
- •Contents
- •Vocabulary
- •Elements and compounds
- •1.6. Read the following text and say if it is true that interatomic distance is fixed in all states of a metal. Read again to answer the questions after it.
- •Vocabulary
- •Three states of matter
- •1.10. Learn to read the following measurements.
- •1.11. Read out the numbers.
- •1.12. A) Compare the spanners. Make sentences.
- •At the Descriptive Geometry Class
- •Vocabulary
- •Characteristic Features of Some Elements
- •Vocabulary Test
- •Grammar Test
- •Vocabulary
- •Materials science in the past and present
- •2.9. Form nouns from the following words:
- •Vocabulary
- •Engineering materials and their properties (Part I)
- •2.12. Reread the text and rewrite the following according to the model, replacing the words in italics with an expression from the text which has a similar meaning.
- •2.16. Read and translate the following text. Talk about the properties of engineering materials in your own words.
- •Vocabulary
- •Engineering materials and their properties (Part II)
- •Vocabulary Test
- •Grammar Test
- •Unit 3. Metals: properties, classification and crystal structure
- •Read the list of words below and choose the ones related to science of materials:
- •Vocabulary
- •Metals, alloys and their uses
- •3.4. Reading comprehension. Read the text Availability, Properties and Classification of Metals and for questions 1–5 (after the text) choose the best answers from a–d.
- •Vocabulary
- •Availability, properties and classification of metals
- •3.5. Use the questions and talk giving the main ideas of the text above.
- •Vocabulary
- •Metallic crystal structure
- •Vocabulary Test
- •Grammar Test
- •Unit 4. Engineering materials. Iron and ferrous metals
- •4.2. Read the text Iron and Its Properties. Answer the following questions. What new have you learnt from the text?
- •Vocabulary
- •Iron and its properties
- •Vocabulary
- •4.4. Connect the two matching parts of the sentences related to the blast furnace operation.
- •Vocabulary
- •Ferrous metals
- •From the history of steelmaking
- •Alloy steels
- •Grammar and Vocabulary Questionnaire
- •Structural steels for shipbuilding
- •Vocabulary Test
- •Grammar Test
- •4.17. Just for fun.
- •4.18. Read the text and agree and disagree with the statements after it.
- •4.19. In the above text, find the English equivalents for the following words and word combinations:
- •4.20. Read the text and write a list of titanium and its alloys qualities that make titanium different from other metals. A wonder metal
- •Long-term corrosion protection for hulls and water jets
- •Nonmetallic materials
- •4.24. What kinds of non-metal things do people use at home and at work in the office? Entitle the text below. Compare metals and non-metals as structural materials.
- •Unit 5. Materials technology
- •Vocabulary
- •Processing and heat treatment of metals
- •Visit to a Plant
- •Hardening plain carbon steel
- •Vocabulary
- •Welding processes
- •Gas welding
- •Hard to define
- •Nanotechnology
- •Larger to smaller: materials perspective
- •References
- •Appendix Summary tips Аннотирование и реферирование
- •Аннотация и реферат
- •Структура реферата
- •Этапы реферирования и аннотирования
- •Некоторые рекомендации по составлению аннотации и реферата
Unit 5. Materials technology
5.1. Read the text Processing and Heat Treatment of Metals and from statements 1–3 below choose the one expressing its main idea.
1. Processing is a variety of technologies.
2. Joining operations are a major step in processing.
3. The properties of metals can be improved by processing.
Vocabulary
processing n |
— |
обработка |
route n |
— |
(технологический) маршрут |
finished article |
— |
готовое изделие |
casting n |
— |
литье, отливка (процесс); отливка (изделие); заливка (металла в форму) |
mould n |
— |
(литейная) форма, изложница |
metalworking industry |
— |
металлообрабатывающая промышленность |
mould cavity |
— |
полость формы |
foundry n |
— |
литейная, литейный цех |
rolling n |
— |
прокатка |
rolled products |
— |
прокат |
sheets and plates |
— |
зд. тонколистовой и толстолистовой прокат |
sheet metal forming |
— |
штамповка листового материала |
shearing n |
— |
обрезка, отрезание |
die n |
— |
штамп, матрица |
section n |
— |
профиль |
bar n |
— |
сортовой прокат, полоса |
rod n |
— |
(круглый) пруток |
machining n |
— |
механическая обработка, обработка на станке |
turning n |
— |
обточка |
drilling n |
— |
сверление |
milling n |
— |
фрезерование |
threading n |
— |
нарезка резьбы |
joining n |
— |
соединение, присоединение |
finishing n |
— |
окончательная обработка, отделка |
grinding n |
— |
шлифование |
painting n |
— |
нанесение краски |
fine powder |
— |
тонкий порошок |
hot pressing |
— |
горячее прессование |
annealing n |
— |
отжиг |
quenching n |
— |
закалка, быстрое охлаждение |
tempering n |
— |
отпуск |
challenge n |
— |
сложная задача; перспектива |
Processing and heat treatment of metals
There are a number of established routes for processing raw metals into finished articles. Conventional forming methods start by melting the basic metal and then casting the liquid metal into a mould. The production of melting castings is one of the basic processes of the metalworking industry. A casting may be defined as a “metal object obtained by allowing molten metal to solidify in a mould”, the shape of the object being determined by the shape of the mould cavity. A foundry is a commercial establishment for producing castings.
Rolling is the most common metalworking process. More than 90% of the aluminium, steel and copper produced is rolled at least once in the course of production. The most common rolled products are sheets and plates. Rolling can be done either hot or cold. If the rolling is finished cold, the surface will be smoother and the product stronger.
Sheet metal forming is widely used when parts of certain shape and size are needed, it includes forging, bending and shearing. Each of these processes may be used alone, but often all the three are applied to the same part.
Forging is the oldest known metalworking process by heating and hammering. Metal shaping by controlled plastic deformation is the basis for all forging operations. Modern forging is done at temperatures ranging from 2500ºF to room temperature. A wide range of processes and equipment have been developed to produce forgings. Part configuration generally determines the forging method chosen. Bending can be done by pressing between two dies. Shearing is a cutting operation similar to that used for cloth.
Shaped components are also made from standard sections (sheet, plate, tube, bar, rod, etc.) by machining. It includes cutting, turning, drilling, milling and threading.
Components are assembled into finished articles by joining operations (e.g. welding) which are usually carried out in conjunction with finishing operations (e.g. grinding or painting). Increasing use is now being made of alternative processing routes. In powder metallurgy the liquid metal is atomized into small droplets which solidify to a fine powder. The powder is then hot pressed to shape, hot pressing is also used for shaping high-technology ceramics.
The properties of a metal can be further improved by use of heat treatment. Heat treatment is the process of controlled heating and cooling of metals to change their structural arrangement and to ensure certain desirable properties. Annealing consists of heating the metal to a temperature slightly above the critical temperature and then cooling slowly to produce an even grain structure, reduce the hardness, and increase the ductility. Quenching or rapid cooling from above the critical temperature by immersion in cold water or some other cooling medium, is a hardening treatment. Tempering consists of reheating the quenched metal to restore ductility to some extent and reduce the brittleness.
New technological processes are rapidly emerging, providing new opportunities and challenges for product design and for more efficient manufacture.
5.2. Read the text and match sentences a, b, c and d to the flow diagram in Fig. 2.
D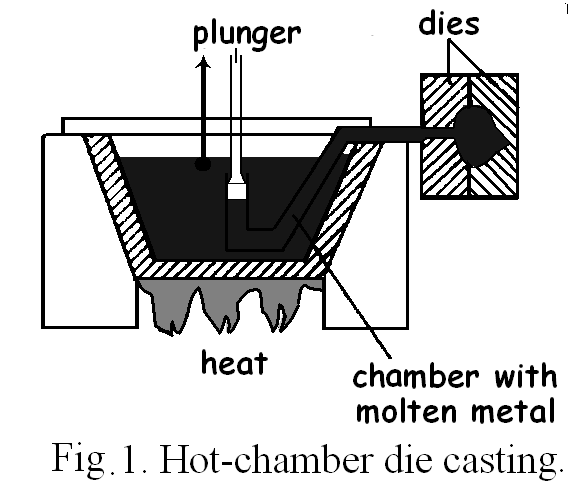 ie
casting is a
common process in the engineering industry. It is used to produce
many machine components. For some metals with a low melting point,
such as a zinc alloy, a process called hot-chamber die casting is
used. For example, a carburettor body is produced by this method.
There are three main stages in the process. In the first stage the
dies are closed. Then the injection plunger is forced downwards and
the molten metal is forced into the dies. Finally, in the third
stage, the dies are opened in order to remove the carburettor body.
ie
casting is a
common process in the engineering industry. It is used to produce
many machine components. For some metals with a low melting point,
such as a zinc alloy, a process called hot-chamber die casting is
used. For example, a carburettor body is produced by this method.
There are three main stages in the process. In the first stage the
dies are closed. Then the injection plunger is forced downwards and
the molten metal is forced into the dies. Finally, in the third
stage, the dies are opened in order to remove the carburettor body.
Notes
die casting – литье под давлением
flow diagram – технологическая схема
Fig. 2. Flow diagram of hot-chamber die casting.
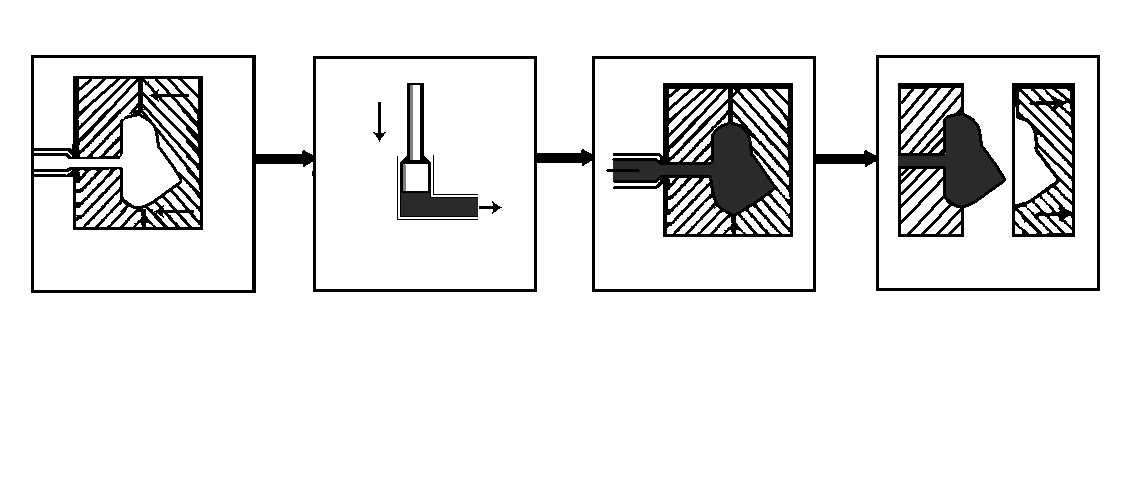
b) The dies are closed. |
c) The metal is forced into the dies. d) The plunger is forced downwards. |
5.3. Read, translate and act out the dialogue Visit to a Plant.
Mr. Ranchi – Foreign Representative (FR), Mumbai
Mr. Belov – Production Manager (PM), St. Petersburg
