
- •Contents
- •Vocabulary
- •Elements and compounds
- •1.6. Read the following text and say if it is true that interatomic distance is fixed in all states of a metal. Read again to answer the questions after it.
- •Vocabulary
- •Three states of matter
- •1.10. Learn to read the following measurements.
- •1.11. Read out the numbers.
- •1.12. A) Compare the spanners. Make sentences.
- •At the Descriptive Geometry Class
- •Vocabulary
- •Characteristic Features of Some Elements
- •Vocabulary Test
- •Grammar Test
- •Vocabulary
- •Materials science in the past and present
- •2.9. Form nouns from the following words:
- •Vocabulary
- •Engineering materials and their properties (Part I)
- •2.12. Reread the text and rewrite the following according to the model, replacing the words in italics with an expression from the text which has a similar meaning.
- •2.16. Read and translate the following text. Talk about the properties of engineering materials in your own words.
- •Vocabulary
- •Engineering materials and their properties (Part II)
- •Vocabulary Test
- •Grammar Test
- •Unit 3. Metals: properties, classification and crystal structure
- •Read the list of words below and choose the ones related to science of materials:
- •Vocabulary
- •Metals, alloys and their uses
- •3.4. Reading comprehension. Read the text Availability, Properties and Classification of Metals and for questions 1–5 (after the text) choose the best answers from a–d.
- •Vocabulary
- •Availability, properties and classification of metals
- •3.5. Use the questions and talk giving the main ideas of the text above.
- •Vocabulary
- •Metallic crystal structure
- •Vocabulary Test
- •Grammar Test
- •Unit 4. Engineering materials. Iron and ferrous metals
- •4.2. Read the text Iron and Its Properties. Answer the following questions. What new have you learnt from the text?
- •Vocabulary
- •Iron and its properties
- •Vocabulary
- •4.4. Connect the two matching parts of the sentences related to the blast furnace operation.
- •Vocabulary
- •Ferrous metals
- •From the history of steelmaking
- •Alloy steels
- •Grammar and Vocabulary Questionnaire
- •Structural steels for shipbuilding
- •Vocabulary Test
- •Grammar Test
- •4.17. Just for fun.
- •4.18. Read the text and agree and disagree with the statements after it.
- •4.19. In the above text, find the English equivalents for the following words and word combinations:
- •4.20. Read the text and write a list of titanium and its alloys qualities that make titanium different from other metals. A wonder metal
- •Long-term corrosion protection for hulls and water jets
- •Nonmetallic materials
- •4.24. What kinds of non-metal things do people use at home and at work in the office? Entitle the text below. Compare metals and non-metals as structural materials.
- •Unit 5. Materials technology
- •Vocabulary
- •Processing and heat treatment of metals
- •Visit to a Plant
- •Hardening plain carbon steel
- •Vocabulary
- •Welding processes
- •Gas welding
- •Hard to define
- •Nanotechnology
- •Larger to smaller: materials perspective
- •References
- •Appendix Summary tips Аннотирование и реферирование
- •Аннотация и реферат
- •Структура реферата
- •Этапы реферирования и аннотирования
- •Некоторые рекомендации по составлению аннотации и реферата
Vocabulary
mark v |
— |
ознаменовать, отмечать |
ornament n |
— |
украшение, орнамент |
related a |
— |
связанный |
shaping n |
— |
придание формы; пластическая обработка |
concrete n |
— |
бетон |
core n |
— |
сердцевина, зд. арматура |
break down phrv |
— |
разобрать (на части) |
recycle v |
— |
повторно использовать |
dump v |
— |
выбрасывать; сбывать |
aluminium bronze |
— |
алюминиевая бронза |
alloying n |
— |
легирование |
adapt v |
— |
приспосабливать |
intricate a |
— |
сложный, замысловатый |
treat v |
— |
обрабатывать |
meet requirements |
— |
удовлетворять требованиям |
range n |
— |
ряд, ассортимент; диапазон |
Metals, alloys and their uses
1. The use of metals marked one of the great stages in the evolution of man. Probably the first metals used by man were gold, silver and copper, which were found in the native or metallic state and used principally as ornaments. The Bronze Age and Iron Age are very significant historical periods related to the discovery and shaping of these metals. Man has used metals for centuries in gradually increasing quantities, but it was not until the Industrial Revolution that they came to be employed in vast quantities.
2. Why do humans use metals still so much today when there are other materials, especially plastics, which are available? A material is generally used because it offers the required strength, and other properties at minimum cost. Appearance is also an important factor. The main advantages of metals are their strength and toughness. Concrete may be cheaper and is often used in building, but even concrete depends on its core of steel for strength.
3. Plastics are lighter and more corrosion-resistant, but they are not usually as strong. Another problem with plastics is what to do with them after use. Metal objects can often be broken down and the metals recycled; plastics can only be dumped or burned.
4. Not all metals are strong, however. Copper and aluminium, for example, are both fairly weak, but if they are mixed together, the result is an alloy called aluminium bronze, which is much stronger than either pure copper or pure aluminium. Alloying is an important method of obtaining properties that are required: strength, toughness, resistance to wear, magnetic properties, high electrical resistance or corrosion resistance.
5. A great variety of metal properties allows the materials to be adapted to intricate machines and structures. Methods of extracting, producing and treating metals are being developed all the time to meet engineering requirements. This means that there is an enormous range of metals and metallic materials available from which to choose.
Notes
it was not until … that – и только после …
they came to be employed – они стали использоваться
a great variety of – большое разнообразие
Why were gold, silver and copper probably the first metals used by man?
What do we call the Bronze Age and the Iron Age?
Since what time have metals been employed in really vast quantities?
What is the selection of a material generally based on?
What is the main advantage of metals?
Is concrete a cheap building material?
Can plastics be recycled?
What is the main advantage of aluminium bronze as compared to pure copper or aluminium?
What makes it possible to use metals in intricate structures?
3.3. Look at the examples and the diagram, then make sentences in the same way. Use the phrases as much (many) … as, half as much (many) … as, twice as much (many) … as, … as much (many) … as.
Example 1: alloy 2: 52% lead; 48% tin
Alloy 2 contains approximately as much lead as tin.
1. alloy 3: |
65% lead; 35% tin |
|
|
2. cement: |
60% lime; 20% silica |
|
|
3. seawater: |
0.04% calcium; 0.04% potassium |
||
4. seawater: |
1% sodium; 2% chlorine |
||
Example 2: Mechanical Engineering; Electrical Engineering
Mechanical Engineering has three times as many students as Electrical Engineering (see Fig. 1).
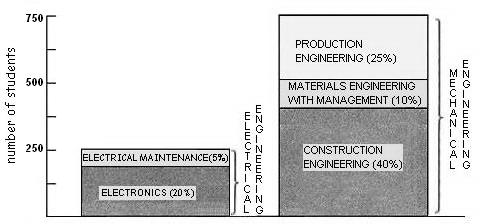
Fig. 1. Percentage of students in the different departments of a technical college.
Electrical Maintenance; Materials Engineering with Management
Electronics; Electrical Maintenance
Electrical Engineering; Production Engineering
Construction Engineering; Electronics
