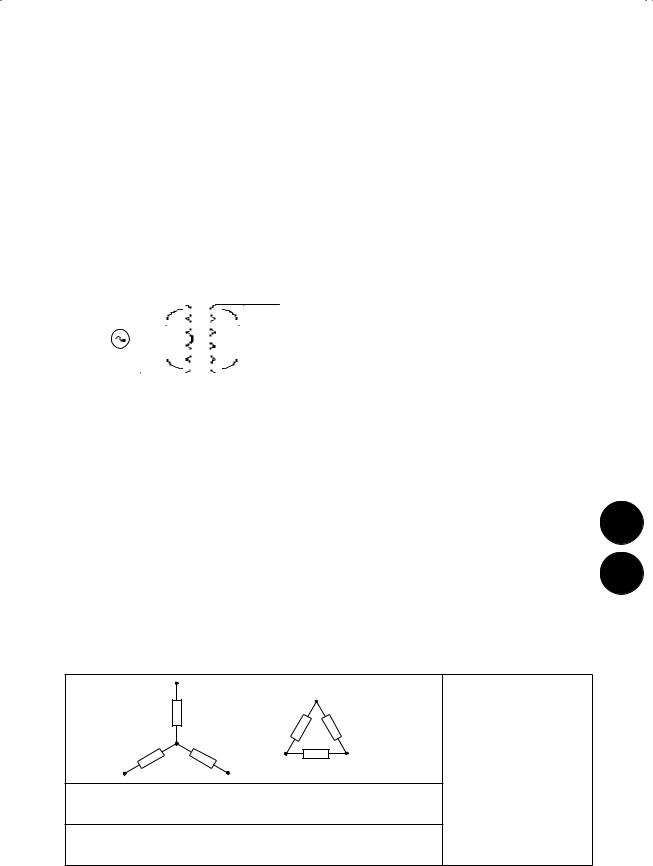
Transformersa
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
n |
turns ratio |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
N1 |
number of primary turns |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
I2 |
|
|
|
N2 |
number of secondary turns |
|
|
|
|
|
Z 1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
V1 |
primary voltage |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
V2 |
secondary voltage |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
V1 |
|
|
|
|
V2 |
Z 2 |
|
I1 |
primary current |
|
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
I2 |
secondary current |
|
|
|
|||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Z out |
output impedance |
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
I1 |
|
N1 |
N2 |
|
|
|
Z in |
input impedance |
|
|
|
|||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Z 1 |
source impedance |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Z 2 |
load impedance |
|
|
|
Turns ratio |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
n = N2/N1 |
(7.163) |
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Transformation of voltage and current |
V2 = nV1 |
(7.164) |
|
|
||||||||||||||||
I2 = I1/n |
(7.165) |
|
|
|||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Output impedance (seen by Z 2) |
|
|
|
Z out = n2Z 1 |
(7.166) |
|
|
|||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
7 |
||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Input impedance (seen by Z 1) |
|
|
|
Z in = Z 2/n2 |
(7.167) |
|
|
|||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
aIdeal, with a coupling constant of 1 between loss-free windings.
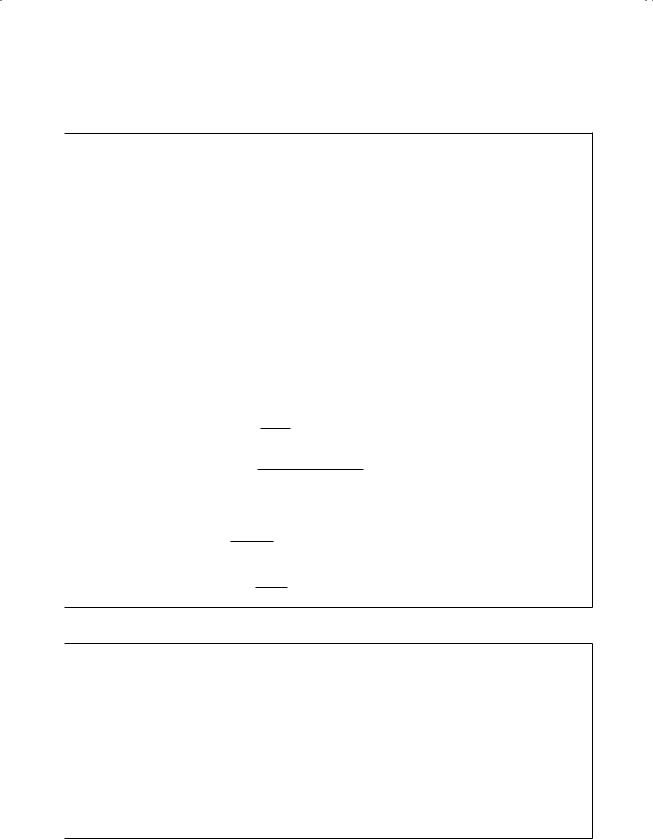
Star–delta transformation
1 |
|
1 |
|
‘Star’ |
|
‘Delta’ |
|
|
|
||
Z1 |
Z12 |
|
Z13 |
|
|
2 |
Z2 |
Z3 |
3 |
2 |
3 |
|
Z23 |
Star |
Zi = |
Zij Zik |
(7.168) |
impedances |
Zij + Zik + Zjk |
Delta |
1 |
1 |
1 |
|
|||
impedances |
Zij = ZiZj |
|
+ |
|
+ |
|
(7.169) |
Zi |
Zj |
Zk |
|||||
i,j,k node indices (1,2, or 3)
Zi impedance on node i
Zij impedance connecting nodes i and j
150 |
Electromagnetism |
|
|
7.7 Transmission lines and waveguides
Transmission line relations
|
|
∂V |
|
|
∂I |
|
||||||||||||||||
Loss-free |
|
|
|
|
= −L |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(7.170) |
|||||||
|
∂x |
∂t |
||||||||||||||||||||
transmission line |
|
|
∂I |
|
|
∂V |
|
|||||||||||||||
equations |
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
∂x = −C ∂t |
(7.171) |
|||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||
Wave equation for a |
|
|
1 ∂2V |
= |
|
∂2V |
(7.172) |
|||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||
|
LC ∂x2 |
∂t2 |
||||||||||||||||||||
lossless transmission |
|
|
1 ∂2I |
|
|
|
|
∂2I |
|
|||||||||||||
line |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
LC ∂x2 = ∂t2 |
(7.173) |
|||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||
Characteristic |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
L |
|
|||||||||||||
impedance of |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Zc = C |
(7.174) |
|||||||||||||||||||||
lossless line |
||||||||||||||||||||||
Characteristic |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
R + iωL |
|
||||||||||||
impedance of lossy |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Z c = G+ iωC |
(7.175) |
|||||||||||||||||||||
line |
||||||||||||||||||||||
Wave speed along a |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
lossless line |
vp = vg = |
√ |
|
|
|
(7.176) |
||||||||||||||||
LC |
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||
Input impedance of |
Z in = Zc |
Z t coskl − iZc sinkl |
(7.177) |
|||||||||||||||||||
a terminated lossless |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2Zc coskl − iZ t sinkl |
|
||||||||||||
line |
|
|
|
|
= Zc |
/Z t if l = λ/4 |
(7.178) |
|||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Reflection coe cient |
|
|
|
|
Z t − Z c |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
from a terminated |
r = |
|
|
(7.179) |
||||||||||||||||||
line |
|
|
|
|
Z t + Z c |
|
||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||
Line voltage |
vswr = |
1 + |r| |
|
(7.180) |
||||||||||||||||||
standing wave ratio |
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1 − |r| |
|
||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||
Vpotential di erence across line
Icurrent in line
Linductance per unit length
Ccapacitance per unit length
xdistance along line
ttime
Zc characteristic impedance
Rresistance per unit length of conductor
Gconductance per unit length of insulator
ωangular frequency
vp phase speed vg group speed
Zin (complex) input impedance
Zt (complex) terminating
impedance
kwavenumber (= 2π/λ)
ldistance from termination
r(complex) voltage reflection coe cient
Transmission line impedancesa
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Coaxial line |
Zc = |
µ |
|
|
|
|
|
|
b |
60 |
|
|
|
b |
|
||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
ln |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
ln |
|
(7.181) |
|||||||||||||||
4π2 |
a |
√ |
|
|
a |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
r |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
Open wire feeder |
Zc = |
µ |
|
|
|
|
l |
120 |
|
|
|
l |
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
ln |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
ln |
|
|
(7.182) |
|||||||||||||
π2 |
r |
√ |
|
|
r |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
r |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
Paired strip |
Zc = |
µ d |
|
377 d |
|
|
|
|
|
|
(7.183) |
||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||
w |
√ |
|
w |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
r |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
Microstrip line |
Zc √ |
|
377 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(7.184) |
|||||||||
|
|
[(w/h) + 2] |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||
|
r |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
Zc characteristic impedance (Ω)
aradius of inner conductor
bradius of outer conductor
permittivity (= 0 r)
µpermeability (= µ0µr)
rradius of wires
ldistance between wires ( r)
dstrip separation
wstrip width ( d)
hheight above earth plane ( w)
aFor lossless lines.

7.7 Transmission lines and waveguides |
151 |
|
|
Waveguidesa
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
kg |
wavenumber in guide |
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
ω |
angular frequency |
|||
Waveguide |
|
ω2 |
|
|
m2π2 |
|
|
|
|
n2π2 |
|
|
a |
|
guide height |
||||||||||||
kg2 = |
− |
|
− |
|
(7.185) |
b |
|
guide width |
|||||||||||||||||||
equation |
c2 |
|
a2 |
|
|
b2 |
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
m,n |
mode indices with respect to |
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
a and b (integers) |
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
c |
|
speed of light |
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
νc = c |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
Guide cuto |
|
m |
! |
2 |
|
|
|
|
|
n |
! |
2 |
|
|
|
νc |
cuto frequency |
||||||||||
frequency |
|
|
+ |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(7.186) |
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||
|
2a |
|
|
2b |
|
|
|
|
ωc |
2πνc |
|||||||||||||||||
Phase velocity |
vp = |
|
|
|
|
c |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(7.187) |
vp |
phase velocity |
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
above cuto |
(2 1 − (νc/ν |
) |
2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
ν |
|
frequency |
||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||
Group velocity |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||
above cuto |
vg = c /vp = c 1 − (νc/ν) |
|
(7.188) |
vg |
group velocity |
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
ZTM |
wave impedance for |
|||
|
ZTM = Z0 |
1 |
|
|
(νc/ν)2 |
|
|
|
|
(7.189) |
|
|
transverse magnetic modes |
||||||||||||||
Wave |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Z |
|
wave impedance for |
||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
− |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
TE |
||||||||
impedancesb |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
transverse electric modes |
||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(νc/ν)2 |
|
(7.190) |
|
|
||||||||||||||||
|
ZTE = Z0/ |
|
1 |
|
|
|
Z |
|
impedance of free space |
||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
− |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
0 |
(= ( |
|
) |
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
µ0/ 0 |
||||||||
Field solutions for TEmn modesc |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
Bx = |
ikgc2 ∂Bz |
|
|
iωc2 ∂Bz |
|
|
|
|||
ωc2 ∂x |
|
Ex = |
2 |
∂y |
|
|
|
|||
|
ikgc2 ∂Bz |
|
|
ωc |
|
|
|
|||
By = |
|
Ey = −i |
ωc2 ∂B |
z |
(7.191) |
|
||||
ωc2 |
∂y |
|
2 |
|
|
|
||||
|
|
mπx |
nπy |
|
ωc |
∂x |
b |
7 |
||
|
|
Ez =0 |
|
|
|
|||||
Bz =B0 cos |
|
cos b |
|
|
|
|||||
a |
|
|
|
|
||||||
Field solutions for TMmn modesc |
|
|
z |
a |
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
x |
|
|
Ex = |
ikgc2 ∂Ez |
|
|
−iω ∂Ez |
y |
|
|
|||
2 |
∂x |
|
Bx = |
|
|
|||||
|
ωc |
|
|
2 |
|
∂y |
|
|
|
|
|
ikgc2 ∂Ez |
|
|
ωc |
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
iω ∂Ez |
|
(7.192) |
|
||||
Ey = ωc2 |
|
|
By = |
|
|
|||||
∂y |
|
ω2 |
∂x |
|
|
|
||||
Ez =E0 sin mπx sin nπy |
|
c |
|
|
|
|
|
|||
Bz =0 |
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
|
a |
b |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
aEquations are for lossless waveguides with rectangular cross sections and no dielectric. |
|
|
||||||||
bThe ratio of the electric field to the magnetic field strength in the xy plane. |
|
|
||||||||
cBoth TE and TM modes propagate in the z direction with a further factor of exp[i(kgz − ωt)] on all components. |
|
|||||||||
B0 and E0 are the amplitudes of the z components of magnetic flux density and electric field respectively. |
|
|||||||||
